From Code to 1010
There are only absolutes in the digital world
- Everything is stored in bits
- 1 = on, 0 = off
Integers

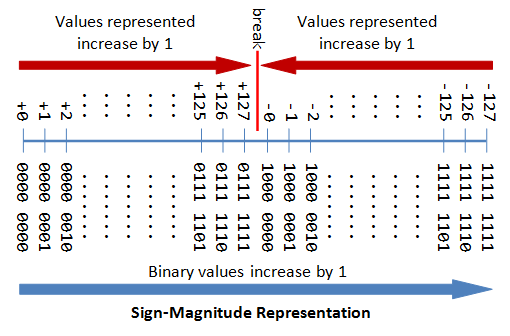
Integers
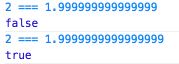
Float values
Machine Code
- CPU instructions


2 main language types
- Interpreted
- Compiled

Compiled
- Needs to be "compiled" before execution
- Compilation - Turns source code into machine code
- Examples
- C/C++
- Go
- C#
- Java
- JavaScript
Compiled
- Compile Time Errors
- Compile Time Optimizations
- Must recompile every change before running
Interpreted
- Translated at execution, one statement at a time
- Examples
- Ruby
- Python
- PHP
- C#
- Java
- JavaScript
Interpreted
- Run Time Errors
- Hard to optimize at run time
- Can re-run after saving source code
- Needs a special library to run
Were you paying attention?
- C#
- Java
- JavaScript

These languages are compiled and interpreted
- Compiled into what is commonly called Bytecode
- Bytecode is Just In Time compiled
What happens when we run the code?
- Interpreted code gets parsed and is executed
- May be executed directly
- May run through a Virtual Machine
- Compiled code gets executed
- May be linked against OS libraries
Virtual Machine?
- Provides a platform agnostic set of instructions
- Platform? OS X, Windows, Linux, iOS
- Virtual Machines are compiled for a specific platform
Major Archtecture Type
- Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC)
- x86, VAX, PDP-11
- Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC)
- ARM, SPARC, Power PC, MIPS
CISC
- Try to create a high level language for the processor
- Each instruction could use multiple memory cycles
- Operations are memory based
RISC
- Fewer memory cycles per instruction
- Some implementations have larger instruction set than CISC
- Operations are Register based

CISC vs RISC
CISC
MULT 2:3, 5:2
RISC
LOAD A, 2:3
LOAD B, 5:2
PROD A, B
STORE 2:3, A
Questions?
Code to 1010
By Dan McClain
Code to 1010
- 3,136



