Linear Regression
Regression techniques are used in machine learning to predict continuous values, for example predicting salaries, ages or even profits.
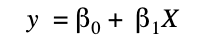
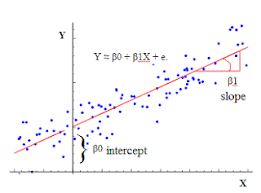
Deep Dive
- Importing the libraries.
- Importing the data set.
- Classifying dependent and independent variables.
- Creating training and test sets
- Creating a Simple Linear Regressor.
- Training the regressor with training data.
- Predicting the salary for a test set.
- Calculating the accuracy of the predictions.
- Comparing Actual and Predicted Salaries for the test set.
Step 1. Data Preprocessing
Step 2. Simple Linear Regression
"""# I. Preparing the dataset """
#1 Importing essential libraries
import pandas as pd
#2 Importing the dataset
#https://drive.google.com/file/d/13_kwGjkC1z7lA0w9FQIEz5huzDKsAOc5/view?usp=sharing
dataset = pd.read_csv('Salary_Data.csv')
#3 classify dependent and independent variables
X = dataset.iloc[:,:-1].values #independent variable YearsofExperience
y = dataset.iloc[:,-1].values #dependent variable salary
print("\nIdependent Variable (Experience):\n", X)
print("\nDependent Variable (Salary):\n", y)
#4 Creating training set and testing set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X ,y, test_size = 1/3,random_state = 0)
print("\n\nTraining Set :\n----------------\n")
print("X = \n", X_train)
print("y = \n", y_train)
print("\n\nTest Set :\n----------------\n")
print("X = \n",X_test)
print("y = \n", y_test)"""# II. Simple Linear Regressor """
#5 import SLR library
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
#6 Train the Regressor with training set
regressor = LinearRegression()
regressor.fit(X_train, y_train)
#7 predict the outcome of test sets
y_Pred = regressor.predict(X_test)
print("\n\nPredictions = ", y_Pred)
#8 Claculating the Accuracy of the predictions
from sklearn import metrics
print("Prediction Accuracy = ", metrics.r2_score(y_test, y_Pred))
#9 Comparing Actual and Predicted Salaries for he test set
print("\nActual vs Predicted Salaries \n-------------------------\n")
print("Actual :\n ", y_test)
print("Predicted :\n ", y_Pred)Multiple Linear Regression
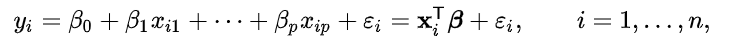
#1 Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#2 Importing the data set
#https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iXn2HmzPYeH2p-ZTHa3jUyEpStoDb8CG/view?usp=sharing
dataset = pd.read_csv('beer_data.csv')
#Printing first 10 rows of the dataset
print("\n----------------------------\n",dataset.head(10))
#3 Dealing with the categorical data
#spliting Cellar Temperature into Maximum and Minimum based on the given data and converting the type from str to int
dataset['Minimum_Cellar_Temp'] = dataset['Cellar Temperature'].apply(lambda x : int(x.split('-')[0].strip()))
dataset['Maximum_Cellar_Temp'] = dataset['Cellar Temperature'].apply(lambda x : int(x.split('-')[1].strip()))
#New dataset with selected features
dataset = dataset[['ABV', 'Ratings','Minimum_Cellar_Temp','Maximum_Cellar_Temp', 'Score']]
#Printing first 10 rows of the dataset
print("\n----------------------------\n",dataset.head(10))
#Printing the summary of the dataset
print("\n----------------------------\n")
print(dataset.info())#4 Classifying dependent and independent variables
#All columns except the last column are independent features- (Selecting every column except Score)
X = dataset.iloc[:,:-1].values
#Only the last column is the dependent feature or the target variable(Score)
y = dataset.iloc[:,-1].values
##5 Creating training and test sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.2,random_state = 0)
#################Data Preprocessing Ends #################################
""" Multiple Linear regression """
#6 Creating the Regressor and training it with the training set
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regressor = LinearRegression(normalize = True)
#7 Feeding the data and training the model
regressor.fit(X_train,y_train)
##8 Predicting the Score for test set observations
y_pred = regressor.predict(X_test)
#printing the predictions
print("\n----------------------------\nPredictions = \n",y_pred)
#9 Calculating score from Root Mean Log Squared Error
def rmlse(y_test, y_pred):
error = np.square(np.log10(y_pred +1) - np.log10(y_test +1)).mean() ** 0.5
score = 1 - error
return score
print("\n----------------------------\nRMLSE Score = ", rmlse(y_test, y_pred))Linear Regression
By Data Science Portal
Linear Regression
Simiple & Multiple Linear Regression Techniques
- 100



