Neue C++ Features
25. Mai 2023
Hello world - C
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
Hello world - C++98
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << "Hello World!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Hello world - C++20
#include <iostream>
#include <format>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::cout << std::format("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}Hello world - C++23
#include <print>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::println("Hello World!");
return 0;
}
Attribution
Modules (C++20)
- Aktuell: glorified c&p
- Zukunft: Modules
- Verhindern Macro leaks
- Verhindern Namenskollissionen
- Reihenfolge der Imports unwichtig
- Wird nur einmal verarbeitet
- Export ist explizit
- Neue Möglichkeit Code zu strukturieren
Modules (C++20)
// chaostreff.cppm -> Module Interface File
export module chaostreff;
namespace ChaosTreff {
auto getChaotischeViertelstunde() {
return "Neue C++ Features - von Gromit";
}
export auto printWelcome() {
std::println("{}", getChaotischeViertelstunde);
}
} // namespace ChaostreffModules (C++20)
// chaostreff.cppm -> Module Interface File
export module chaostreff;
namespace ChaosTreff {
auto getChaotischeViertelstunde() {
return "Neue C++ Features - von Gromit";
}
export auto printWelcome() {
std::println("{}", getChaotischeViertelstunde);
}
} // namespace Chaostreff
// main.cpp
import chaostreff;
int main() {
ChaosTreff::printWelcome();
return 0;
}Ranges, Algorithms (C++20)
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::vector<int> v{3,2,4,1};
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
std::sort(v.begin(), v.end());
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
return 0;
}Ranges, Algorithms (C++20)
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <fmt/ranges.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::vector<int> v{3,2,4,1};
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
std::ranges::sort(v);
fmt::print("{}\n", v);
return 0;
}Ranges, Views & Filter
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
std::vector<int> v{6, 3, 2, 4, 1};
auto result{ data
// [6, 2, 4]
| views::filter([](const auto& a){ return a % 2 == 0; })
Ranges, Views & Filter (C++20)
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
std::vector<int> v{6, 3, 2, 4, 1};
auto result{ data
// [6, 2, 4]
| views::filter([](const auto& a){ return a % 2 == 0; })
// [12, 4, 8]
| views::transform([](const auto& a){ return a * 2.0; })
Ranges, Views & Filter (C++20)
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
std::vector<int> v{6, 3, 2, 4, 1};
auto result{ data
// [6, 2, 4]
| views::filter([](const auto& a){ return a % 2 == 0; })
// [12, 4, 8]
| views::transform([](const auto& a){ return a * 2.0; })
// [4, 8]
| views::drop(1)
Ranges, Views & Filter (C++20)
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
std::vector<int> v{6, 3, 2, 4, 1};
auto result{ data
// [6, 2, 4]
| views::filter([](const auto& a){ return a % 2 == 0; })
// [12, 4, 8]
| views::transform([](const auto& a){ return a * 2.0; })
// [4, 8]
| views::drop(1)
// [8, 4]
| views::reverse
Ranges, Views & Filter (C++20)
- Aktuell: iteratoren
- Zukunft: Ranges
std::vector<int> v{6, 3, 2, 4, 1};
auto result{ data
// [6, 2, 4]
| views::filter([](const auto& a){ return a % 2 == 0; })
// [12, 4, 8]
| views::transform([](const auto& a){ return a * 2.0; })
// [4, 8]
| views::drop(1)
// [8, 4]
| views::reverse
// ["4", "8"]
| views::transform(
[](const auto& i){ return std::to_string(i); }) };Coroutines (C++20)
- Funktion, die eines der folgenden Keywords enthält:
- co_await: schlafen, warte auf andere Berechnung
- co_yield: gebe Wert zurück & schlafen, dann weiter
- co_return: return aus der Coroutine
- Warum co_?
- Usecases:
- Generators
- Async I/O
- Event-driven Kram
- Lazy Computations
Concepts (C++20)
- Constraints für Template Parameter
Refresher: Templates
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
Refresher: Templates
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
float add(float a, float b) {
return a + b;
}
Refresher: Templates
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
float add(float a, float b) {
return a + b;
}
std::string add(const std::string& a,
const std::string& b) {
return a + b;
}Refresher: Templates
template<typename T>
T add(const T& a, const T& b) {
return a + b;
}
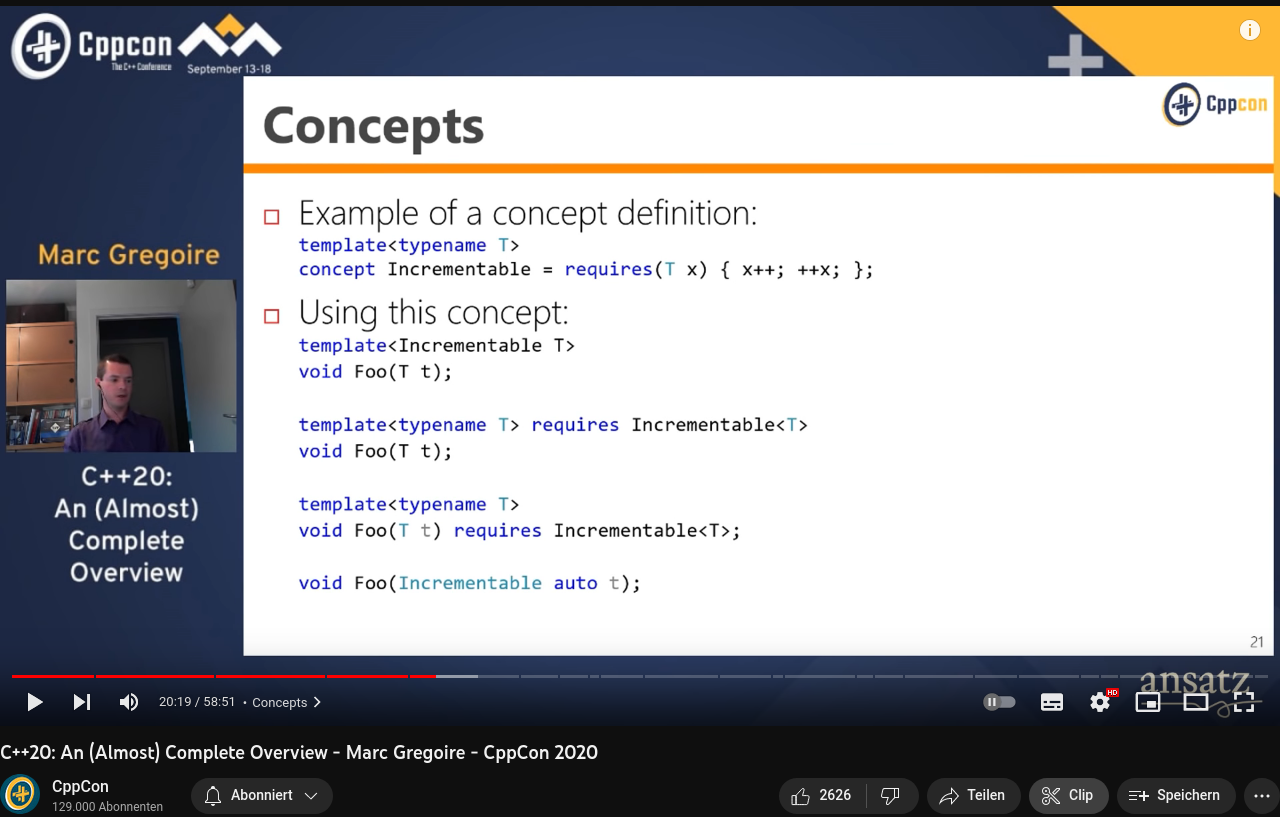
Concepts (C++20)
- Constraints für Template Parameter
template<typename T>
concept Addable = requires(T a, T b) { a + b; };
template<Addable T>
T add(const T& a, const T& b) {
return a + b;
}Concepts (C++20)
- Constraints für Template Parameter
template<typename T>
concept Addable = requires(T a, T b) { a + b; };
auto add(Addable const auto& a,
Addable const auto& b) {
return a + b;
}- z.B. schon vordefiniert:
- derived_from
- convertible_to
- integral
- sortable, mergeable, permutable
Spaceship Operator <=>
- Offiziell: Three-Way-Comparison
- So funktionierts:
-
(a <=> b) < 0 // true if a < b
-
(a <=> b) > 0 // true if a > b
-
(a <=> b) == 0 // true if a == b
-
- Common Usecase:
// compiler will generate functions
auto X::operator<=>(const Y&) const = default;- Advanced: Selber Schreiben
- Custom implementation
- return: strong_ordering, partial_ordering, weak_ordering
Spaceship Operator <=>
class Point {
int x; int y;
public:
friend bool operator==(const Point& a, const Point& b) { ... };
friend bool operator< (const Point& a, const Point& b) { ... };
friend bool operator!=(const Point& a, const Point& b) { ... };
friend bool operator<=(const Point& a, const Point& b) { ... };
friend bool operator> (const Point& a, const Point& b) { ... };
friend bool operator>=(const Point& a, const Point& b) { ... };
// other functions
};Spaceship Operator <=>
#include <compare>
class Point {
int x; int y;
public:
auto operator<=>(const Point&) = default;
// other functions
};
Text Formatting (C++20)
- Aktuell: I/O Streams
- Typesafe & extensible
- Schwierig zu lesen, schwierig mit locales zu versehen
- Scheiße langsam
- Zukunft <format> bzw. <print> basierend auf "fmt"
#include <format>
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::cout << std::format("Read {0} bytes from {1}!\n",
256, "file.txt");
return 0;
}
Text Formatting (C++23)
- Aktuell: I/O Streams
- Typesafe & extensible
- Schwierig zu lesen, schwierig mit locales zu versehen
- Scheiße langsam
- Zukunft <format> bzw. <print> basierend auf "fmt"
#include <format>
#include <print>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
std::println("Read {0} bytes from {1}!",
256, "file.txt");
return 0;
}
Stacktraces (C++23)
#include <iostream>
#include <stacktrace>
int nested_func(int c)
{
std::cout << std::stacktrace::current() << '\n';
return c + 1;
}
int func(int b)
{
return nested_func(b + 1);
}
int main()
{
std::cout << func(777);
}if consteval (...) (C++23)
// compile-time pow for uints
consteval std::uint64_t ipow_ct(std::uint64_t base,
std::uint8_t exp) {...}
constexpr std::uint64_t ipow(std::uint64_t base, std::uint8_t exp) {
// use a compile-time friendly algorithm
if consteval {
return ipow_ct(base, exp);
}
// use runtime evaluation
else {
return std::pow(base, exp);
}
}
int main(int, const char* argv[]) {
static_assert(ipow(0,10) == 0 && ipow(2,10) == 1024);
std::cout << ipow(std::strlen(argv[0]), 3) << '\n';
}Links
- Cppreference:
- https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/20
- https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/23
- YouTube:
- Marc Gregoire: C++20 An (almost) Complete Overview
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FRkJCvHWdwQ - Sy Brand: What's new in C++23
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbHWDvY59SQ
- Marc Gregoire: C++20 An (almost) Complete Overview
Fragen
Neue C++ Features
By Christian Heusel
Neue C++ Features
- 302



