Software Craftsmanship
Introduction and Philosophy
April 19, 2016
Introduction
Scott Franks
Feb 2013
RDT
Rage ATM
Osborne, Austin
July 2015
Security Tech Ops - Data Lake
Purple Rain
Walters, Darwin
Feb 2015
Card
Mainstreet DevOps
https://pollev.com/scottfranks188
What is Software Craftsmanship?
I see software development as a creative blend of art, science, and engineering, whose purpose is to deliver effective systems. The best way I have been able to describe this idea is by talking about software craftsmanship. The software craftsmanship metaphor allows developers to acknowledge all aspects of their craft – the artistic and aesthetic aspects as well as the measurable and mechanical aspects. - Peter McBreen
Software Craftsmanship is a metaphor. The goal being to emphasize personal skill, mastery of tools and techniques, along with productive relationships with your peers and clients.
Software as a Craft
A craftsman or artisan is a skilled manual worker who makes items that may be functional or strictly decorative.
- How is software a craft?
- How is software different from typical crafts?
- What things make programmers artisans?
- Why is it important to improve in your craft?
- What are important qualities of a skilled craftsman?
- How can you improve your crafting skills?
Software as an Art
Writing code is similar to painting a picture. A programmer who writes clean code is an artist who can guide a blank screen through a series of transformations until it is an elegantly coded system.
-
Easy to recognize a good painting.
-
Hard to paint a good picture.
Programmers are authors – responsible for communicating well with their readers.
-
You write for readers who need to comprehend your motivation and intentions.
-
The ratio spent reading vs. writing code is usually at least 10:1.
Software as a Science
The communal growth of Software Craftsmanship is analogous to the Scientific Method. There have been many developers before you:
-
If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants. - Isaac Newton
The best practices, design patterns, and design principles we are going to go over in this course were created by "giants". Leveraging them will allow you to produce more value than reinventing the wheel through trial and error.
The Scientific Method
Tackle development tasks with a structured approach.
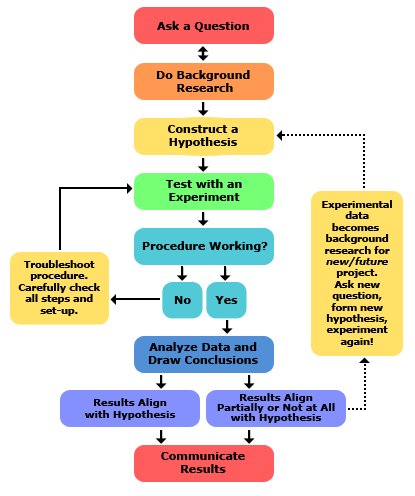
Science
UI/UX Design
Programming
Bridge Building
Ask a Question
Background Research
Construct Hypothesis
Test with Experiment
Analyze Data &
Draw Conclusions
Communicate Results
Identify a User Problem
User Research and Interviews
Construct
Prototype
User Testing and Feedback
Incorporate Feedback
Hand Off / Implement Design
Proposal Request
Survey Site
Design to Specifications
CAD and Physical Model
Improve Structure
Build Bridge
Identify Technical Problem
Gather Requirements
Plan Stories and Design System
PoC, User and Perf Testing
Improve Structure
QS Validation and Release
Why think of software development as a science?
Thinking of software development as a Science will help break the bad habit of:
"I don't know what to do so I'll just write code and see what happens..."
A civil engineer wouldn't say:
"I don't know what to do so I'll just start building this bridge and see what happens..."
Why think of software development as a craft/art?
Effective way to transition from the college mindset of software development to a professional mindset.
- From "journeyman" to "master"
Aligns with Capital One's objective of becoming an industry leader in technology.
Important for improving your technical skills and succeeding in the workplace.
From Journeyman to Master
As a student:
- Solve it
- Test it
- Fix it
- Turn it in
- Forget about it
As a professional:
- Solve it
- Make it easy to understand
- Make it easy to use
- Make it easy to change
- Test it
- Fix it
- Review it
- Commit it
- Test it
- Release it
- Support it
Mantras of a Software Craftsman
-
Broken windows
- One broken window, left unrepaired, instills in the community a sense of abandonment.
-
Boy Scout rule
- "Leave the campground cleaner than you found it."
-
Tests are your parachute
- Keep them free of holes and obstructions.
Your Knowledge Portfolio
Your knowledge and experience are your most important professional assets.
Unfortunately, they're expiring assets.
- Invest regularly
- Diversify
- Manage risk
- Buy low, sell high
- Review and rebalance
Expand your knowledge portfolio regularly; not only with technical expertise but also Capital One expertise.
Care about your craft
Think about your work
Continuously make small improvements
Code Reading Competition
https://gist.github.com/ClassicThunder/17f860ec37bc0e304ccc369911f865c8
Copy of Software Craftsmanship - Intro & Philosophy
By cof_softwarecraftsmanship
Copy of Software Craftsmanship - Intro & Philosophy
2016 - Day 1.1 - Session 2 Nova
- 351



