Digital Methods for Art Historians
ryan clement
geocoding + GIS
2020-02-24
data services librarian
what we're doing
- GIS and mapping: basic concepts
- geocoding with Awesome Table & Google Sheets
- mapping with ArcGIS Online
Raster data
Raster data is stored as a grid of values which are rendered on a map as pixels. Each pixel value represents an area on the Earth’s surface.
Vector data
Vector data structures represent specific features on the Earth’s surface. Vectors are composed of discrete locations (x, y values) known as vertices that define the shape of the object. Organization of the vertices determines whether we are working with: point, line or polygon.
Raster data
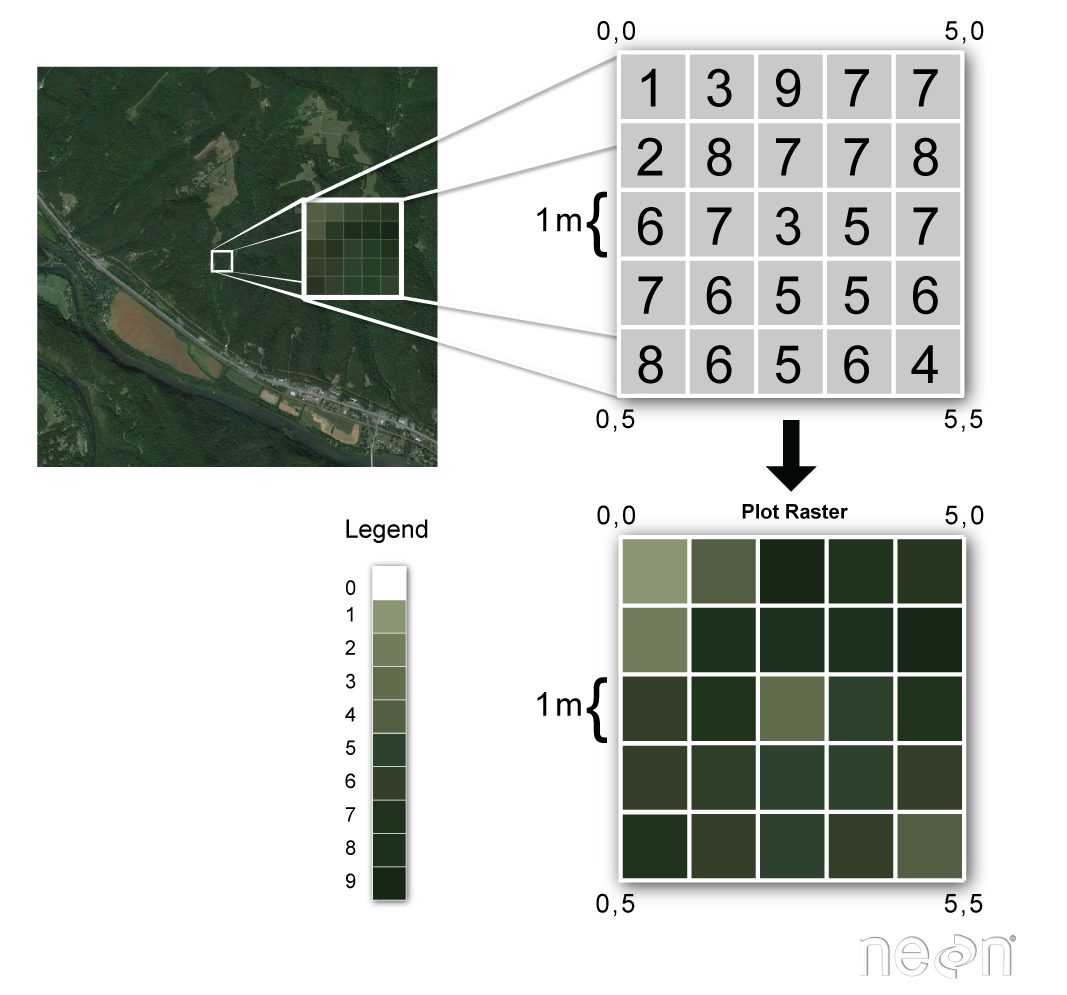
image credit: National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON)
Vector data
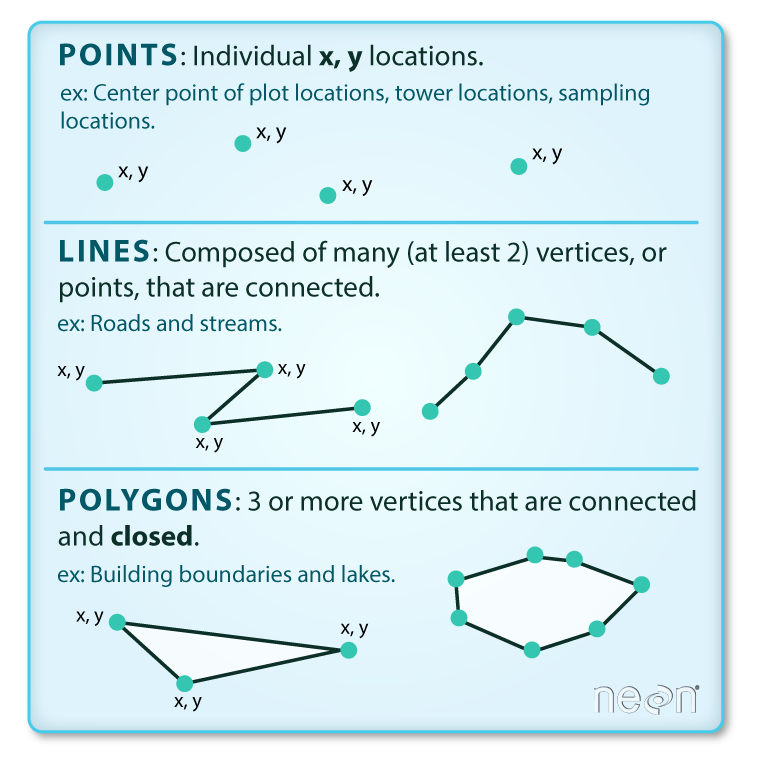
image credit: National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON)
Coordinate Reference Systems

Source: opennews.org
datum: what shape the earth is
projection: how you flatten that shape


geocoding
partial address -> standardized address -> standardized coordinates
GIS Tools
- GIS software tools and packages for programming languages: https://datacarpentry.org/organization-geospatial/04-geo-landscape/index.html
- Geocoding with AwesomeTable and Google Sheets
mapping with ArcGIS online
First...what is GIS?
- GIS stands for Geographic Information System
- GIS is a tool used to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present geographic data
- The data used with GIS is spatial data (data that is referenced to points on the Earth)
- GIS is not a map!
maps are made of layers
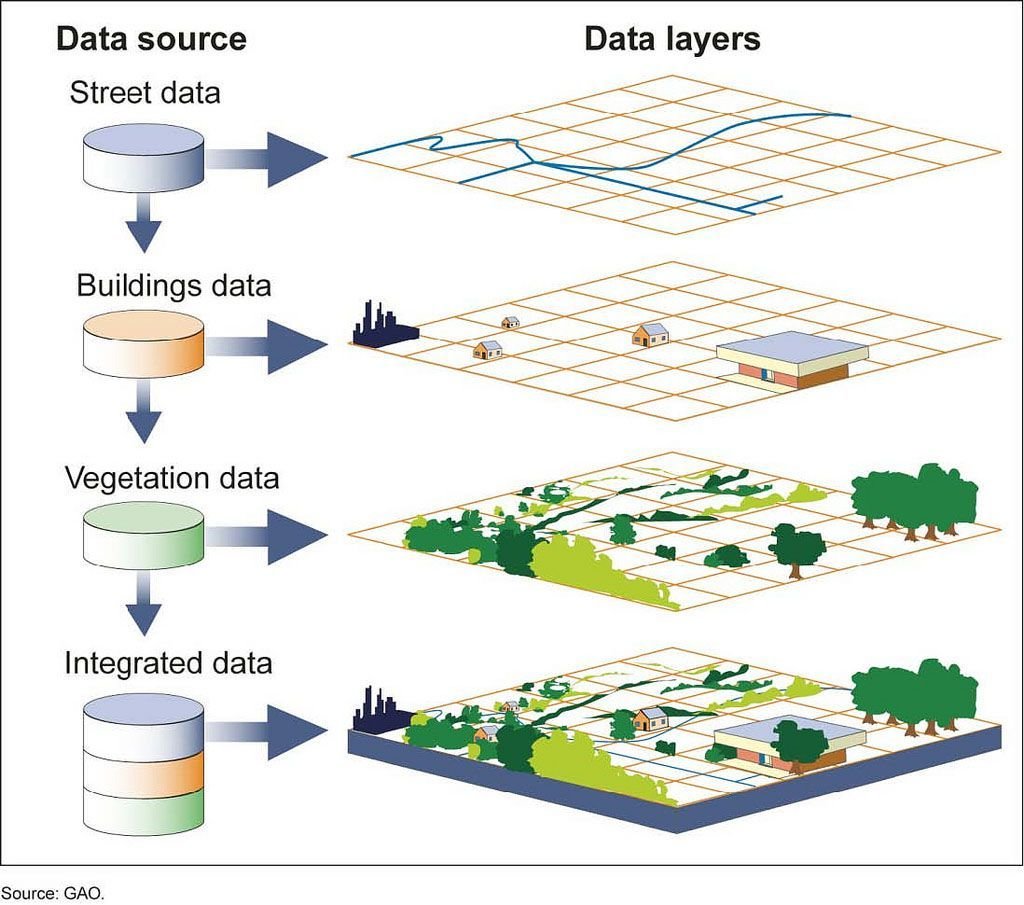
What are our possible layers?
- basemap
- locations of archaeological finds
- locations of dealers/collectors
- locations of museums
- etc...
let's make a map!
ArcGIS Online: go/arcgisonline/
more resources for ArcGIS Online
harc0355 geocoding + gis
By Ryan Clement
harc0355 geocoding + gis
- 1,065



