Introduce React
Motivation
- 了解現代框架
- 將有用的概念套用到現有程式中
What is React
-
專注於建立 UI 的 library
- 與說是個 framework,更像是 library
- 不管商業邏輯 等
- 與 Angular 呈現強烈的對比
React - Characteristic
-
Declarative
- 描述 UI 的樣子,而非直接 DOM 操作控制顯示
- 對比 JQuery
-
Component Based
- 提倡將 UI 上的每個元件都拆成 Component
- 每個 Component 都有各自封裝的狀態 / 邏輯
-
Learn once, write anywhere
- Moblie (React Native)
- Server Rendering (Next)
- 可惜不是 Write once, run anywhere
What is JSX
- React 採用的特殊 JS 語法
- 為 JavaScript 的擴充語法
- 支援在 JavaScript 中撰寫 XML-like 語法
- 需經轉譯變回一般 JavaScript 語法
- e.g. Babel
const name = 'Josh Perez';
const element = (
<h1 className="greeting">
Hello, Henry
</h1>
);
ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('root')
);const name = 'Josh Perez';
const element = React.createElement(
'h1',
{className: 'greeting'},
'Hello, world!'
);
ReactDOM.render(
element,
document.getElementById('root')
);Why JSX
-
呼應 Component Based 理念
-
High Cohesion : 強化 Component 的內聚力
- 認為 template & logic 難以分割 (ng-if ...etc)
- 對比 Angular / Vue ...etc
- Low coupling : 分離 Component 間的耦合性
-
High Cohesion : 強化 Component 的內聚力
function LoginButton(props) {
return <button>Login</button>;
}
function LogoutButton(props) {
return <button>Logout</button>;
}
function LoginStatusPanel(props) {
if (props.isLoggedIn) {
return <LogoutButton/>;
}
return <LoginButton/>;
}Component
- function based / class based
- pure function
- 不可修改 input 的內容
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}class Welcome extends React.Component {
// componentDidMount() {}
// componentWillUnmount () {}
// state
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name);
}
}Component - Props
- Props
-
為上層 Component 傳入,且不可修改的參數
-
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Welcome name="Henry" />
<Welcome name="Cahal" />
<Welcome name="Edite" />
</div>
);
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root')
);Component - State
- State
- 為 Component 自己創建 / 管理的私有狀態
-
自己的狀態只能自己改
- 使用 setState 修改
class Clock extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {date: new Date()};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.timerID = setInterval(
() => this.tick(),
1000
);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timerID);
}
tick() {
this.setState({
date: new Date()
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<h2>It is {this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Clock />,
document.getElementById('root')
);Component - Props / State
- Props
-
為上層 Component 傳入,且不可修改的參數 - 上層的狀態只能上層改
-
- State
- 為 Component 自己創建 / 管理的私有狀態
- 自己的狀態只能自己改
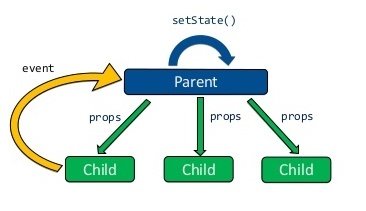
React - Unidirectional flow
- 資料往下流
- props: immutable
- state: mutable
- 對比 AngularJS 的 two way binding

Handling Events
- 如原生 JavaScript 一樣,可以傳遞事件給上層知道
- 以事件角度去命名 attr,而非以 action 的角度去命名
- 不預設銜接者要拿此事件作甚麼
- 抽象取代具體
// JSX
const element = (
<a onClick={activateLasers}>
Activate Lasers
</a>
);
function activateLasers() {
console.log('laser activated');
}// JSX
const element = (
<FriendList onItemClicked={openAvatar}>
Activate Lasers
</FriendList>
);
function openAvatar(id) {
console.log(`avatar ${id} opened`);
}Lifting States up by Events
- 把 Event 往上層丟
- 上層接到 Event 後修改 state
React - Unidirectional flow
- 資料往下流
- props: immutable
- state: mutable
- 藉由 Event 間接觸發 state 改變
- 對比 AngularJS 的 two way binding

What can we learn from React
-
Component Based
- 增加 可重用性
- 封裝各 UI 的邏輯
- 孤立每個 UI 各自的 bug
-
Event 的概念
- 點了會做甚麼 -> 點了觸發什麼事件
- 不預設銜接者要拿此事件作甚麼
- 抽象取代具體
-
Pure function / Unidirectional flow
- 讓資料只有唯一的修改點
- 限制 bug 能出現的地方
References
Introduce React
By Chang Henry
Introduce React
- 47



