Demand Functions and Demand Curves
Christopher Makler
Stanford University Department of Economics
Econ 50: Lecture 13
Welcome back alumni!
Ruru Hoong

Class of 2019
Worked for 1 year at Boston Consulting Group in London
Currently a 5th-year Ph.D. student in Economics at Harvard
Research interests are in...
TA for Econ 50

Today's Agenda
Part 1:
General Theory
Part 2:
Functional Forms and Behavior
- Cobb-Douglas
- Perfect Substitutes
- Quasilinear
- Demand Functions
- Demand Curves
Last Class: What is the optimal bundle for a given budget line?
Today: What happens to the optimal bundle when prices/income change?
🍏
🍌
BL1
We will be solving for the optimal bundle
as a function of income and prices:
The solutions to this problem will be called the demand functions. We have to think about how the optimal bundle will change when \(p_1,p_2,m\) change.
BL2
Specific Prices & Income
General Prices & Income
Plug tangency condition back into constraint:
Tangency Condition: \(MRS = p_1/p_2\)
Specific Prices & Income
General Prices & Income
OPTIMAL BUNDLE
DEMAND FUNCTIONS
(optimization)
(comparative statics)
The Demand Function Illustrates Three Relationships
...its own price changes?
Movement along the demand curve
...the price of another good changes?
Complements
Substitutes
Independent Goods
How does the quantity demanded of a good change when...
...income changes?
Normal goods
Inferior goods
Giffen goods
(possible) shift of the demand curve
(Wednesday)
Three Relationships
...its own price changes?
Movement along the demand curve
How does the quantity demanded of a good change when...
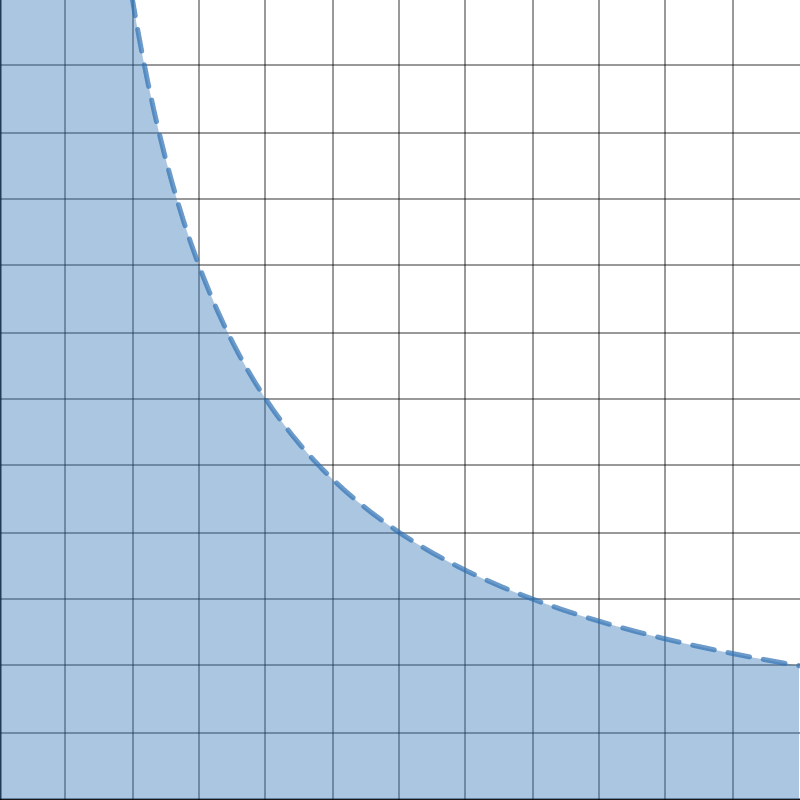
The demand curve for a good
shows the quantity demanded of that good
as a function of its own price
holding all other factors constant
(ceteris paribus)
DEMAND CURVE FOR GOOD 1
"Good 1 - Good 2 Space"
"Quantity-Price Space for Good 1"
Note: Maximum Possible Quantity Demanded

Quantity of Good 1 \((x_1)\)
Price of Good 1 \((p_1)\)
All demand curves must be in this region
Quantity bought at each price if you spent all your money on good 1
Worked Examples
(link to PowerPoint)
Econ 50 | Lecture 13
By Chris Makler
Econ 50 | Lecture 13
Demand Functions and Demand Curves
- 859



