Test automation & TDD
David Molinero
Who am I?
Software Engineer
Why is it important?

Essential VS Accidental complication
Essential VS Accidental complication
- Essential complication
Essential VS Accidental complication
- Essential complication

Essential VS Accidental complication
- Accidental complication
Essential VS Accidental complication
- Accidental complication

Essential VS Accidental complication
- Cost of a feature
Essential complication + accidental complication
Essential VS Accidental complication
- Eliminate accidental complication

- Unit tests
Categories of tests
- Functional
- E2E
- Other
- Integration tests
- Exploratory
- Performance
- Acceptance
Unit tests
- They are the foundation
- Test a single unit, usually a class or function
- Guide you to design your classes following the SRP
- Use test doubles to get quicker feedback
- Allow you to test not only an expected output but an expected behaviour
- Advantages
Unit tests
- Easy to write and fast to execute
- Serve as documentation in sync with the code
- Disadvantages
- They don't provide enough level of confidence
- Promote good design and quality of the code - TDD
- More coupled to current implementation
- Test communication with databases, external systems, APIs
Integration tests
- First defensive line over things that we don't control
- Allow the creation of interfaces for external dependencies
- Enable the use of doubles for external dependencies
- Test the joints of the application
- Advantages
Integration tests
- Check the integration with external systems
- Disadvantages
- Take more time to execute
- First step to improve confidence
- Useful to identify dependencies
- More prone to failures
Integration test (Example)
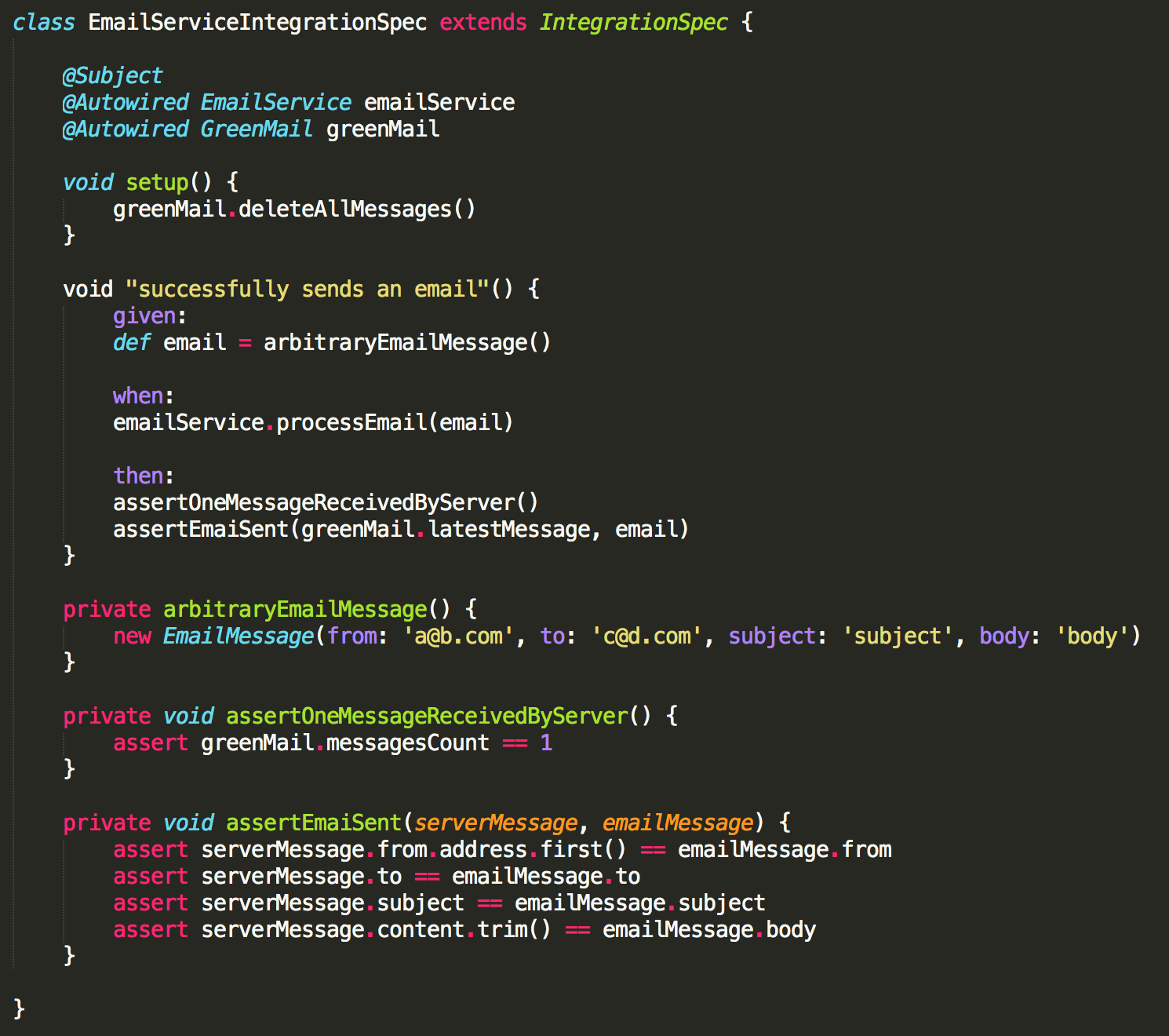
- The goal is to verify an application fits the spec
Functional
- Cover multiple layers of your application
- They might require partial stubbing of third parties
- Use domain terms to make them descriptive
- Advantages
Functional
- Provide higher confidence
- Check the behaviour of multiple components
- Disadvantages
- Time consuming during development
- Slower to execute
Functional test (Example)
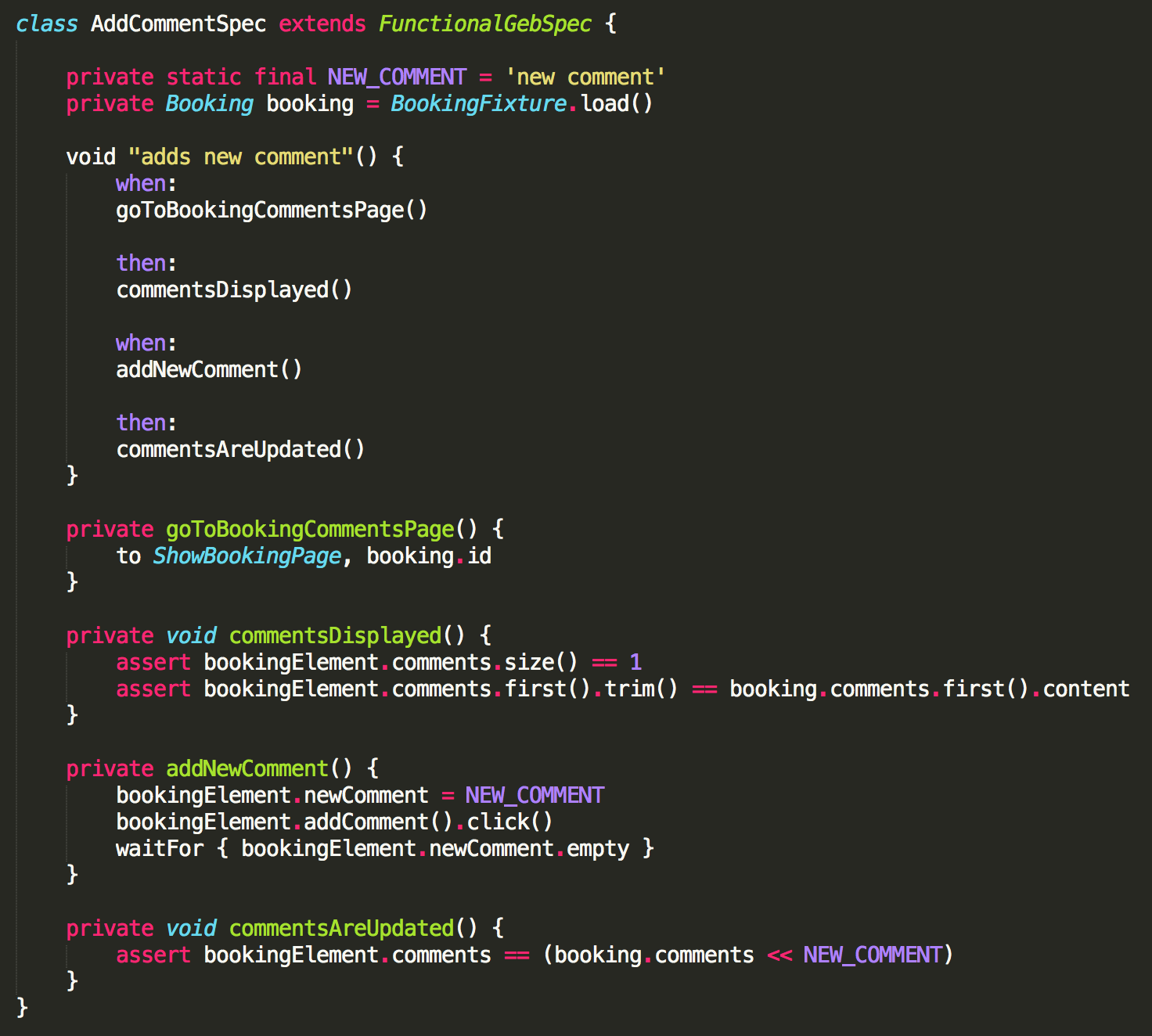
E2E
- They don't mock any parts of the system
- The goal is to verify an application works as a whole
- Validate both the main Software system as well as all the interconnected Sub-Systems.
- Run in an environment close to production
- Advantages
E2E tests
- Provide the highest level of confidence
- Disadvantages
- Expensive to development and maintain
- Really slow to execute
- They might fail if a system is slow to respond
- Good for smoke testing
- PO can write the specification of these tests
Acceptance test
- Document the system from the perspective of the stakeholder
- Run on an environment close to production
- The specification is written in a human readable language
- Advantages
Acceptance test
- Ensure a feature with business value works
- Good as high level documentation
- Readable even for non tech people
- Useful to establish a Definition of Done
- Disadvantages
- Same disadvantages as E2E tests
Acceptance test (Example I)

Acceptance test (Example II)
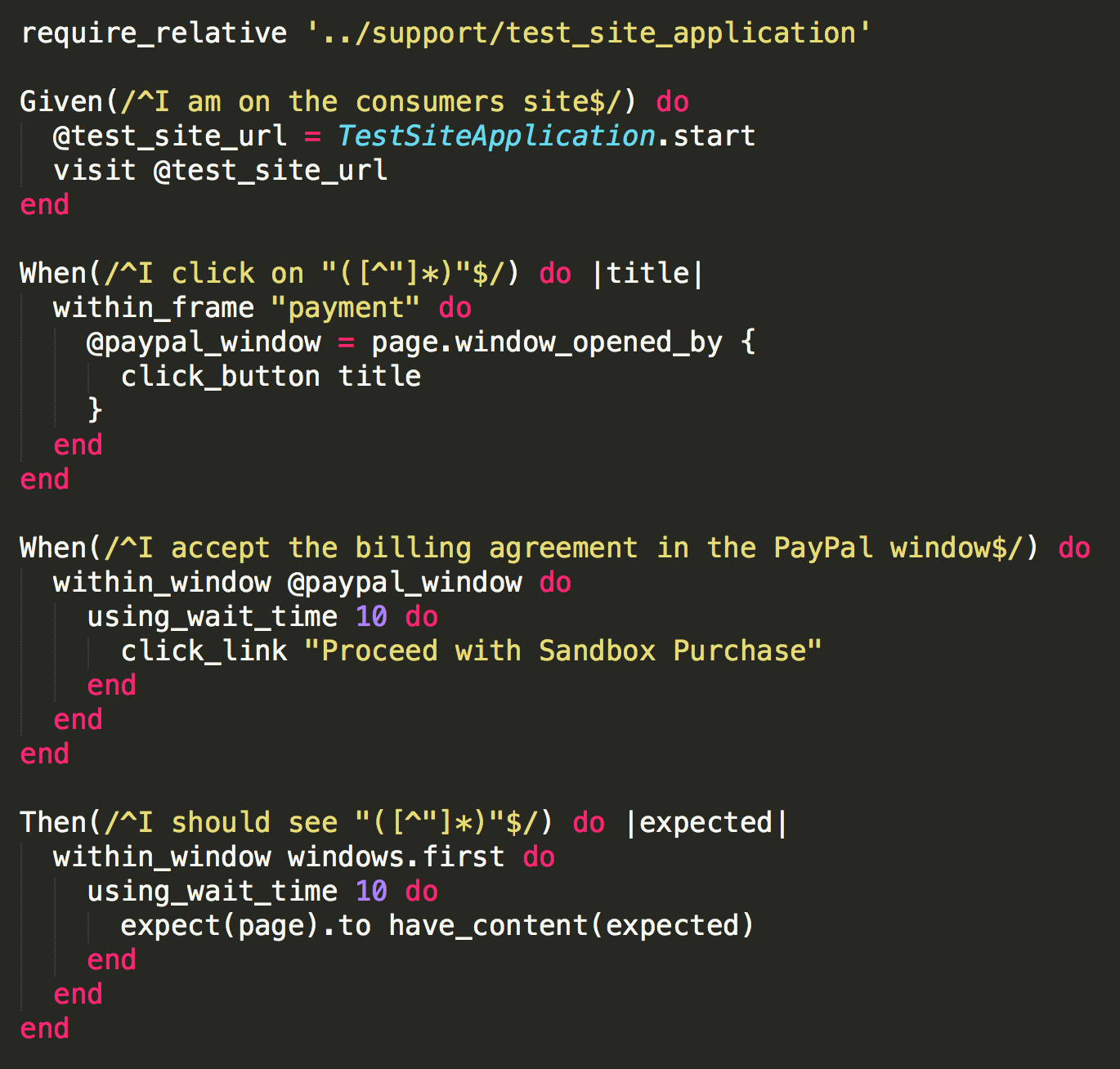
- Advantages
Exploratory tests
- Good to spot issues not caught by devs
- Disadvantages
- Difficult and expensive to automate
- Good to exercise weird scenarios
- Good to spot issues difficult to be noticed by machines
- Advantages
Other tests
- Good to ensure non functional requirements are met
- Good to test infrastructure and fail recovery procedures
Pyramid of testing
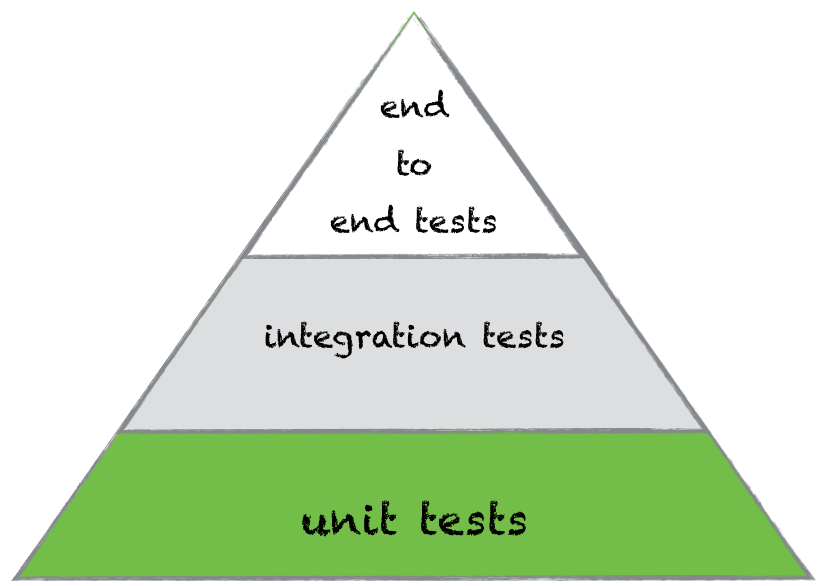
Types of doubles
- Spy
- Stub
- Mock
- Fake
Spy (Code)
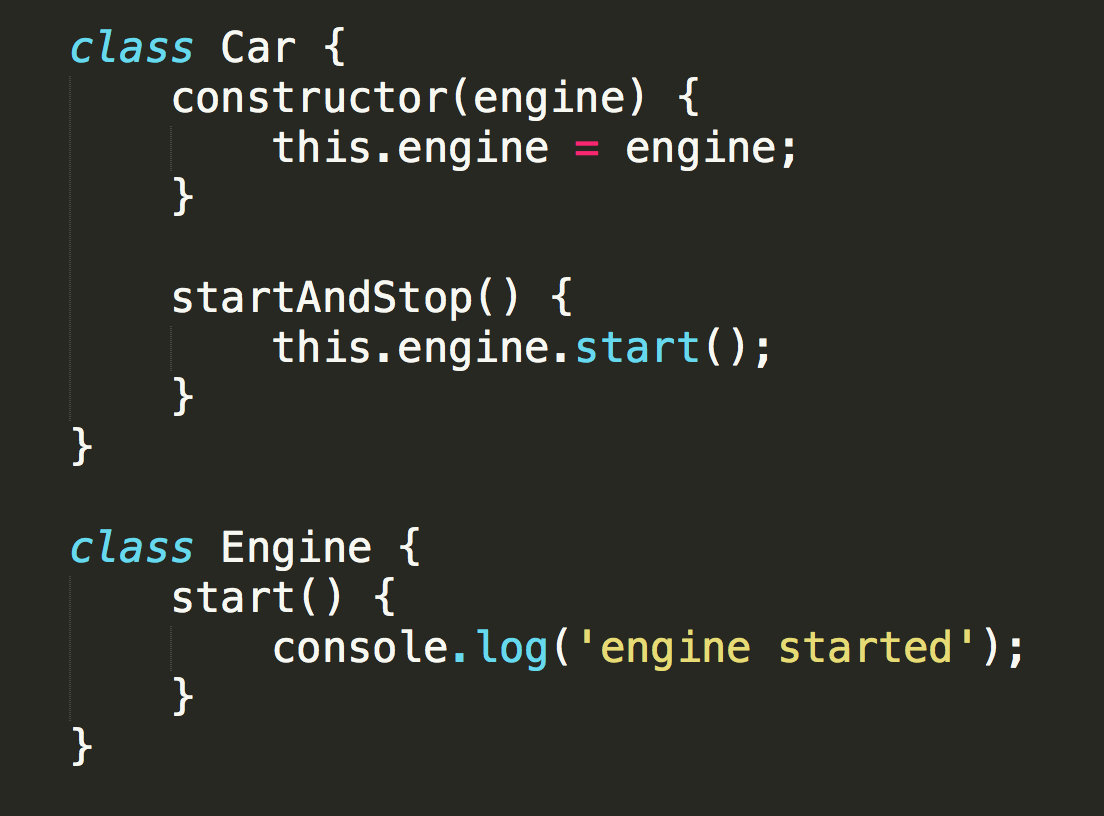
Spy (Test)
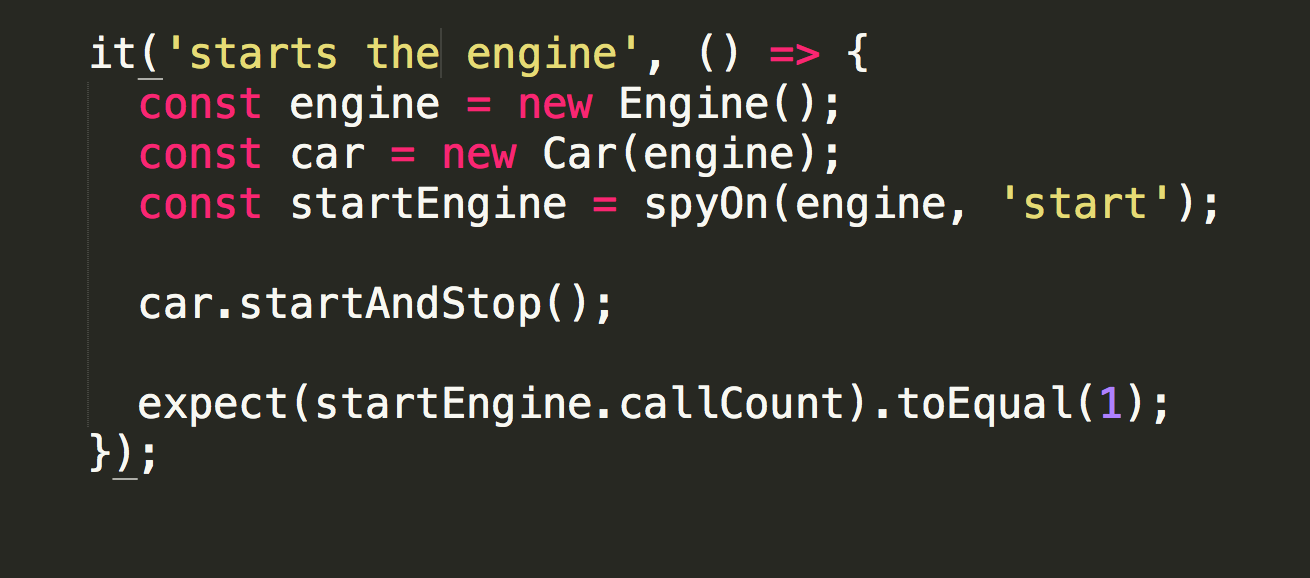
It will print "engine started" in the console
Stub (Code)
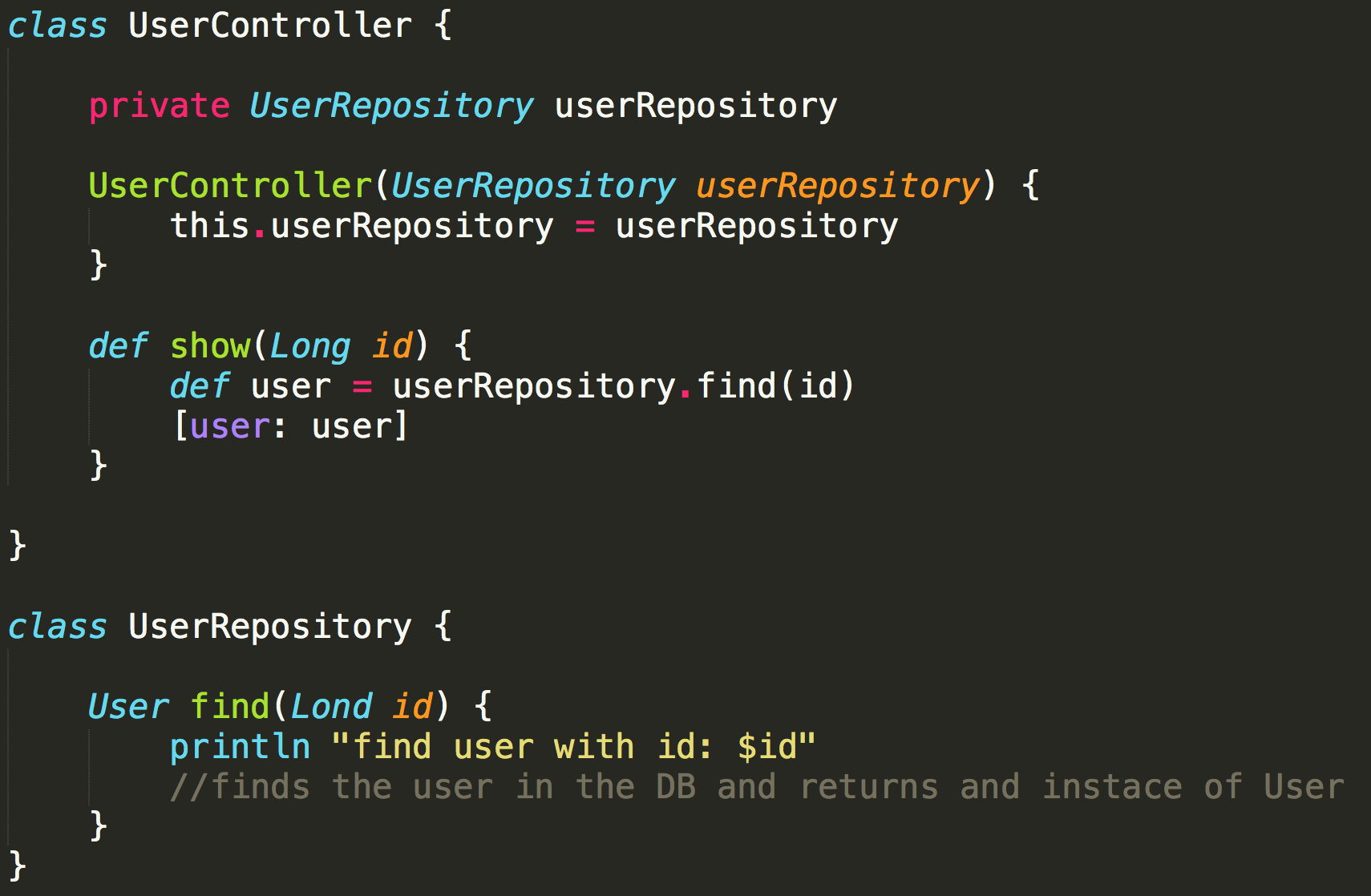
Stub (Test)
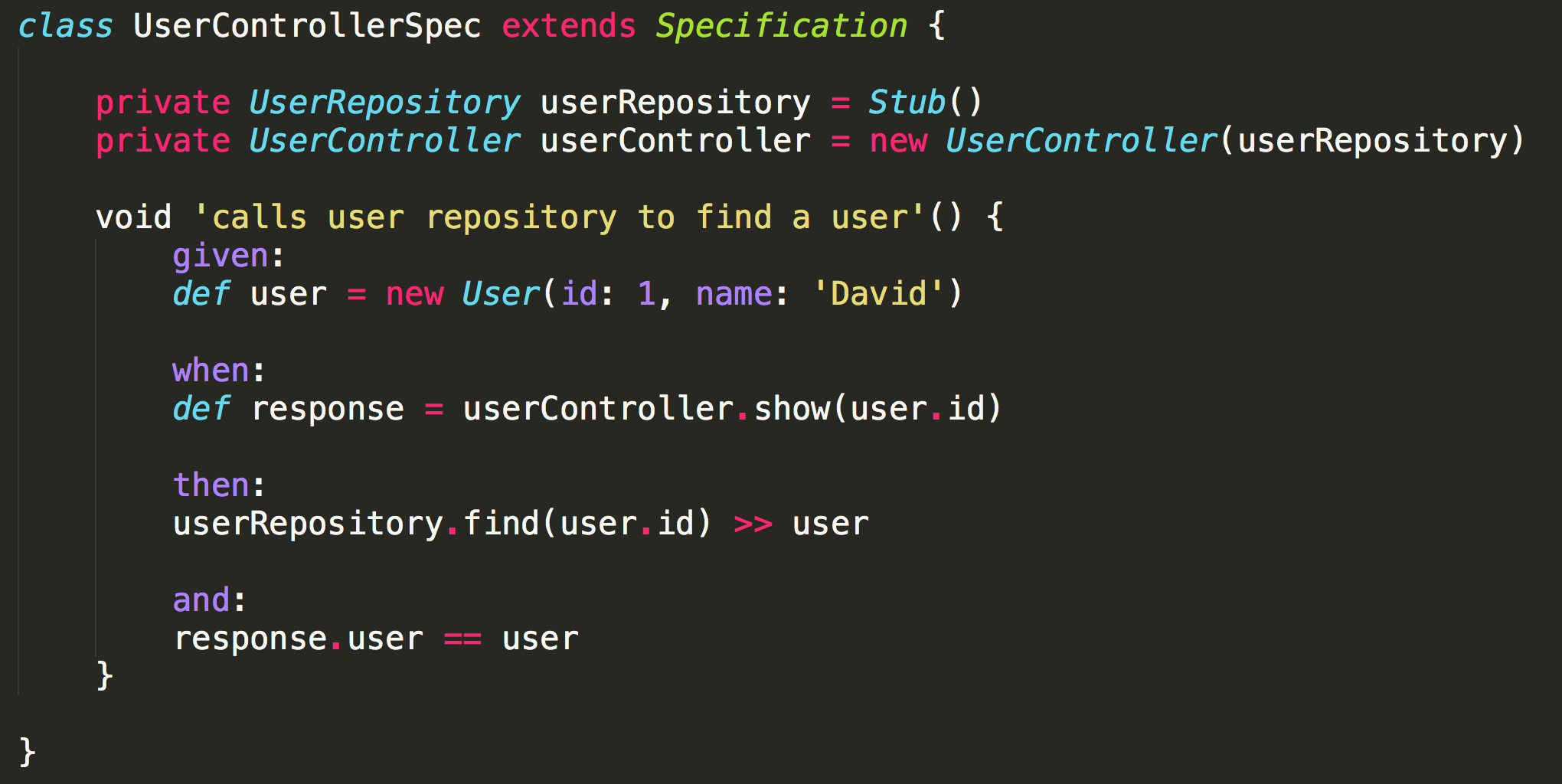
It won't print "find user with id..." in the console
Mock (Test)

It won't print "find user with id..." in the console
Fake
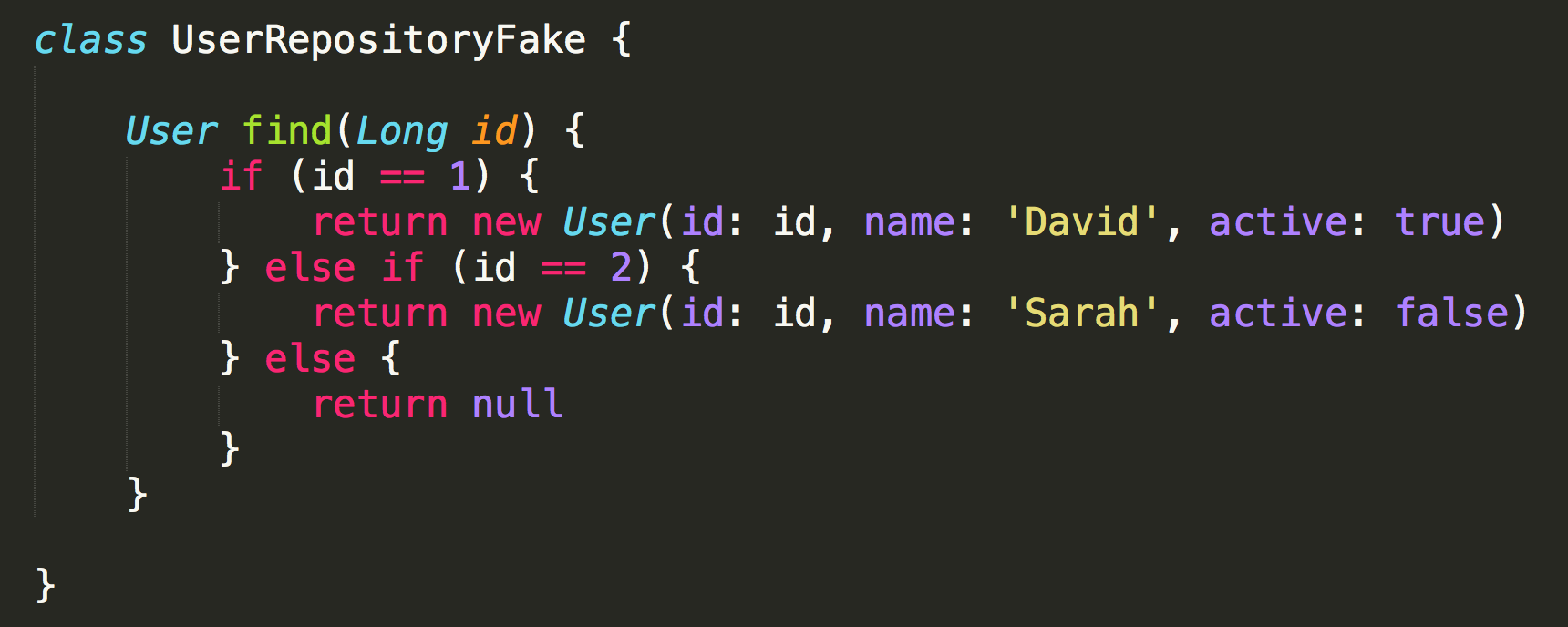
Common aspects
- Act as living documentation of the system under test
- Provide concrete evidence that your software works
- Increase the confidence
- Fast to execute
Tips I
- Treat your tests as if they were production code
- Seeing them fail is just as important as seeing them pass
- The name of the test should tell you what it is doing
- Assert one thing
- Do not depend on results from previous tests
Tips II
- Avoid flaky tests, they kill your confidence
- Make them run as fast as possible
- If they fail they should clearly tell you why
- Be able to run test independently, one test at a time
Tools
- Frameworks & Libraries
- xUnit, Hamcrest, Cucumber, Concordion, Mockito, Spock, Geb, Jasmine, Specs2
- Other utilities
- RestAssured, Spring rest docs, Cobertura, Wiremock, Betamax
- Building tools
- Maven, Gradle, SBT
Don't be afraid of trying new stuff, innovate.
CI
- The vitals sign monitor
- A Red CI should be every team member concern
- A healthy CI increases confidence
- Avoid a slow pipeline so releases can be done quickly
- Have only one pipeline
TDD
TDD
Test Driven Development is a software development technique and one of the key factors of XP Methodology
TDD is a discipline, is a particular way of writing unit test, it is a particular way of writing code

TDD
- It leads to think about how to use a component first and then about how to implement it
- It is not only a testing technique but also a design technique
- It is not only about proving the correctness of a particular behaviour, but also about documenting that behaviour
3 Rules of TDD
1) You are not allowed to write any production code unless it is to make a failing unit test pass.
3 Rules of TDD
1) You are not allowed to write any production code unless it is to make a failing unit test pass
2) You are not allowed to write any more of a unit test than is sufficient to fail
3 Rules of TDD
1) You are not allowed to write any production code unless it is to make a failing unit test pass.
2) You are not allowed to write any more of a unit test than is sufficient to fail
3) You are not allowed to write any more production code than is sufficient to pass the one failing unit test
Why is it important to follow the rules?
- Avoids code untested because it has been tested manually
- Avoids code that can not be unit tested
- Forces less coupled designs
- Code is testable by definition
- Improves the quality of the software
- Avoids over engineering
Why is it important to follow the rules?
- Bugs are caught earlier
- Allows you to stay away from the debugger, saving you time
- Tests become living documentation
- They are written with the aim of fullfilling a user story
- Shortens the programming feedback loop
Fundamental principles
- Think about what you are trying to do
- Follow the TDD cycle and the 3 laws
- Continually make small incremental changes
- Never write new functionality without a failing test
Some design principles
- Loosely coupled systems
- Dependency injection
- Strive for simplicity
- SRP
- Clean code
- Remove duplication
What to do when a bug is found?
- First, create a test case to reveal the bug
- Modify the production code so that the failed test passes
- Finally, run all the test to ensure the bug is fixed and covered
Ability to deliver
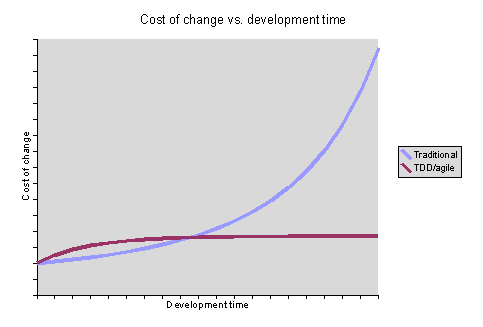
The green button

QA?
Testing - TDD
By David Molinero
Testing - TDD
- 590



