crash
course
Node.js
agenda
[
"Kick Off",
"Hands-On Coding",
"Review & Next Steps"
]HOW DOES node.js WORK?
what is node?
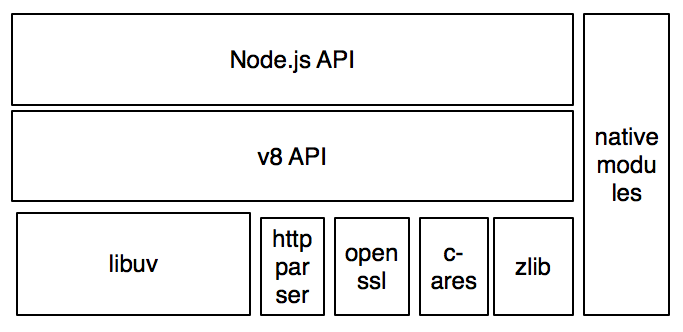
why node?
Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient, perfect for data-intensive real-time applications that run across distributed devices.
nodejs.org
"
"
Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model that makes it lightweight and efficient, perfect for data-intensive real-time applications that run across distributed devices.
non-blocking

i/o
Database (MongoDB, CouchDB, Redis)
Third-party APIs (Twitter, Facebook, APNS)
Websockets (real-time)
Files (image resizer, video editor)
read data from Facebook API
process data
send data to the clienttasks
callbacks
non-linear thinking
pseudocode
callbacks
non-linear thinking
var data = load(...)
var info = process(data)
send(info)What would happen if we ran this in Node?
node
callbacks
non-linear thinking
load(function loaded(data) {
process(data, function processed(info) {
send(info)
})
})
Node follows the 'observer' pattern
frontend
node
target.addEventListener('click', function(e) {...});response.on('data', function(d) {...});events
One-to-one dependency
callbacks
events
comparison
Many-to-many "subscription" API
command line
node
...is the package manager for node
npm
(pedantic note: npm does not stand for node package manager)
(duh)
...live at
... & express, grunt-cli, etc.
/usr/local/bin
command line
...is the version manager for node
nvm
(side note: this is more important now that io.js exists)
modules
third-party
connect is
built-in
express is connect plus templating
http.Server
plus static
plus over 130,000 more
(disclaimer: over-simplification)
http(s), fs, url, events, modules
http(s), fs, url, events
modules
how modules work
// model.js
var User = function(name, email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
};// someRoute.js
var Model = require('./model');
var u = new Model.User();module.exports.User = User;how modules work
// user.js
var User = function(name, email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
};// someRoute.js
var User = require('./user');
var u = new User();module.exports = User;(see the difference?)
folders as modules
organizing your code
index.js
package.json
(1)
(2)
how modules work
one more thing...
require()
modules that you
are cached
based on file name
modules
a few favorites...
async
for tasks in a series or in parallel
lodash
for "functional"
/
underscore
tasks like mapping and filtering
passport
for managing authentication
express
A QUICK DETOUR...
REST
GET
retrieves a resource or collection
POST
creates member(s) of a collection
(disclaimer: over-simplification)
REST
GET
http://.../api/coll
...to retrieve a collection
GET
http://.../api/coll/1
...to retrieve specific resource
A QUICK DETOUR...
(disclaimer: over-simplification)
REST
http://.../api/coll
POST
...to create or update a resource
{
"someKey": "someValue"
}A QUICK DETOUR...
(disclaimer: over-simplification)
express
// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.listen(1337);node app.js
npm install express --save
(1)
(2)
(3)
express
your app
// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);
// application
// routing logic
// and middleware
// goes here// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);routing logic
where do requests go?
app.get('/', function(req, res, next) {
res.status(200).send('hello world');
})// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);routing logic
using regular expressions
app.get('/:id([A-Za-z0-9]{10})', function(req, res, next) {
res.status(200).send('hello ' + req.params.id);
});
app.all('/*', function(req, res, next) {
res.status(200).send('hello world');
});
// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);routing logic
chaining
app.all('/*', function(req, res, next) {
// authentication logic => 401 or...
next();
});
app.get('/*', function(req, res, next) {
res.status(200).send('hello world');
});
routing logic
advanced topics
vhost
for routing to subdomains
express.Router
to make your
routing logic modular, given a path
Request
function(req, res, next) { ... }
an incoming object
middleware
response
function(req, res, next) { ... }
the outgoing response
middleware
coming up
function(req, res, next) { ... }
go to the next handler, but...
only if no response has been sent
middleware
middleware
// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);where does it fit in?
app.get('/', function(req, res, next) {
/* this is middleware */
});middleware
which came first?
// app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);
app.get(/** 404 middleware **/);
app.get(/** static middleware **/);rendering with templates
templates
using jade
// base.jade
html
head
title Hello World
link(rel='stylesheet', href='/css/base.css')
block head
body
block body
script(src='/js/base.js')// index.jade
extends base
append body
h1 #{message}templates
using jade
// app.js
var express = require('express');
var jade = require('jade');
var app = express();app.listen(1337);
app.set('views', './views');
app.set('view engine', 'jade');
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.render('index', { message: 'Hello world!'});
});
hands-on
bitly.com/thinkful-media-app
Crash Course — node.js
By Cameron Hendrix
Crash Course — node.js
- 1,407

