Kotlin for Backend

Hi!
linkedin.com/in/cosminstefan
cosmin@greenerpastures.ro



Goal for today?
We've all heard
of Kotlin
But why?
A quick recap
Very powerful
General Purpose
Easy to learn
Great tooling (by JetBrains)
JVM compatible
Open Source (Apache 2.0)
Platform targeting

Android (Kotlin/JVM)
Server (Kotlin/JVM)
iOS (Kotlin/Native)
Browser (Kotlin/JS)
Fine... Kotlin...
What now?
Quite a few options!
Many Server-side Frameworks
Spring
Vert.x
Spark
Http4K
Ktor

Ktor

Framework for building asynchronous servers and clients in connected systems using Kotlin
Written in pure Kotlin
Jetbrain's official framework
Strong backers:
Lightweight & unopinionated
Very fast boot & routing
Performance:
Backed by Coroutines
Suspending API via NIO
Asynchronous I/O:
Servlet containers (Tomcat, Jetty)
Standalone (Docker, Fat JAR)
Hosting (AppEngine, Heroku)
Unopinionated deploy:
Authentication
CORS
Serialization
Powerful features:
Sessions
Templating
Compression
Static content
HSTS
Web Sockets
And even more features:
Auto-reload
Metrics
Logging
And many more ...
Project Setup
Ktor

start.ktor.io / IntelliJ Plugin
Base project structure
Bootstrapping:
start.ktor.io
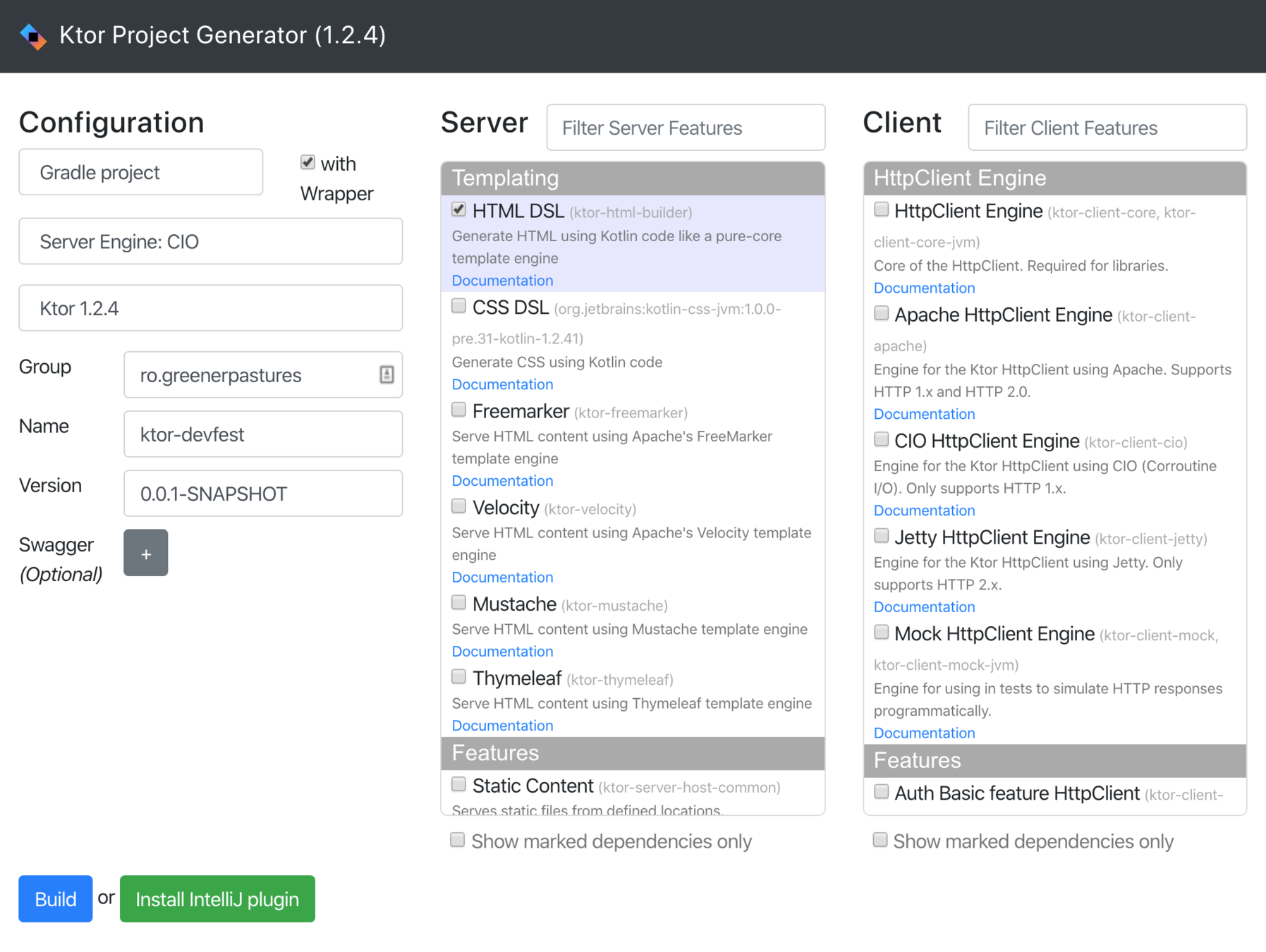
Base project
Gradle Build Setup
Pre-Configured dependencies
Ready to run
fun main(args: Array<String>): Unit = io.ktor.server.cio.EngineMain.main(args)
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
install(ContentNegotiation) { ... }
install(Compression) { ... }
install(AutoHeadResponse)
install(CallLogging) { ... }
install(CORS) { ... }
routing {
get("/") {
call.respondText("Hello World!", contentType = ContentType.Text.Plain)
}
get("/html-dsl") {
call.respondHtml {
body {
h1 { +"HTML" }
ul {
for (n in 1..10) {
li { +"$n" }
}
}
}
}
}
get("/json/gson") {
call.respond(mapOf("Hello" to "World"))
}
}
}Easy-win Features
Ktor

Defaults to SLF4J & Logback
Auto Call Result Logging
Logging:
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
log.debug("App has initialized at: {}", Instant.now())
install(CallLogging) {
level = Level.INFO
filter { call -> call.request.path().startsWith("/") }
}
...
}
Fast feedback loop cycle
Simple setup: watch list
Autoreload:
# In application.conf
ktor {
deployment {
port = 8080
watch = [ main, module1, module2 ]
}
…
}
Then just build the app!

Compress outgoing content
gzip, deflate, identity
Compression:
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
install(Compression) {
gzip {
priority = 1.0
}
deflate {
priority = 10.0
minimumSize(1024) // condition
}
}
...
}
Automatic content conversion
Based on Content-Type and Accept headers
Content negotiation:
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
install(ContentNegotiation) {
register(ContentType.Application.Json, JacksonConverter())
}
...
routing {
get("/data") {
call.respond(MyDataClass("Hello", "World"))
}
post("/data") {
val myRequest = call.receive<MyRequestClass>()
}
}
}
Automatic handling
Opens API for JavaScript calls
CORS Support:
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
install(CORS) {
method(HttpMethod.Patch)
method(HttpMethod.Options)
header(HttpHeaders.XForwardedProto)
host("example.org")
host("example.com", subDomains = listOf("www"))
}
...
}
Build HTML responses
Freemarker, Mustache, Thymeleaf, Veolcity, KotlinX
Templating:
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
install(Mustache) {
mustacheFactory = DefaultMustacheFactory("templates")
}
routing {
get("/html-mustache") {
val todo = Todo("Prepare presentation")
call.respond(MustacheContent("todos.hbs", mapOf("todo" to todo)))
}
get("/html-dsl") {
call.respondHtml {
body {
h1 { +"HTML" }
ul {
for (n in 1..10) {
li { +"$n" }
}
}
}
}
}
...
}
}Routing
Ktor

Support for simplifying and structuring
request handling
Valid paths for requests
Functions that process the requests
Main roles:
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
routing {
get("/") {
call.respondText("Hello World!")
}
route("/api/todos") {
// Final path: /apis/todos
get {
val todosList: List<Todo> = dataRepository.loadTodos()
call.respond(todosList)
}
// Final path: /apis/todos/items
post("/items") {
val item = call.receive<Todo>()
dataRepository.addTodo(item)
}
}
}
}route defines a base path for children
APIs can be separated
Keeping a clean structure:
fun Routing.todosApi() {
val dataRepository: DataRepository = ... // inject repository
route("/todos") {
// Resolves to /todos
get {
val todosList: List<Todo> = dataRepository.loadTodos()
call.respond(todosList)
}
route("/items") {
// Resolves to /todos/items
post {
val item = call.receive<Todo>()
dataRepository.addTodo(item)
}
// Resolves to /todos/items/{id}
delete("/{id}") {
val itemId = call.parameters["id"]
dataRepository.removeTodo(itemId)
}
}
}
}fun Application.module() {
routing {
route("/api/v1") {
// Install TODOs API module (Final path: /api/v1/todos)
todosApi()
// Install User Profile API module (Final path: /api/v1/profile)
profileApi()
}
// Install main HTML Web app module
webApp()
}
}Dependency Injection
Koin

A pragmatic lightweight dependency injection framework for Kotlin
No proxy
No code generation
No reflection
Performance:
Define modules
Lazy inject at
consumption location
Main principles:
class AuthenticationService {
...
}
class DataRepository(val authenticationService: AuthenticationService) {
...
}
val mainModule = module {
single { AuthenticationService() }
single { DataRepository(get()) }
}
fun Application.module(testing: Boolean = false) {
install(Koin) {
// Use SLF4J Koin Logger
slf4jLogger()
// Declare used modules
modules(mainModule)
}
...
routing {
// Lazy inject DataRepository
val dataRepository: DataRepository by inject()
get("/data") {
call.respond(dataRepository.loadData())
}
...
}
}
SQL Framework
Exposed

A lightweight SQL library for Kotlin, by Jetbrains
Typesafe SQL wrapping DSL
Lightweight data access objects (DAOs)
Layers of database access:
Typesafe
Full querying support
Comprehensive features:
PostgreSQL, MySQL, H2
MariaDB, Oracle, SQLite, SQL Server
Currently supported dialects:
object Users : Table("users") {
val id = integer("id").autoIncrement().primaryKey()
val name = varchar("name", 128)
}
object Todos : Table("todos") {
val id = integer("id").autoIncrement().primaryKey()
val description = varchar("description", 256)
val reminderAt = datetime("reminder_at")
val userId = integer("user_id").references(Users.id, ReferenceOption.CASCADE)
}class TodosRepository {
init {
Database.connect("jdbc:h2:mem:todos", driver = "org.h2.Driver")
transaction {
addLogger(Slf4jSqlDebugLogger)
SchemaUtils.create(Users, Todos)
}
}
...
}class TodosRepository {
...
fun loadTodos(): List<String> = transaction {
// SELECT * FROM TODOS WHERE TODOS.USER_ID = {userId}
Todos.select { Todos.userId eq userId }.map { it[Todos.description] }
// SELECT TODOS.DESCRIPTION FROM TODOS
Todos.slice(Todos.description).selectAll().map { it[Todos.description] }
}
}class TodosRepository {
...
fun addTodo(userId: Int, description: String): Int = transaction {
// INSERT INTO TODOS (DESCRIPTION, REMINDER_AT, USER_ID) VALUES ('Do stuff', NULL, 1)
val todoId = Todos.insert {
it[Todos.description] = "Do stuff"
it[Todos.userId] = userId
} get Todos.id
return@transaction todoId
}
}Deploying to the cloud
AppEngine

Project on Google Cloud
gcloud cli
Pre-requisites:
buildscript {
ext.appengine_version = '1.9.60'
ext.appengine_plugin_version = '1.3.4'
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
...
classpath "com.google.cloud.tools:appengine-gradle-plugin:$appengine_plugin_version"
}
}
apply plugin: 'kotlin'
apply plugin: 'war'
apply plugin: 'com.google.cloud.tools.appengine'
sourceSets {
main.kotlin.srcDirs = [ 'src/main/kotlin' ]
}
...
dependencies {
....
providedCompile "com.google.appengine:appengine:$appengine_version"
}
task run(dependsOn: appengineRun)# Run the app locally, on http://localhost:8080
./gradlew :google-appengine-standard:appengineRun
# Setup the project on Google Cloud
gcloud app create
# Deploy the application to the cloud, to https://demo-ktor.appspot.com
gradle :google-appengine-standard:appengineDeploy
What to keep in mind?
Thank you!

Kotlin for Backend
By Cosmin Stefan
Kotlin for Backend
Kotlin is a great fit for developing server-side applications, allowing you to write concise and expressive code while maintaining full compatibility with existing Java-based technology stacks and a smooth learning curve. We’ll be going over the process of building an entire backend API using Kotlin, with the right tools, from dependency injection to routing to database access.
- 1,118



