C++第三堂課
二維陣列
二維陣列
直的為第i排
橫的為第j格
陣列從[0][0]開始
建立二維陣列
a[20][30];
前面的20代表有20排
後面的30代表有每排有30格
二維陣列
//建立二維陣列
int a[10][10] = {};
int a[10][10] = {0};//在建立二維陣列時塞入數字
int a[3][3] = {{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6},{7, 8, 9}};
二維陣列
//輸入
for(int i = 0; i<r; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<c; j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}//輸出
for(int i = 0; i<r; i++){
for(int j = 0j<c; j++){
cout<<a[i][j];
}
}小試身手
1.輸入1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9進二維陣列
並用九宮格形狀輸出
2.輸入1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9進二維陣列
輸入i, j後輸出第[i][j]格的數字
設立圍牆
圍牆是用於避免碰到陣列數字以外的地方
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[4][4];
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<4; j++){
a[i][j] = -1;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i<2+1; i++){
for(int j = 1; j<2+1; j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
}字元字串
字元字串
字元字串用於輸入文字
字元輸入一個文字
字串輸入一串文字
可以將字串轉為字元
把字串中每個字分開來做運算
字元字串
在使用字元字串功能時
需要先引入<string .h>函式庫
賦值 : str1 = str2
相等 : str1 == str2
串接字串 : str1 += str2
字串大小 : str1.size()
字串為空 : str1.empty()
字串長度 : str1.length()
字元字串
可以把字串想像為字元的陣列型態
string a = "hello";
|
|
|---|
h
e
l
l
O
'\0'
char b[] = a;
字元字串
如何用for迴圈運行字串中的每一項
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string a;
cin>>a;
for(int i = 0; i<a.length(); i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
//或是
for(int i = 0; a[i] != '\0'; i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
小試身手
輸入一個數字n,代表接下來有幾個字母
將字母輸入char陣列再統一 輸出
寫完之後試試看a109:小瑛拼單字
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char a[100];
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cout<<a[i];
}
}
小試身手
輸入一個字串,將字串倒轉後輸出
設輸入hello
則輸出olleh
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string a;
cin>>a;
for(int i = a.length()-1; i>=0; i--){
cout<<a[i];
}
}
ASCII碼
ASCII碼
每個字母,還有數字在字元中都有一個代表數,這個數就是ASCII碼
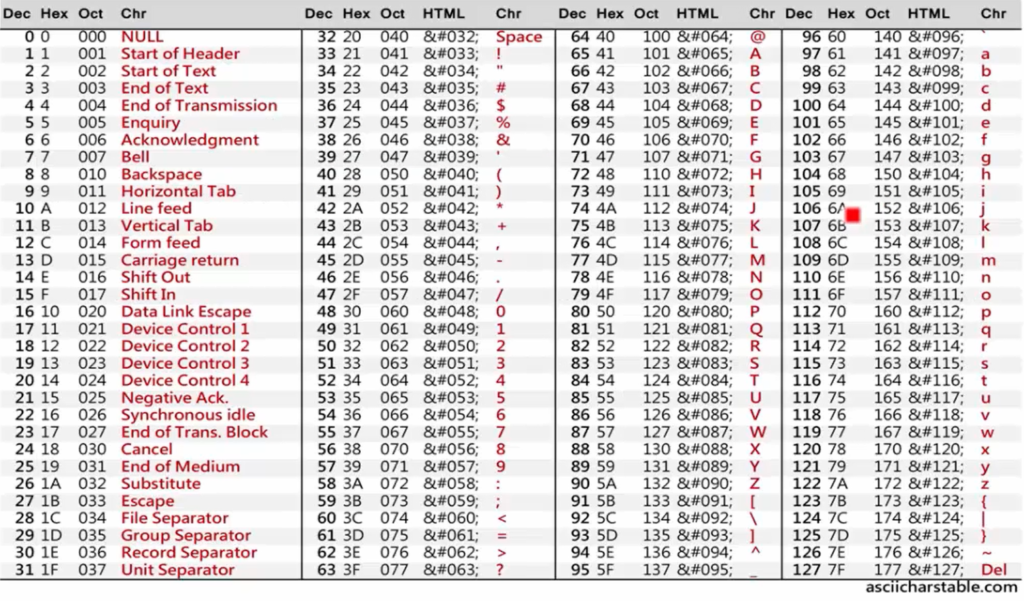
ASCII
ascii可以代替字元進行比較
在電腦中ascii碼則是字元的概念
你可以
//輸入一個大寫字母,輸出他與字母A距離多遠
#include<iostream>
#include<string .h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char a;
cin>>a;
cout<<a-'A';
//或是
cout<<a-65;
}deck
By CMIOC 29
deck
- 131



