collect image data
- seamlessly connect to standard PACS with Query/Retrieve
- direct access to server filesystem
- drag-n-drop from local client into server
- ssh/scp underpinning for secure network transfers


analyze image data
- a "plugin" mechanism offers the ability to accept feed data and process data
- ChRIS is usually configured to communicate transparently with an HPC
- plugins are mostly non-interactive analysis pipelines
- interactivity is available as a pre-processing step


manage image data
- all "data is stored in a time-based feed
- feeds are basically file-browsers
- feeds can be annotated with free form notes
- shared feeds can support comments between parties


view image data
- image data in feed can be viewed directly in simple drop down window
- image data can be viewed in more sophisticated fashion with specialized viewing modes
- advanced sharing using 3rd party backends (Google Real Time API / Dropbox API)


Web 2.0 and Beyond: Leveraging Web Technologies as Middleware in Healthcare Research
High Performance Compute Clusters: Data, Apps, Results, Sharing and Collaboration
Rudolph Pienaar, PhD
Technical Director
Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging and Developmental Science Center
Staff Scientist Instructor in Radiology
Boston Children's Hospital Harvard Medical School
overview of talk
Part I - Informatiomics in healthcare
- Forces acting on information
- Patterns of information flow
- Typical "apps"
- Rise of the walled information silos
- The coming information tsunami


overview of talk
Part II - Informatiomics and ChRIS
- Unmet need
- Core components
- Demo


overview of talk
Part I - Informatiomics in healthcare
- Forces acting on information
- Patterns of information flow
- Typical "apps"
- Rise of the walled information silos
- The coming information tsunami


Forces acting on healtcare workflows
External
- Regulatory
- Data ownership
- Owned by individual, not institution
Internal
- Internal Review Board
- Locality
- Department specific access
- Idiosyncratic, isolated technolgoies


Forces acting on healtcare workflows
Compounding Complexity
- Data is distributed in multiple places
- EMRs
- Modality databases
- Department databases
- Different formats
- Data is structured and unstructured
- "Voice" recordings
- "Free form text"



Forces acting on healtcare workflows
Compounding Complexity
- Inconsistent/variable definitions
- Qualitative interpretations
- Quantitative measurement variability
- T(R) on Siemens might be different to GE
- Data itself is complex
- genomics
- radiomics (images)
- combinatorial explosion



Forces acting on healtcare workflows
Compounding Complexity
- Locked in isolation due to regulatory forces
- Data movement out of institutions is complex
- "Compute" movement into institutions is complex.



Forces acting on healtcare workflows
| Act | Applies to |
|---|---|
| HITECH | Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, sets meaningful use of interoperable EHR adoption in the health care system as a critical national goal and incentivized EHR adoption. |
| Sarbanes-Oxley | Privacy and integrity of financial data in publicly traded corporations. |
| HIPAA | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability of health care information. |
| PCI | Confidentiality of credit card information stored and used by merchants. |
| GLBA | Confidentiality and integrity of personal financial information stored by financial institutions. |
| SB 1386 | Confidentiality of customers' personal information stored by any organization that does business in the state of California. |
| BASEL II | Confidentiality and integrity of personal financial information stored by financial institutions. Availability of financial systems. Integrity of financial information as it is transmitted. Authentication and integrity of financial transactions. |



Forces acting on healtcare workflows
| Scope | Applies to |
|---|---|
| IRB | Internal committee formally designated to approve, monitor, and review biomedical and behavioral research involving humans. |
| Technology | Extremely static environment, typically on clinical side, with slow updates/changes to computational resources, especially as related to web-based technologies and mobile |
| Department | Supplementary technology is often department focused and department centric. |



Patterns of information flow in healthcare
Current
- Unidirectional
- Isolated
- Non-integrative
- Static
Future
- Multi-directional
- Collaborative
- Integrative
- Dynamic


Typical hospital "web" apps...



Typical hospital "web" apps...



Typical hospital "web" apps...
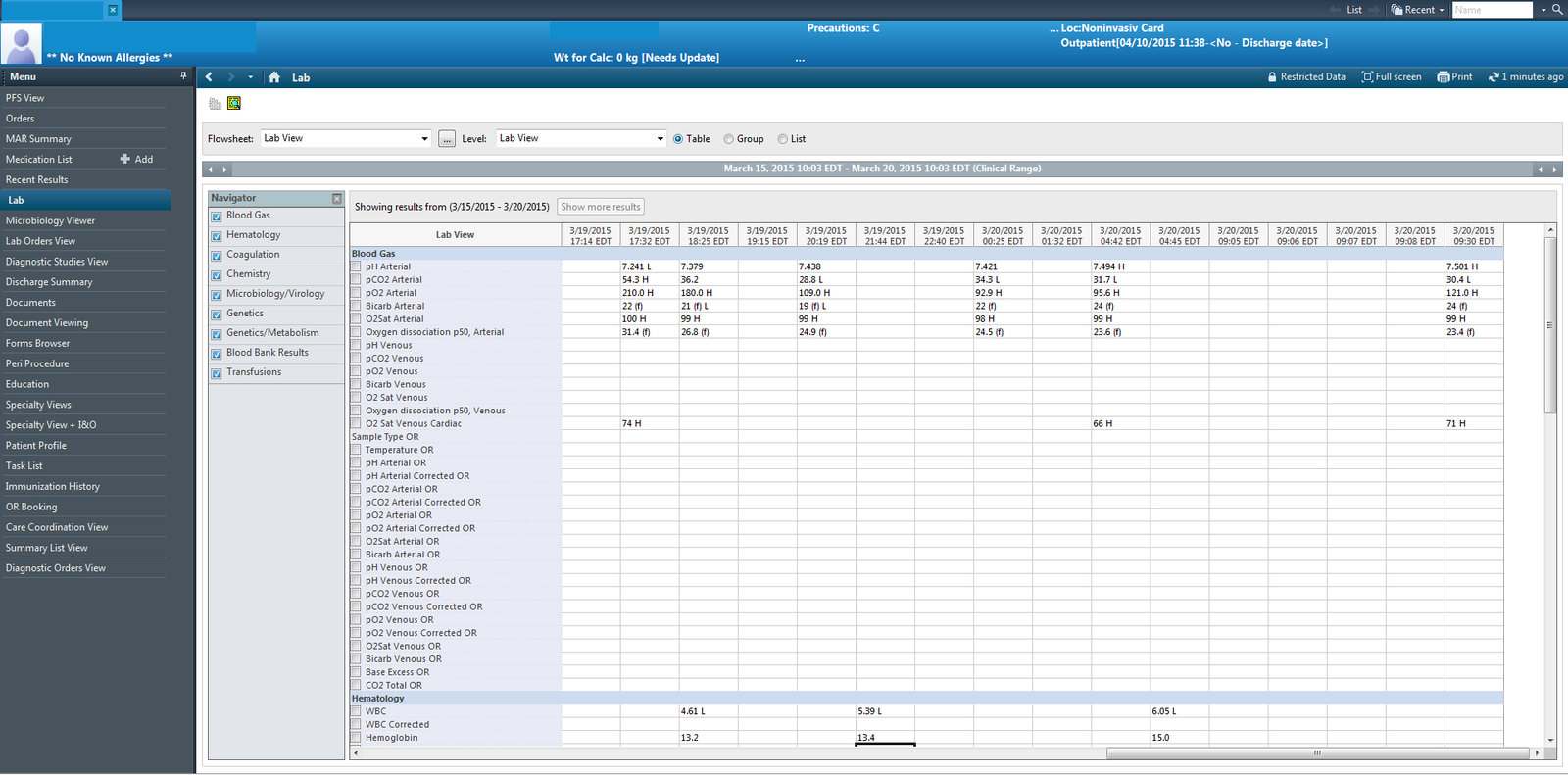


Typical hospital "web" apps...
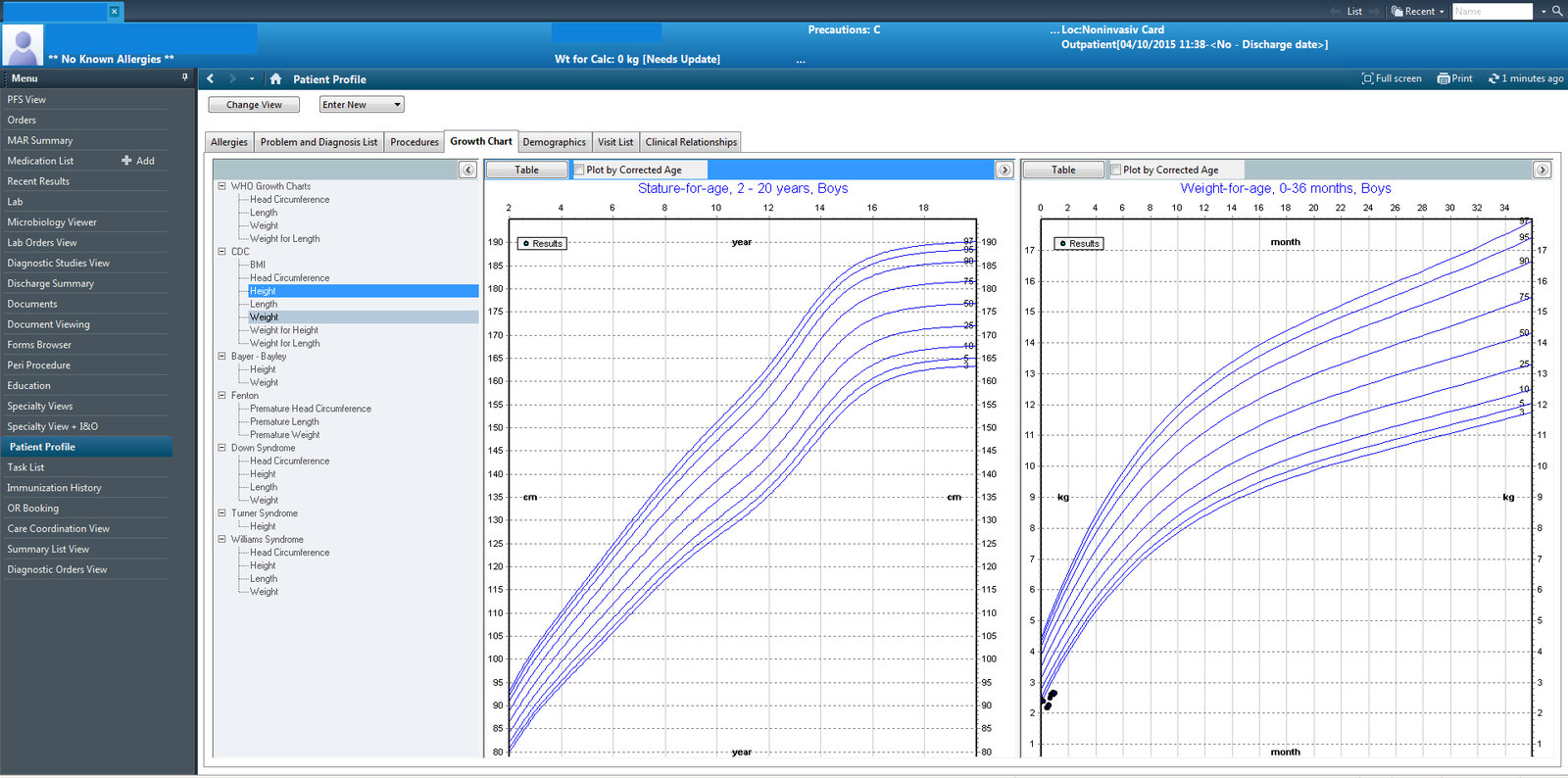


Typical hospital "web" apps...



Typical hospital "web" apps...
Current App Philosophy
- Old-style "web" apps subsumed to look like desktop apps.
- Reflect an "app" centric model, not "data" centric.
- Not really "web" apps:
- Typically limited to obsolete versions of Internet Explorer
- No support for mobile or other platforms.
- No cross-app integration on data level.


Typical hospital "web" apps...
- Typically no provision for "automated" or scripted interaction using modern techniques
- REST API



The rise of information silos...
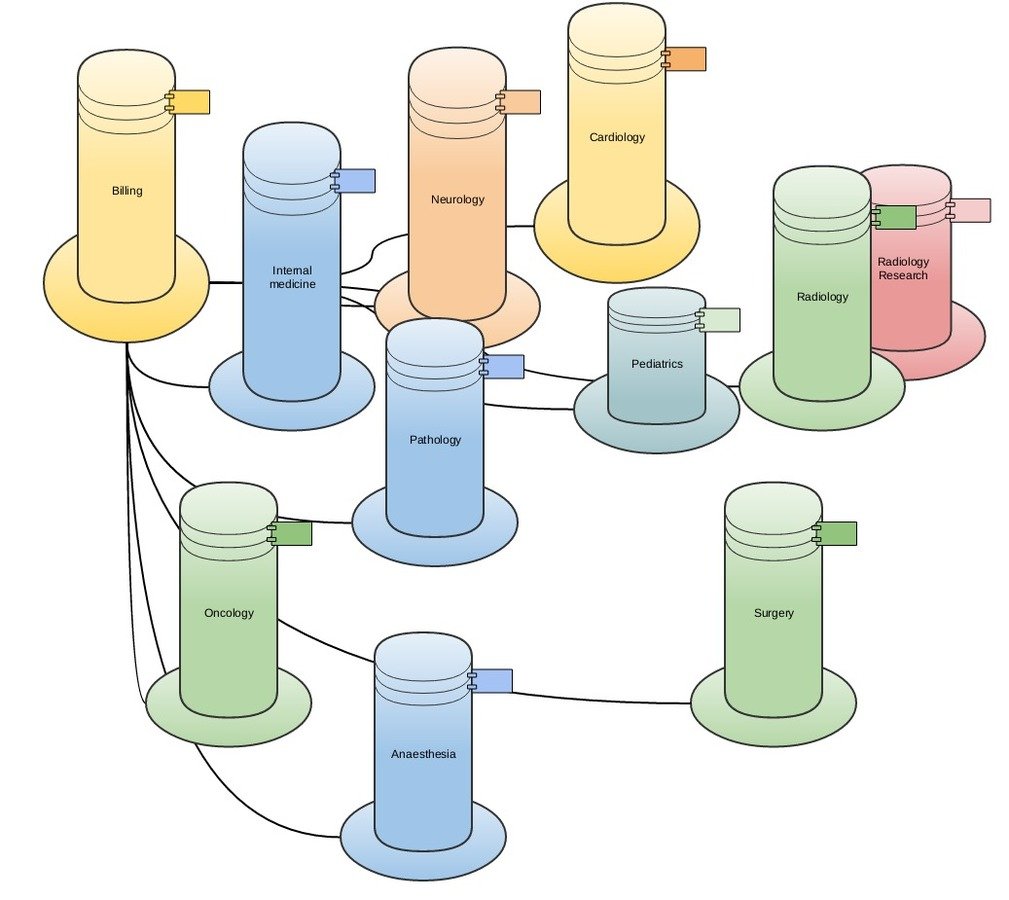


The rise of information silos...
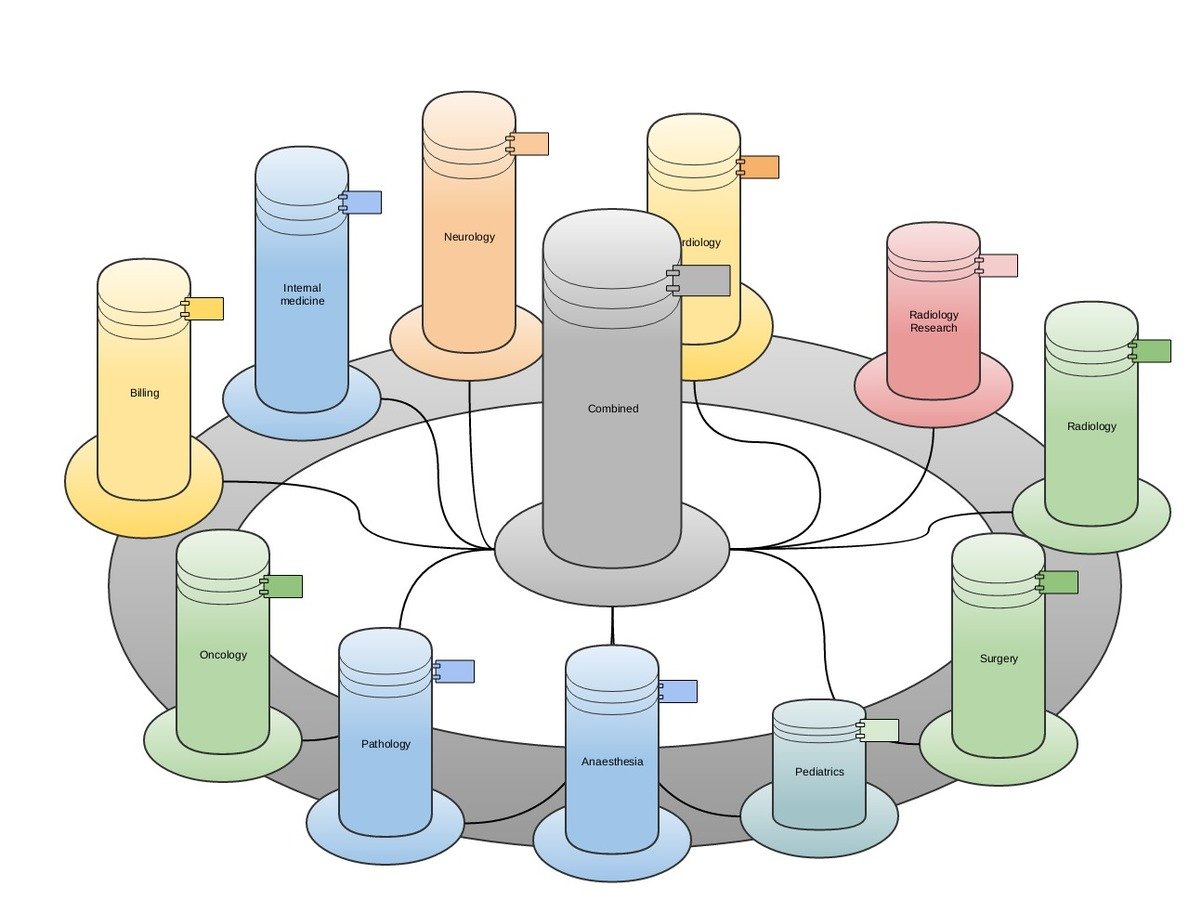


The rise of information silos...
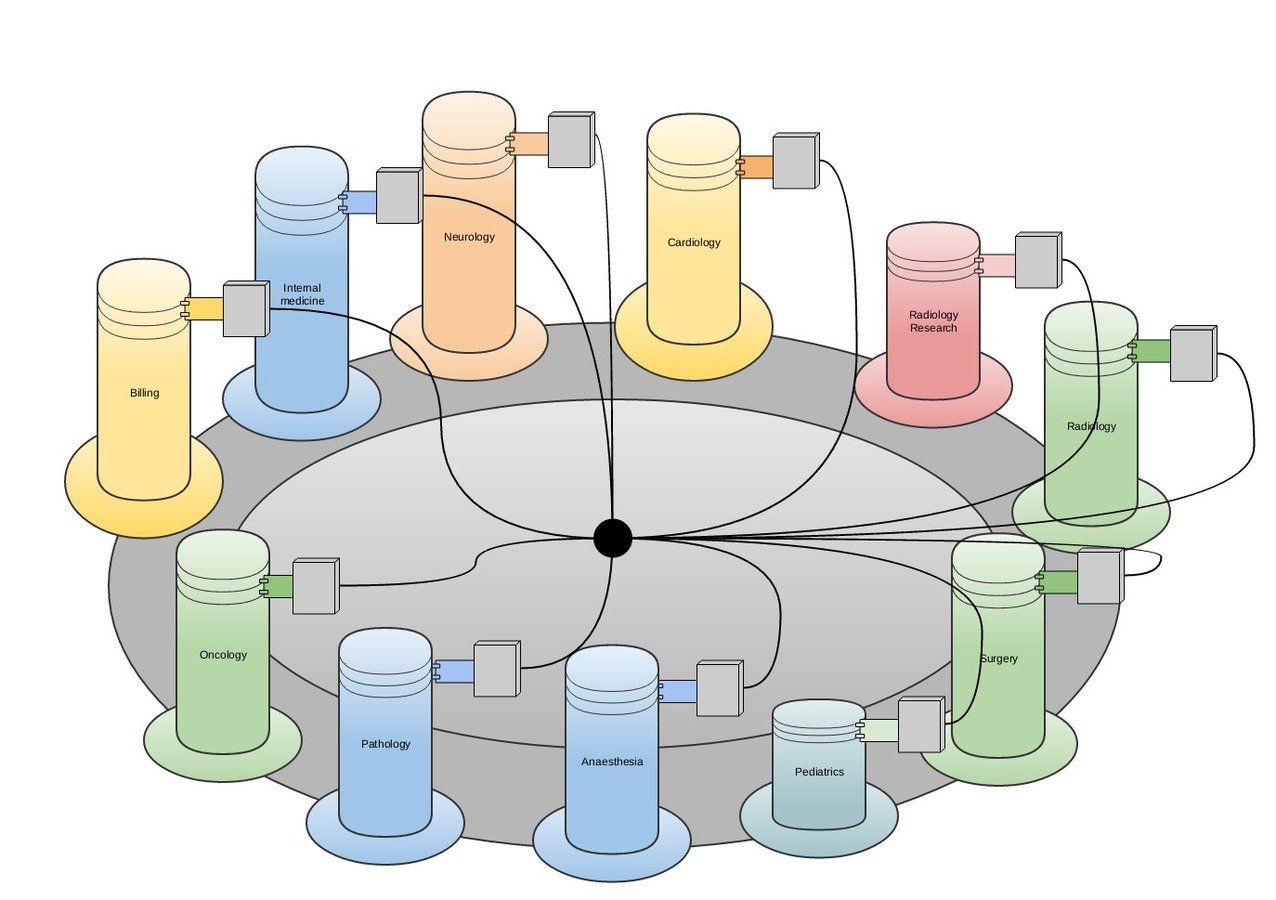


The rise of information silos...


FHIR: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources
- Defines an API for exchanging EHR
- HL7 compliant
- Uses modern web based APIs (HTTP/REST)
- JSON or XML for data representation
- Provides an alternative to document centric approaches by directly exposing discrete data elements as services

Old-vs-new app philosophies...



Old:
- App (UI) focused
- Single Purpose
- "Human" consumer
New:
- Data focused
- Loosely coupled
- Multi purpose
- "Other software agents" consumer
Information explosion...






Information explosion...


Information explosion...
| Market | Electronic Laboratory Notebook | Lab Info Management | Image Post-Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segment Size | $284 million (2017) | $1.5 billion (2015) | $1.3 billion (2014) |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate | Unknown | 4.7% | 11.0% |
| Key Players | Agilent Technologies Inc., Amphora Research Systems, Accelerys, Waters, Cognium Systems, IDBS, Axiope | Abbot, Perkin, Thermofisher, Labware, Labvantage, Core Informatics | Abbot, Perkin, Thermofisher, Labware, Labvantage, Core Informatics |



Information explosion...
| Market | Laboratory Automation | Medical Imaging Data | Genomics Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segment Size | $3.1 billion (2012) | $32.2 billion (2014) | $1.3 billion (2012) |
| Compound Annual Growth Rate | 6.4% | 7.0% | 16.3% |
| Segment | ELN, LIMS | Post-processing | ELN, LIMS |



Information explosion...



Information explosion...
Square kilometer array
- Radio telescope being built in Australia and South Africa
- Total collecting area of one square kilometer
- 50 times more sensitive than any other radio instrument
- Data transport from dishes will produce 10 times the 2010 entire global internet traffic


Information explosion...



Information explosion...
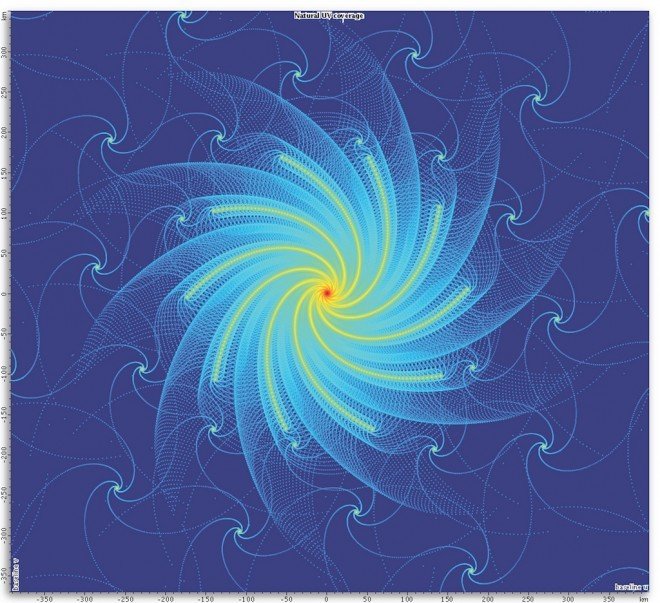
SKA (daily estimated data generation)
- 1 exabyte
- 1,000 petabytes
- 1 million terabytes
- 1 billion gigabytes


1% of the 2010 world's total internet traffic every two days
Information explosion...

Annual global IP traffic will pass the zettabyte (1000 exabytes) threshold by the end of 2016, and will reach 2 zettabytes per year by 2019.
-
By 2016, global IP traffic will reach 1.1 zettabytes per year, or 88.4 exabytes (nearly one billion gigabytes) per month, and by 2019, global IP traffic will reach 2.0 zettabytes per year, or 168 exabytes per month.
Global IP traffic has increased fivefold over the past five years, and will increase threefold over the next five years.
-
Overall, IP traffic will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23 percent from 2014 to 2019.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/VNI_Hyperconnectivity_WP.html

Information explosion...

Two-thirds of all IP traffic will originate with non-PC devices by 2019.
-
In 2014, only 40 percent of total IP traffic originated with non-PC devices, but by 2019 the non-PC share of total IP traffic will grow to 67 percent.
Traffic from wireless and mobile devices will exceed traffic from wired devices by 2016.
- By 2016, wired devices will account for 47 percent of IP traffic, and Wi-Fi and mobile devices will account for 53 percent of IP traffic. In 2014, wired devices accounted for the majority of IP traffic, at 54 percent.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/VNI_Hyperconnectivity_WP.html

Information explosion...

Global Internet traffic in 2019 will be equivalent to 66 times the volume of the entire global Internet in 2005.
-
Globally, Internet traffic will reach 37 gigabytes (GB) per capita by 2019, up from 15.5 GB per capita in 2014.
The number of devices connected to IP networks will be more than three times the global population by 2019
-
There will be more than three networked devices per capita by 2019, up from nearly two networked devices per capita in 2014. Accelerated in part by the increase in devices and the capabilities of those devices, IP traffic per capita will reach 22 GB per capita by 2019, up from 8 GB per capita in 2014.
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/VNI_Hyperconnectivity_WP.html

Information explosion...



Information explosion...
Healthcare



Information explosion...
Healthcare
- 1.65M tumors measured in various modalities
- > 4 exabytes of data in various localities
- 1 petabyte of data (0.001EB) to transfer
- On current Internet, would take about 21 days to transfer this data around.



overview of talk
Part II - Informatiomics and ChRIS
- Unmet need
- Core components
- Demo


Enter ChRIS...


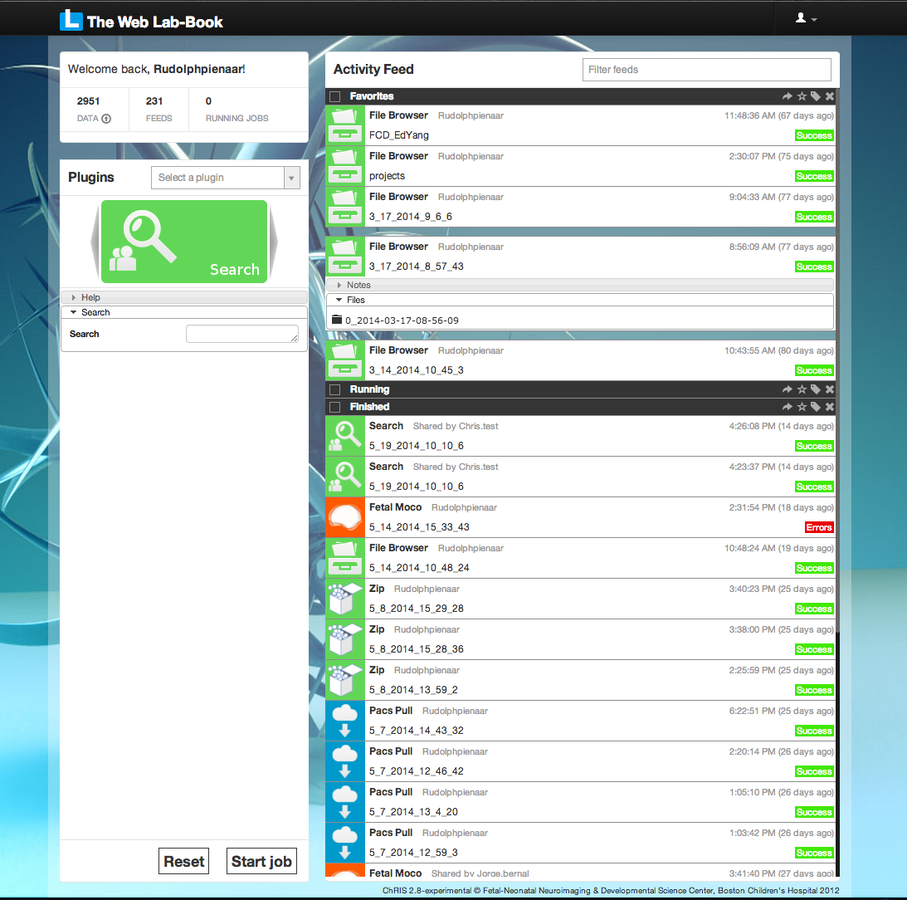
ChRIS
ChRIS is:
- [Boston's] " Children's Research Informatics System"
- a scalable web-based research/clinical workflow manager
- HPC aware
- and more...


Doesn't "fix" big data, but reduces end user complexity to big data by using a single "entry" point to many workflows and data sources.
ChRIS



ChRIS


Data collection and management
Data processing and
analysis
Data visualization
Information sharing and collaboration
ChRIS
- Persistent time-based data feeds
- Plugins
ChRIS






use the web, Luke...
shifting to the web allows for:
- more familiar interface metaphor
- web 2.0 "social" interaction
- posting/sharing
- moves the burden of maintenance away from end user
- allows for mobile
















components
- collect
- manage
- analyze
- view
- collaborate


collect image data






analyze image data







real time collaboration
- image data can be shared between collaborators
- Google RealTime API
- a realtime JSON object is shared and updates each viewer independently
- (akin to multi-player games)
- shared screen components (like cursor)


real time collaboration








real time demo...
- ChRIS instance



real time demo...
- ChRIS instance



Ancilliary projects
- https://fnndsc.github.io/mi2b2


Development team
- Jorge "To Be" Bernal, PhD
- Nicolas "VJ" Rannou, MSc
- Rudolph "Cat Herder" Pienaar, PhD
- Daniel "X Slicer" Haehn, PhD
- Daniel "Game On" Ginsburg, MSc
- Ellen "Rad" Grant, MD








further references...
-
https://github.com/FNNDSC/chrisreloaded
-
https://github.com/FNNDSC/ChRIS_API
-
https://github.com/FNNDSC/viewerjs
-
https://github.com/FNNDSC/mi2b2
-
https://github.com/FNNDSC/vjs
-
https://github.com/slicedrop
-
https://goxtk.com


thank you...


CHPC_Web2.0_and_beyond-ChRIS
By Rudolph Pienaar
CHPC_Web2.0_and_beyond-ChRIS
A general overview of ChRIS... shortcomings in conventional approaches, live demo, video, mi2b2.
- 2,048



