Amazon MemoryDB for Redis Hands-On
Demo
MemoryDB = Primary Database (durable, persistent storage) ElastiCache = Cache Layer (fast, temporary storage)
Fundamental Difference
In this demo, we will:
- Set up networking infrastructure (VPC and security groups)
- Create a MemoryDB subnet group
- Deploy a MemoryDB cluster with Multi-AZ configuration
- Configure parameter groups for optimal performance
- Connect to the cluster using EC2 instance
- Interact with MemoryDB using CLI and Python Program
- Clean up resources
Agenda
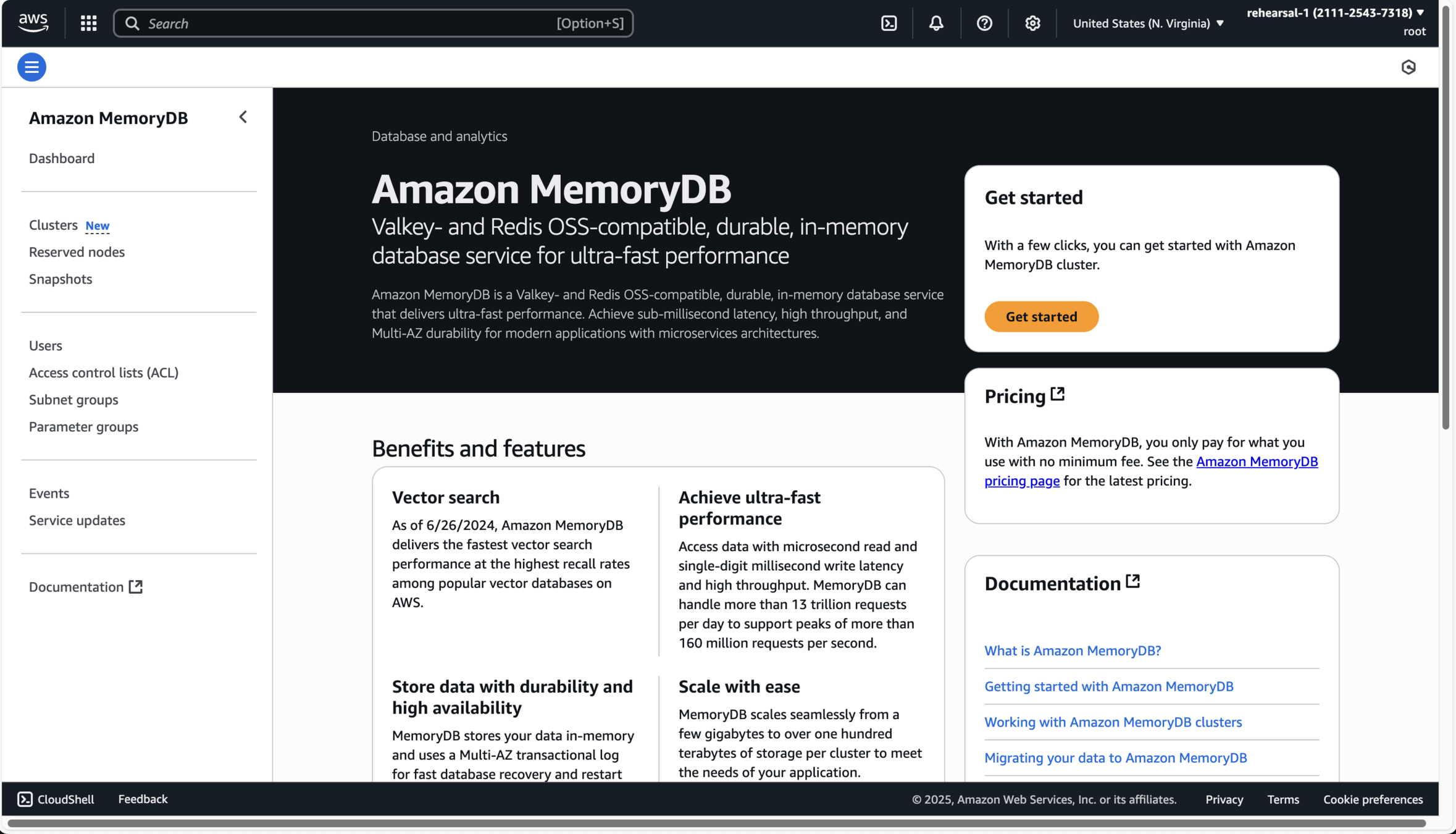
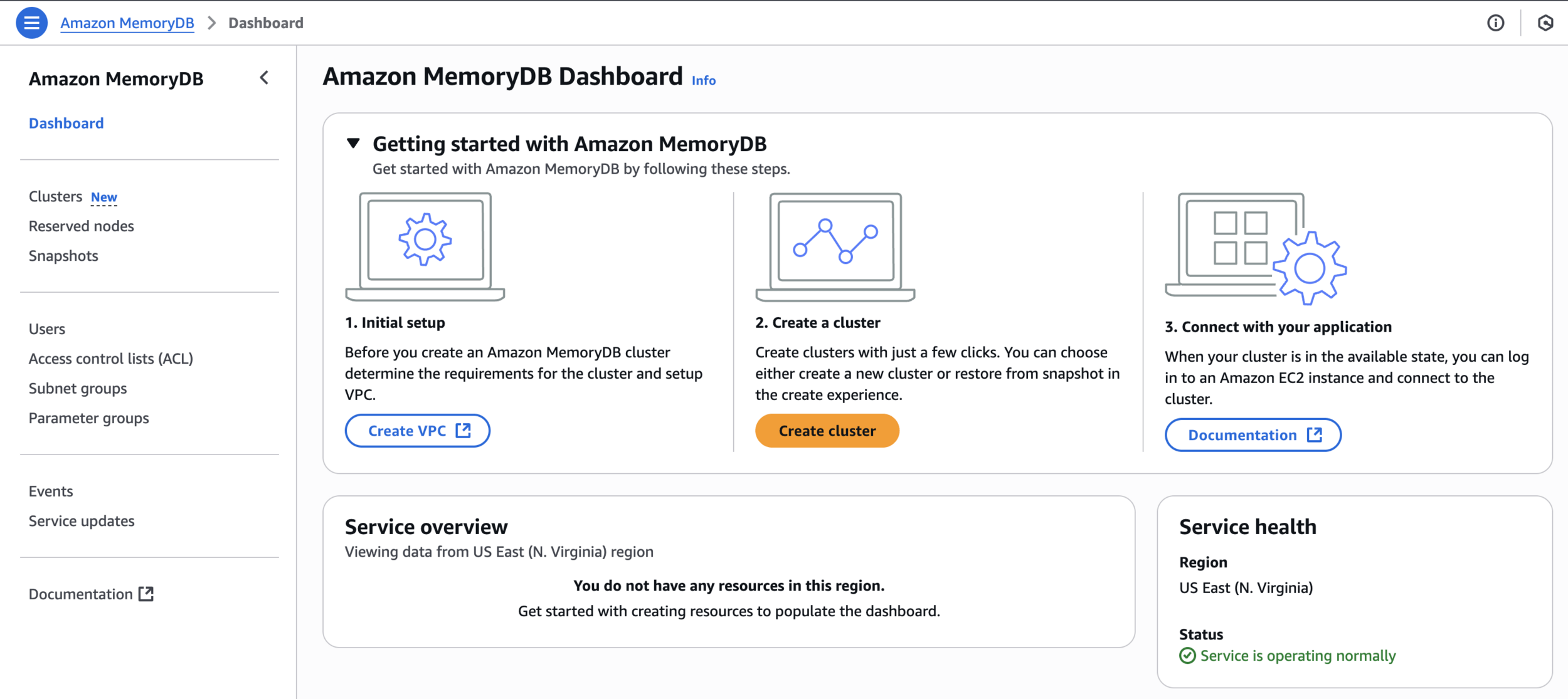
Amazon MemoryDB Dashboard
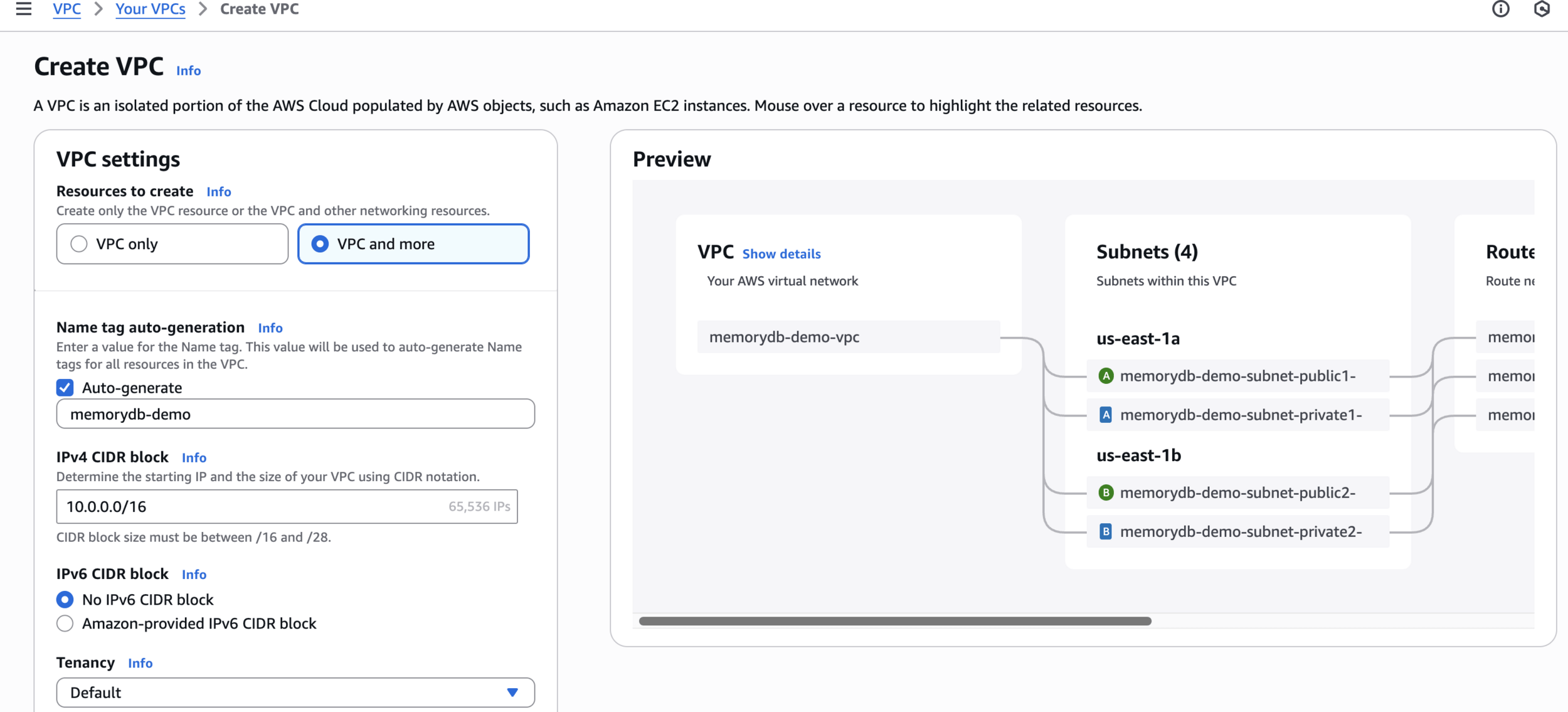
memorydb-demoCreate VPC
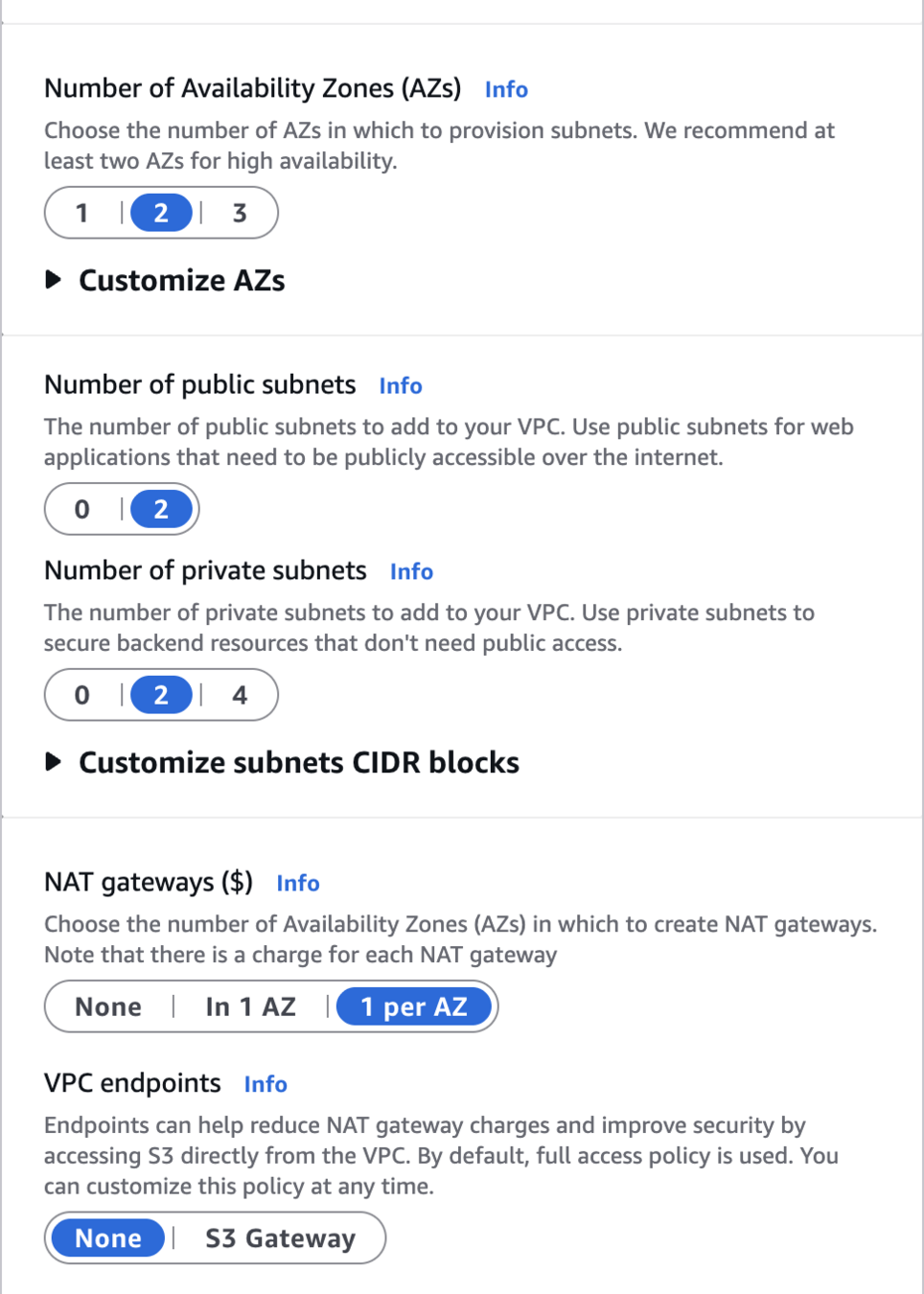
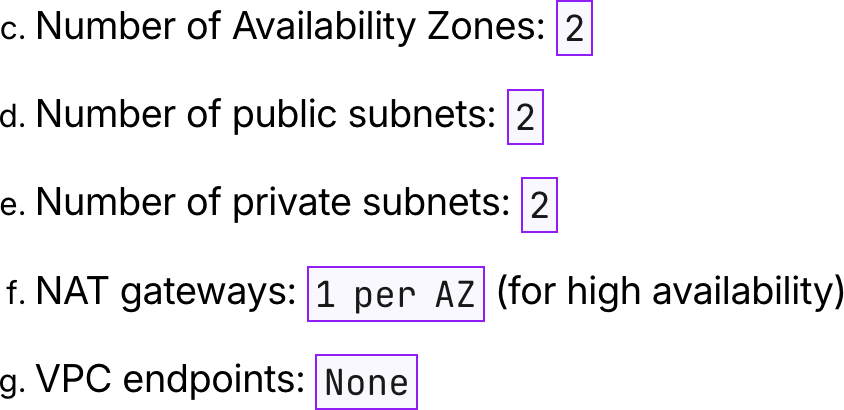
Number of Availability Zones
Create VPC

View VPC
Security Groups
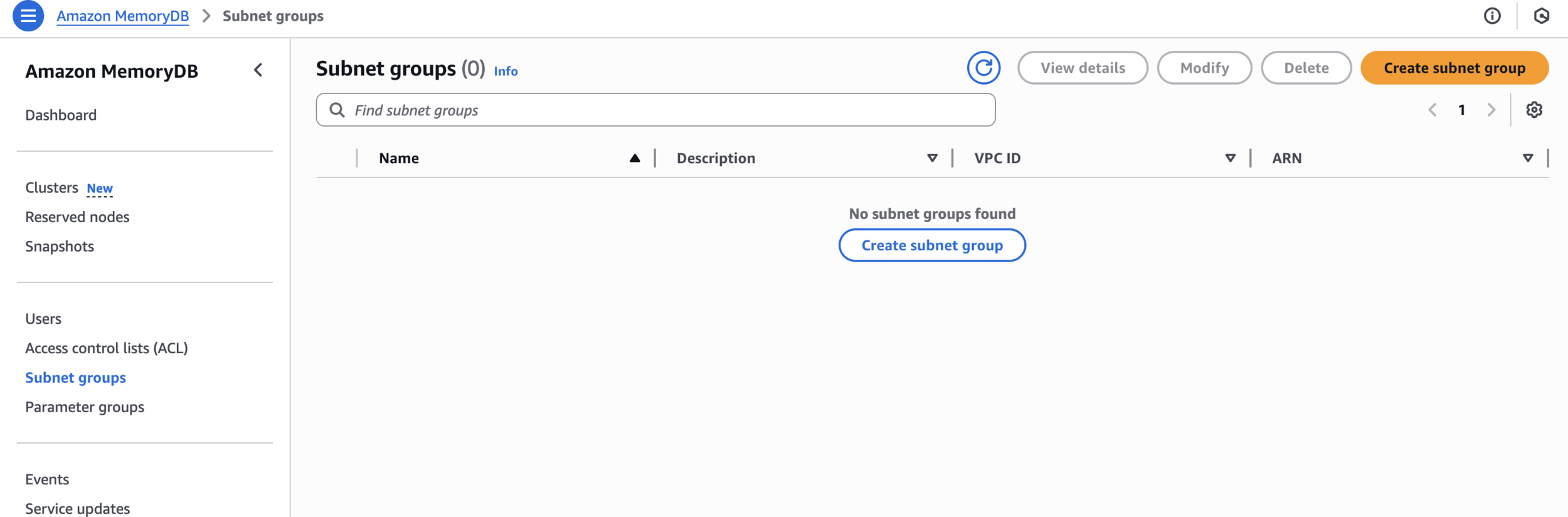
Create Subnet Group
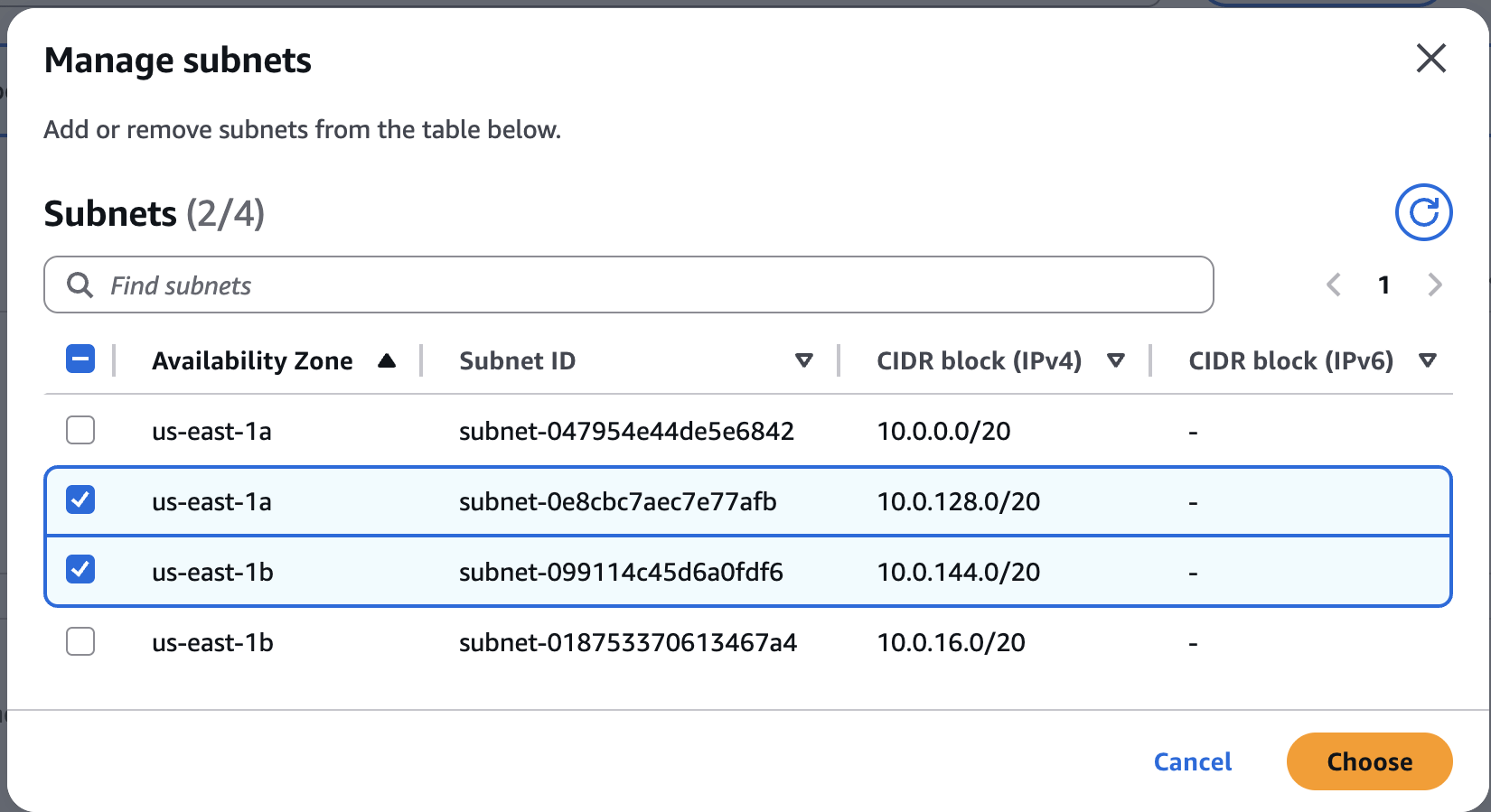
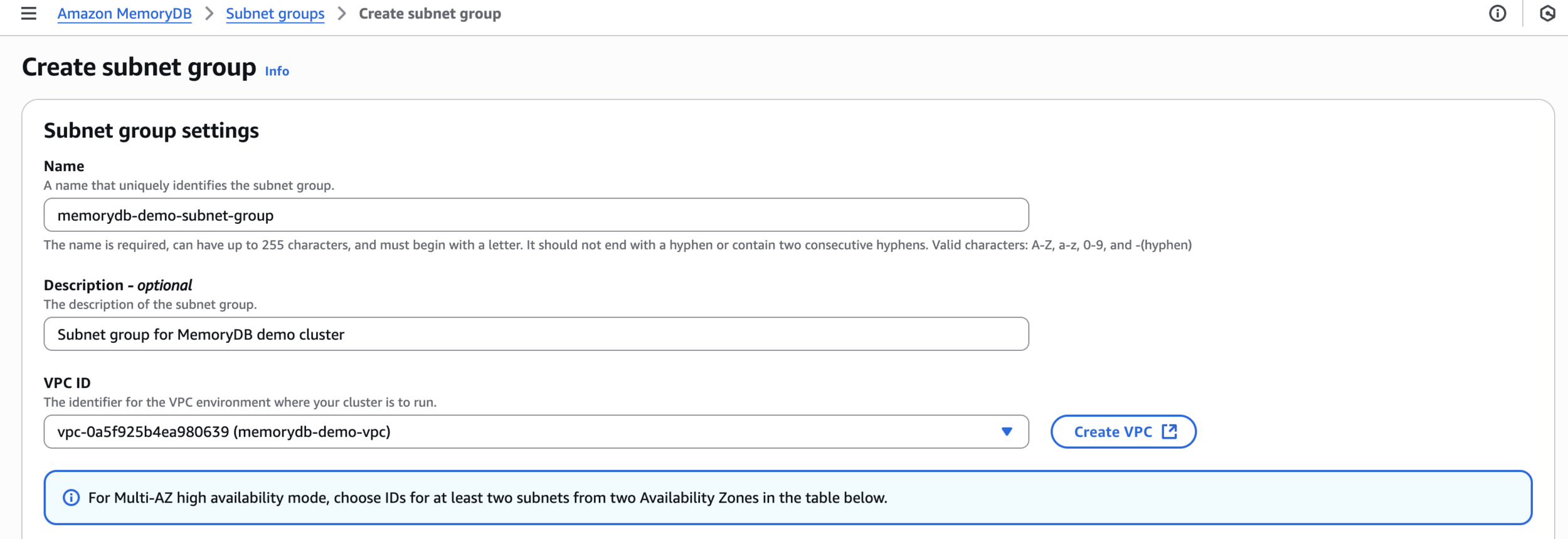
memorydb-demo-subnet-groupSubnet group for MemoryDB demo clusterCreate subnet group

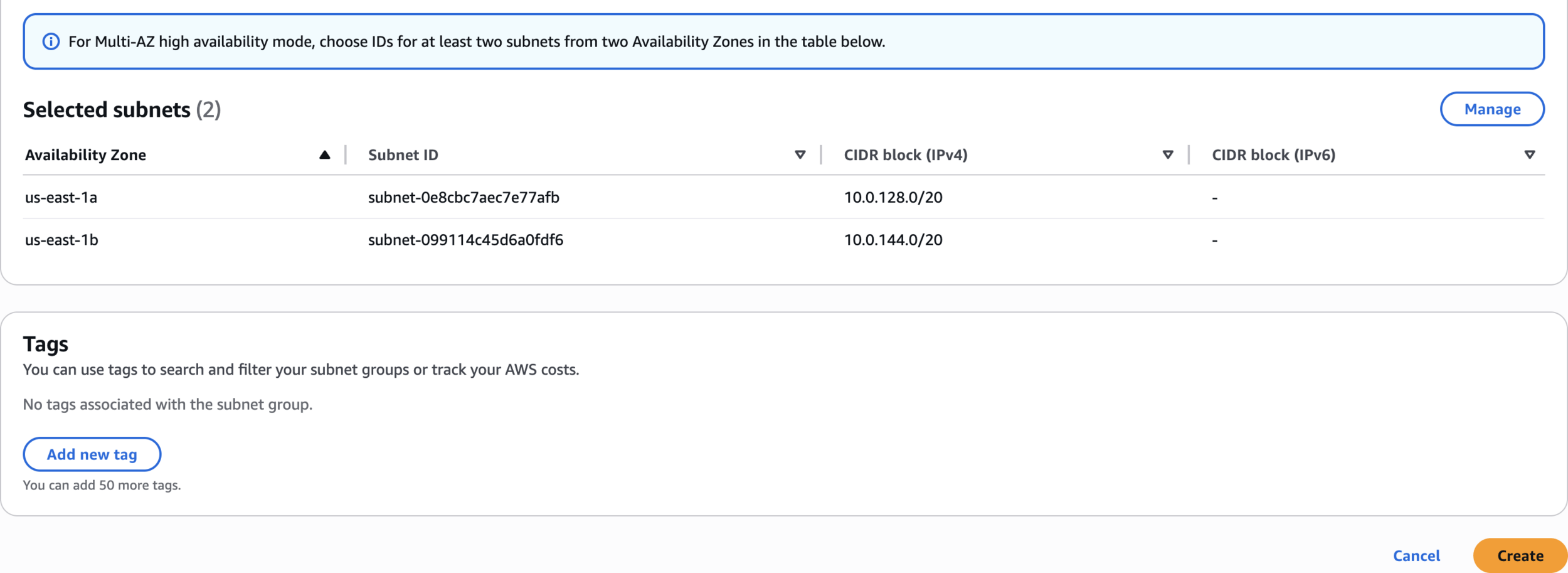
Selected subnets

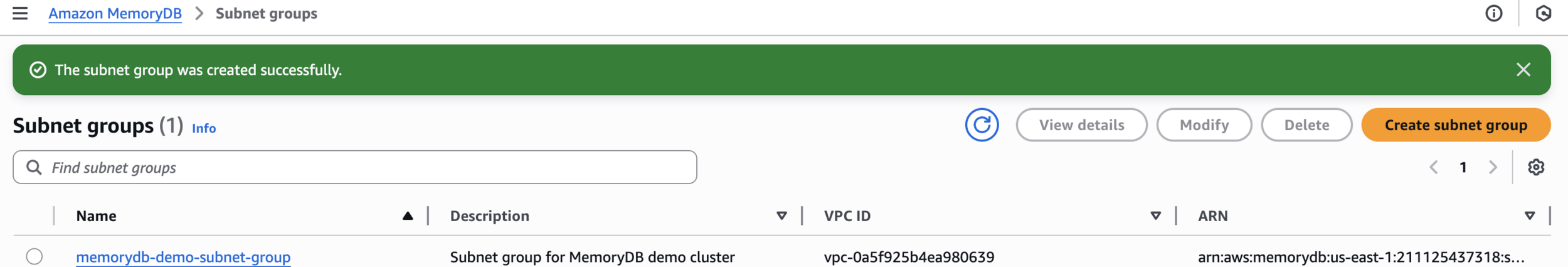
The subnet group was created successfully
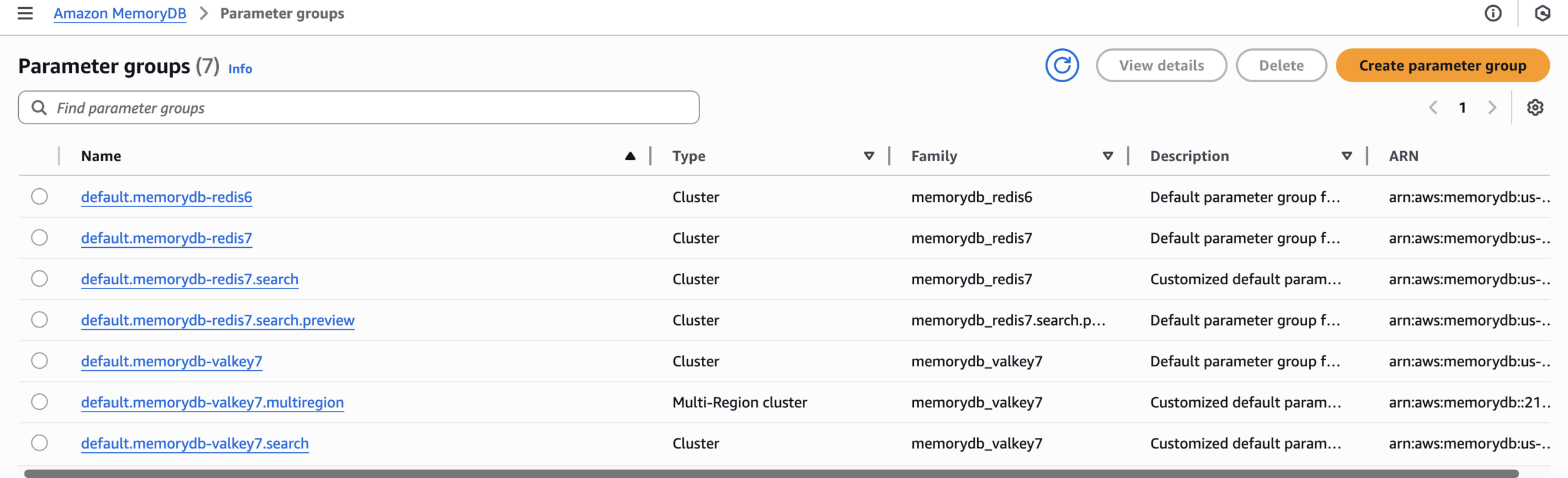
Create MemoryDB Parameter Group
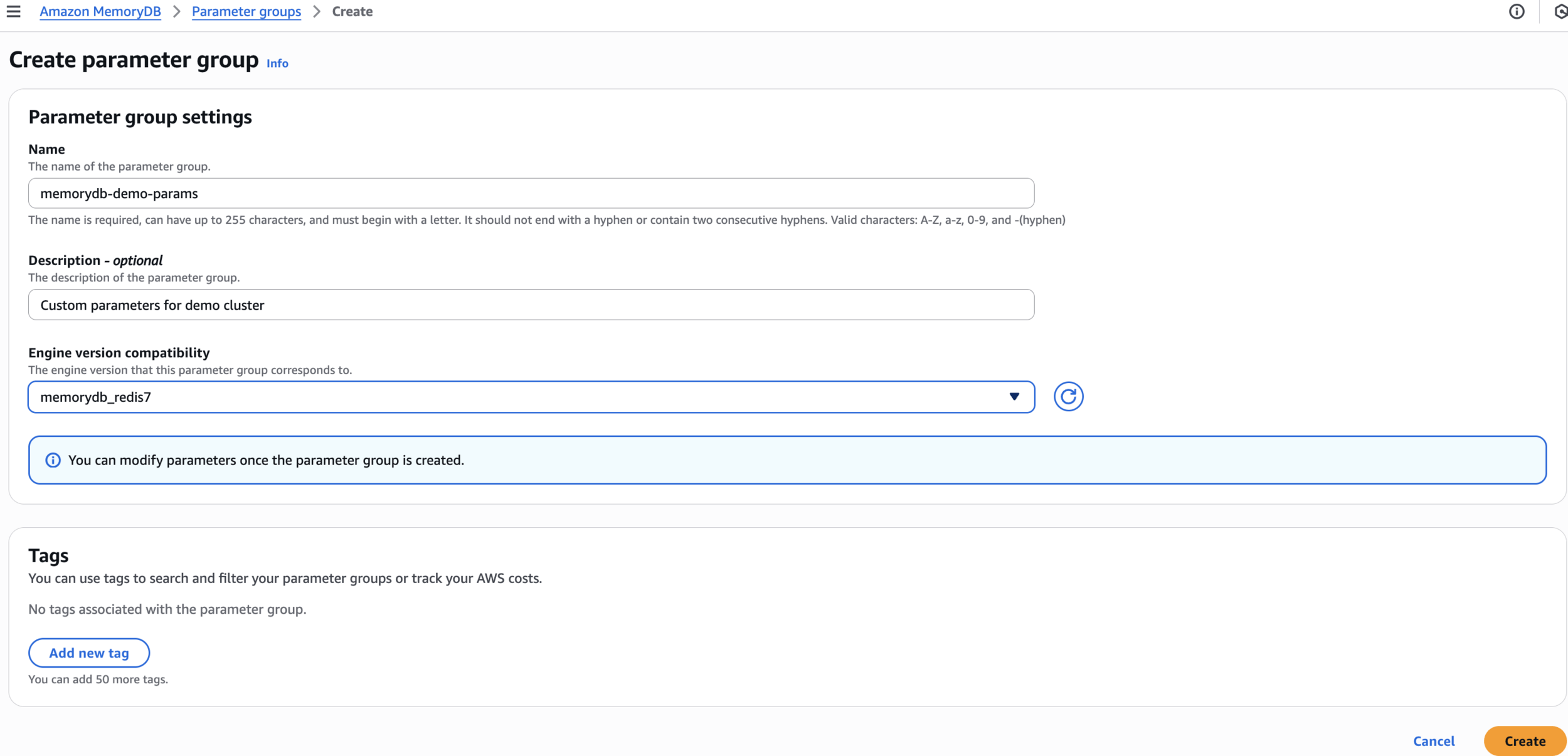
memorydb-demo-paramsCreate parameter group
Custom parameters for demo cluster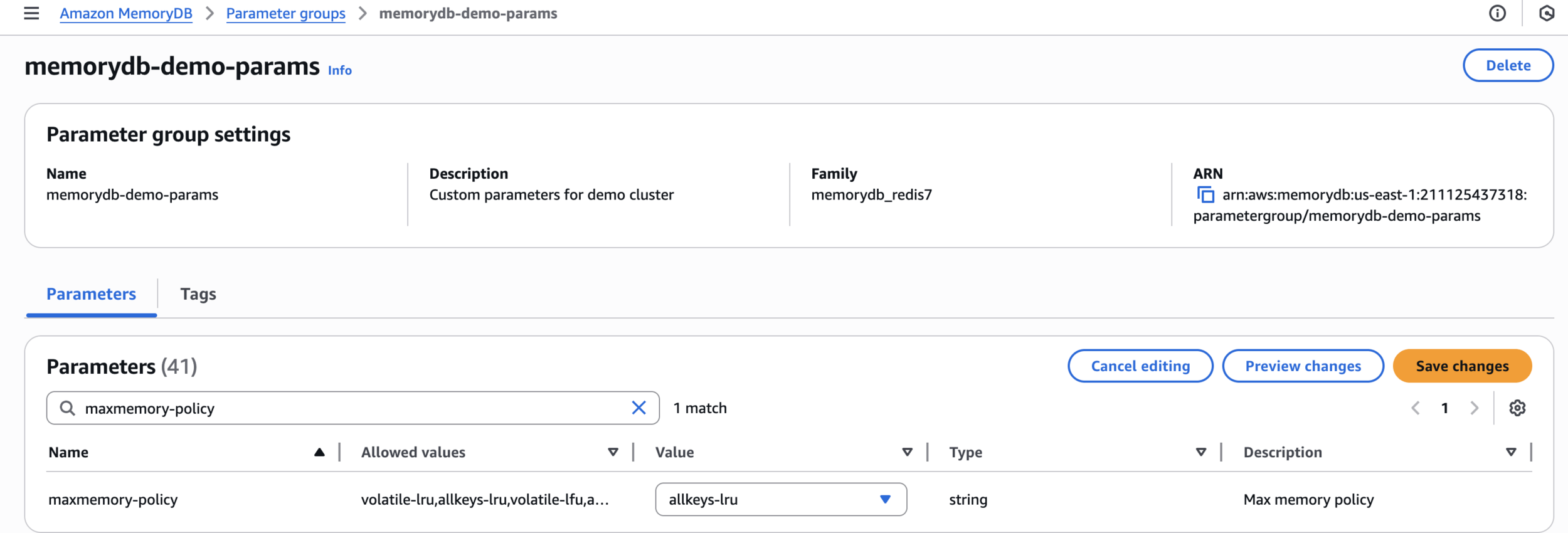

Edit parameters
maxmemory-policy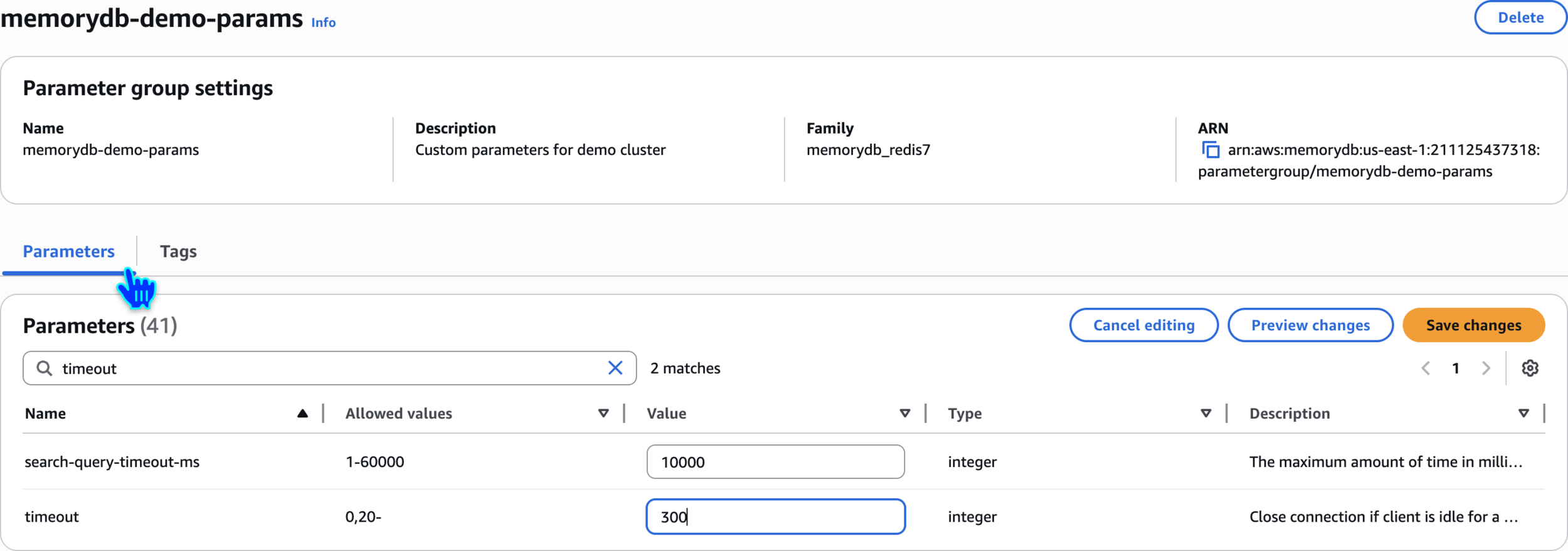

Edit parameters
Create cluster
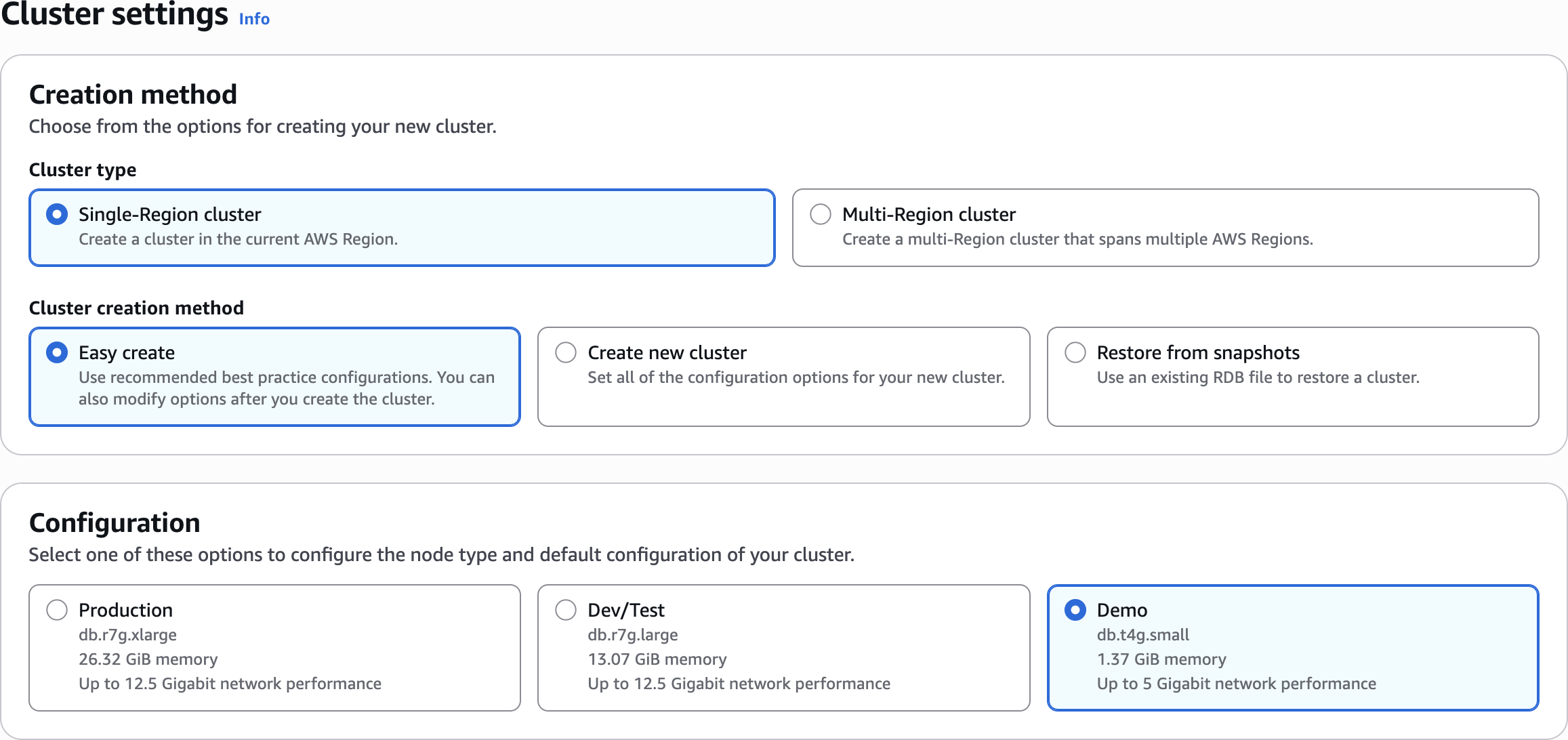
Cluster settings
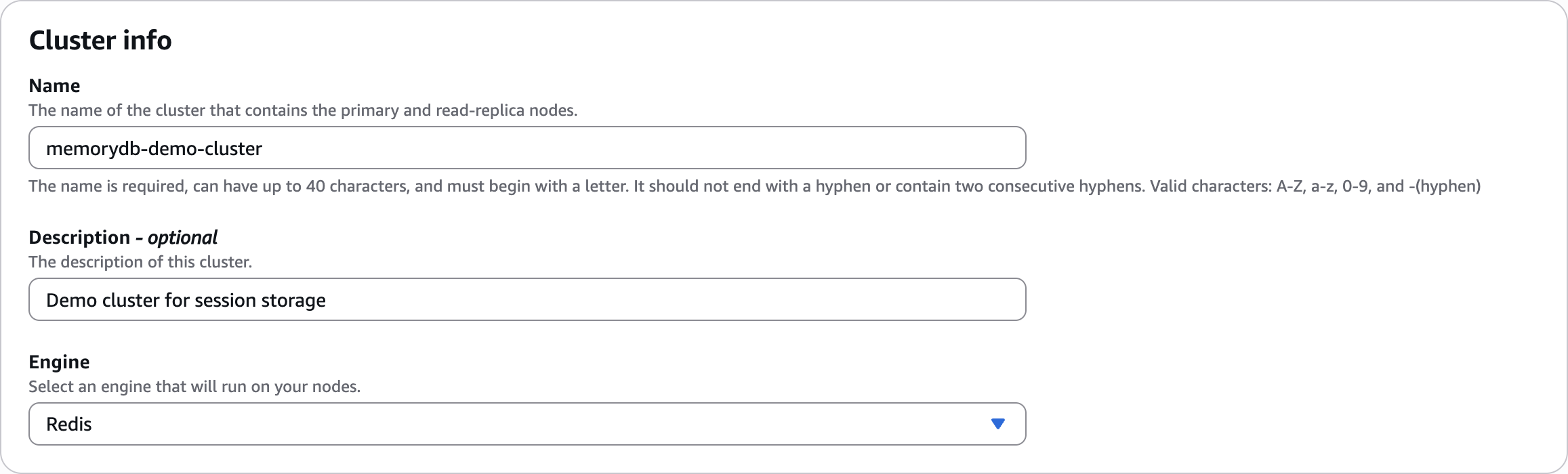
memorydb-demo-clusterCluster info
Demo cluster for session storage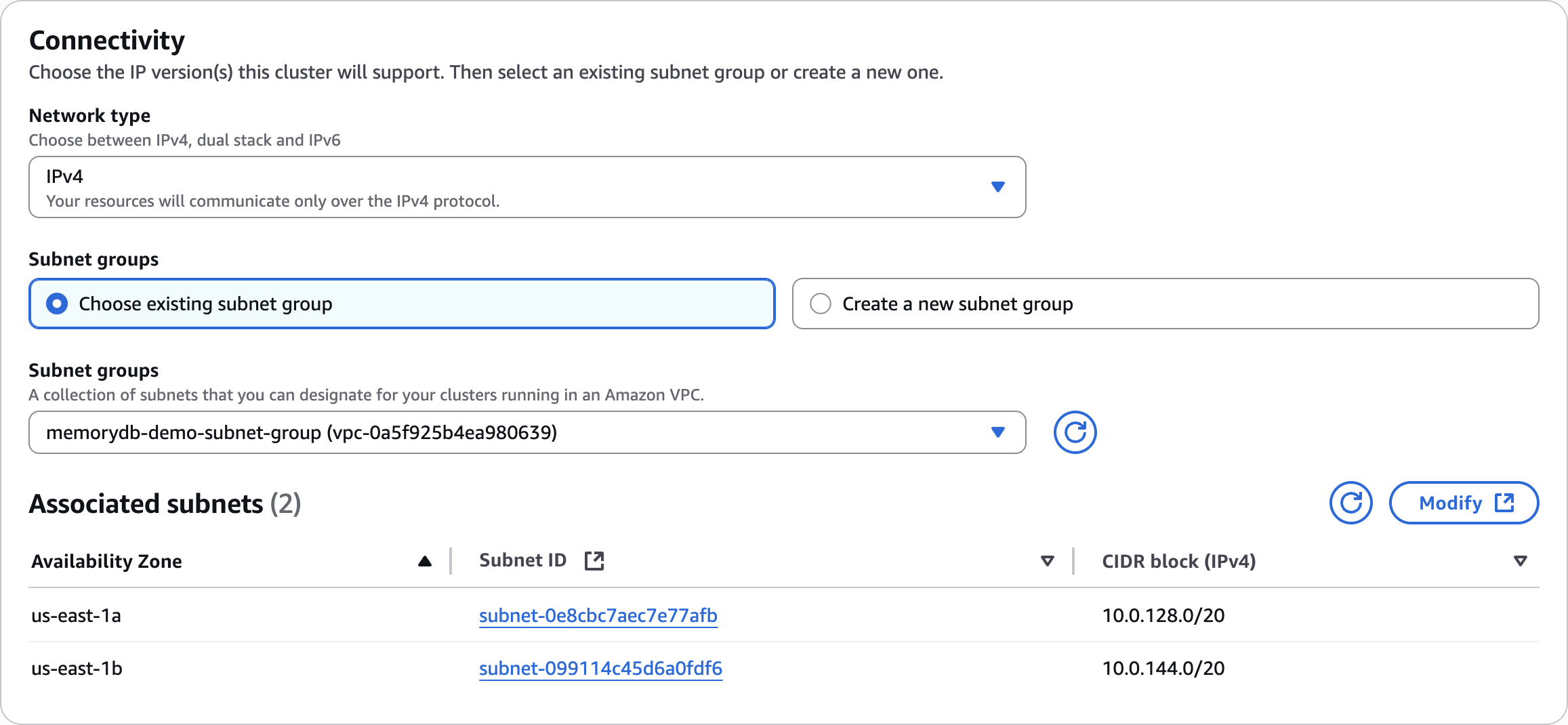
Connectivity
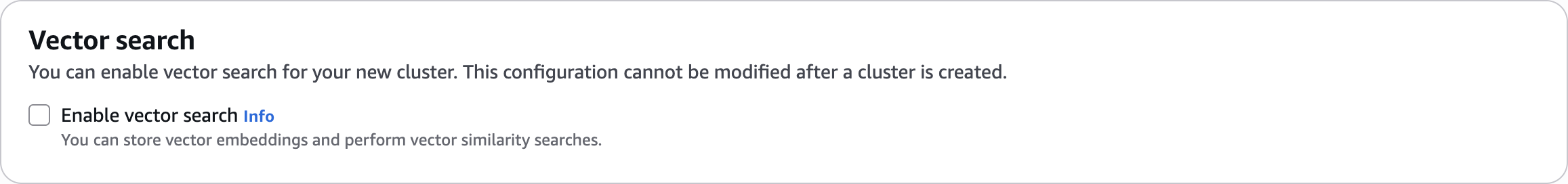
Vector search
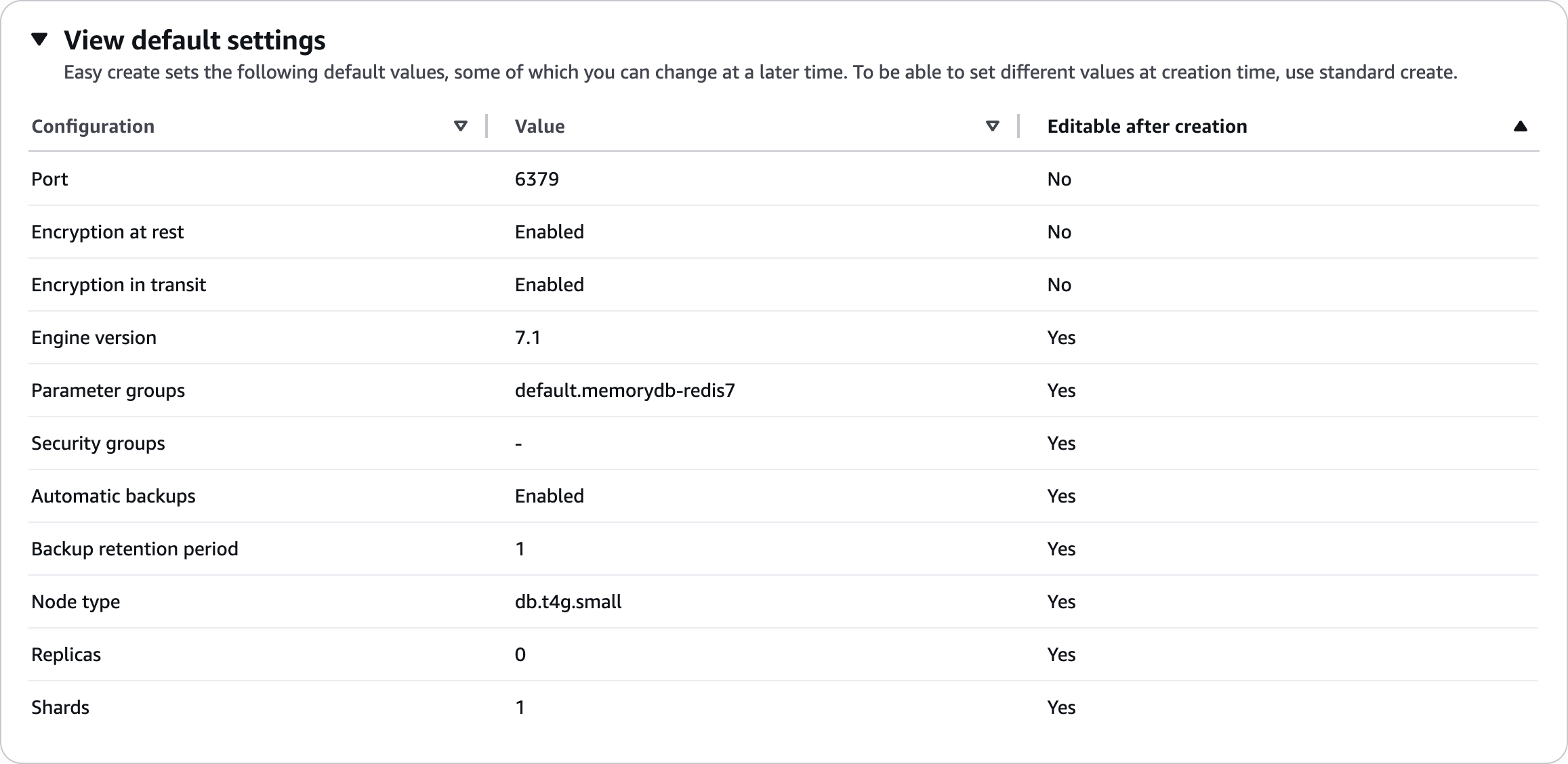
View default settings
Create
Create SSM Role for EC2
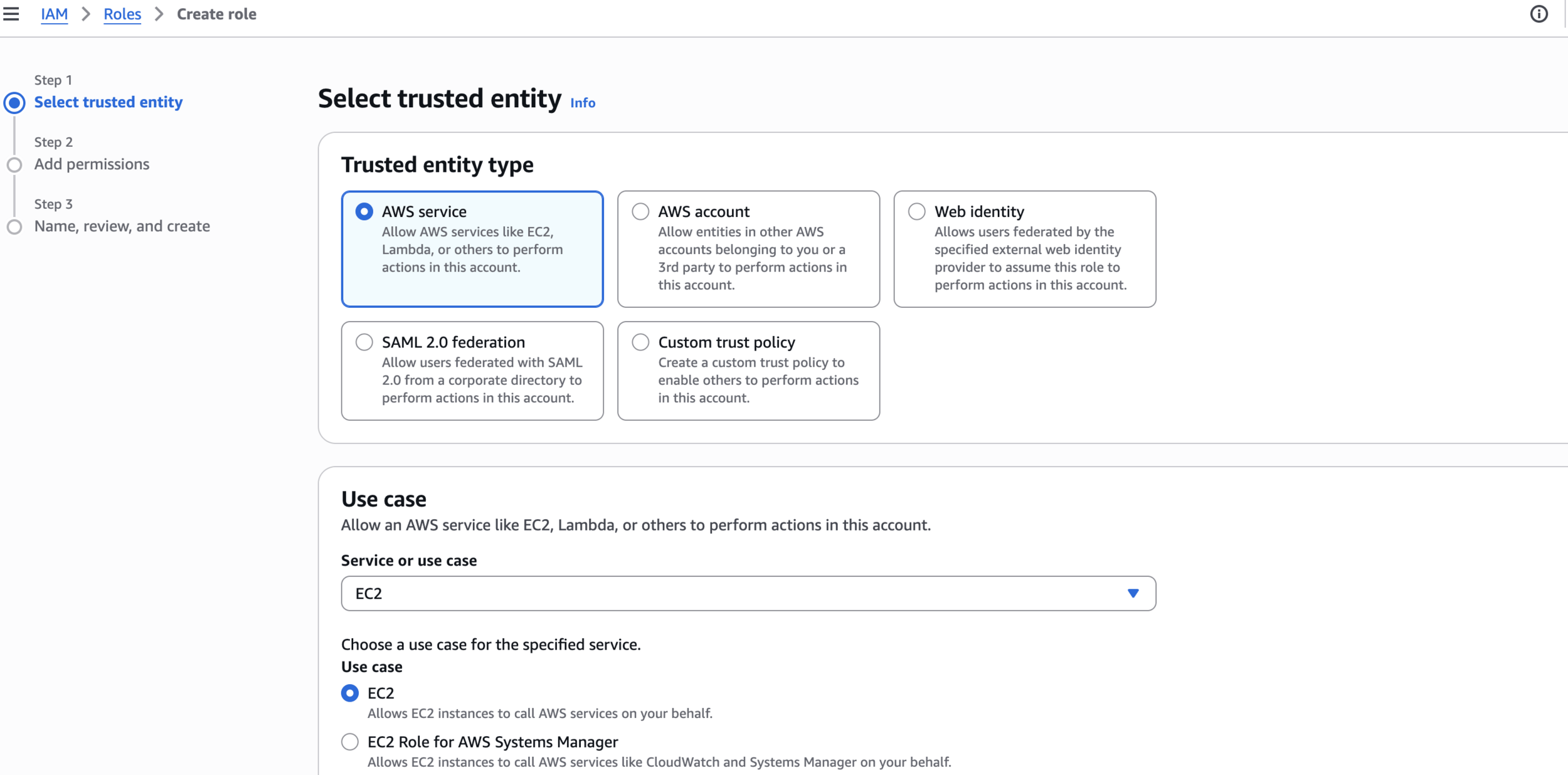
Select trusted entity
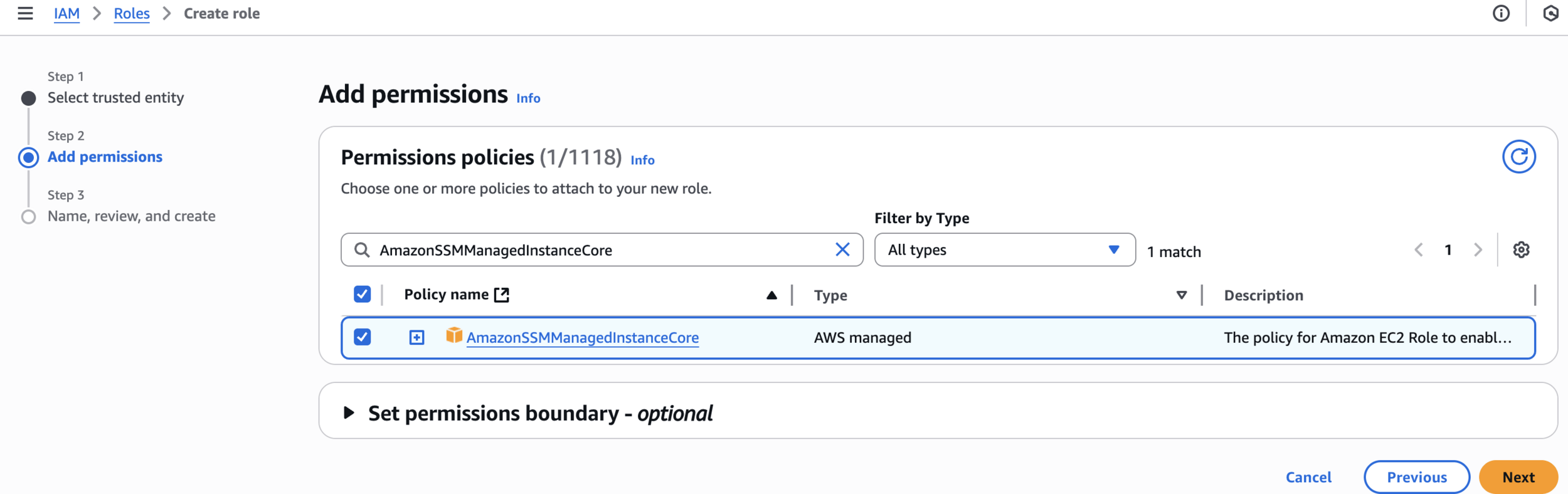
Add permissions

Name, review, and create
SSMInstanceRole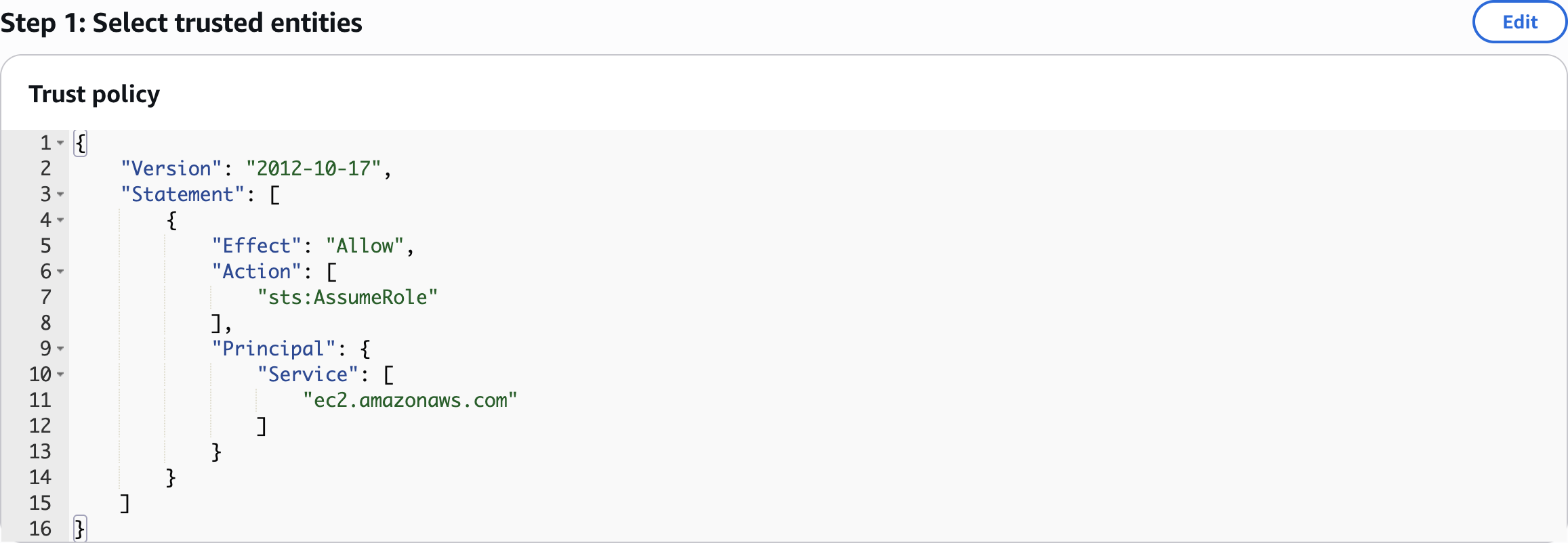
Step 1: Select trusted entities
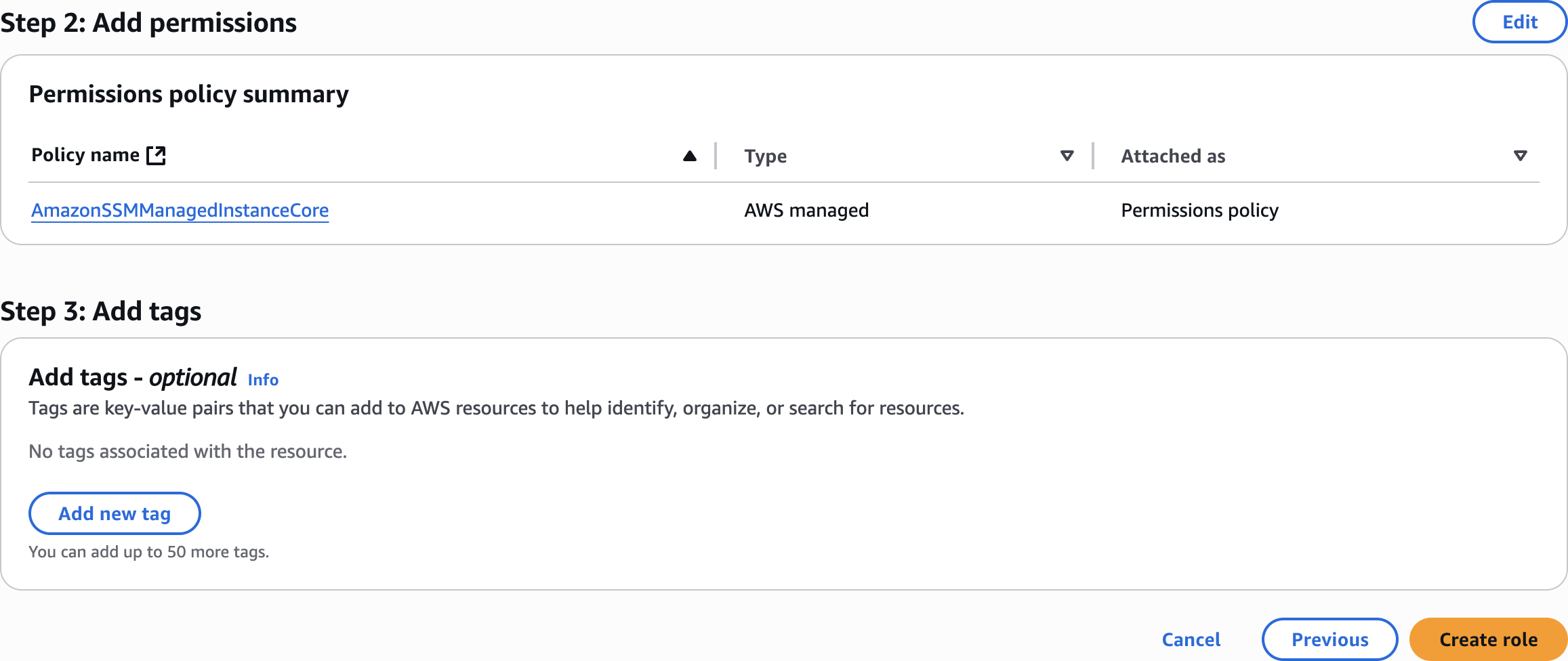
Step 2: Add permissions
Create EC2 Machine
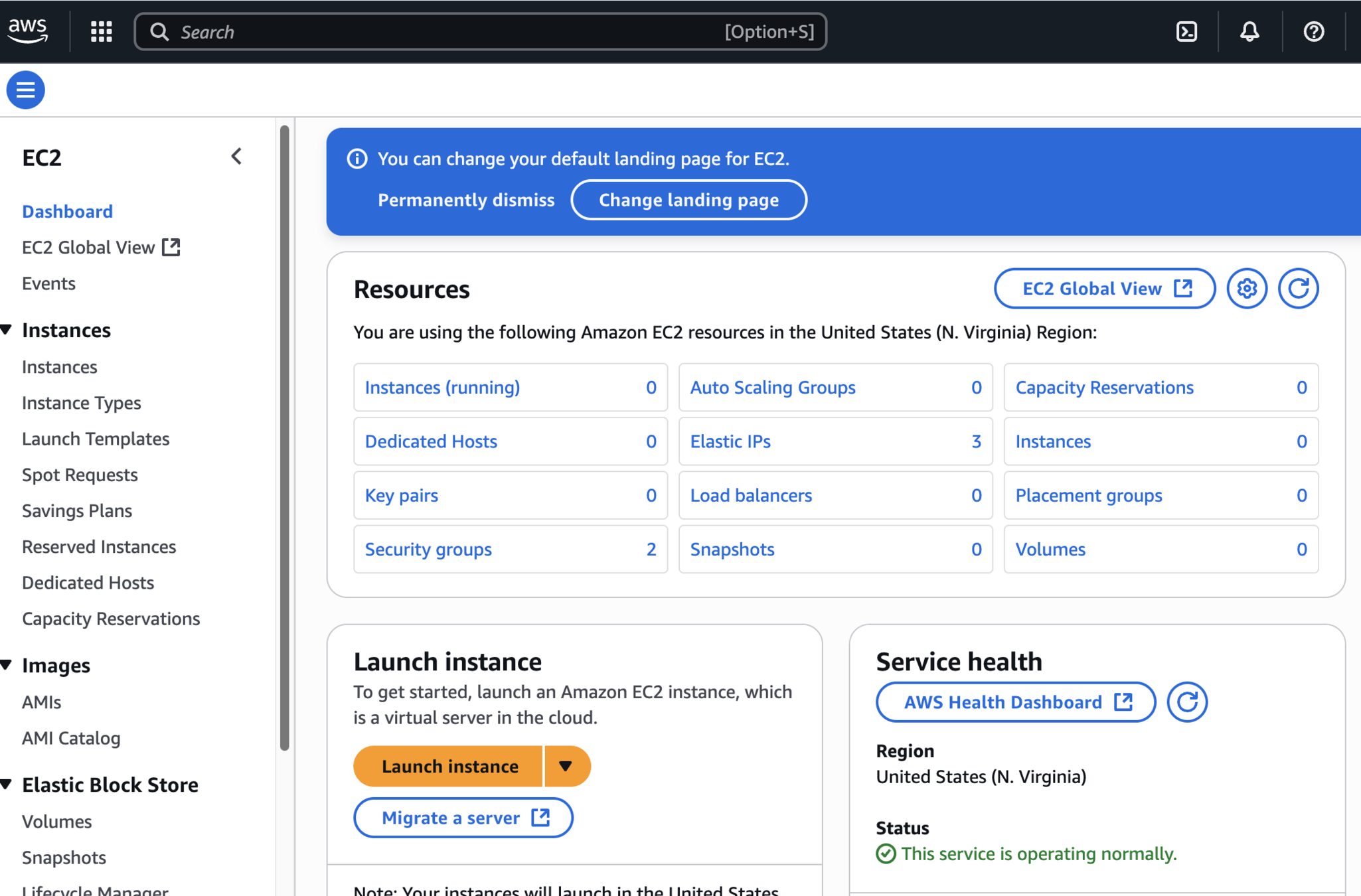
Launch EC2 Instance for Testing
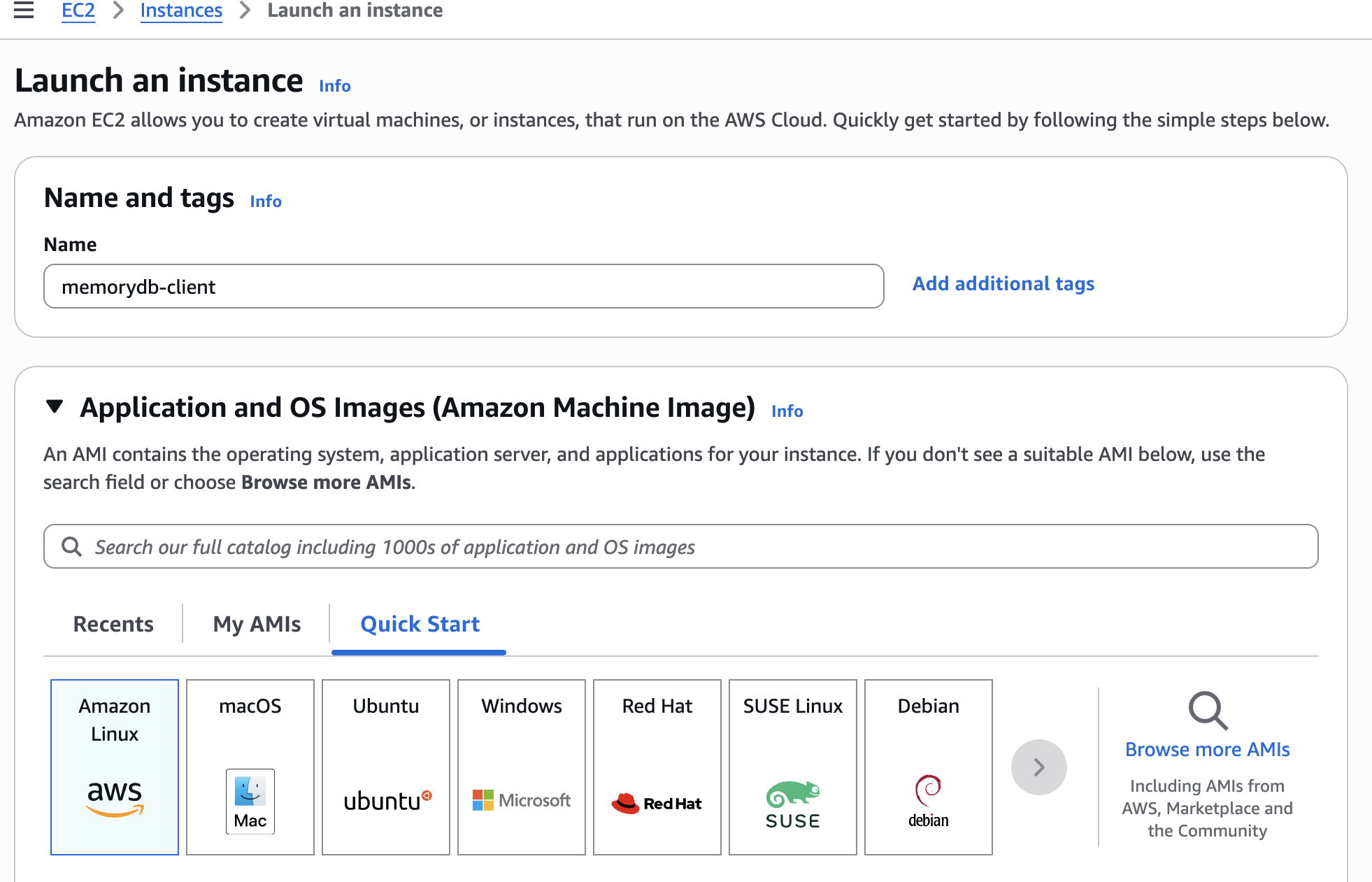
memorydb-client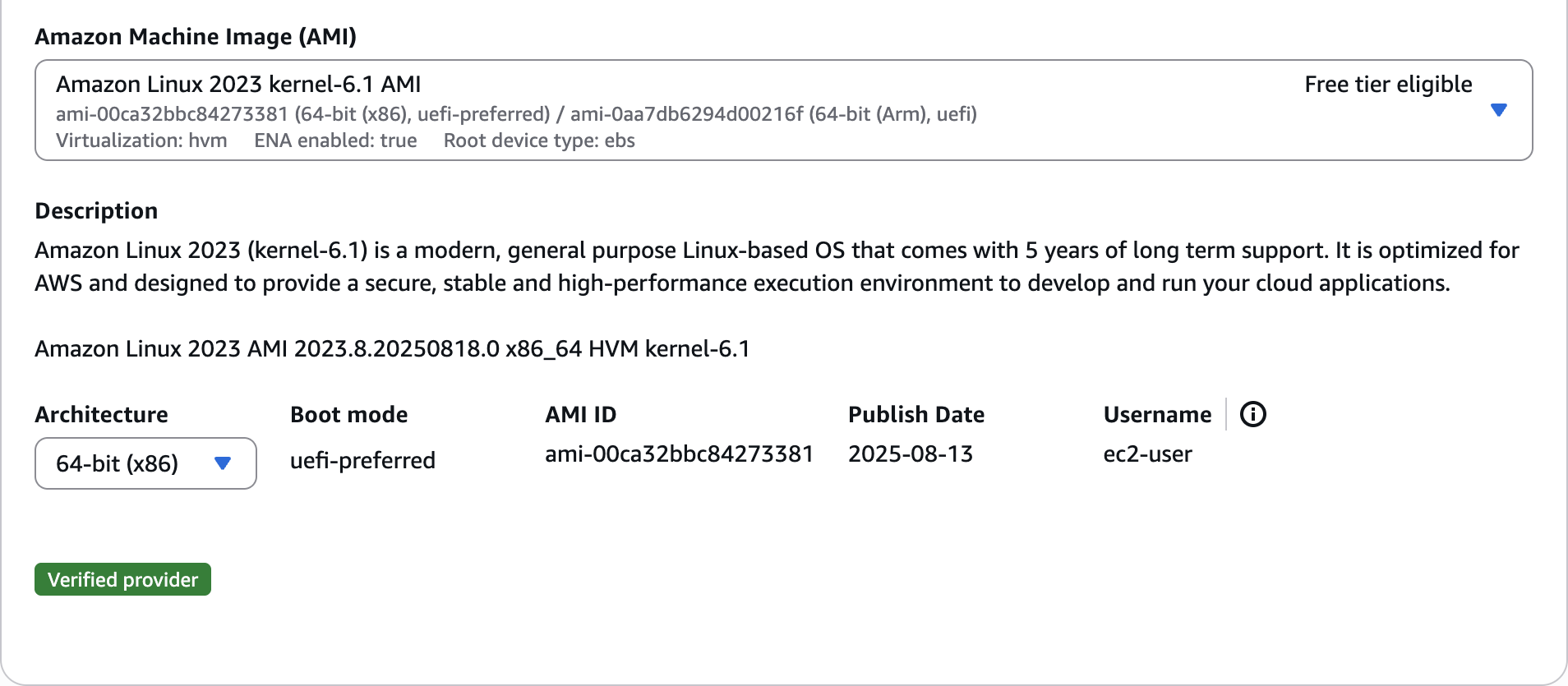
Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
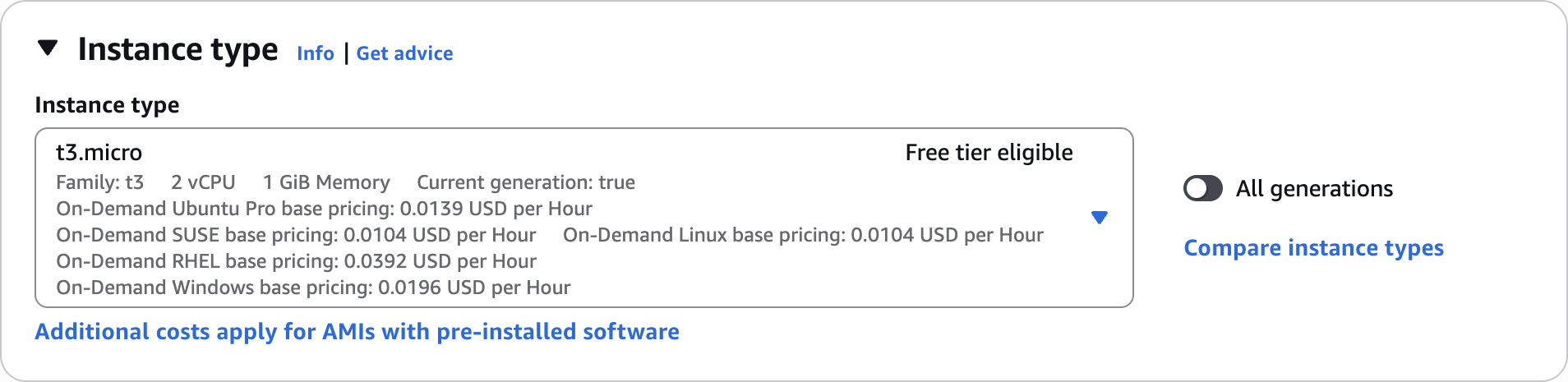
Instance type
Key pair (login)
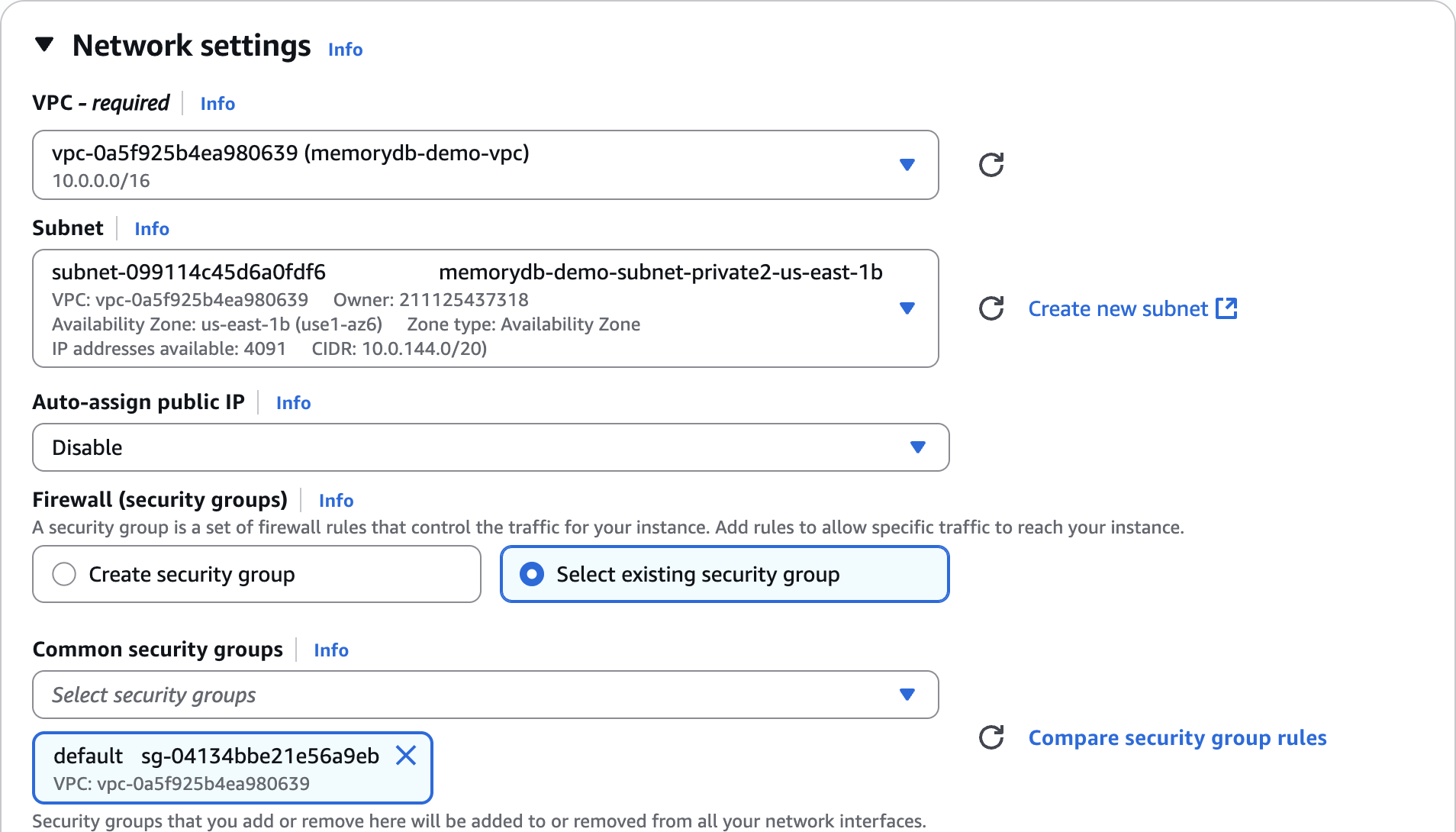
Network settings
Configure storage
IAM instance profile
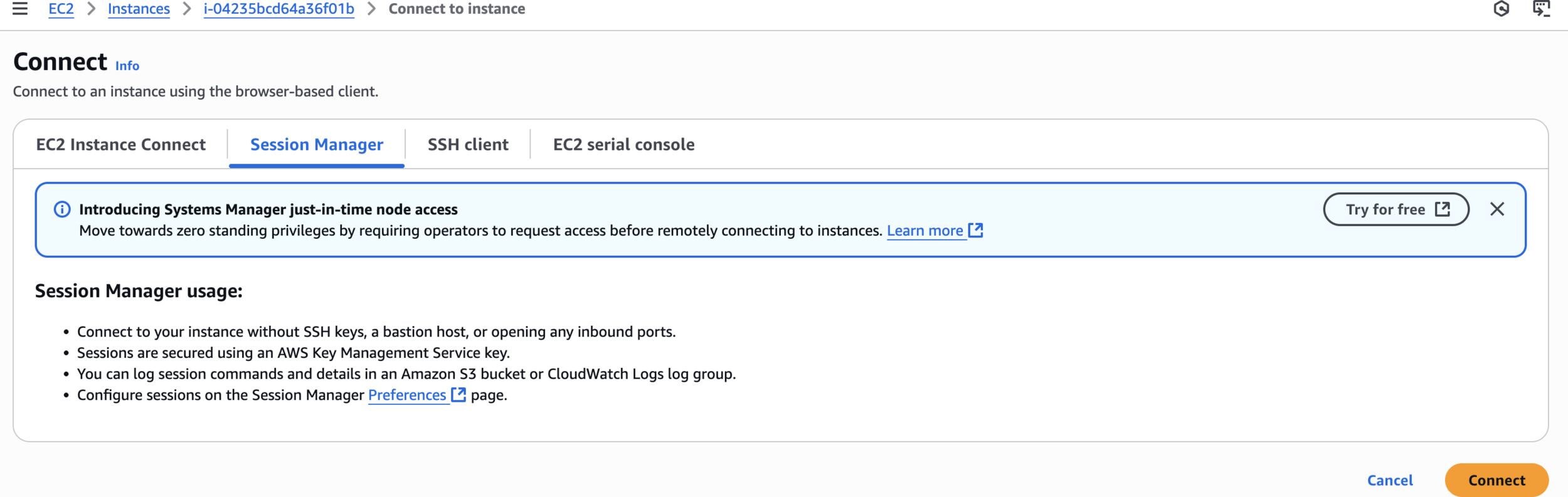
Session Manager
Connect and Test MemoryDB Cluster
# Update package cache
sudo dnf update -y
# Install Redis directly
sudo dnf install -y redis6
# Verify installation
redis6-cli --versionInstall Redis CLI
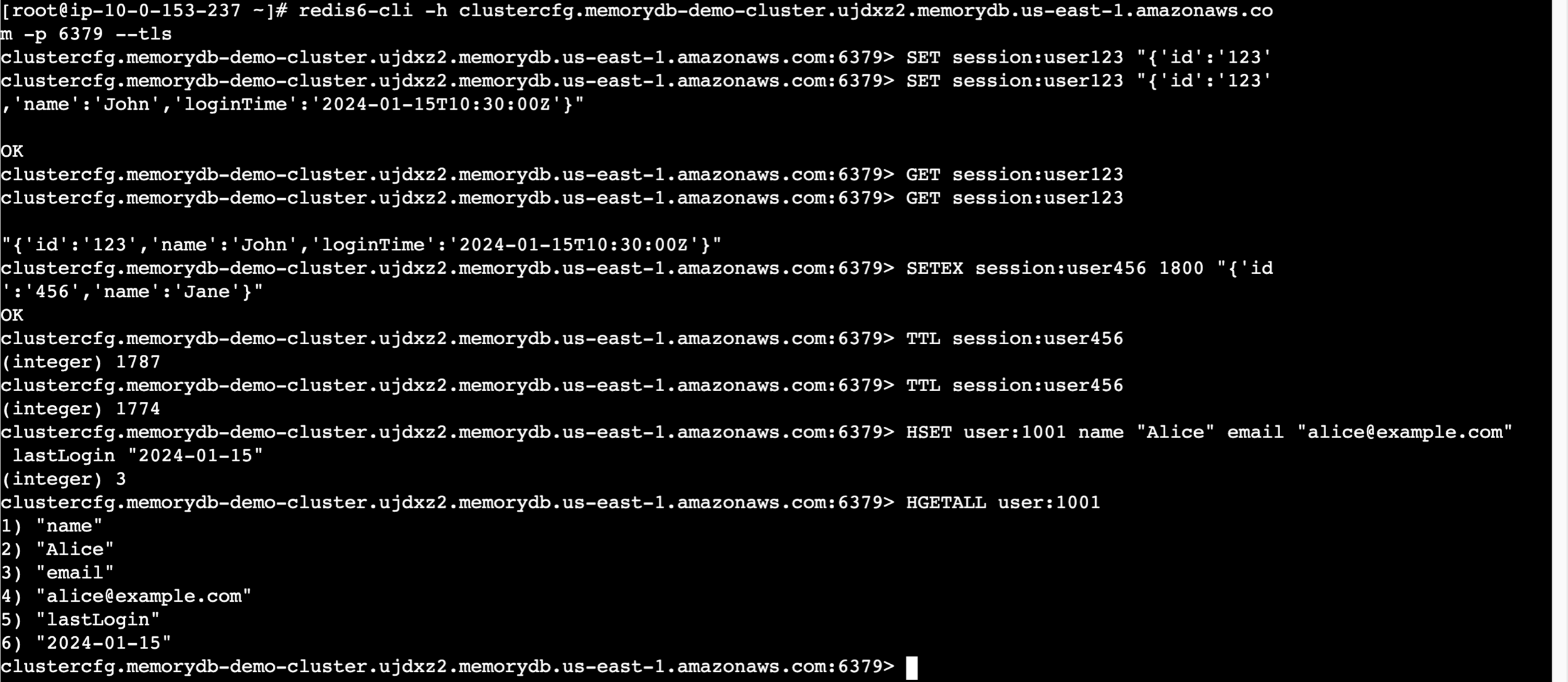
ENDPOINT=redis6-cli -h ${ENDPOINT} -p 6379 --tls# Set a key
SET session:user123 "{'id':'123','name':'John','loginTime':'2024-01-15T10:30:00Z'}"# Get the key
GET session:user123# Set key with expiration (30 minutes)
SETEX session:user456 1800 "{'id':'456','name':'Jane'}"# Check time to live
TTL session:user456Connect to MemoryDB cluster:
Test basic operations:
Creates a key with automatic expiration after 1800 seconds (30 minutes) for session timeout
# Test data structures
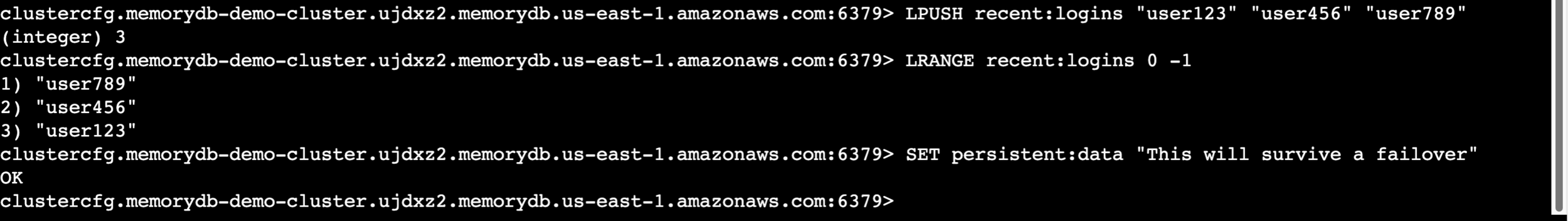
HSET user:1001 name "Alice" email "alice@example.com" lastLogin "2024-01-15"HGETALL user:1001# List operations
LPUSH recent:logins "user123" "user456" "user789"LRANGE recent:logins 0 -1# Test persistence
SET persistent:data "This will survive a failover"Uses Redis hash data structure to store multiple user attributes efficiently
Pushes user IDs to a list to track recent login activity in chronological order
Sets a test key to verify data persistence through cluster failover events
sudo dnf install -y python3 python3-pip
pip3 install redisInstall Python and Redis client
Test Application Integration
cat > test_memorydb.py << EOF
import redis
import json
import sys
from datetime import datetime
# Check for command line argument
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: python3 test_memorydb.py <your-cluster-endpoint>")
print("Example: python3 test_memorydb.py memorydb-demo-cluster.abc123.memorydb.us-east-1.amazonaws.com")
sys.exit(1)
cluster_endpoint = sys.argv[1]
# Configure connection
try:
r = redis.Redis(
host=cluster_endpoint,
port=6379,
ssl=True,
decode_responses=True
)
# Test connection
r.ping()
print(f"✓ Successfully connected to MemoryDB cluster: {cluster_endpoint}")
except redis.ConnectionError as e:
print(f"✗ Failed to connect to {cluster_endpoint}")
print(f"Error: {e}")
print("\nPlease check:")
print(" - Cluster endpoint is correct")
print(" - Security group allows port 6379 from this instance")
print(" - Instance and cluster are in the same VPC")
sys.exit(1)
# Session management example
def create_session(user_id, username):
session_data = {
'user_id': user_id,
'username': username,
'login_time': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
# Store session with 30-minute expiration
r.setex(f'session:{user_id}', 1800, json.dumps(session_data))
print(f"✓ Session created for {username}")
def get_session(user_id):
session = r.get(f'session:{user_id}')
if session:
return json.loads(session)
return None
# Test the functions
print("\n--- Testing Session Management ---")
create_session('user001', 'alice')
session = get_session('user001')
print(f"✓ Retrieved session: {session}")
# Cache example with automatic expiration
print("\n--- Testing Cache with TTL ---")
r.setex('cache:api_response', 300, json.dumps({'data': 'cached response'}))
print(f"✓ Cache created with TTL: {r.ttl('cache:api_response')} seconds")
# Additional tests for data persistence
print("\n--- Testing Data Persistence ---")
r.set('persistent:data', 'This will survive a failover')
print(f"✓ Persistent data stored")
# Test various data structures
print("\n--- Testing Redis Data Structures ---")
# Hash
r.hset('user:1001', mapping={
'name': 'Alice',
'email': 'alice@example.com',
'lastLogin': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
print(f"✓ Hash created: {r.hgetall('user:1001')}")
# List
r.lpush('recent:logins', 'user001', 'user002', 'user003')
print(f"✓ List created: {r.lrange('recent:logins', 0, -1)}")
# Set
r.sadd('active:users', 'alice', 'bob', 'charlie')
print(f"✓ Set created with {r.scard('active:users')} members")
print("\n✓ All tests completed successfully!")
EOF# Replace with your actual MemoryDB cluster endpoint
python3 test_memorydb.py ${ENDPOINT}Run the Python Script

Clean Up
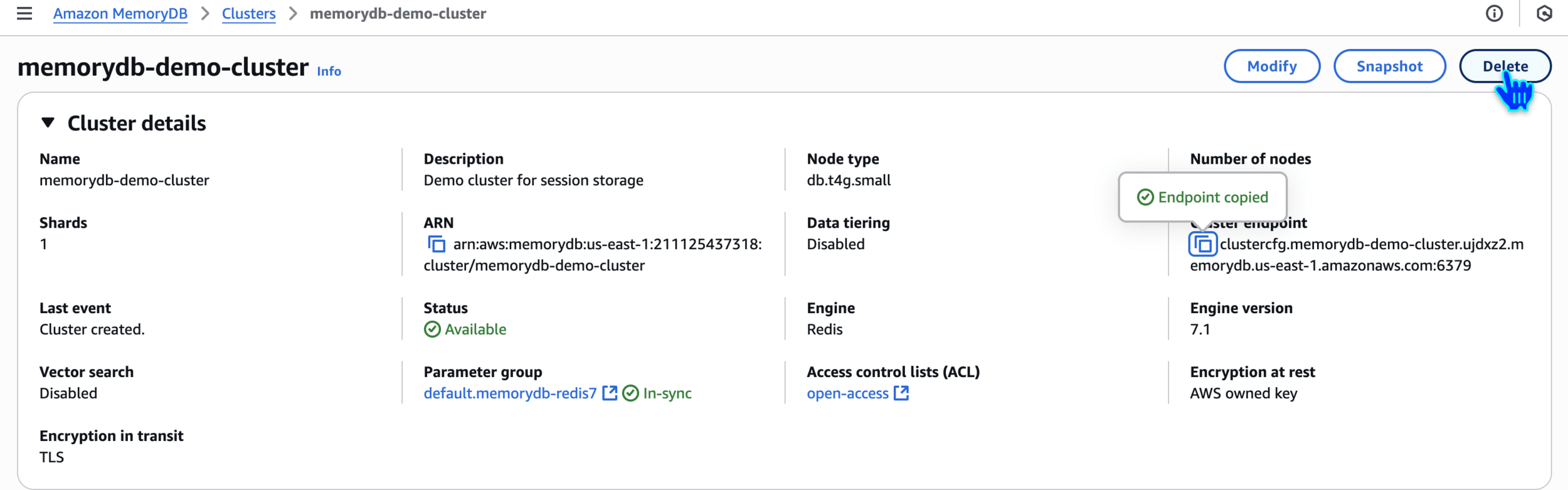
Delete MemoryDB Cluster
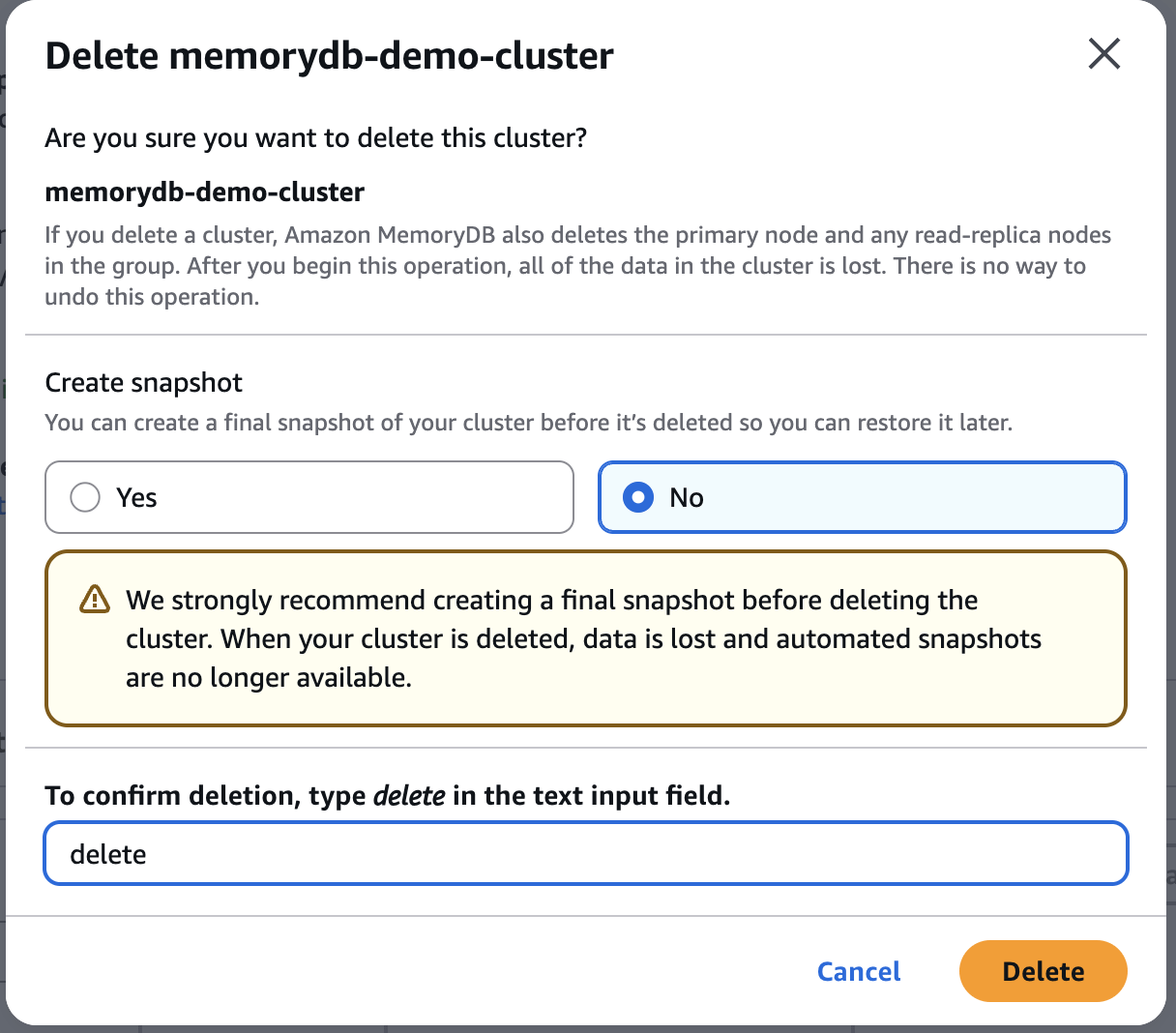
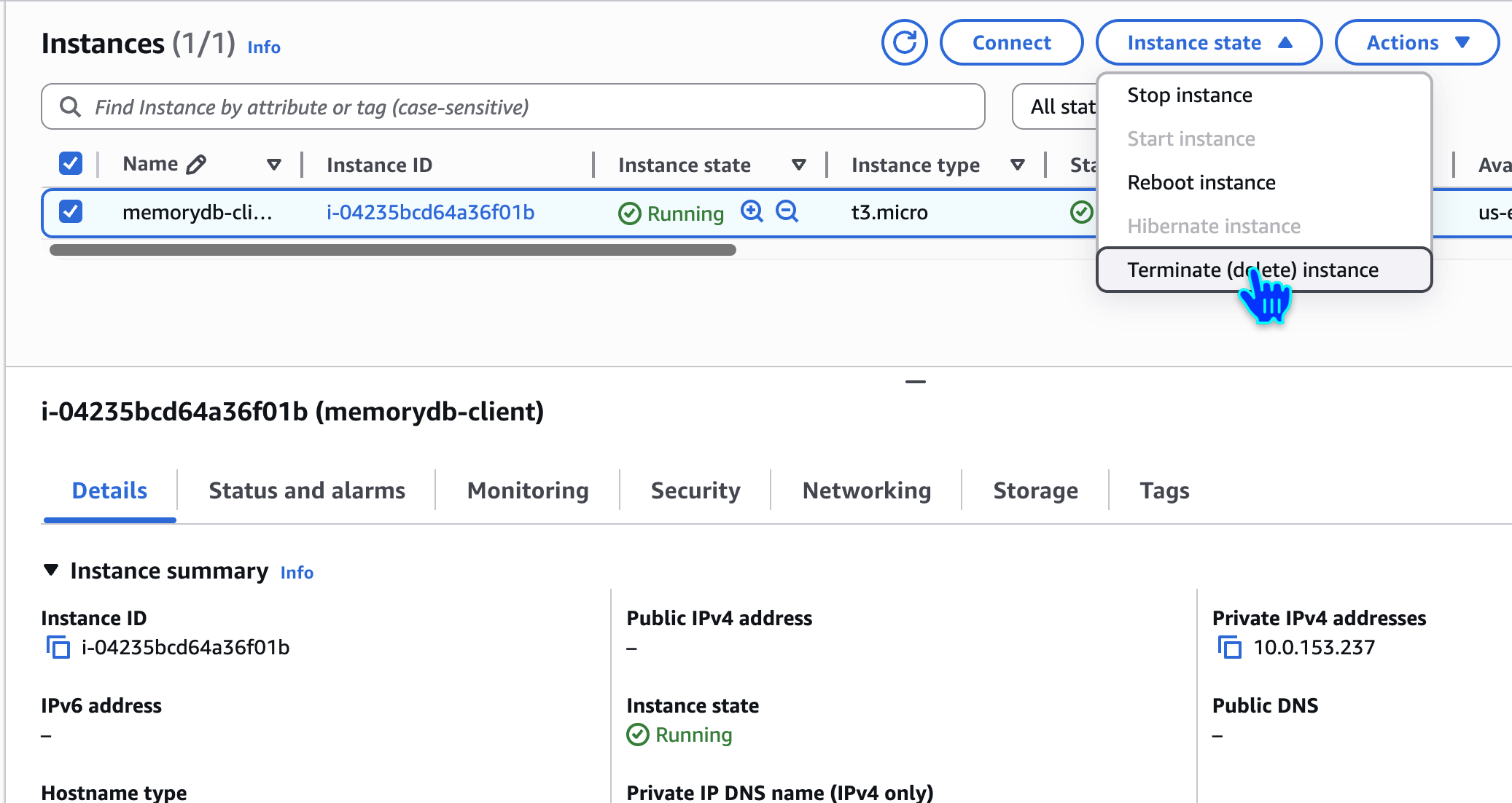
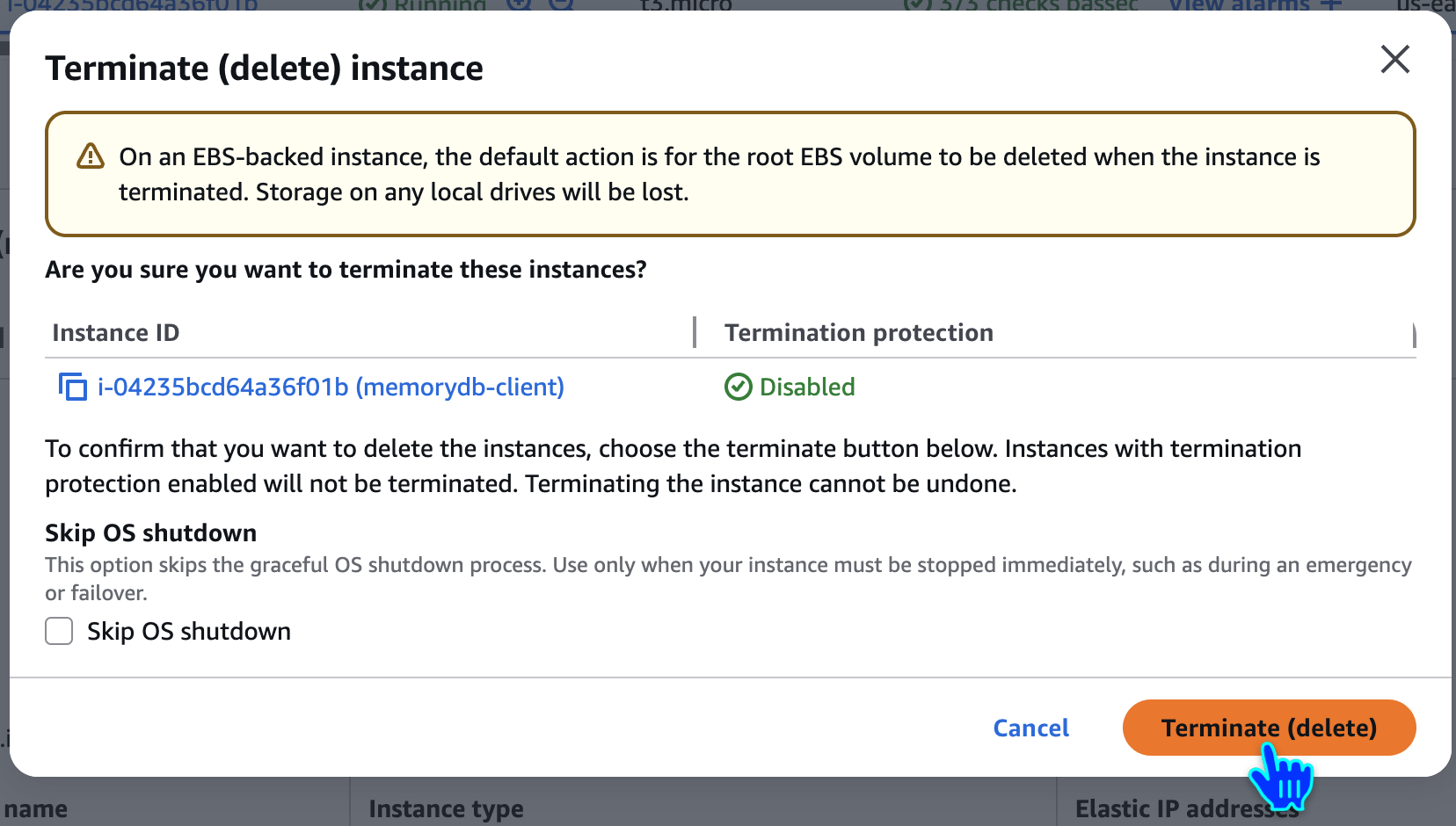
Delete EC2 Instances
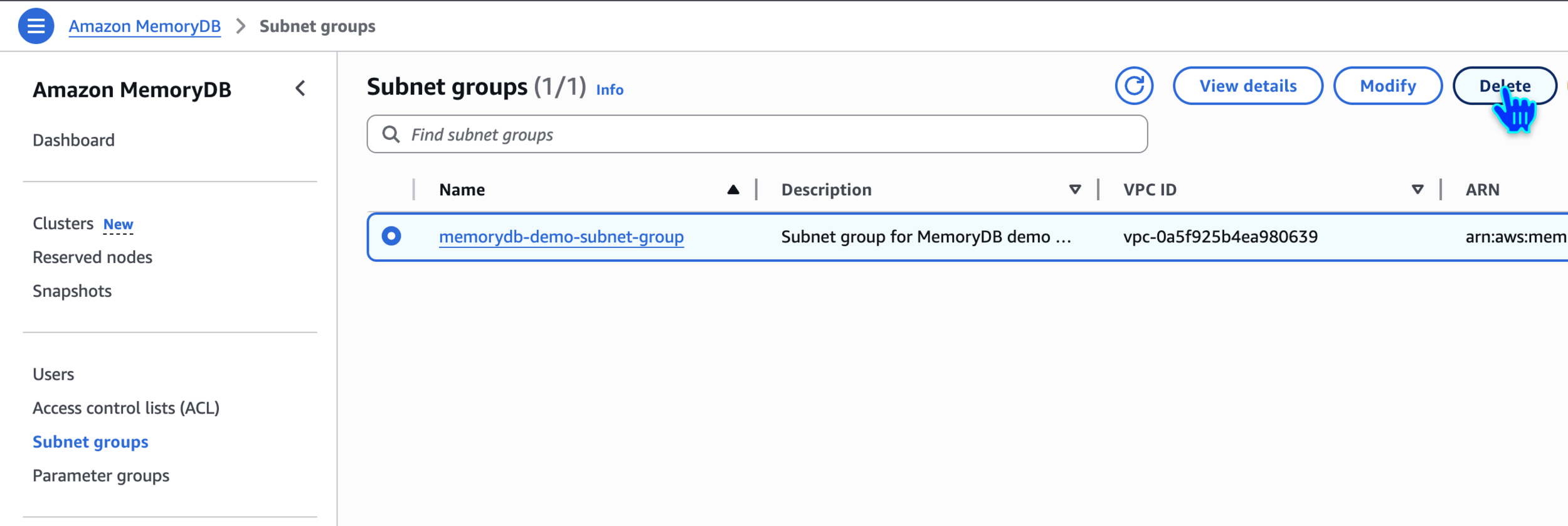
Delete Subnet Group
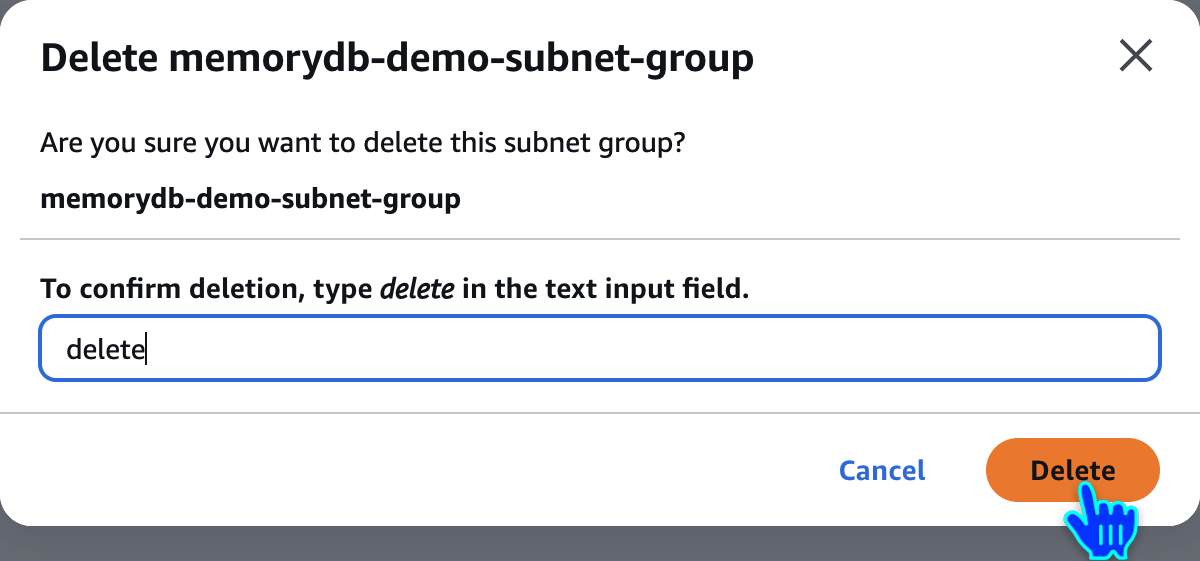
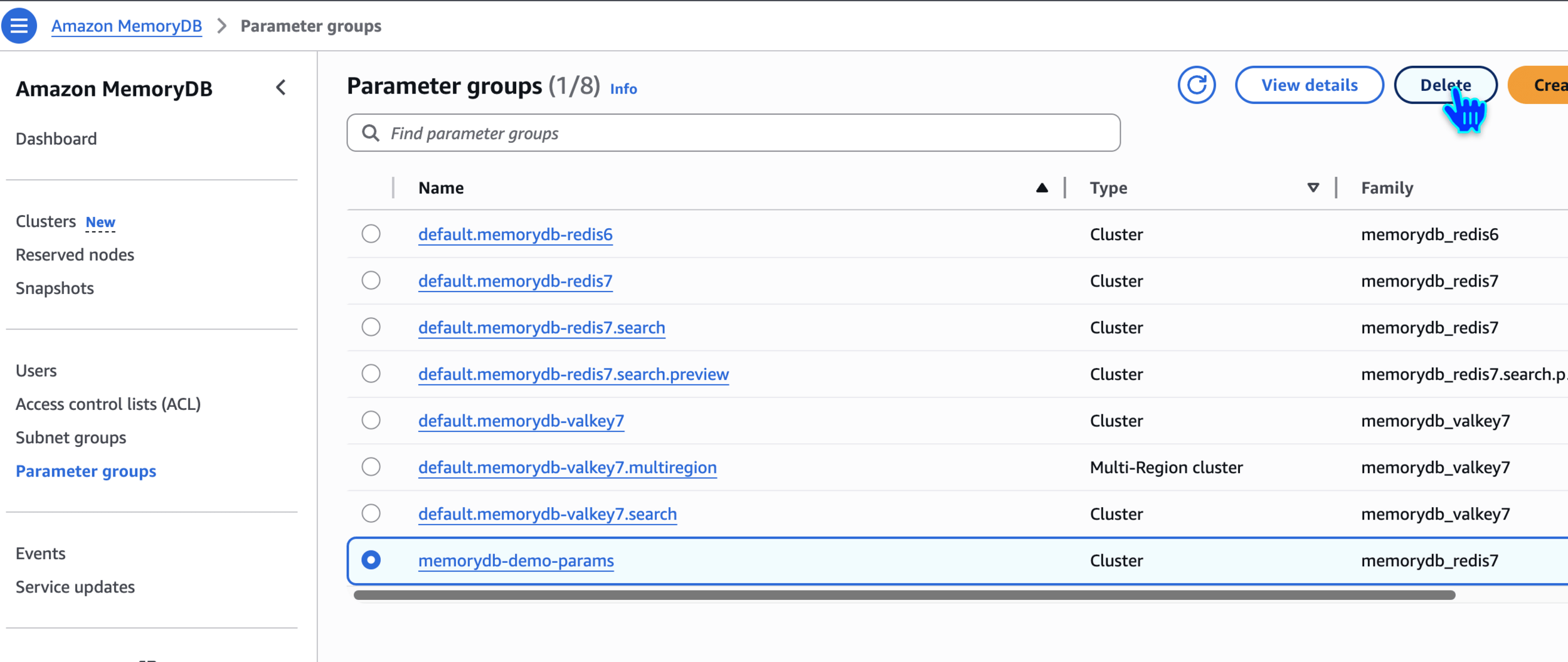
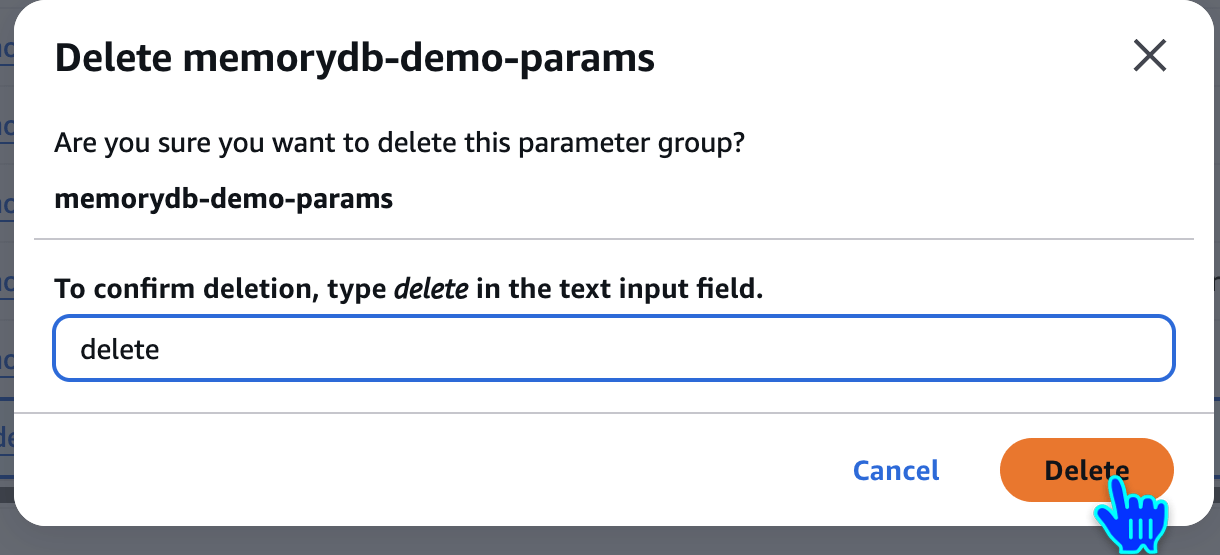
Delete Parameter Group
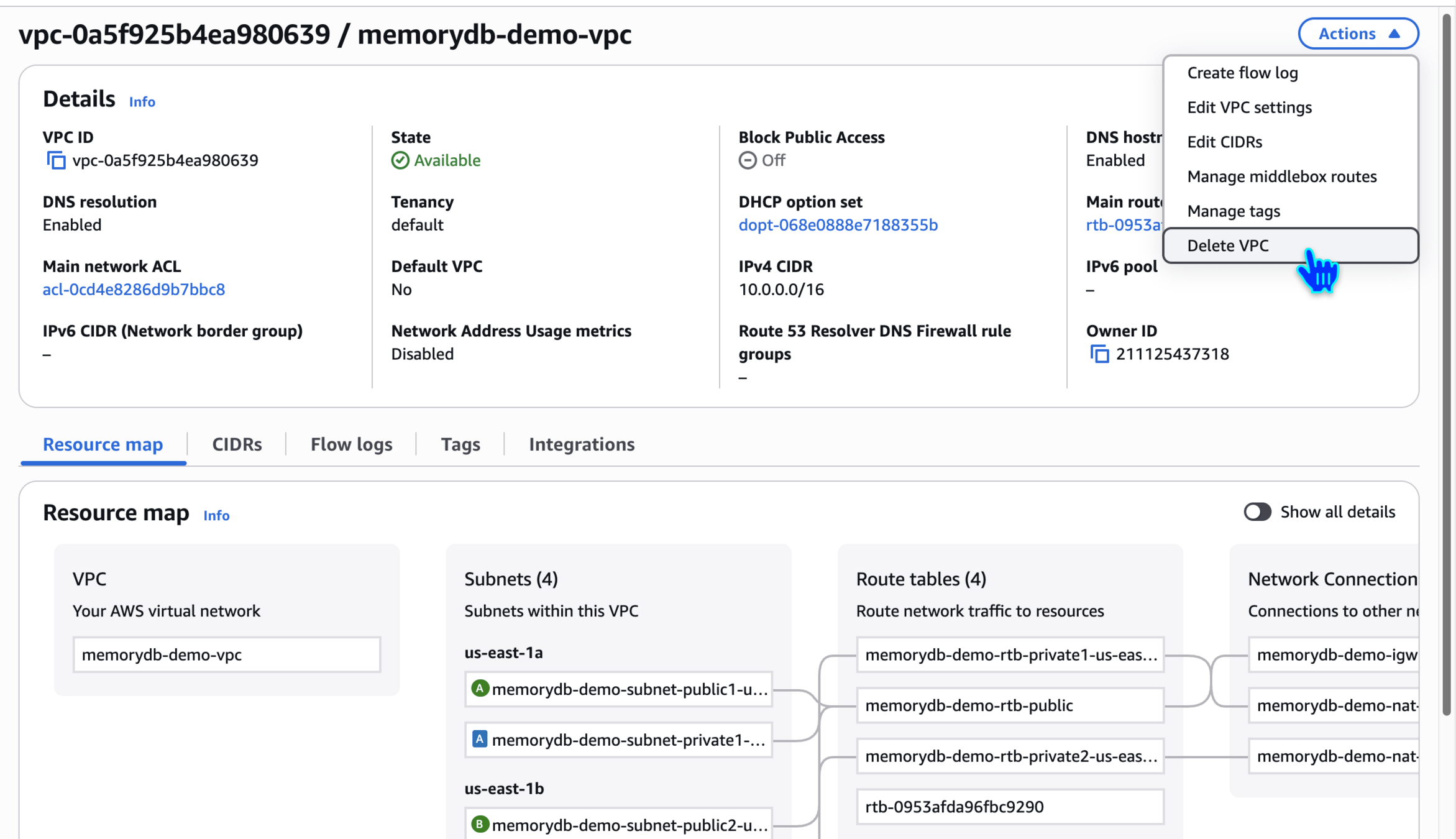
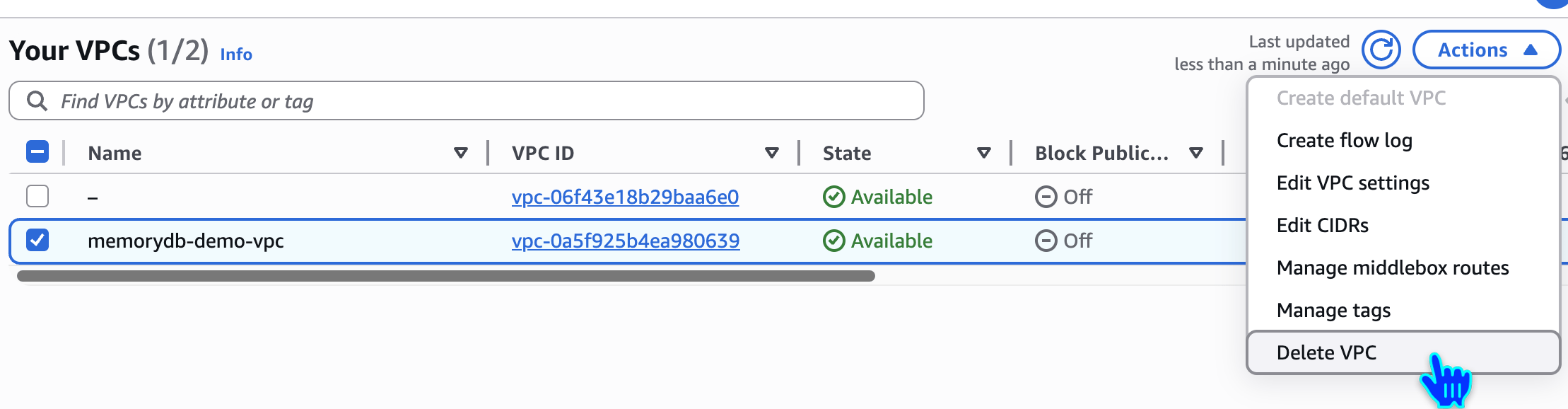
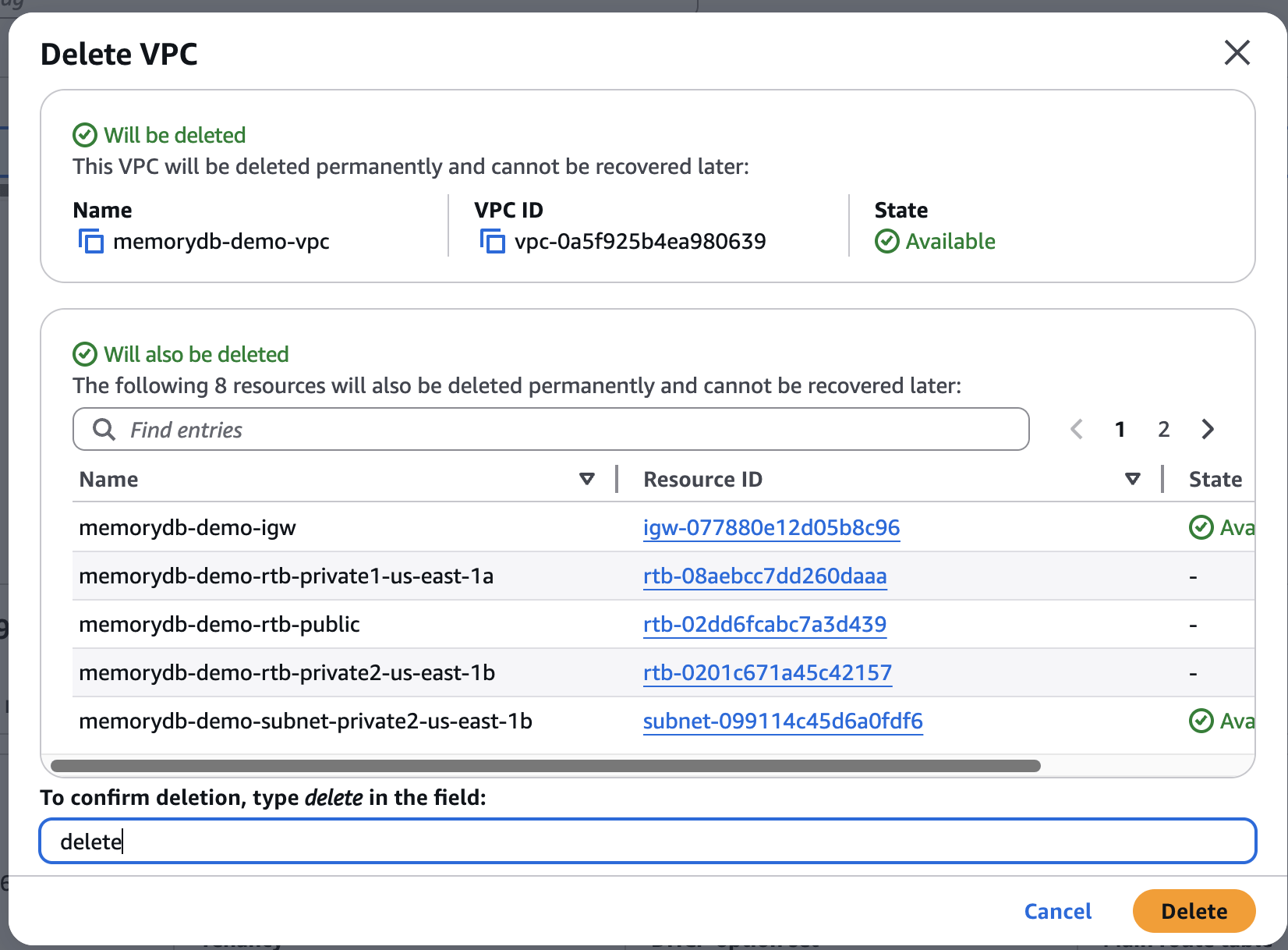
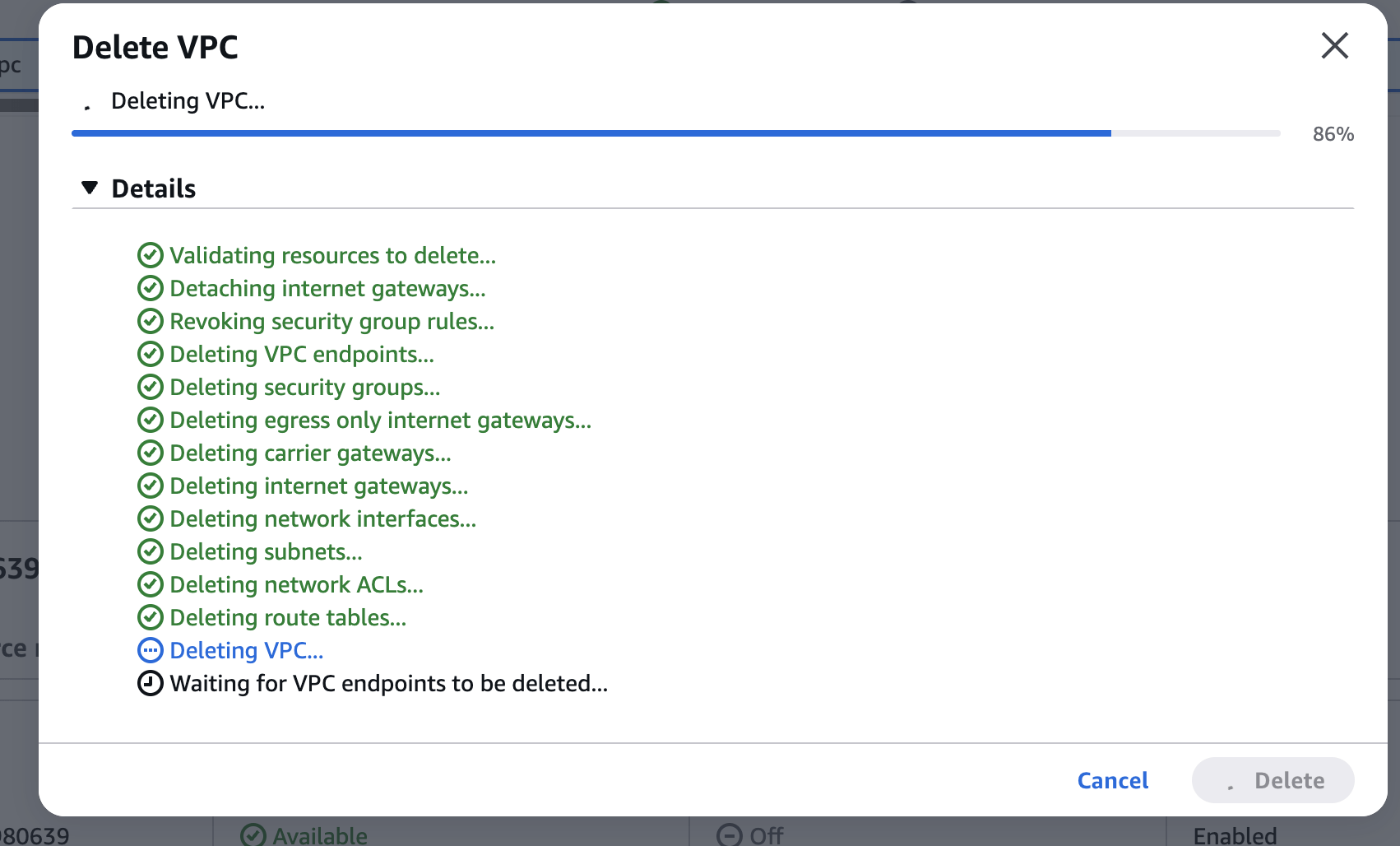
Delete VPC
Delete NAT Gateway
🙏
Thanks
for
Watching
Amazon MemoryDB - Hands-On Demo
By Deepak Dubey
Amazon MemoryDB - Hands-On Demo
Amazon MemoryDB - Hands-On Demo
- 324



