The Immutable Way: A Guide to Cleaner, More Predictable JavaScript
Chris Laughlin
WHO AM I?
Principal UI Engineer @Rapid7

Jack of all trades master of none
Worst hangover I have ever had
Creator
tiktok.com/@thedyslexicdeveloper
Freelance Writer
@SitePoint & @Logrocket
"Immutability in programming refers to data that cannot be changed after it's created"
📕
Mutation
📖
📖
🥸
🥸
📕
📖
🖨️
IMMUTABILITY
📖
🥸
let name = "Chris";
console.log(name); // 'Chris'
name = "Christopher";
console.log(name); // 'Christopher'
const speaker = {
name: "Chris",
location: "Belfast",
age: 100,
};
speaker = { name: "Christopher" };
// Uncaught SyntaxError: "speaker" is read-only
speaker.name = "Christopher";
console.log(speaker);
// {name: 'Christopher', location: 'Belfast', age: 100}const speaker = {
name: "Chris",
location: "Belfast",
age: 100,
};
const fullNameSpeaker = { ...speaker };
fullNameSpeaker.name = "Christopher";
console.log(speaker);
// {name: 'Chris', location: 'Belfast', age: 100}
console.log(fullNameSpeaker);
// {name: 'Christopher', location: 'Belfast', age: 100}const speaker = {
name: "Chris",
location: {
city: "Belfast",
country: "UK",
},
age: 100,
};
const fullNameSpeaker = {
...speaker
};
fullNameSpeaker
.location
.city = "Derry";console.log(speaker);
/*
{
"name": "Chris",
"location": {
"city": "Derry",
"country": "UK"
},
"age": 100
}
*/console.log(fullNameSpeaker);
/*
{
"name": "Chris",
"location": {
"city": "Derry",
"country": "UK"
},
"age": 100
}
*/ATTRIBUTE mutation
const speaker = {
name: "Chris",
location: {
city: "Belfast",
country: "UK",
},
age: 100,
};
const fullNameSpeaker = structuredClone(speaker);
fullNameSpeaker
.location
.city = "Derry";console.log(speaker);
/*
{
"name": "Chris",
"location": {
"city": "Belfast",
"country": "UK"
},
"age": 100
}
*/console.log(fullNameSpeaker);
/*
{
"name": "Chris",
"location": {
"city": "Derry",
"country": "UK"
},
"age": 100
}
*/structured clone
const speaker = {
name: "Chris",
location: "Belfast",
age: 100,
};
Object.freeze(speaker);
speaker.name = "Christopher";
//Uncaught TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'name' of object '#<Object>'object freeze

const speaker = {
name: "Chris",
location: "Belfast",
age: 100,
};
Object.seal(speaker);
speaker.name = "Christopher";
console.log(speaker.name);
speaker.occupation = "Software Engineer";
// TypeError: Cannot add property occupation,
// object is not extensibleobject seal

Real world Example
Arrays
[].forEach(callbackFn)
[].filter(callbackFn)
[].pop(callbackFn)
[].push(callbackFn)
[].map(callbackFn)
[].slice(callbackFn)
[].reduce(callbackFn)
[].sort(callbackFn)
es2023 array methods
.reverse vs .toReversed()
const messages = [
{
sender: "Alice",
text: "Hi Bob, how are you?",
timestamp: 1693830400000, // Timestamp in milliseconds
},
{
sender: "Bob",
text: "I'm doing well, thanks! How about you?",
timestamp: 1693830500000,
},
{
sender: "Alice",
text: "I'm good too. What are you up to today?",
timestamp: 1693830600000,
},
];
// Using Array.reverse()
messages.reverse();
// Display messages in reverse chronological order
messages.forEach((message) => {
console.log(`${message.sender}: ${message.text}`);
});
Alice: I'm good too. What are you up to today?
Bob: I'm doing well, thanks! How about you?
Alice: Hi Bob, how are you?.reverse vs .toReversed()
// Using Array.reverse()
const reversedMessages = messages.toReversed();
// Display messages in reverse chronological order
reversedMessages.forEach((message) => {
console.log(`${message.sender}: ${message.text}`);
});
console.log("##########");
console.log(messages);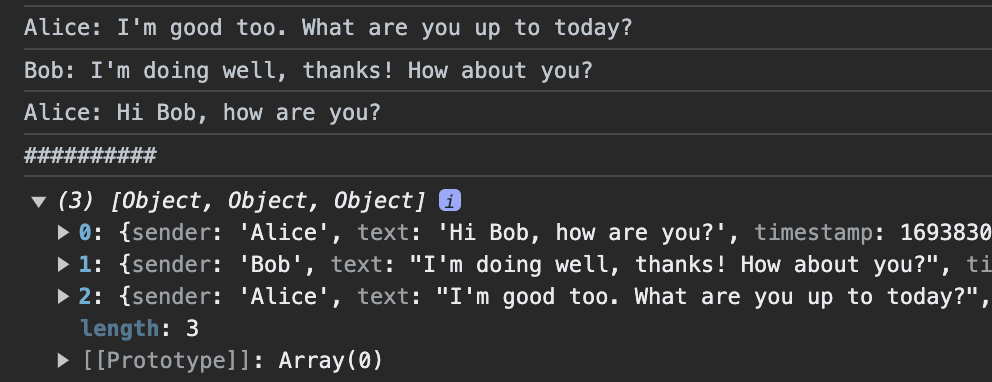
.sort vs .toSorted()
const products = [
{ name: "Product C", price: 20 },
{ name: "Product A", price: 15 },
{ name: "Product B", price: 25 },
];
// products.sort((a, b) => a.price - b.price);
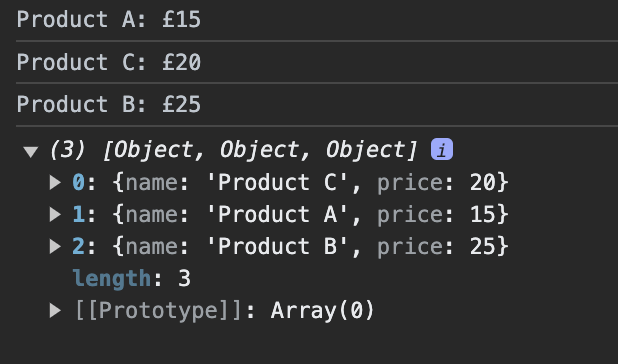
const sortedProducts = products.toSorted((a, b) => a.price - b.price);
// Display sorted products
sortedProducts.forEach((product) => {
console.log(`${product.name}: £${product.price}`);
});
console.log(products);
.splice vs .toSpliced()
const cartItems = [
{ id: 1, name: "Item A", price: 10 },
{ id: 2, name: "Item B", price: 15 },
{ id: 3, name: "Item C", price: 20 },
{ id: 4, name: "Item D", price: 25 },
];
// Remove the second item (index 1)
const newCart = cartItems.toSpliced(1, 1);
// Remove the last two items
const reducedCart = cartItems.toSpliced(-2);
// Replace the third item (index 2)
const updatedCart = cartItems.toSpliced(2, 1, {
id: 5,
name: "New Item",
price: 30,
});
// Display the modified carts
console.log(newCart);
console.log(reducedCart);
console.log(updatedCart);
// Display thr orginal cart
console.log(cartItems);
Immutable LIBRARIES

import { Map } from 'immutable';
const map1 = Map({ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 });
const map2 = map1.set('b', 50);
map1.get('b') + ' vs. ' + map2.get('b'); // 2 vs. 50import {produce} from "immer"
const nextState = produce(baseState, draft => {
draft[1].done = true
draft.push({title: "Tweet about it"})
})conculsion
Thank You!
The Immutable Way: A Guide to Cleaner, More Predictable JavaScript
By Chris Laughlin
The Immutable Way: A Guide to Cleaner, More Predictable JavaScript
- 158



