深入CSS
CSS优先级
选择符优先级
- Inline style
- Id选择符 #id
- Class选择符 .class :hover [href='']
- Tag选择符 div :before
来源优先级
- 浏览器默认规则 (User Agent declarations)
- 用户自定义规则 (user normal declarations)
- 网页作者指定规则 (author normal declarations)
- 网页作者指定重要规则 (author important declarations)
- 用户自定义重要规则 (user important declarations)
优先级
- 后设优先
盒子模型(Box Model)
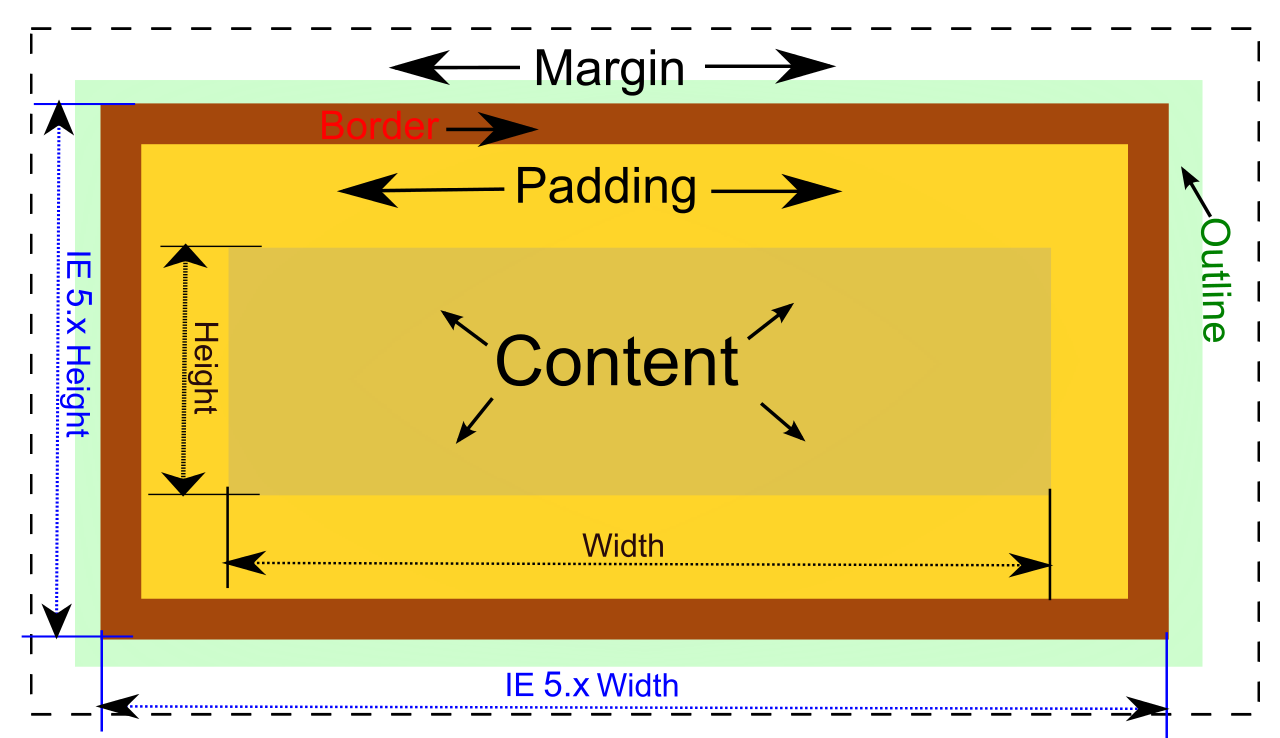
相关CSS属性
- 基本属性
- Width/Height
- Padding
- Margin
- Boder
- Outline
- 偏移量属性
- Top/Left/Bottom/Right
- Top/Left/Bottom/Right
- 和.NET WinForm的区别:
- 默认情况下Width/Height不包含Padding
- Margin/Padding属性的四个值的顺序是top right bottom left (顺时针吮吸)
所有东西都是盒子
-
块级盒子 (Block Box) 和 匿名块级盒子(Anonymouse Block Box)
- <div>Some text<div>another text</div></div>
- Inline Box & Anonymouse Inline Box
- <div>Text<em>Text</em></div>
- 行盒子(Line Box)
- <div>Some textlong and long</div>
Some text long and long
纵向Margin合并
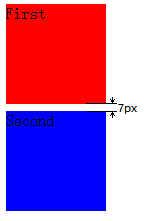
<div style="margin:5px;background:red;">
First
</div>
<div style="margin:7px;background:blue;">
Second
</div>Position属性
- Static 普通流布局(Normal flow)
- Relative 支持偏移量属性的普通流布局
- Absolute 在容器元素内绝对定位的布局
- Fixed 在显示范围内的绝对定位布局
Float属性
- Float box被从正常流布局中移除
- Float box只会影响设置了clear属性的块级元素和inline元素的布局。
- 默认情况下容器元素计算高度的时候,不会计算浮动型子元素,除非设置容器元素的overflow为auto.
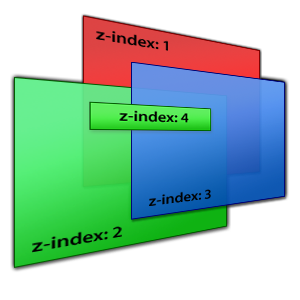
Stacking context
Stacking context
- the root element (HTML),
- positioned (absolutely or relatively) with a z-index value other than "auto",
- a flex item with a z-index value other than "auto",that is the parent element display: flex|inline-flex,
- elements with an opacity value less than 1. (See the specification for opacity),
- elements with a transform value other than "none",
- elements with a mix-blend-mode value other than "normal",
- elements with a filter value other than "none",
- elements with isolation set to "isolate",
- position: fixed
- specifying any attribute above in will-change even if you don't specify values for these attributes directly
- elements with -webkit-overflow-scrolling set to "touch"
浏览器会给符合下面规则的dom元素分配一个Stacking context。
z-index
- z-index的默认值是“auto",而不是”0“
- 只有Positioned(Position不为static,或者作为flex布局的子元素)元素的z-index属性才有效
- z-index为"auto"的元素,即使Positioned,也不会生成Stacking context,因此这些元素的子元素的z-index会被合并考虑
- z-index可以是负数
- 没有z-index或z-index无效的元素(参见第二条)相当于z-index为0;
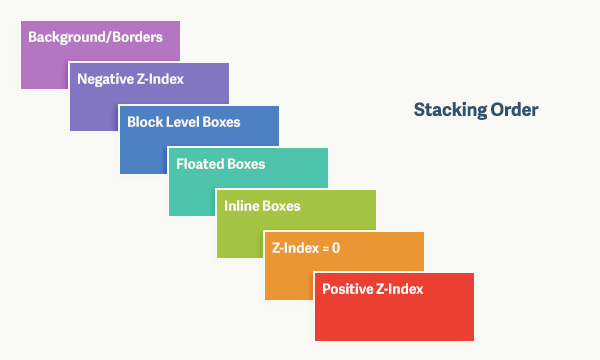
Stacking order
Elements with stacking context
- 根据DOM树结构,具有stacking context的元素会形成一个树形结构。
- 一个stacking context中的元素会根据z-index决定叠加顺序。z-index大的靠上
- z-index 0级元素中,有stacking context的元素的叠加顺序靠前
- 以上条件不能区分时,使用DOM树中的顺序决定叠加顺序。
性能

不做性能测试的性能优化都是耍流氓
像素渲染流水线

- Style
- 降低样式选择器的复杂度
- 减少需要执行样式计算的元素的个数
- Layout
- 尽可能避免触发布局
- 几乎所有的布局都是在整个文档范围内发生的。
- 使用flexbox替代老的布局模型
- 避免强制同步布局事件的发生
- 避免快速连续的布局
- 尽可能避免触发布局
像素渲染流水线

- Paint
- 除了transform和opacity之外,修改任何属性都会触发绘制
- 提升移动或渐变元素的绘制层
- 减少绘制区域
- 简化绘制的复杂度
- Composite
CSS 选择器性能
- 一个选择器的最右端是这个选择器的关键条件(Key Selector)
- 浏览器按照从右向左的方式匹配选择器,因此应该将更具体的条件尽可能放在右端。
- 避免使用*规则
- 选择器尽可能短
- ID选择符前面不要再加限定符
- 没必要用Tag选择符限定Class选择符
Thank you
深入CSS
By Colin Han
深入CSS
- 2,462


