Blockchain
@cosmycx
Text
Decentralization
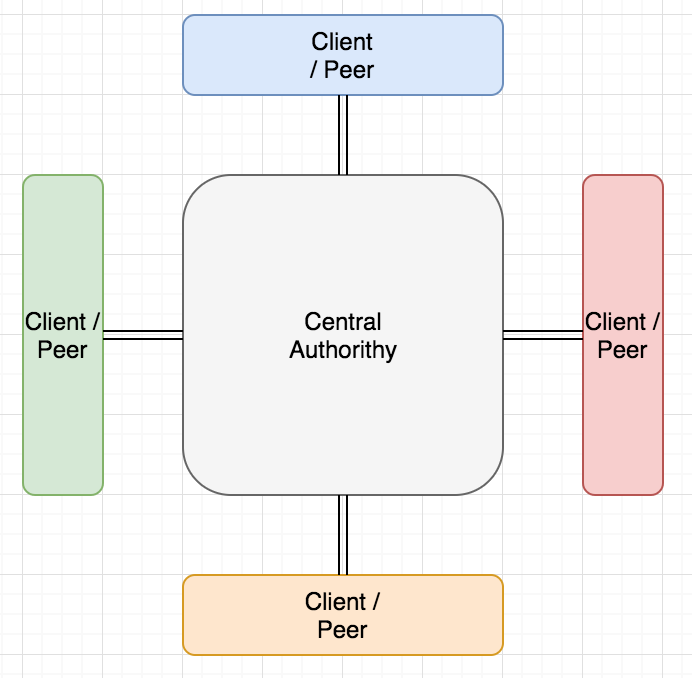
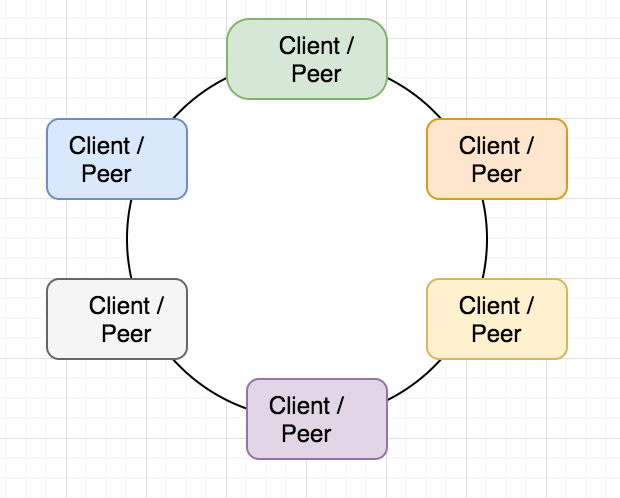
Distributed System
How it Started
https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
- October 2008, Nakamoto (group or individual) published a paper on Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
- "A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution"
What Makes it Possible
Computer Networks Protocols: TCP/IP
Mathematics and Cryptography
Digital Signature: Private - Public key pair
Cryptographic Hash Functions
sign with Private key, anyone can verify authenticity by using the corresponding Public key
maps data of arbitrary size to unique data of a fixed size, a.k.a. checksum, digest, digital fingerprint


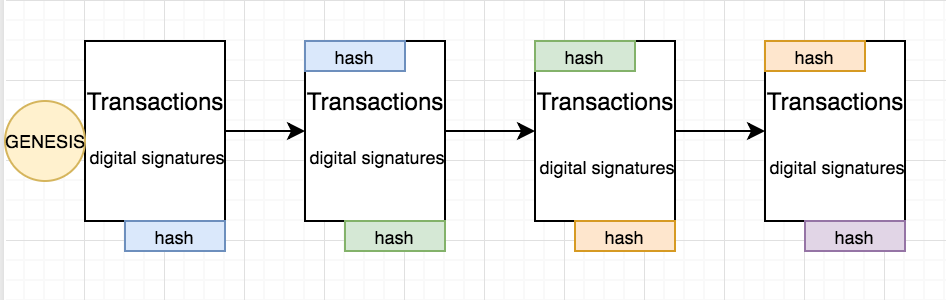
Blockchain

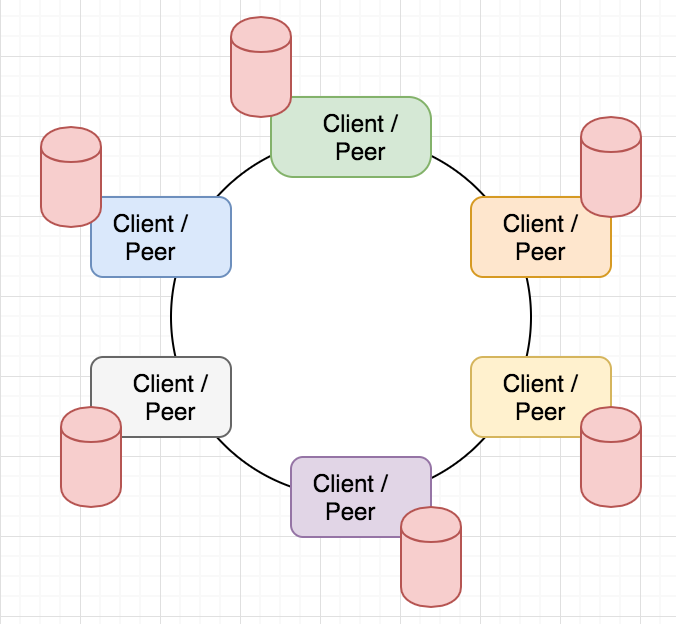
Each peer has the ledger (database)
Transaction history is connected in an immutable chain
Ledger is advanced in a process called mining where peers take turns to make the next block based on mathematics
Why Care?
Each peer has the ledger (database)
Transaction history is connected in an immutable chain
- data exchanges
- supply chain
- audit
- proof of existence
- state (value) layer of internet
- trustless
- distributes trust
- minimized amount of trust needed
But Wait There is More
Smart Contracts
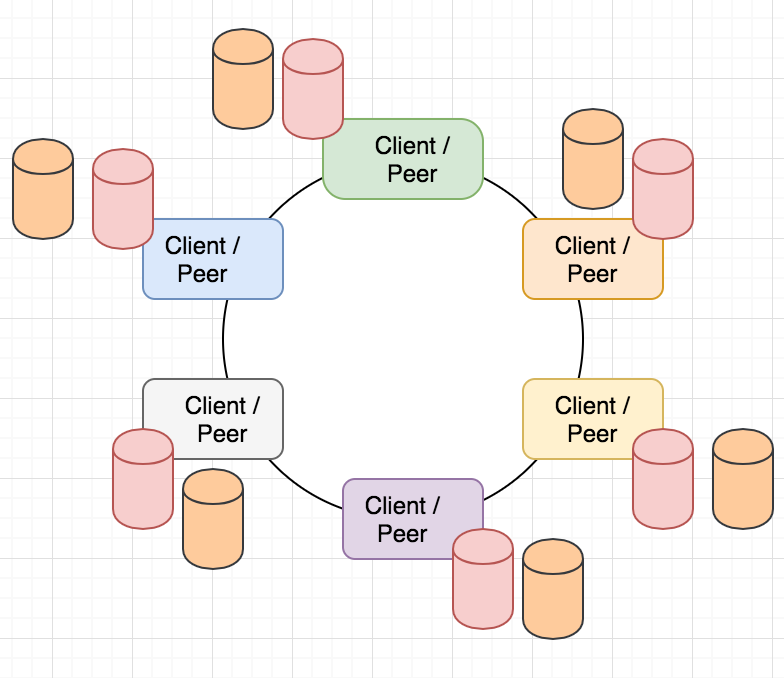
Smart Contracts Shared Ledger
Code that is guaranteed to perform as deployed, immutable.
Each peer has the ledger (database)

Why the Interest?
Smart Contracts
- tokens
- trustless agreements
- agreements without a third party
- digital identity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ERC-20
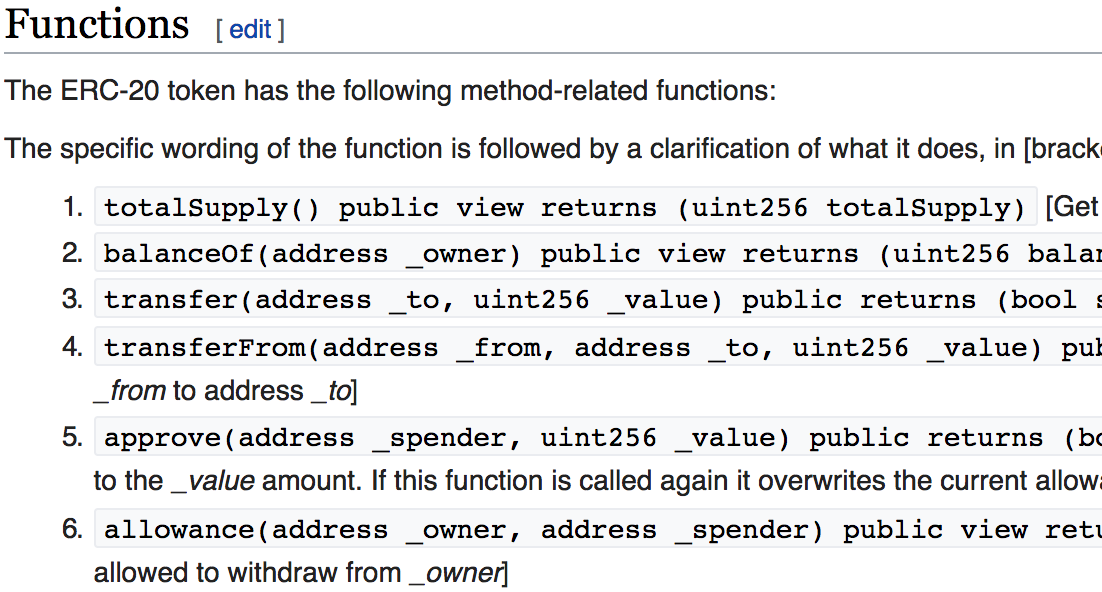
Example: Token Contract
Code that is guaranteed to perform as deployed, immutable.
Even More
Decentralized Storage

Distributed Storage




Decentralized Distributed System


Trust moves from Central Authority to the System
DEMO
Running a Bitcoin simulation in JavaScript
Blockchain
By Cosmin P
Blockchain
simplified
- 838



