An Introduction to PyTorch
Daniel Yukimura
yukimura@impa.br
Class Overview
- A modular approach.
- Deep Learning Software.
- PyTorch basics: Tensors and Autograd.
- Representing NNs computationally.
- Handling Data.
- Optimization.
- Training Loop
- Validation Loop
Modularity
Breaking a complex system (software) in smaller and more simple pieces.
- Deep Learning is highly modular.
- Easy maintenance.
- Reusability.
- Efficiency.
- Robustness
Deep Learning Frameworks
Caffe
Caffe2
(UC Berkeley)
(Facebook)
Torch
PyTorch
(NYU / Facebook)
(Facebook)
Theano
TensorFlow
(U Montreal)
(Google)
Others:
- MXNet (Amazon)
- CNTK (Microsoft)
- PaddlePaddle (Baidu)
- ...
PyTorch Basics
Installing and Setting
PyTorch Basics
Tensors
import torch
# 2x2 tensor built from a regular array
T = torch.tensor( [ [1,2], [3, 4] ] )
# It has structures similar to numpy
T_zeros = torch.zeros(100, 100)
T_ones = torch.ones( 100, 100)
T_random = torch.randn(100, 100)
# dtype sets the data type
T_int = torch.tensor( [ [1,2], [3, 4] ], dtype=torch.int )
T_double = torch.randn( 3, 5, 7, dtype=torch.double) #same as torch.float64
print(T.dtype)
print(T.size())PyTorch Basics
Tensors
import torch
x = torch.randn(3, 3, dtype=torch.float64)
y = torch.randn(3, 3, dtype=torch.float64)
#Addition and subtraction
z = x + y
z = torch.add(x, y)
w = x - y
w = torch.sub(x, y)
#Element-wise multiplication and division
u = x * y
u = torch.mul(x, y)
u = x / y
u = torch.div(x, y)
#Inplace operations
y.add_(x)
x.mul_(y)PyTorch Basics
Tensors
import torch
x = torch.randn(6, 6, dtype=torch.float64)
y = torch.randn(6, 6, dtype=torch.float64)
#Indexing and Slicing
x_row = x[3,:]
x_cln = x[:,3]
x_e = x[0,0].item()
#Reshape
z = y.view(36)
w = y.view(-1, 9) #4x9 tensorPyTorch Basics
Tensors
import torch
import numpy as np
x = torch.randn(10)
y = x.numpy()
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
b = torch.tensor(a)PyTorch Basics
Tensors
import torch
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#1200x1200 image
cat = cv2.imread('cat.jpg')
cat_T = torch.from_numpy(img)
plt.imshow(cat)
half_cat = cat_T[0:600]
plt.imshow( half_cat.numpy() )
column_half_cat = cat_T[:,0:600]
plt.imshow( column_half_cat.numpy() )
cat_T[400:800, 400:800] = 0
plt.imshow( cat_T.numpy() )


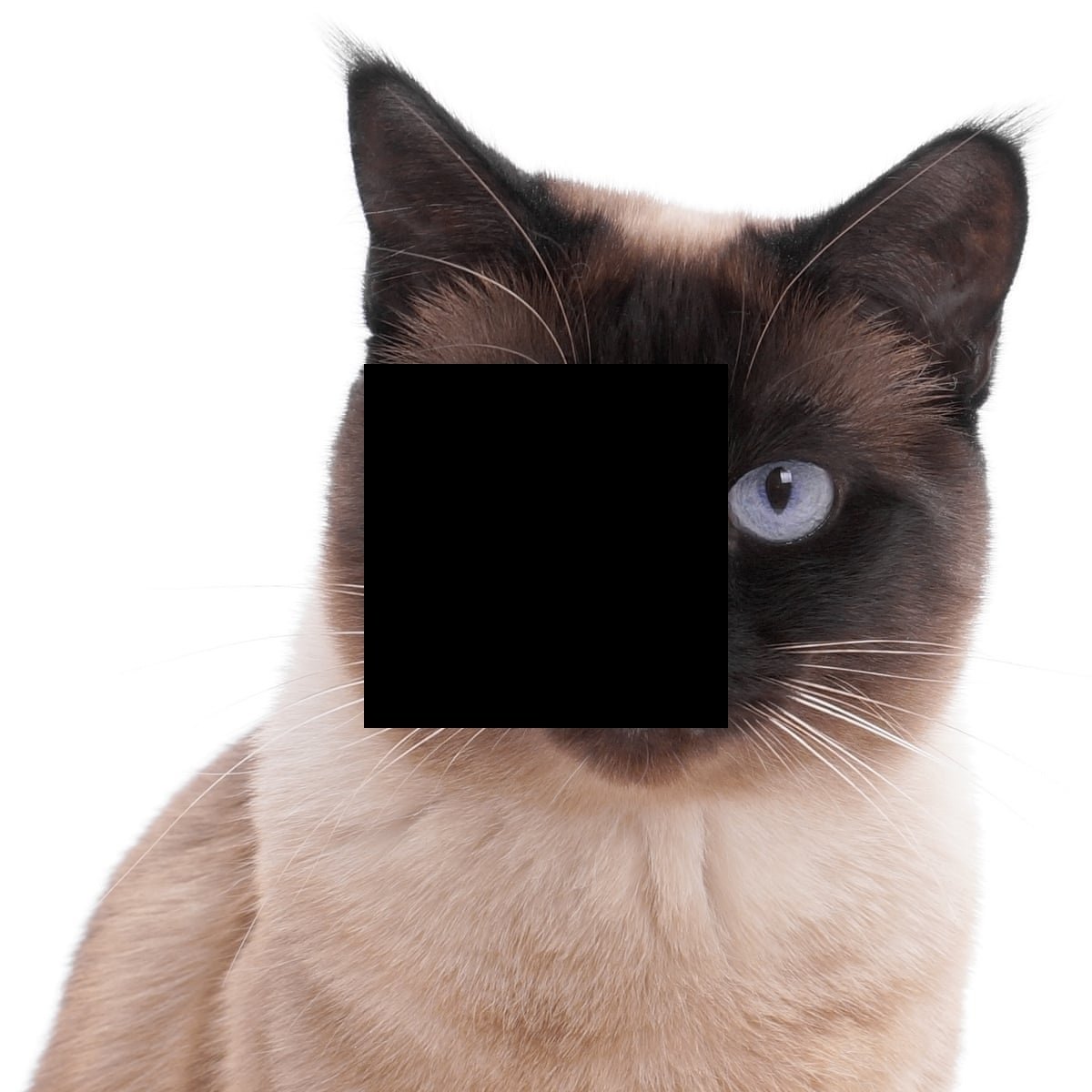
PyTorch Basics
Tensors
import torch
device = torch.device("cuda")
x = torch.randn(5,5, device=device)
device2 = torch.device("cuda:2")
x2 = torch.randn(5,5, device=device2)
y = torch.ones(5,5)
y.to(device)
#Operations must be done on the same device
z = x + y
# z2 = x2 + yPyTorch Basics
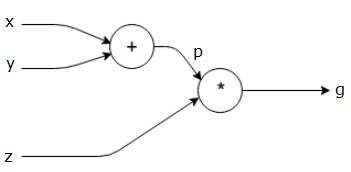
Autograd
import torch
x = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
z = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=False)
p = x+y
g = p*z
g = g.mean()
g.backward() #dz/dx
print(x.grad)
x.requires_grad(False)
y.detach()
with torch.no_grad():
...
PyTorch Basics
Autograd
import torch
W = torch.randn(4, requires_grad=True)
for epoch in range(3):
out = (W*5).sum()
out.backward()
#Gradients accumulate
print(W.grad)
W.grad.zero_()PyTorch Basics
Layers - torch.nn
import torch
L = torch.nn.Linear(10, 25)
x = torch.randn(3,10)
y = L(x)
print(y.size())
model = torch.nn.Sequential( L,
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Linear(25,5))
y = model(x)
print(y.size())PyTorch Basics
Layers - torch.nn
- nn.Linear(...)
- nn.Conv2d(...)
- nn.LSTM(...)
- nn.ReLU(...)
- nn.Sigmoid(...)
- nn.Dropout(...)
- nn.Module(...)
- nn.Sequential(...)
- nn.Softmax(...)
- nn.CrossEntropyLoss(...)
- nn.MSELoss(...)
- nn.Transformer(...)
Building Neural Networks
with PyTorch

input
output
Layers
DATA IN
PREDICTION
MODEL
Building Neural Networks
with PyTorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class TwoLayerNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out):
super(TwoLayerNN, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_hidden)
self.act = nn.ReLU()
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(dim_hidden, dim_out)
def forward(self, x):
h = self.linear1(x)
h = self.act(h)
y = self.linear2(h)
return y
n_batch, dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out = 32, 100, 50, 10
x = torch.randn(n_batch, dim_in)
model = TwoLayerNN(dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out)
pred = model(x)Handling Data
import torch
import torchvision
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, random_split
from torchvision import transforms
import os
mnist_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(),
download=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor())
data_loader = DataLoader(mnist_data,
batch_size=4,
shuffle=True)
Handling Data
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, ..., transform=None):
...
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
data = self.data[idx]
...
sample = {'image': image, 'label': label}
if self.transform:
sample = self.transform(sample)
return sampleLoss Functions
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
x, y = mnist_data.__getitem__(0)
dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out = x.size(1)*x.size(2), 100, 10
model = TwoLayerNN(dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out)
pred = model(x.view(x.size(0),-1))
loss = F.cross_entropy(pred, torch.tensor([y]))- nn.MSELoss
- nn.NLLLoss
- nn.functional.l1_loss
- nn.functional.cross_entropy
Optimizer
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out = x.size(1)*x.size(2), 100, 10
model = TwoLayerNN(dim_in, dim_hidden, dim_out)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9)
for batch in data_loader:
x, y = batch
pred = model(x.view(x.size(0),-1))
loss = F.cross_entropy(pred, torch.tensor([y]))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
- optim.SGD
- optim.Adam
Validation Loop
import torch
from torchvision.datasets import MNIST
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, random_split
mnist_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train, val = random_split(mnist_data, [55000, 5000])
data_train = DataLoader(train)
data_val = DataLoader(val)
...
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in data_val:
x, y = batch
loss = loss_function(model(x), y)
print(loss)
...
#accuracyThanks
deck
By Daniel Yukimura
deck
- 842



