Async Javascript

- Why Async
- Callback
- Promise
- async await





Loading....
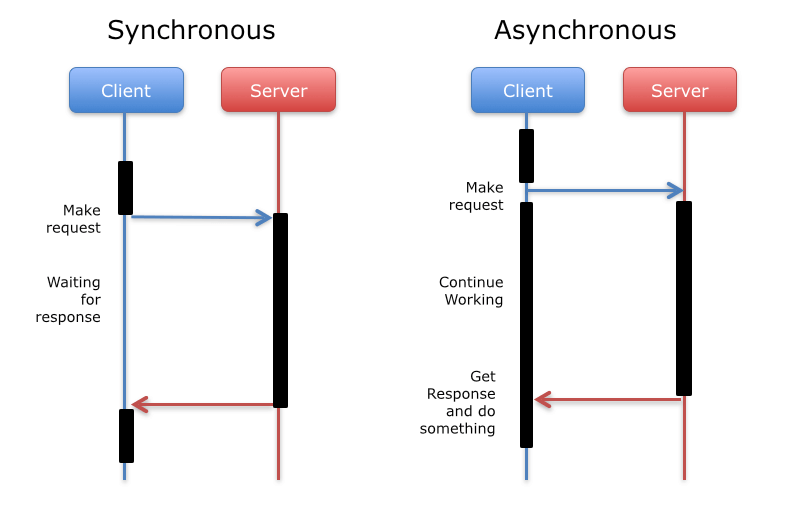
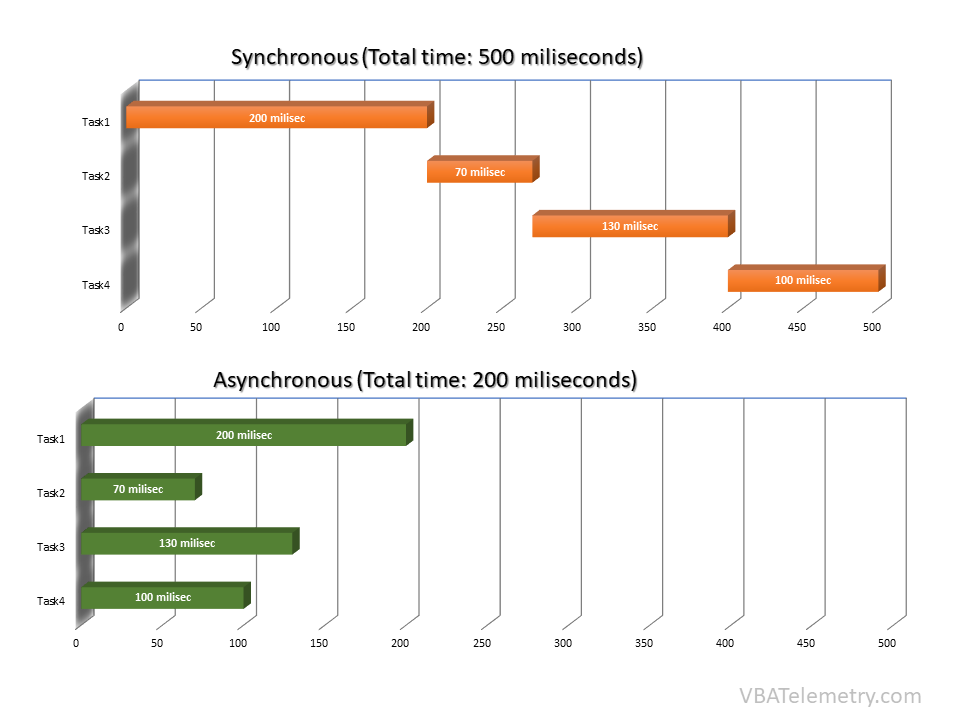
still we can do lots of things



Loading....
still we can do lots of things

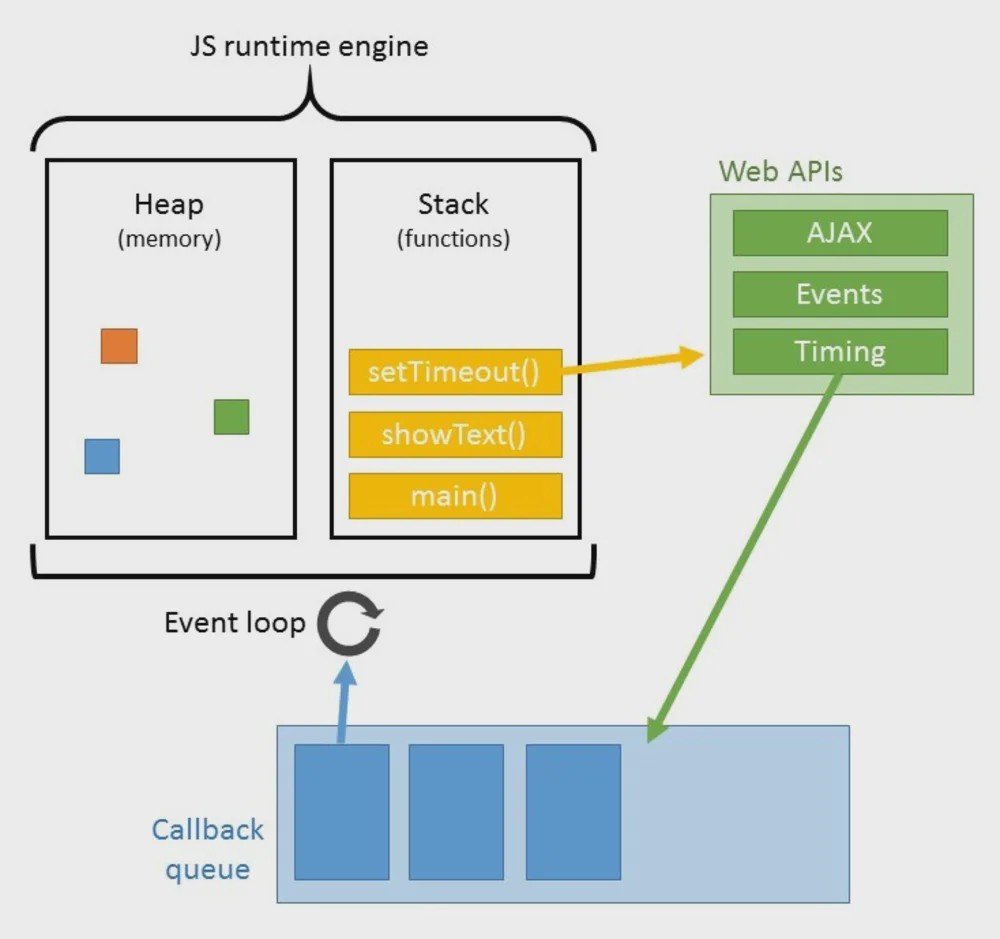

next..CALLBACK

CALLBACK
ok
Async 가 좋은 것은 알겠는데..
순서를 제어하고 싶은 경우엔 어떻게?

const printString = (string) => {
setTimeout(
() => {
console.log(string)
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
)
}
const printAll = () => {
printString("A")
printString("B")
printString("C")
}
printAll() // what do you expect?Here comes CALLBACK


A way to handle async

const printString = (string, callback) => {
setTimeout(
() => {
console.log(string)
callback()
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
)
}
const printAll = () => {
printString("A", () => {
printString("B", () => {
printString("C", () => {})
})
})
}
printAll() // now what do you expect?Callback
Text
const somethingGonnaHappen = callback => {
waitingUntilSomethingHappens()
if (isSomethingGood) {
callback(null, something)
}
if (isSomethingBad) {
callback(something, null)
}
}Callback error handling Design

somethingGonnaHappen((err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.log('ERR!!');
return;
}
return data;
})Usage
callback is great but..
there is one thing, callback HELL
Callback

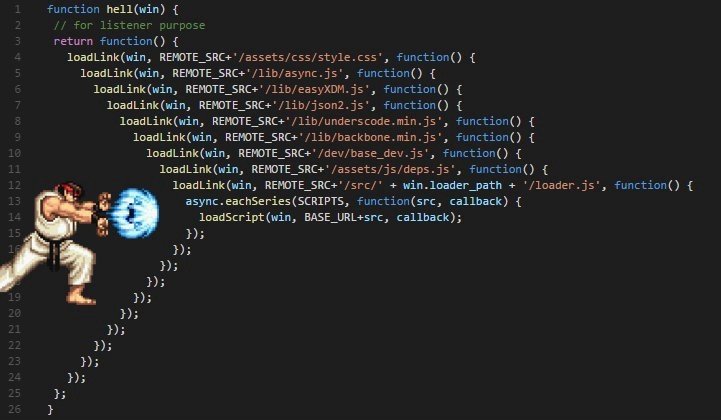
next... Promise

Promise
How to deal with callback chain


Promise
How to deal with callback chain

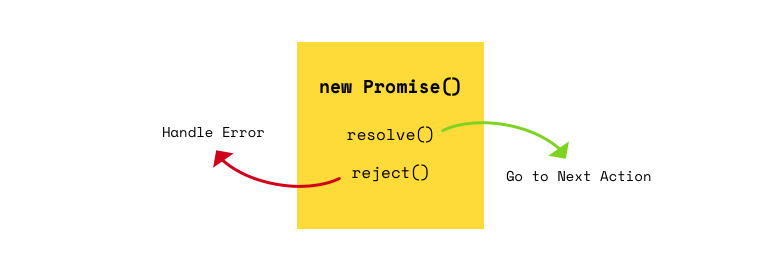

const printString = (string, callback) => {
setTimeout(
() => {
console.log(string)
callback()
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
)
}
const printAll = () => {
printString("A", () => {
printString("B", () => {
printString("C", () => {})
})
})
}
printAll() // now what do you expect?Callback

const printString = (string) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(
() => {
console.log(string)
resolve()
},
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
)
})
}
const printAll = () => {
printString("A")
.then(() => {
return printString("B")
})
.then(() => {
return printString("C")
})
}
printAll()Callback -> Promise
Promise
How to deal with callback chain

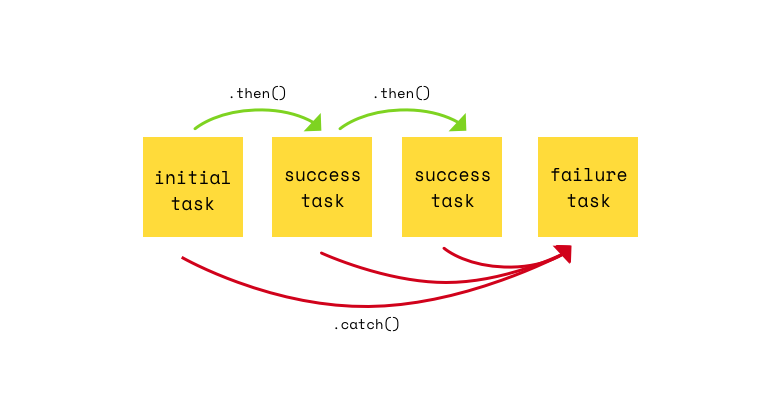
remember callback hell?
Callback Hell and.. Promise Hell


function gotoCodestates() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('1. go to codestates') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function sitAndCode() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('2. sit and code') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function eatLunch() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('3. eat lunch') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function goToBed() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('4. goToBed') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
gotoCodestates()
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
sitAndCode()
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
eatLunch()
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
goToBed()
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
})
})
})
})Promise Hell

function gotoCodestates() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('1. go to codestates') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function sitAndCode() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('2. sit and code') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function eatLunch() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('3. eat lunch') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function goToBed() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('4. goToBed') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
gotoCodestates()
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
return sitAndCode()
})
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
return eatLunch()
})
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
return goToBed()
})
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
})Promise Chaining

function gotoCodestates() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('1. go to codestates') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function sitAndCode() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('2. sit and code') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function eatLunch() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('3. eat lunch') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
function goToBed() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('4. goToBed') }, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1)
})
}
const result = async () => {
const one = await gotoCodestates();
console.log(one)
const two = await sitAndCode();
console.log(two)
const three = await eatLunch();
console.log(three)
const four = await goToBed();
console.log(four)
}
result();async await

THE END

Async Javascript
By Codestates
Async Javascript
v2.0
- 1,308


