JavaScript
Lexical Scope
You don't know JS
Outline
- Scope
- Lex-time
- Look-ups
- Cheating Lexical
- eval
- with
- Disadvantage
Scope
Two types of scope :
-
Lexical scope
- JS, Java, C++, ...etc
- Most of languages
-
dynamic scope
- bash, perl, ...etc
Lex-time
-
Lexical scope is scope that is defined at Lexing time
- Most of it
- You can always trace scope by your code at author-time
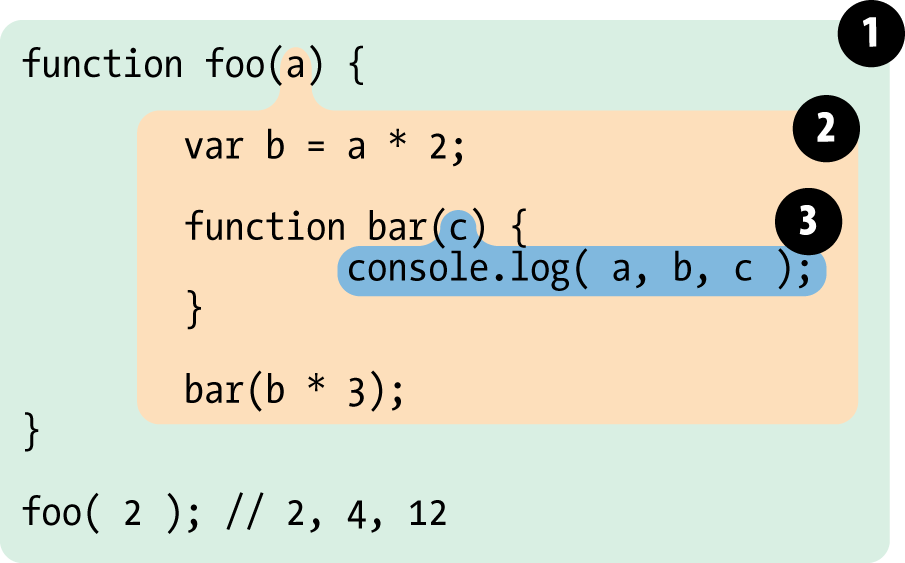
Strict nested !!!
Look-ups
Rules
-
if found: stops at the first match
- may cause shadowing
-
if not found:
- depends on RHS/LHS & is strict

Cheating Lexical
- JS have some way to Modifies lexical scope in run-time
- Not dynamic scope
Cheating Lexical
eval
- Parameter: String
- Usage: treats the string as authored code at that point
- Tech details: Modifies lexical scope in run-time
function foo(str, a) {
eval( str ); // cheating!
console.log( a, b );
}
var b = 2;
foo( "var b = 3;", 1 ); // 1 3Cheat add new var: b to foo
- Note: can't add new var at strict mode
Cheating Lexical
eval
Similar functions:
- new Function
- setTimeout / setInterval
Cheating Lexical
with
var obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
};
// more "tedious" to repeat "obj"
obj.a = 2;
obj.b = 3;
obj.c = 4;
// "easier" short-hand
with (obj) {
a = 3;
b = 4;
c = 5;
}- Parameter: Object
- Usage: making multiple property references against an object without repeating obj.
- Tech details: New a lexical scope in run-time
Cheating Lexical
with
var obj = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3
};
// more "tedious" to repeat "obj"
obj.a = 2;
obj.b = 3;
obj.c = 4;
// "easier" short-hand
with (obj) {
d = 6;
}
obj.d === undefined // true
window.d === 6 // true-
Dangerous:
- May write to window if not strict mode
- deprecated
Cheating Lexical
Disadvantage
-
Bad Readability:
- Scope can't be determined at author-time
-
Bad performance:
- Engine can't determine scope at author-time
- Can't optimize
- Simply doesn't perform any optimizations at all
- Critical
Review
- Two types of Scope
- Determined in Lex-time
- Scope bubble look-ups
- Cheating Lexical
- eval
- with
- Bad performance/readablilty
Quiz
function foo() {
var a = 1;
function bar() {
var a = 2;
var b = 3;
console.log('inner a: ', a); // 2
console.log('inner b: ', b); // 3
}
bar();
console.log('a: ', a); // 1
console.log('b: ', b); // ReferenceError
}
foo();JavaScriptLexical Scope
By Chang Henry
JavaScriptLexical Scope
- 24



