Git & Command Line
Fiches d'aide
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Installation
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Afin d'utiliser Git et la ligne de commande il faut pour cela avoir Git installé ainsi qu'un terminal.
Afin d'installer les prérequis sur rendre sur https://git-scm.com/download/win
Ouvrir un terminal
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
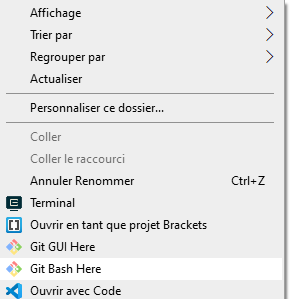
- Faire un clique droit sur le dossier ou l'on veut ouvrir un terminal
- Cliquer sur « Ouvrir un terminal » sur Mac ou « Git Bash Here » pour windows
Utiliser la ligne de commande
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Une fois le terminal ouvert il est possible d'utiliser des commandes dont voici les principales :
# Affiche le répertoire ou l'on se situe actuellement
pwd
# Liste les fichier du répertoire en cours
ls
# Change de répertoire
cd NomDuRepertoire
# Retourner au répertoire parent
cd ..
# Se déplacer dans le répertoire "Home"
cd ~Faire des commits
# Initialize un repository git dans le répertoire actuel
git init
# Affiche le status du « Buffer » en cours
git status
# Ajoute un fichier dans l'index
git add <nom_du_fichier>
# Ajoute tout les fichiers dans l'index
git add .
git add *
git add --all
# Fais un commit
git commit -m "Le message de mon commit"
# Annule la modification d'un fichier qui n'est pas dans l'index
git checkout <nom_du_fichier>par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Les branches
# Liste les branches
git branch
# Créé une branche
git branch <nom_de_la_branche>
# Supprimer une branche
git branch -d <nom_de_la_branche>
# Changer de branche
git checkout <nom_de_la_branche>
# Créé puis changer de branche
git checkout -b <nom_de_la_branche>
# Pousser une branche sur le remote (github)
git push origin <nom_de_la_branche>
# « Merger » une branche dans la branche en cours
git merge <nom_de_la_branche>par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Convention de nomage des branches
# Développer une fonctionalité (feature)
git branch feature/<nom_de_ma_fonctionalité>
# Faire un corréctif (hotfix)
git branch hotfix/<nom_de_mon_correctif>par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Utiliser un remote (github)
# « Clone » un remote (ou repository github)
git clone <url_du_repository>
# Ajoute un remote sur un repository locale existant
git remote add <nom_du_remote> <url_du_remote>
# Liste les remote configuré
git remote -v
# « Push » une branche sur un remote
git push <nom_du_remote> <nom_de_la_branche> # ex: git push origin ma_branche
# Par défault le remote github est nomée origin:
# git push origin <nom_de_la_branche> (envoie la branche
# sur github)
# « Fetch » (récupérer) une branche depuis le remote
git fetch <nom_du_remote> <nom_de_la_branche_sur_le_remote>:<nom_de_la_branche_en_locale>
# « Fetch » (récupérer) des modifications du remote sur ma branche locale
git pull origin <nom_de_la_branche_sur_github>par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Consulter l'historique
# Affiche l'historique des commits sur la branche en cours
git log
# Affiche le même historique en plus conscie
git log --oneline
# Affiche l'historique d'un fichier
git log -p <chemin_du_fichier>
# Affiche toutes les modification en cours
git diffpar David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
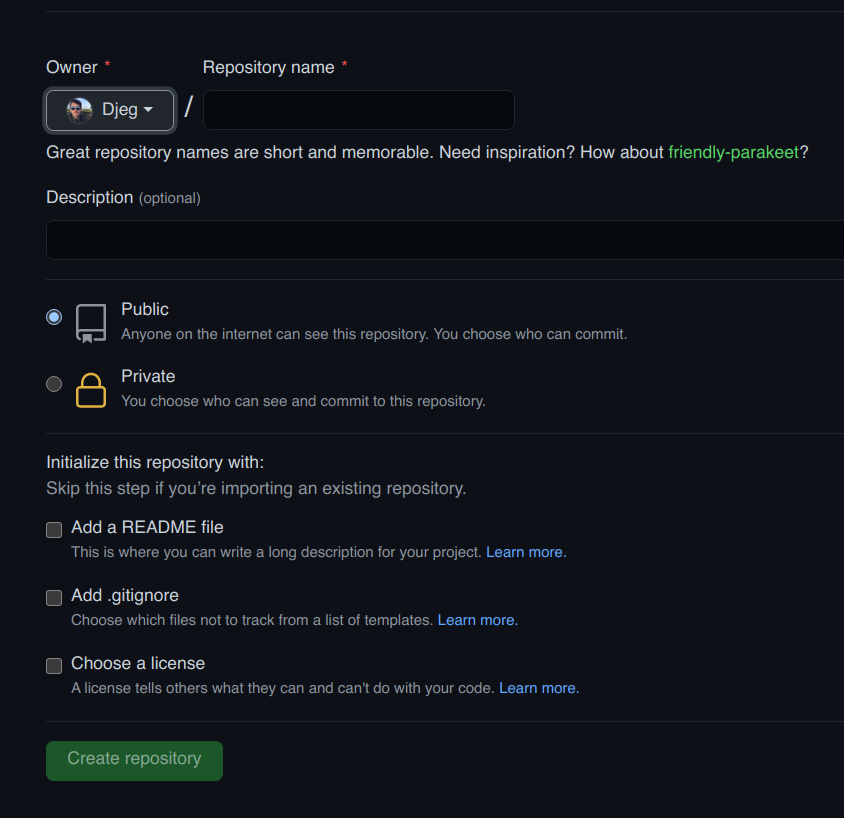
Créer un repo GitHub
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Récupérer l'adresse d'un repo
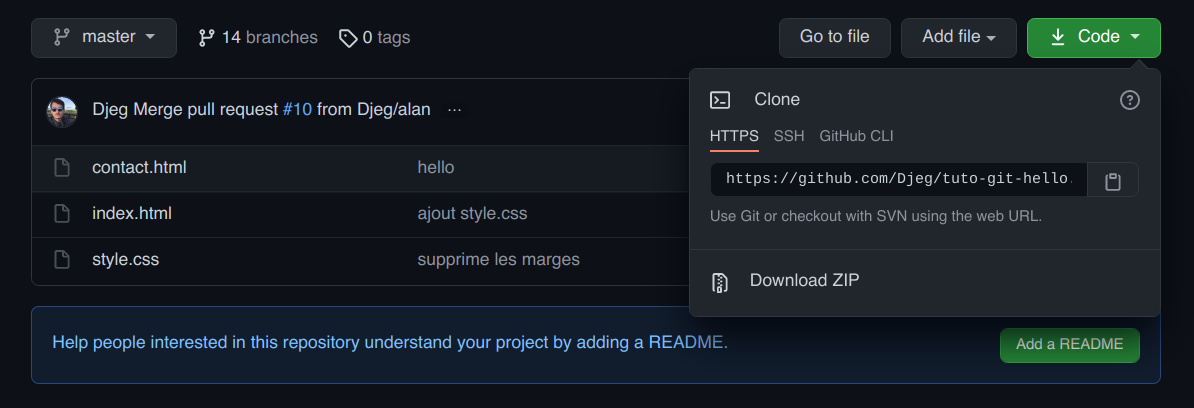
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
« Fork » un repository github
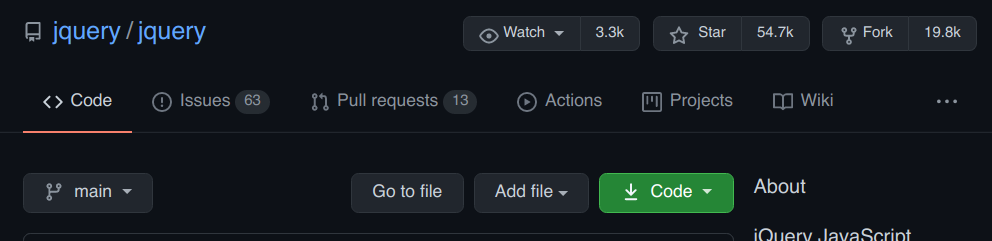
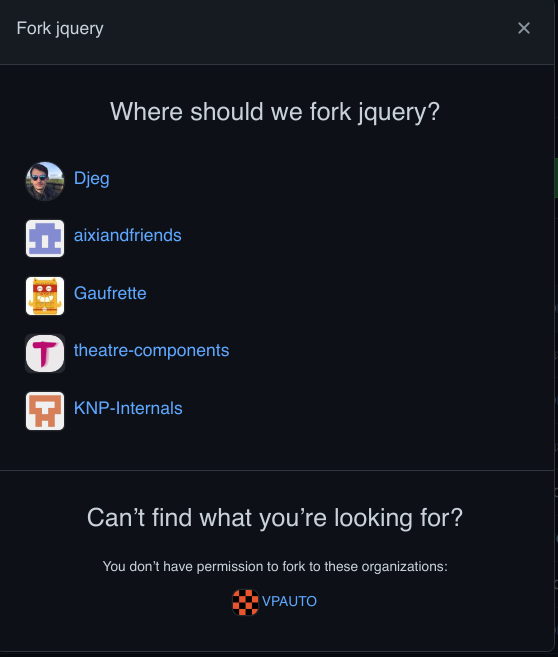
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
Faire une pull request
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
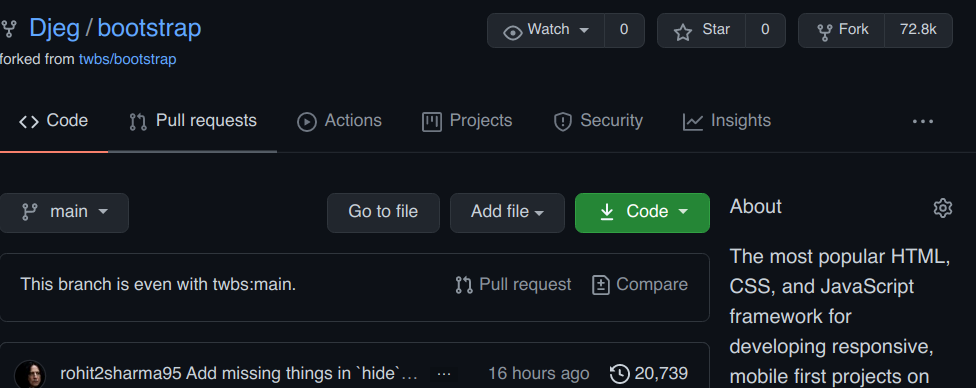
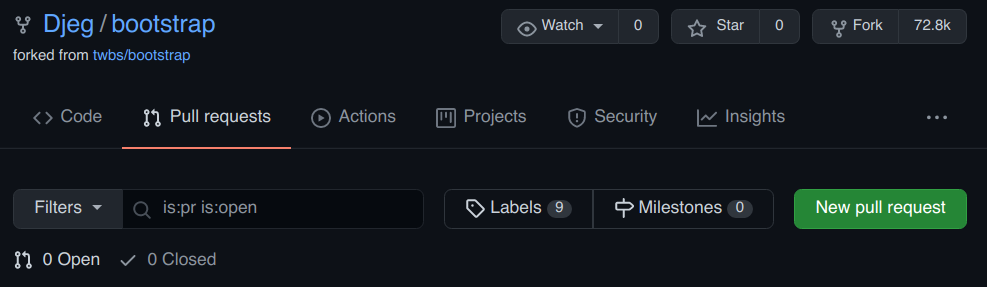
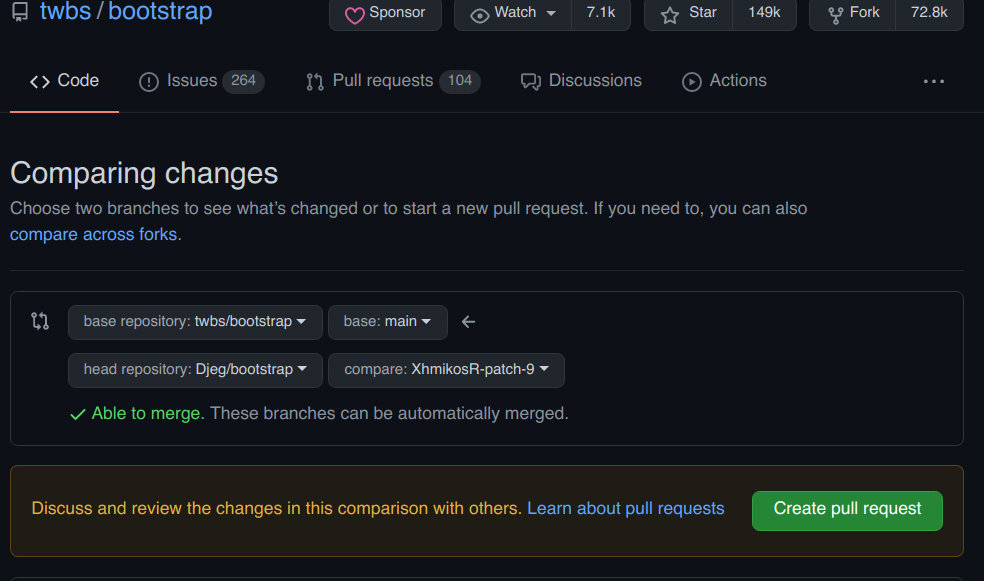
Repository de destination
Branche de destination
Repository d'origine (votre repository)
Votre branche
Petit exo
par David Jegat - david.jegat@gmail.com - https://github.com/Djeg
- Fork https://github.com/Djeg/tuto-git-hello
- Cloner le repo que vous venez de fork
- Créer une branche feature/contact
- Aller sur la branche feature/contact
- Ajouter une balise <a> dans index.html qui pointe sur la page contact.html
- Faire un commit
- Pousser sur github
- Faire une pull request
Git & Command Line Fiche D'AIDE
By David Jegat
Git & Command Line Fiche D'AIDE
Une aide simple pour ne pas se perdre sur git !
- 296



