Intro to Graph Databases
and Neo4j
About Me
@dabernathy89
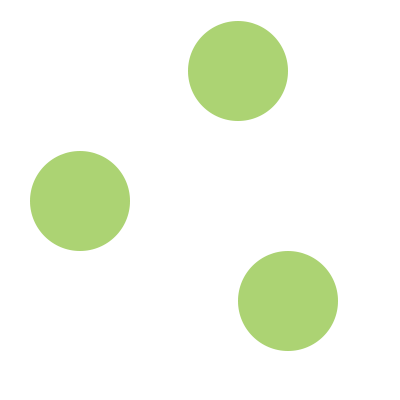
What's a graph?
Nodes
And relationships between nodes
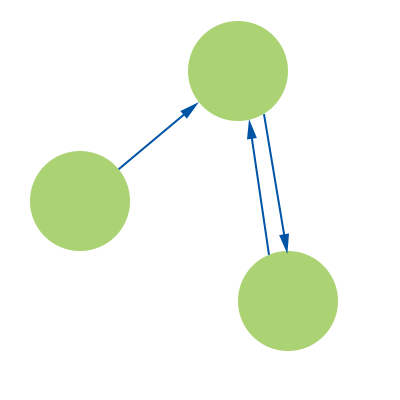
Property Graph Model
Animal
"name" : "Banana",
"color" : "orange"
Furnishing
"type" : "carpet"
Scratched
"timestamp" : 1417126199
Barfed On
"timestamp" : 1417136235
- Nodes and relationships have properties
- Relationships have names and a direction
- Any number of relationships between nodes
Relationships
- Relationships are considered "first class citizens"
- just as important as nodes
- Allows for "index free adjacency"
- nodes point directly to connected nodes
- Even with many 'joins', query performance is only limited by the portion of the graph that is searched.
Graph: E-Commerce
Stored the same way you might describe your data naturally
Reflects your application's domain
NoSQL
Graph databases are part of the NoSQL family
... but they're pretty different.
NoSQL
Aggregate-Oriented
- Key/Value
- Column Family
- Document Store
2 main categories of NoSQL databases:
Graph Databases
When people talk about NoSQL, they're usually referring to the aggregate oriented databases.
Querying with Cypher
Parentheses = nodes
(user)
Arrows and square brackets = relationships
-[:has]->
Together
(user)-[:has]->(role)
Querying with Cypher
Variables
(foo:User)-[bar:has]->()
- Used for referring to later in the query
Labels
- let you differentiate between nodes
- multiple are allowed
(creature:Dog)
Relationship types
- required, only one allowed
[:purchased]
Querying with Cypher
Properties
(:Customer {name:"Daniel"}) -[:PURCHASED {timestamp: 1417631772}]-> (:Product {id: "abc", price: 35.5})
Querying with Cypher
Querying is about matching patterns
Example: find customers who have purchased the same product as current customer
MATCH (c:Customer)-[:PURCHASED]->()<-[:PURCHASED]-(c2)
WHERE c.email = "customer@example.com"
return c2Performance
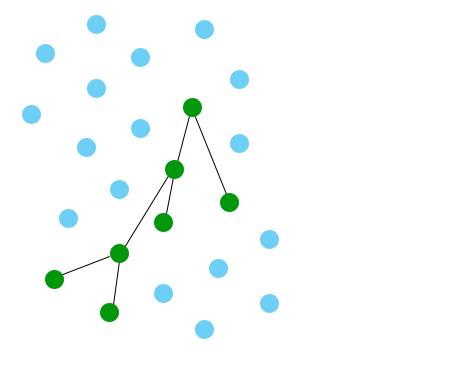
This graph search...
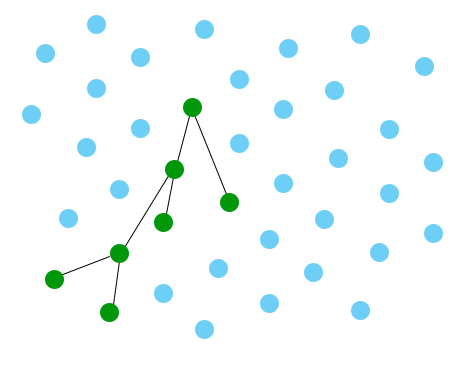
... has the same performance as this one
Graph advantages summarized:
- Graph databases are a natural representation of your data.
- Graph query languages like Cypher are extremely readable.
- Graphs make complex questions simpler to ask.
- When dealing with many relationships and complex joins, graph databases can provide better performance.
- They're fun, especially with visualizations.
PHP
- REST API wrappers
- ORM
- More at Neo4j
Resources
Videos
Books
- "Graph Databases" - O'Reilly
- "Learning Neo4J" - Packt
Services
- Graph Story - Neo4j hosting
PHP/Neo4j People
- Michelle Sanver
- Christophe Willemsen
- Ed Finkler
Lightning Talk: Intro to Graph Databases
By Daniel Abernathy
Lightning Talk: Intro to Graph Databases
- 1,959



