Organizing & Describing Your Data
Ryan Clement | Fall 2015
What we'll cover
- Why data management is important
- File naming conventions
- Organization
Why
Manage Data?
Look Familiar?
What is research data?
University of Edinburgh
MANTRA Research Data Management Training,
‘Research Data Explained’
Unlike other types of information, research data are collected, observed, or created, for the purposes of analysis to produce and validate original research results.”
Why manage data?
The Researcher Perspective
Manage your data for yourself to:
- Keep yourself organized
- Track your research processes for reproducibility
- Better control versions of data
- Quality control your data more efficiently
Why manage data?
The Researcher Perspective
Manage your data for yourself to:
- Make backups to avoid data loss
- Be prepared: Document your data for your own recollection, accountability & re-use (by yourself or others)
- Format your data for re-use (by yourself or others)
- Prepare it to share it – gain credibility & recognition for your science efforts!
Organizing & Describing

File Naming

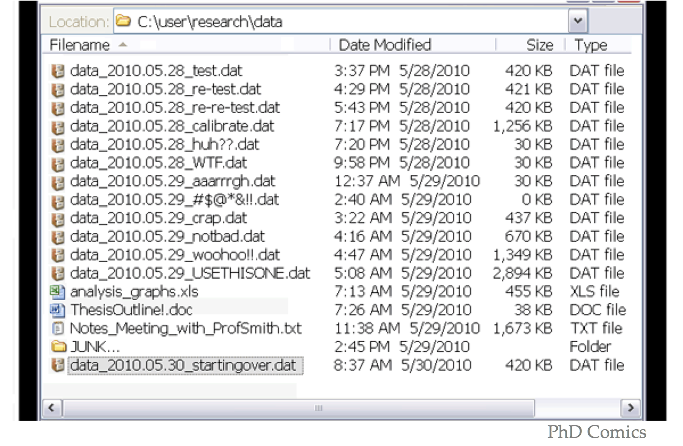

File Naming Best Practices
BE CONSISTENT
Have conventions for naming:
- Directory structure
- Folder names
- File names
-
Always include the same information
- (e.g. date and time)
-
Retain the order of information
- (e.g. YYYYMMDD, not MMDDYYY )
File Naming Best Practices
BE DESCRIPTIVE
- Try to keep file and folder names under 32 characters
Within reason, Include relevant information such as:
- Unique identifier (ie. Project Name or Grant # in folder name)
- Project or research data name
- Conditions (Lab instrument, Solvent, Temperature, etc.)
- Run of experiment (sequential)
- Date (in file properties too)
- When using sequential numbering, make sure to use leading zeros to allow for multi-digit versions. For example, a sequence of 1-10 should be numbered 01-10; a sequence of 1-100 should be numbered 001-010-100.
- No special characters: & , * % # ; * ( ) ! @$ ^ ~ ' { } [ ] ? < > - + /
-
Use only one period and before the file extension
- (e.g. name_paper.doc NOT name.paper.doc OR name_paper..doc)

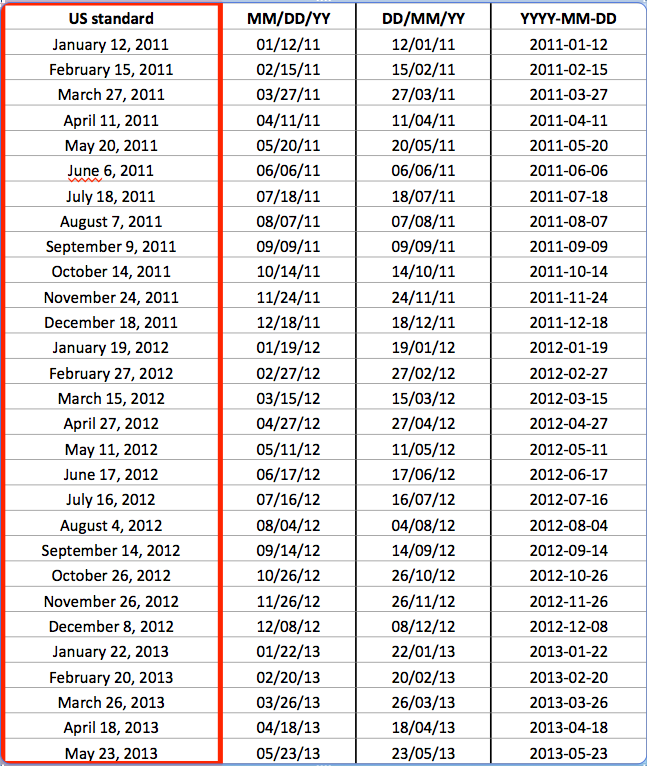
Why use ISO
Date Formatting?

Why use ISO
Date Formatting?
Why use ISO
Date Formatting?
If we sort by month, dates are out of order.
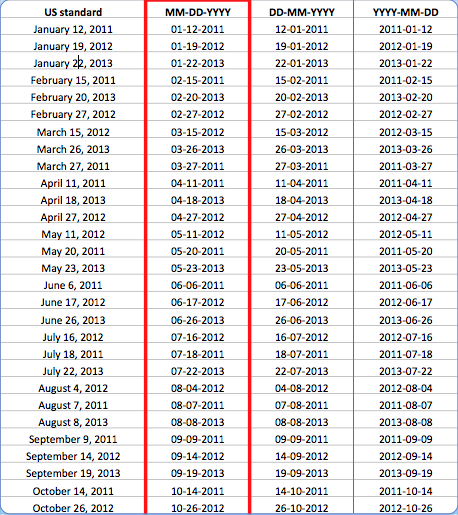
Why use ISO
Date Formatting?
If we sort by day, dates are out of order.
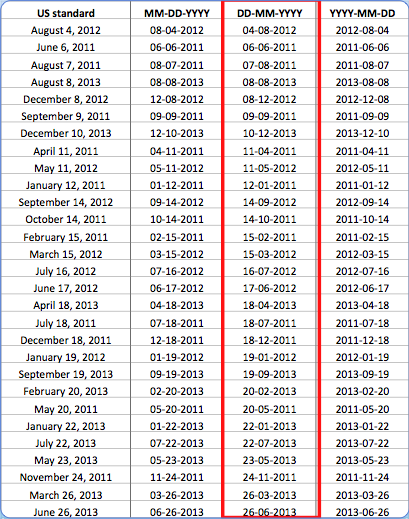
Why use ISO
Date Formatting?
If we sort by year, dates are in order!
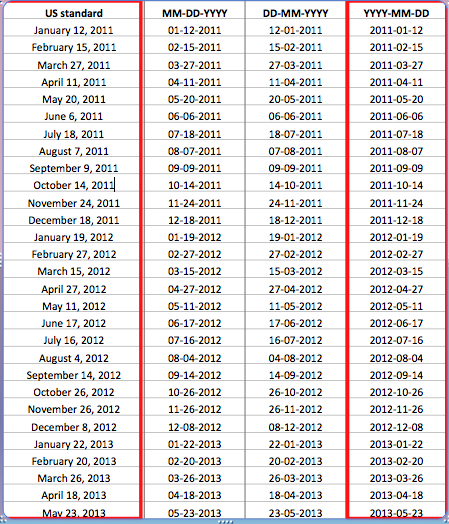
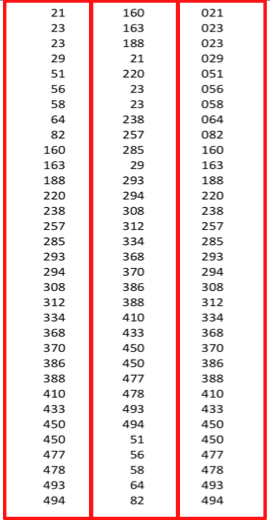
Why use
Leading Zeros?
Same reasoning as date ordering...
File
Organization
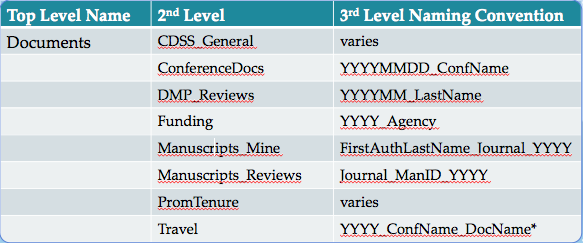
One approach...
But there is no "one solution"!
ThoughtfulConsistent
Document


Organizing & Describing Your Data
By Ryan Clement
Organizing & Describing Your Data
- 1,526



