Vue.js

Reactive Components for Modern Web Interfaces
What you should know about Vue.js

Vue.js – Intro
- View-layer library
- Simple
- Lightweight (~24kb min+gzip)
- Fast
- Reactive
- Component based
Simply said Vue is...

Vue.js – Intro
Awesome!
How to start?

Vue.js – Basics
var object = {
message: 'Hello world!'
}<div id="example">
{{ message }}
</div>new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: object
})This is now reactive!
Reactivity - how does it work?

Vue.js – Basics
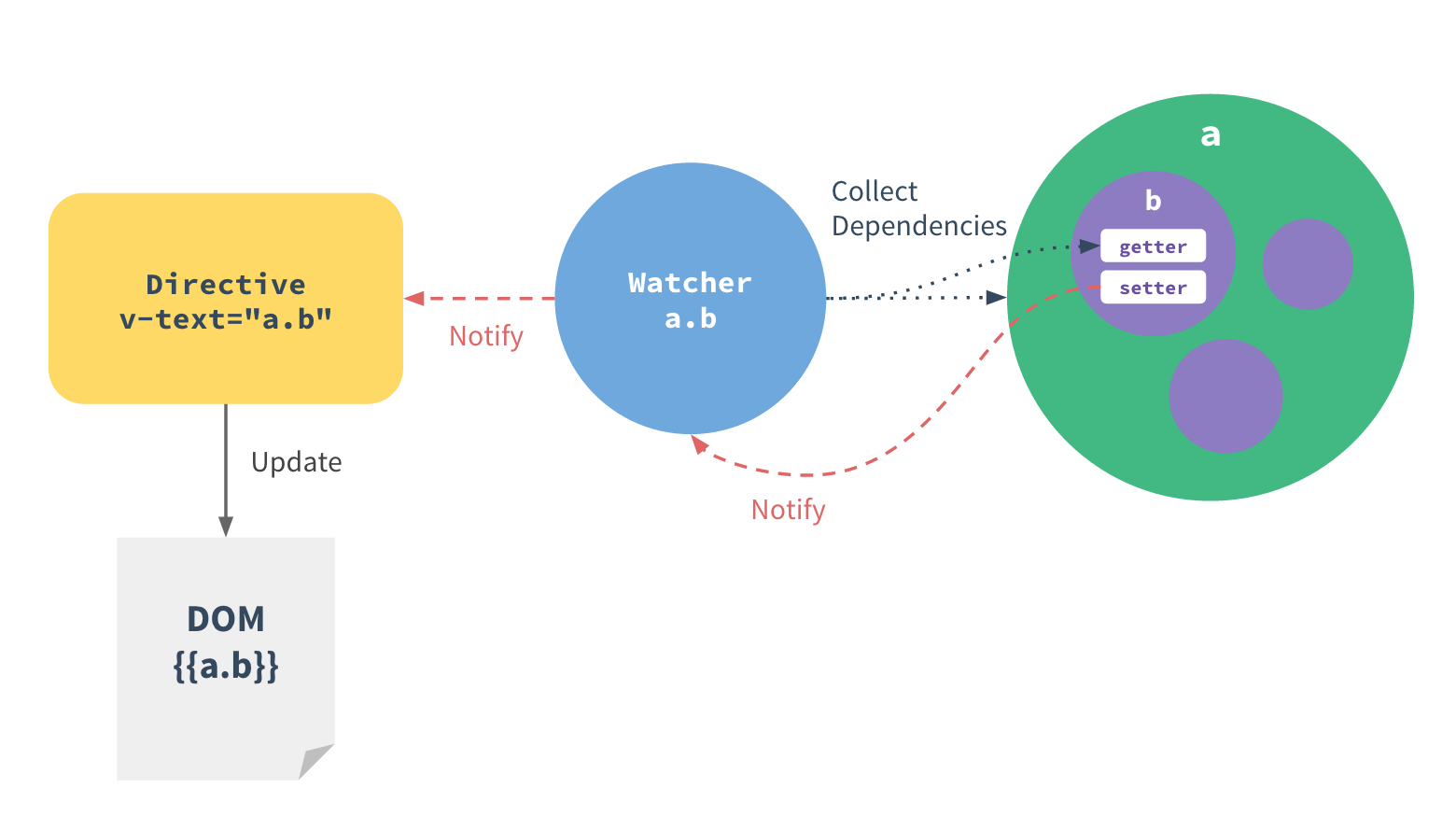
When passing an object to the Vue instance as it’s data option, Vue.js walks through all it’s properties and converts them to getter/setters using Object.defineProperty.
For every directive / data binding in the template, there will be a corresponding watcher object. When a dependency’s setter is called, it triggers the watcher to re-evaluate, and in turn causes its associated directive to perform DOM updates.
Reactivity - how does it work

Vue.js – Basics

Vue.js – Basics
You can use it „jQuery style”, but actually in a good way. Just add the library from the CDN and you’re ready to go.
Simple to use
No need for JSX, Webpack / Browserify, TypeScript or silly React.createElement().
You can use it to enhance your old projects and keep using all your favorite tools: Slim, Sass, CoffeeScript or simply es5. Vue doesn’t care.

Vue.js – Basics
However if you decide to go for a full blown SPA, you get all the tools you need.
Going full SPA
Vue-cli
- Webpack / Browerify
- Hot reloading
- Linting
- Unit tests
- CSS extraction
Vue ecosystem
- Vue-router
- Vuex
- Vue-devtools
- Vue-touch
- Vue-validation
- Vue-resource

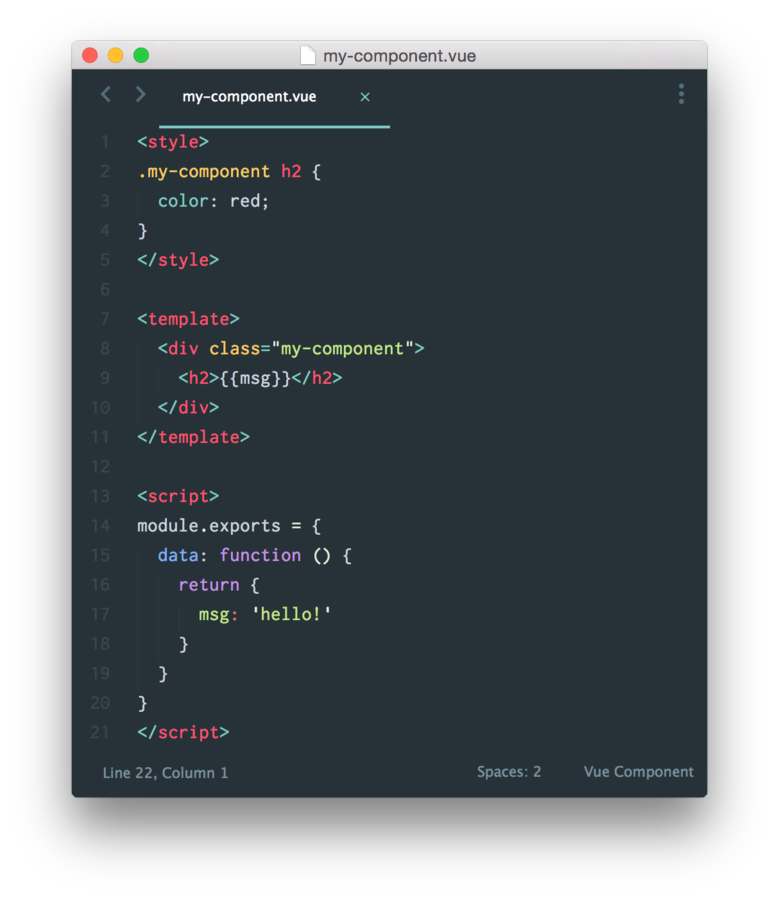
Vue.js – Basics
Single
File
Component

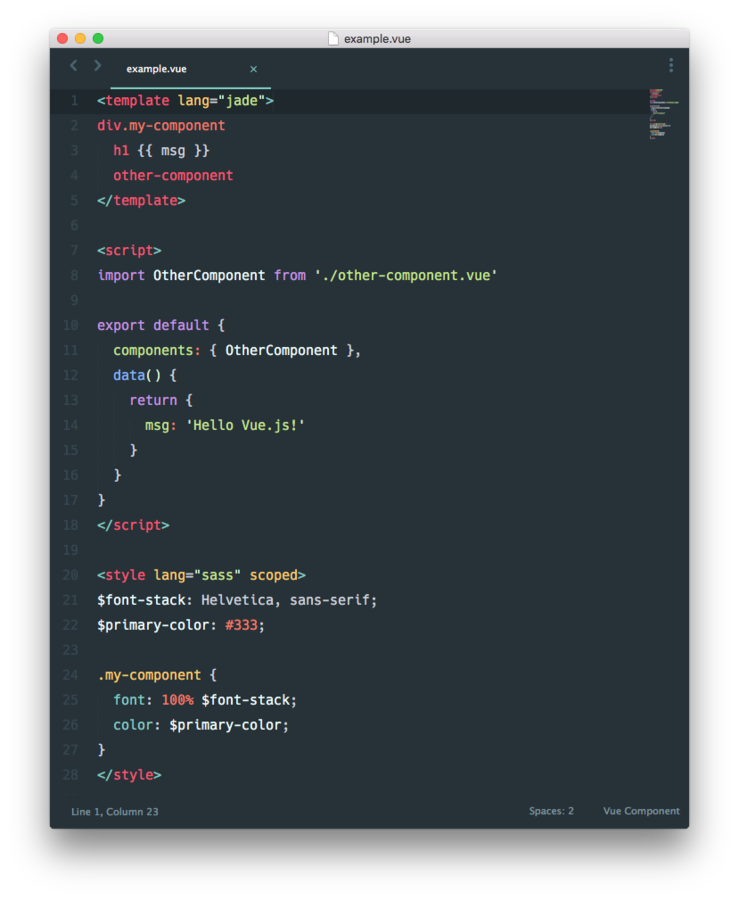
Vue.js – Basics
Single
File
Component
(with preprocessors!)

Vue.js – Basics
What’s with the scoped attribute?
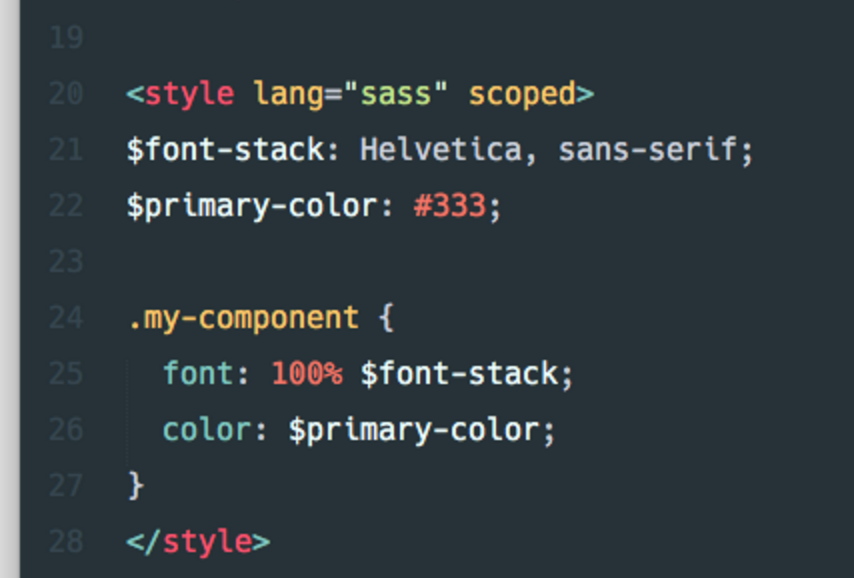
The one liner that does most of what CSS Modules do.

Scopes your CSS.

Vue.js – Basics
Try it out!
Data binding

Vue.js – Basics
<!-- Text interpolation -->
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>Interpolation
<!-- One time interpolation -->
<h1>This won’t change: {{ * title }}</h1><!-- Raw HTML interpolation with triple brackets -->
<div>{{{ raw_html }}}</div><!-- Interpolation in attributes -->
<input type="text" id="form-{{ inputId }}"/>Note that attribute interpolations are disallowed in Vue.js directives and special attributes. Don’t worry, Vue.js will raise warnings for you when mustaches are used in wrong places.
Data binding

Vue.js – Basics
JavaScript expressions
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}Data binding

Vue.js – Basics
Filters
{{ message | capitalize }}
<!-- Chaining filters -->
{{ message | filterA | filterB }}
<!-- Parameters for filters -->
{{ message | filterA 'string' expression }}Data binding

Vue.js – Basics
Directives
<!-- Renders the paragraph if greeting evaluates to true -->
<p v-if="greeting">Hello!</p>
<!-- Puts the value url into the href attribute -->
<a v-bind:href="url"></a>
<!-- Creates click event listener that runs the doSomething method -->
<a v-on:click="doSomething">Data binding

Vue.js – Basics
Shorthands
<!-- full syntax -->
<button v-bind:disabled="someDynamicCondition">Button</button>
<!-- shorthand -->
<button :disabled="someDynamicCondition">Button</button>
or
<!-- full syntax -->
<a v-on:click="doSomething"></a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<a @click="doSomething"></a>Computed values

Vue.js – Basics
<div id="example">
a={{ a }}, b={{ b }}
</div>var vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
a: 1
},
computed: {
// a computed getter
b: function () {
// `this` points to the vm instance
return this.a + 1
}
}
})Computed setter

Vue.js – Basics
// ...
computed: {
fullName: {
// getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
// setter
set: function (newValue) {
var names = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1]
}
}
}
// ..
// When calling vm.fullName = 'John Doe', the setter will
// be invoked and vm.firstName and vm.lastName
// will be updated accordingly.Class & styles bindings

Vue.js – Basics
<div class="static" :class="{ 'class-a': isA, 'class-b': isB }"></div>
<!-- Given that data = { isA: true, isB: false } this will render -->
<div class="static class-a"></div>
or
<div v-bind:class="classObject"></div>
<!-- Where
data: {
classObject: {
'class-a': true,
'class-b': false
}
}
Will render the same result. This can be used with computed properties. --> Array syntax

Vue.js – Basics
<div v-bind:class="[classA, isB ? classB : '']">
<!-- This will always add the `classA` class, but `classB` will only be added if `isB` is true -->
also
<!-- You can mix array syntax with object syntax -->
<div v-bind:class="[classA, { classB: isB, classC: isC }]">Style bindings

Vue.js – Basics
<div v-bind:style="{ color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }"></div>
<!-- Works mostly the same as with classes -->Additionally
When you use a CSS property that requires vendor prefixes in v-bind:style, for example transform, Vue.js will automatically detect and add appropriate prefixes to the applied styles.
Conditional rendering

Vue.js – Basics
<h1 v-if="ok">Yes</h1>
<h1 v-else>No</h1>Templates
<template v-if="ok">
<h1>Title</h1>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
</template>The final rendered result will not include the<template> element.
The v-else element will render only if `ok` evaluates to false.
List rendering

Vue.js – Basics
var example1 = new Vue({
el: '#example-1',
data: {
items: [
{ message: 'Foo' },
{ message: 'Bar' }
]
}
})<ul id="example-1">
<li v-for="item in items">
{{ $index }} – {{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- Where $index is the index
of the current item -->
or
<ul>
<template v-for="item in items">
<li>{{ item.msg }}</li>
<li class="divider"></li>
</template>
</ul>
<!-- Where the <template> element
won’t render -->List rendering

Vue.js – Basics
new Vue({
el: '#repeat-object',
data: {
object: {
FirstName: 'John',
LastName: 'Doe',
Age: 30
}
}
})<ul id="repeat-object" class="demo">
<li v-for="value in object">
{{ $key }} : {{ value }}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- Where `$key` is well... the key -->
or
<div v-for="(key, val) in object">
{{ key }} {{ val }}
</div>List | filterBy | orderBy

Vue.js – Basics
<!-- Filtering -->
<li v-for="user in users | filterBy name in 'name'">
{{ user.name }}
</li>
<!-- Ordering -->
<li v-for="user in users | orderBy 'name'">
{{ user.name }}
</li>Or
Use a computed value where you can apply
complex logic for filtering/ordering arrays.
Methods & Events handling

Vue.js – Basics
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
name: 'Vue.js'
},
// define methods under the `methods` object
methods: {
greet: function (user, event) {
// `this` inside methods point to the Vue instance
alert('Hello ' + user + ' this is ' + this.name + '!')
// `event` gives us access to original DOM event
}
}
})
// you can invoke methods in JavaScript too
vm.greet('Monterail') // -> 'Hello Monterail this is Vue.js!'<button @click="greet('Monterail', $event)">Greet</button>Event modifiers

Vue.js – Basics
<!-- the click event's propagation will be stopped -->
<a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a>
<!-- the submit event will no longer reload the page -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form>
<!-- modifiers can be chained -->
<a @click.stop.prevent="doThat">
<!-- just the modifier -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent></form>
<!-- only trigger handler if event.target is the element itself -->
<!-- i.e. not from a child element -->
<div @click.self="doThat">...</div>
<!-- Support for key aliases as modifiers -->
<input @keyup.enter="submit">
<!-- List of aliases: enter, tab, delete ,esc, space, up, down, left, right;
or create your own with Vue.directive('on').keyCodes.f1 = 112 -->Form input bindings

Vue.js – Basics
<!-- Text -->
<input type="text" v-model="message" placeholder="edit me">
<!-- Checkbox -->
<input type="checkbox" id="checkbox" v-model="checked">
<!-- Radio -->
<input type="radio" id="one" value="One" v-model="picked">
<input type="radio" id="two" value="Two" v-model="picked">
<!-- Select -->
<select v-model="selected" multiple>
<option selected>A</option>
<option>B</option>
<option>C</option>
</select>
<!-- Adding `number` attr saves data as numbers -->
<input v-model="age" number>
<!-- Debounces the writing into data object -->
<input v-model="msg" debounce="500">Form input bindings

Vue.js – Basics
<input type="checkbox" id="jack" value="Jack" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="jack">Jack</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="john" value="John" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="john">John</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="mike" value="Mike" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="mike">Mike</label>
<br>
<span>Checked names: {{ checkedNames | json }}</span>new Vue({
el: '...',
data: {
checkedNames: []
}
})
When checkboxes are bound to the same array.
Components

Vue.js – Components
<div id="example">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>// define
var MyComponent = Vue.extend({
template: '<div>A component!</div>'
})
// register
Vue.component('my-component', MyComponent)
// create a root instance
new Vue({
el: '#example'
})<!-- Which will render -->
<div id="example">
<div>A component!</div>
</div>Local registration

Vue.js – Components
var Child = Vue.extend({ /* ... */ })
var Parent = Vue.extend({
template: '...',
components: {
// <my-component> will only be available in Parent's template
'my-component': Child
}
})Props

Vue.js – Components
Vue.component('child', {
// declare the props
props: ['myProp'],
// the prop can be used inside templates, and will also
// be set as `this.msg`
template: '<span>{{ myProp }}</span>'
})<child my-prop="hello!"></child>
<!-- The prop will be passed as string -->Remember: When using camelCased prop names as attributes, you need to use their kebab-case equivalents.
Dynamic props

Vue.js – Components
<div>
<child :my-value="obj"></child>
</div>var Parent = Vue.extend({
template: '...',
components: {
Child
},
data: function () {
return {
obj: { name: 'Vue', ext: 'JS' }
}
}
})This will pass the whole object as prop.
Prop validation

Vue.js – Components
Vue.component('example', {
props: {
// basic type check (`null` means accept any type)
propA: Number,
// a required string
propB: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// a number with default value
propC: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// object/array defaults should be returned from a
// factory function
propD: {
type: Object,
default: function () {
return { msg: 'hello' }
}}}}Prop validation 2

Vue.js – Components
Vue.component('example', {
props: {
// indicate this prop expects a two-way binding. will
// raise a warning if binding type does not match.
propE: {
twoWay: true
},
// custom validator function
propF: {
validator: function (value) {
return value > 10
}
},
// coerce function (new in 1.0.12)
// cast the value before setting it on the component
propG: {
coerce: function (val) {
return val + '' // cast the value to string
}
}
}Slots

Vue.js – Components
<!-- Component template -->
<div>
<h1>This is my component!</h1>
<slot>
This will only be displayed if there is no content
to be distributed.
</slot>
</div>
<!-- Parent template -->
<my-component>
<p>This is some original content</p>
<p>This is some more original content</p>
</my-component>
<!-- Rendered result -->
<div>
<h1>This is my component!</h1>
<p>This is some original content</p>
<p>This is some more original content</p>
</div>Named slots

Vue.js – Components
<!-- Component template -->
<div>
<slot name="one"></slot>
<slot></slot>
<slot name="two"></slot>
</div>
<!-- Parent template -->
<multi-insertion>
<p slot="one">One</p>
<p slot="two">Two</p>
<p>Default A</p>
</multi-insertion>
<!-- Rendered result -->
<div>
<p slot="one">One</p>
<p>Default A</p>
<p slot="two">Two</p>
</div>Dynamic components

Vue.js – Components
new Vue({
el: 'body',
data: {
currentView: 'home'
},
components: {
home: { /* ... */ },
posts: { /* ... */ },
archive: { /* ... */ }
}
})<component :is="currentView">
<!-- component changes when vm.currentview changes! -->
</component>Mixins

Vue.js – Mixins
// define a mixin object
var myMixin = {
created: function () {
this.hello()
},
methods: {
hello: function () {
console.log('hello from mixin!')
}
}
}
// define a component that uses this mixin
var Component = Vue.extend({
mixins: [myMixin]
})
var component = new Component() // -> "hello from mixin!"Mixing mixins

Vue.js – Mixins
var mixin = {
created: function () {
console.log('mixin hook called')
}
}
new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
created: function () {
console.log('component hook called')
}
})
// -> "mixin hook called"
// -> "component hook called"Mixing mixins

Vue.js – Mixins
var mixin = {
methods: {
foo: function () {
console.log('foo')
},
conflicting: function () {
console.log('from mixin')
}
}
}var vm = new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
methods: {
bar: function () {
console.log('bar')
},
conflicting: function () {
console.log('from self')
}
}
})
vm.foo() // -> "foo"
vm.bar() // -> "bar"
vm.conflicting() // -> "from self"Vue.js vs Angular 1.x

Vue.js – Mixins
Simpler API and design.
Less opinionated, easier to combine with other libraries.
One-way data binding. Supports explicit two-way bindings.
Better performance and easier to optimize.
Complex API, hard to master.
Very opinionated, requires doing things angular-way.
Two-way bindings. Explicit one-way bindings (1.3+).
Dirty-checking. Nuff said.
Differences:
Vue.js vs Angular 1.x

Vue.js – Mixins
Components and directives
Template bindings (ng-if, ng-repeat vs v-if, v-for)
Concepts naming i.e. scope, watcher, directive, filters
Similarities:
Vue.js vs React

Vue.js – Mixins
DOM with references to real nodes.
Clean separation of HTML & JS. Easier to visually think about designs.
Prefers and makes good use of mutating state
Virtual DOM, rerender and patch DOM on every update.
Puts HTML inside JS. Easy to leak lots of logic inside render function.
Prefers immutable state
Differences:
Vue.js vs React

Vue.js – Mixins
Works on real DOM
Easy support for popular preprocessors for HTML, JS, CSS
Friendly for newcomers and easier to get productive fast
Actually more fun!
Tricky to perform DOM
manipulations
More Everything-in-JS approach
Due to functional nature, steeper learning curve
More platform-agnostic
Differences:
Vue.js vs React

Vue.js – Mixins
Reactive and based on components
Just the View layer. Support for different state management solutions e.g. Flux/Redux. Vue also introduces Vuex.
Performant!
Still better than Angular 2!
Similarities:
Vue.js Intro
By Damian Dulisz
Vue.js Intro
- 2,603



