Secure AI inference techniques:
A tutorial
Chen-Mou Cheng
Chang Gung University
September 28, 2024
Outline
- Secure AI inference
- TEE: Trusted Execution Environment
- FHE: Fully Homomorphic Encryption
- MPC: (secure) Multi-Party Computation
- ZKP: Zero-Knowledge Proof
Secure AI inference
- ChatGPT is great! Love asking it all kinds of questions
- How can I ask ChatGPT a private question without telling OpenAI the secret?
TEE
-
Hardware isolation for secure execution
-
Ex: Intel SGX, ARM TrustZone
-
-
Low latency but limited scalability
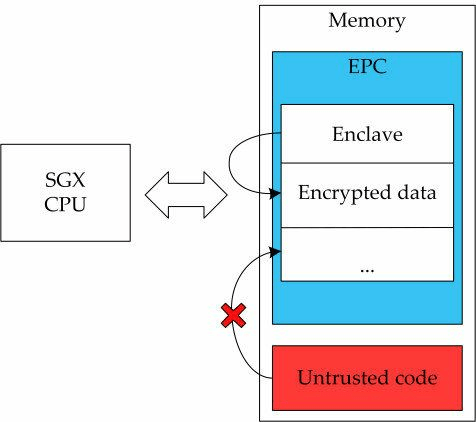
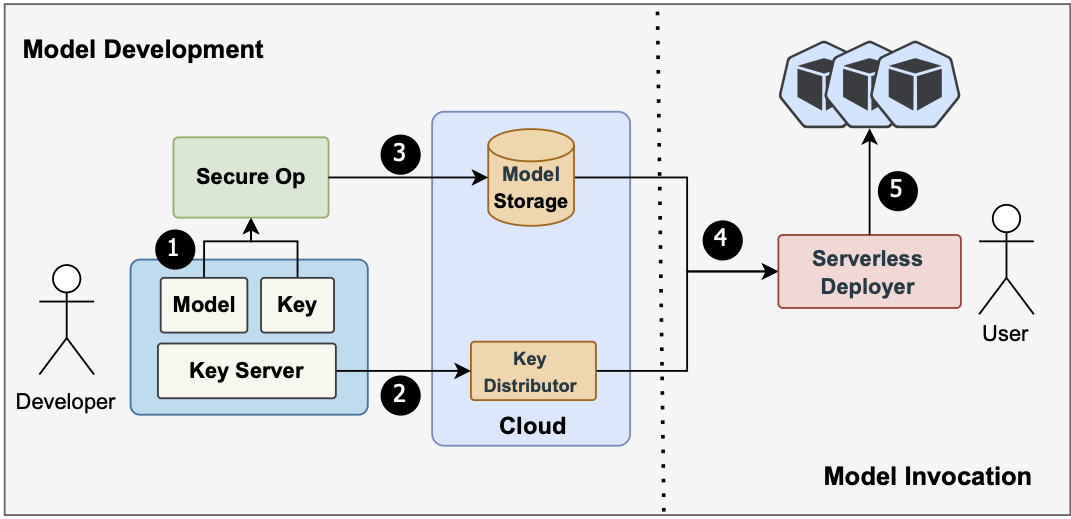
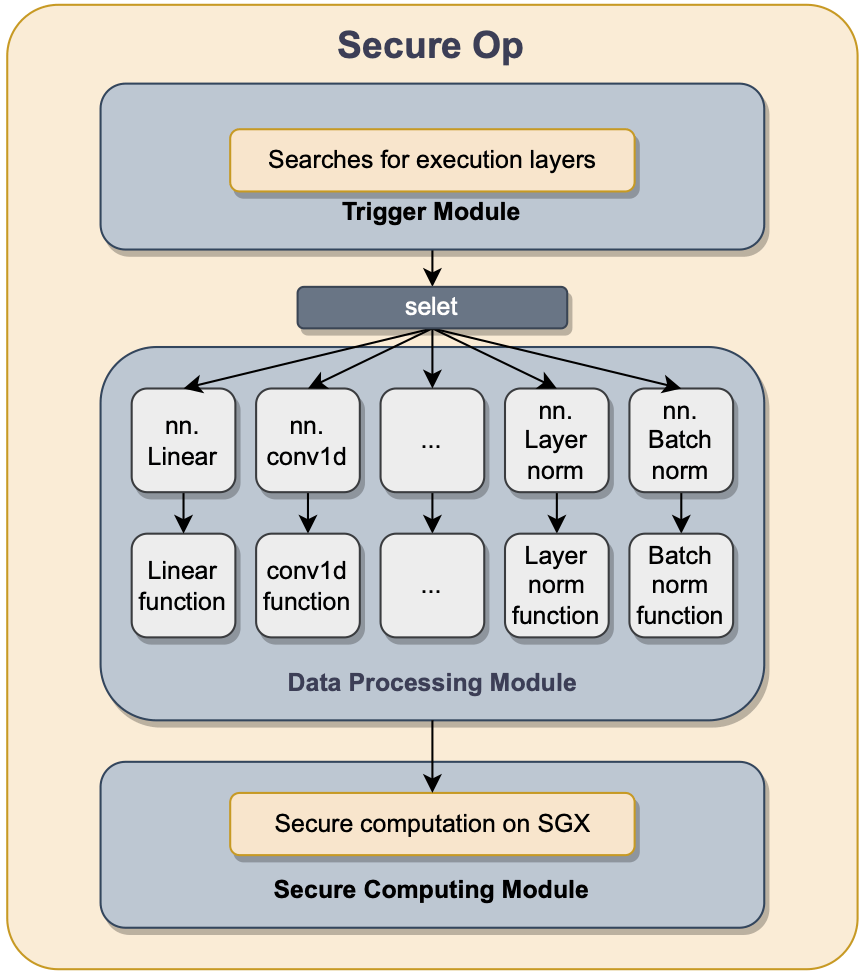
Ex: LLMaaS (with SGX)
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10601537
- Model Owner doesn't trust Cloud (but Data Owner does)
- Break up Transformer computation
- Run each piece inside Enclave trusted by Model Owner
- Pros: Straightforward, very little overhead
- Cons: Scalability to larger models & GPU/ASIC

LLMaaS workflow
FHE
-
Computation on encrypted data
-
Strong privacy but very high overhead
$$\tilde T\text{ is such that }\forall m,d.\,\text{Dec}_{sk}\left(\tilde T_m\big(\text{Enc}_{pk}(d)\big)\right)=T_m(d)$$
Data Owner
$$\begin{aligned}c_1 & \leftarrow \text{Enc}_{pk}(\color{blue}d\color{black}) \\ r & \leftarrow\text{Dec}_{\color{blue}sk\color{black}}(c_2)\end{aligned}$$
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{2em}c_1\hspace*{2em}}$$
$$\xleftarrow{\hspace*{2em}c_2\hspace*{2em}}$$
Model Owner
$$\begin{aligned}c_2\leftarrow\tilde T_{\color{red}m\color{black}}(c_1)\end{aligned}$$
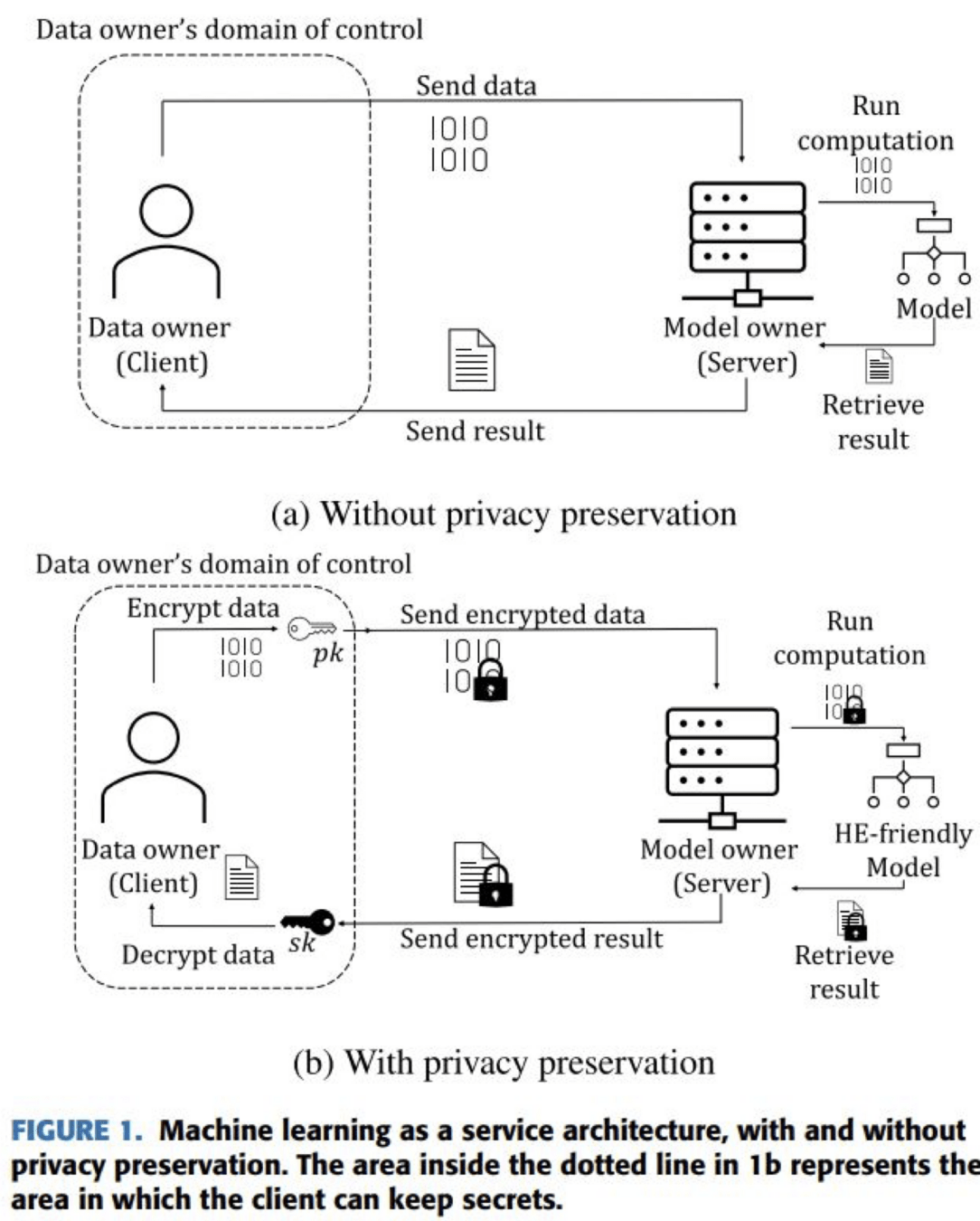
Source: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9936637
MPC
-
Joint computation while keeping inputs private
-
Ex: Garbled Circuit
-
-
High computational+communication overhead
Data Owner
$$\color{blue}d\color{black}$$
$$\downarrow$$
$$T_{\color{red}m\color{black}}(\color{blue}d\color{black})$$
Model Owner $$\color{red}m\color{black}$$
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{2em}c_1\hspace*{2em}}$$
$$\xleftarrow{\hspace*{2em}c_2\hspace*{2em}}$$
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{2em}c_3\hspace*{2em}}$$
$$\xleftarrow{\hspace*{2em}c_4\hspace*{2em}}$$
$$\hspace*{2.5em}\vdots\hspace*{2.5em}$$
Garbled Circuit
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{1em}\begin{array}{|c|}\hline \text{Garbled Table} \\\hline\hline \text{Enc}_{\color{blue}X_0^a,X_0^b\color{black}}(\color{blue}X_{f(0,0)}^c\color{black}) \\\hline \text{Enc}_{\color{blue}X_0^a,X_1^b\color{black}}(\color{blue}X_{f(0,1)}^c\color{black}) \\\hline \text{Enc}_{\color{blue}X_1^a,X_0^b\color{black}}(\color{blue}X_{f(1,0)}^c\color{black}) \\\hline \text{Enc}_{\color{blue}X_1^a,X_1^b\color{black}}(\color{blue}X_{f(1,1)}^c\color{black}) \\\hline\end{array}\hspace*{1em}}$$
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{4.5em}X_1^a\hspace*{4.5em}}$$
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{3em}\text{OT}\left(\color{blue}X_0^b\color{black},\color{blue}X_1^b\color{black}\right)\hspace*{3em}}$$
$$\xleftarrow{\hspace*{4em}X_{f(1,0)}^c\hspace*{4em}}$$
$$\xrightarrow{\hspace*{2.5em}f(1,0)\text{ (optional)}\hspace*{2.5em}}$$
Data Owner
$$\color{blue}a=1\color{black}$$
Model Owner $$\color{red}b=0\color{black}$$
$$\text{Dec}_{X_1^a,\color{red}X_0^b\color{black}}(?)$$
Ex: MARILL
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03561
- Hack fine-tuning to minimize MPC in inference
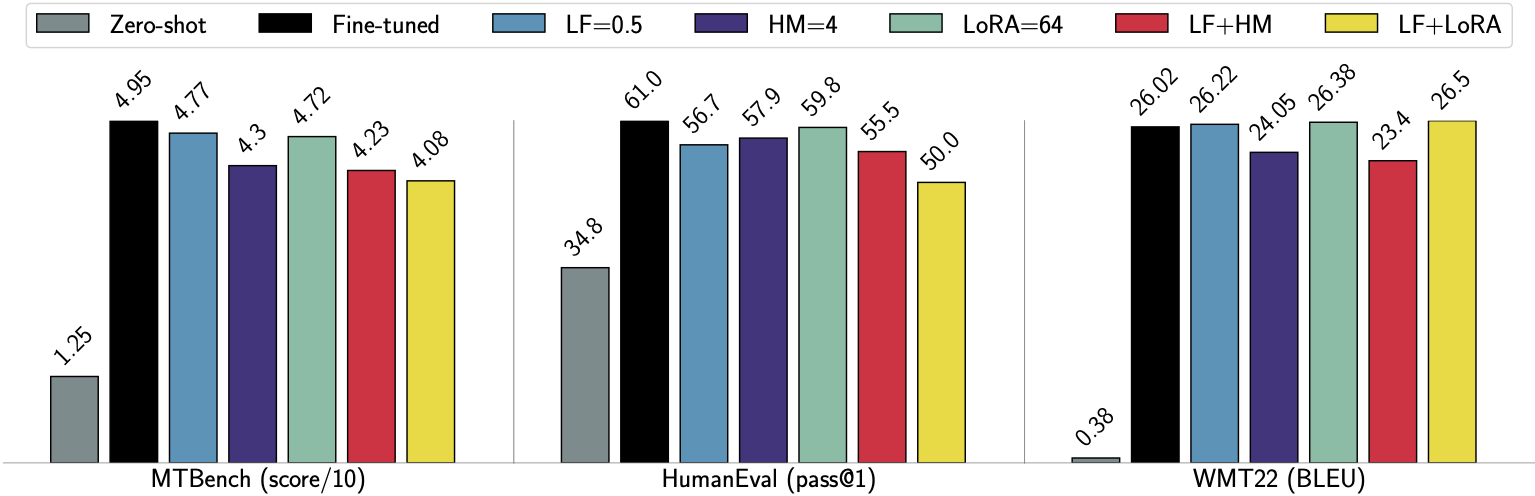
- Layer freezing
- LoRA to reduce matrix dimensions in MPC
- Head merging instead of pruning in MPC
$$\text{head}_j=\text{softmax}\left(\frac{\sum_{\ell=jm}^{(j+1)m}Q_\ell K_\ell^T}{\sqrt{md}}\right)\left(V_{jm}||\ldots||V_{(j+1)m}\right)\in\mathbb R^{b\times md}$$
- Vs. standard fine-tuned model in inference
- \(\text{3.6--11.3}\times\) better runtime
- \(\text{2.4--6.9}\times\) better communication
State of the art in 2023
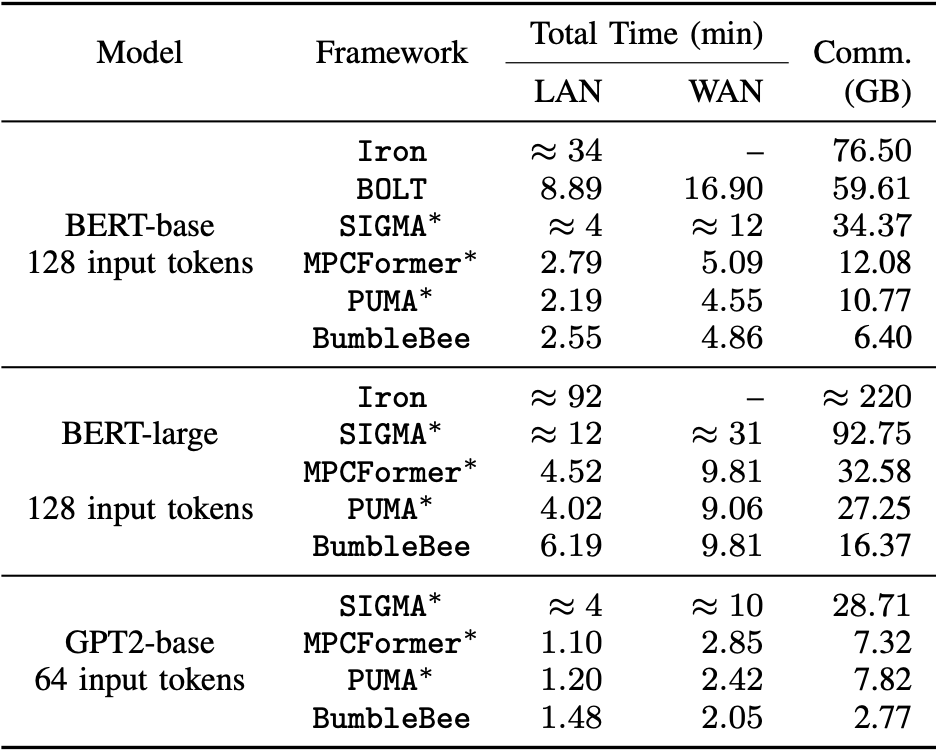
MARILL workflow
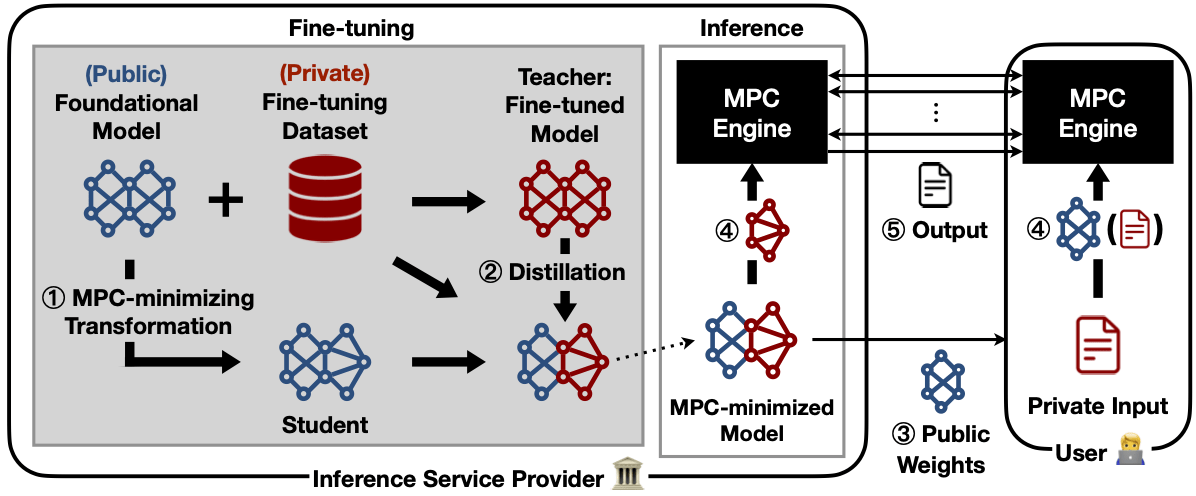
MARILL techniques
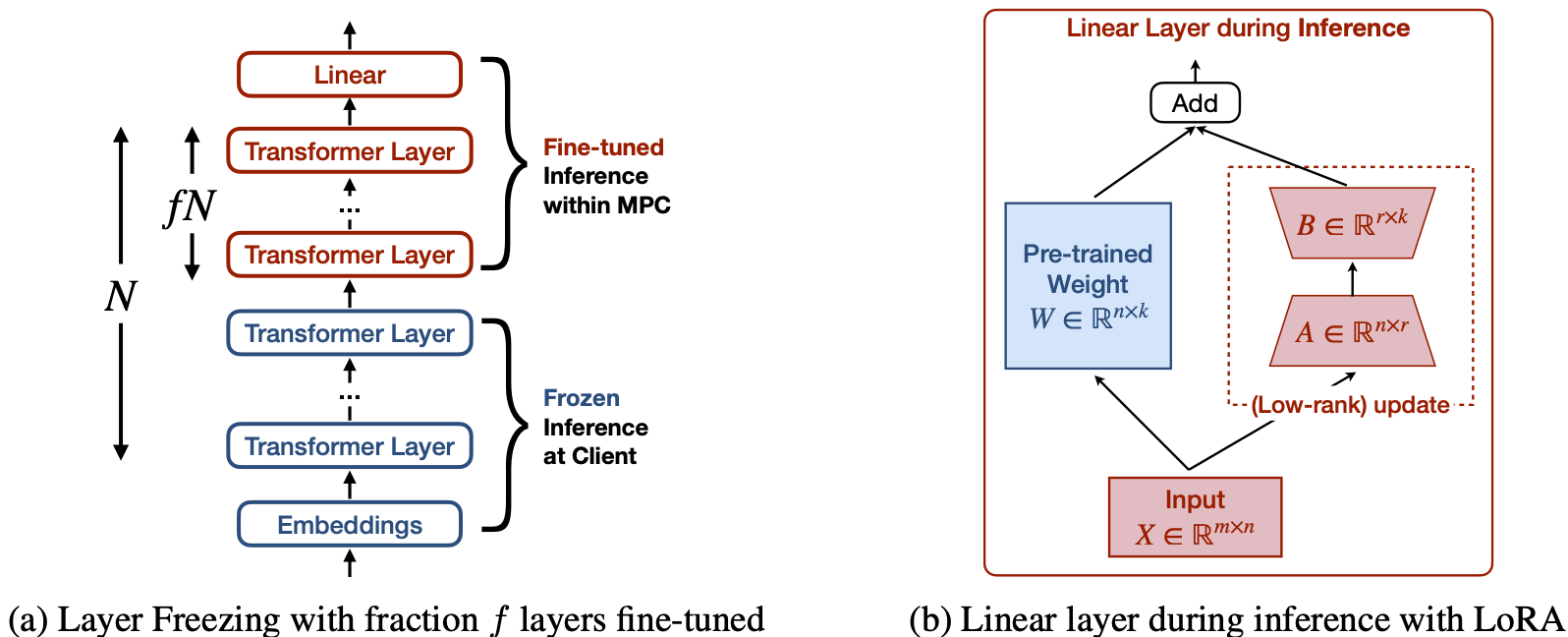
Inference performance
ZKP
- Learns nothing beyond "Statement S is true"
- Consider special S: \( y=f(x,\color{red}w\color{black}) \)
- Can simulate the dialogues without knowing \(\color{red}w\color{black}\)
- Ex: Colorblind test with two balls of different colors
Serialization via commitment
(How to play rock-paper-scissors over internet)
- Cryptographic commitment
- Commit: \( c=\text{commit}(r,m) \)
- Verify: \( \text{verify}\Big(r,m,c\Big)? \)
- Security properties
- Hiding: difficult to find \( m \) given \( c=\text{commit}\left(r,m\right) \)
- Binding: difficult to find \( r',m'\neq m \) s.t. \( \text{verify}\Big(r',m',\text{commit}(r,m)\Big) \)
Proving \( f(x)=y \)
- Syntax of (polynomial) functional commitment
- \( c=\text{commit}(r,f) \)
- \( (y,\pi)=\text{eval}(r,f,x) \)
- \( \text{verify}\Big(c,x,y,\pi\Big) \) iff \( \exists r\text{ s.t. }c=\text{commit}(r,f) \) and \( f(x)=y \)
- Example (Merkle tree)
- Leaves \( y_0,y_1,\ldots,y_{n-1} \) define \( f:\Big\{0,1,\ldots,n-1\Big\}\rightarrow Y \)
- Authentication path encodes (binary expansion of) \( i\in\Big\{0,1,\ldots,n-1\Big\} \) and thus proves \( f(i)=y_i \)
Toy ZKP example
- Prover: "I know integers \( \color{red}p\color{black},\color{red}q\color{black} \) s.t. \( n=\color{red}pq\color{black} \)"
- Prover commits to three polynomial functions: \[ \color{red}r_p\color{black}X+\color{red}p\color{black},\color{red}r_q\color{black}X+\color{red}q\color{black},\text{ and }\color{red}r_pr_q\color{black}X^2+(\color{red}r_pq\color{black}+\color{red}pr_q\color{black})X+n \]
- Verifier challenges Prover with random \( r \) and checks whether \( (\color{red}r_p\color{black}r+\color{red}p\color{black})(\color{red}r_q\color{black}r+\color{red}q\color{black})\stackrel{?}{=}\color{red}r_pr_q\color{black}r^2+(\color{red}r_pq\color{black}+\color{red}pr_q\color{black})r+n \)
- Lemma [Schwartz-Zippel] \[ \text{Pr}_{r\in k}\Big(f(r)=g(r)\Big)\leq\frac{d}{|k|}\text{ for }f\neq g\text{ with }\deg f,\deg g\leq d \]
Ex: zkLLM
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.16109
- Guarantee authenticity of LLM outputs
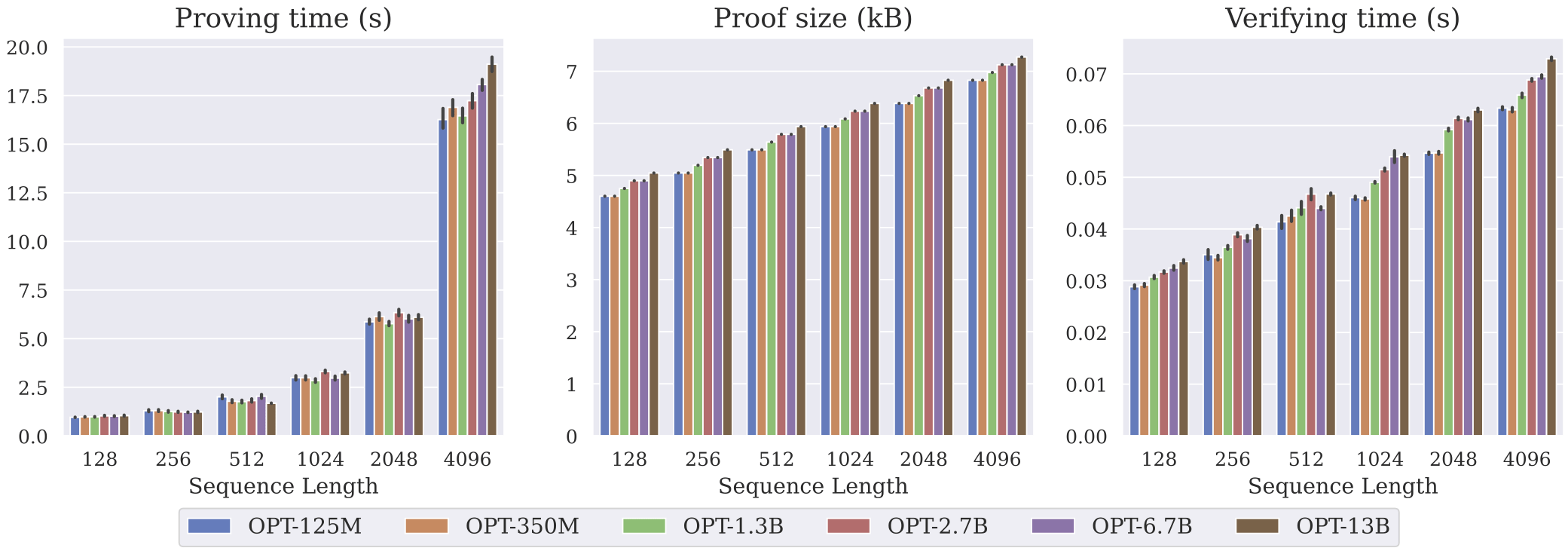

Text
Text
$$\text{Attention}(\mathbf Q,\mathbf K,\mathbf V):=\text{Softmax}\left(\frac{\mathbf{QK}^T}{\sqrt d}\right)\mathbf V$$
Thank you!
Questions or comments?
Secure inference
By Chen-Mou Cheng
Secure inference
- 210



