Vue.js 入門介紹
邱俊霖
Vue.js
- 建構畫面的漸進式框架
- 專注在視圖層,簡單易上手
- 方便與第三方函式庫或計有項目整合
- Virtual DOM
Virtual DOM
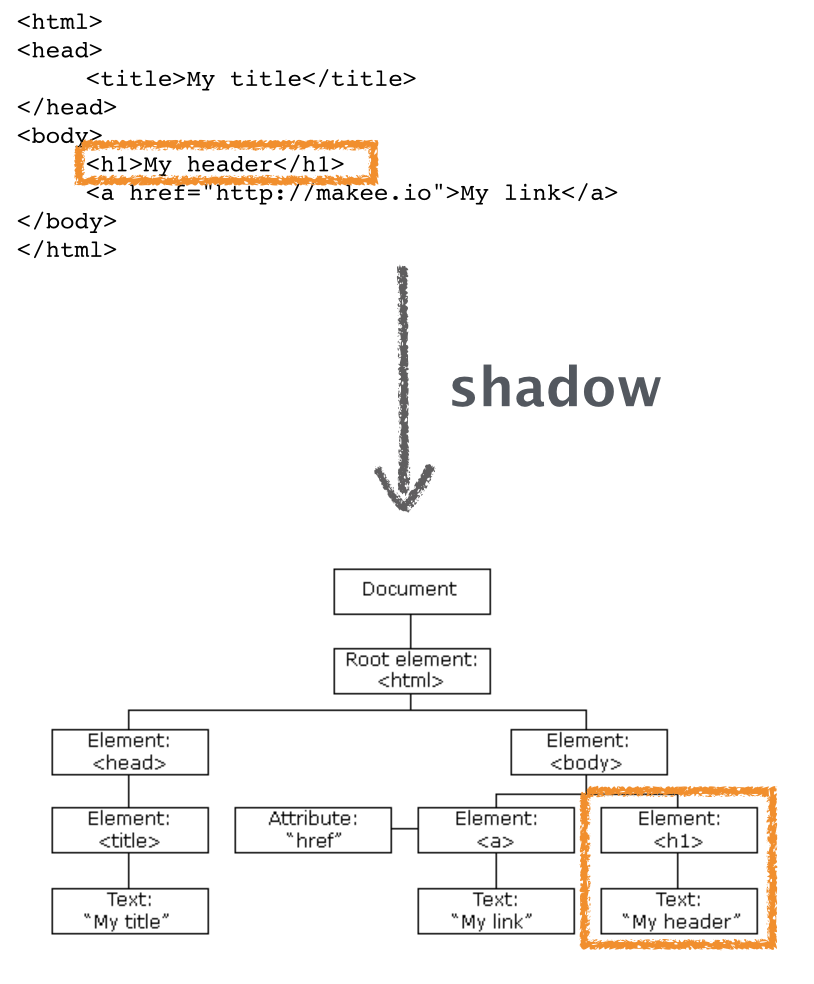
Photo by Jollen Chen
來啊!互相傷害啊!
React.js vs Vue.js
- Virtual DOM
- Reactive and Composable
- Focus in the core library.
- Routing
- Global state management


React.js
The richness of ecosystem
Vue.js
- BootstrapVue ( don't use VueStrap )
- awesome-vue

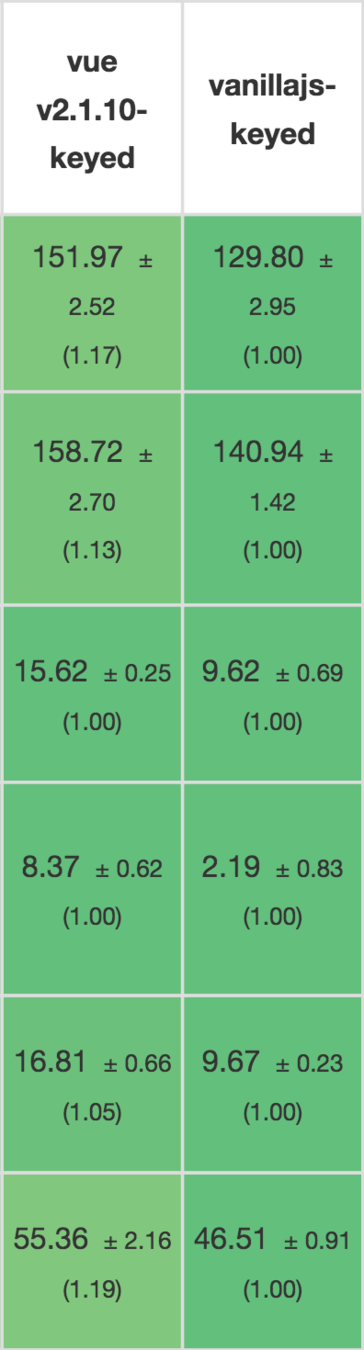
| Vue | React | |
|---|---|---|
| Fastest | 23ms | 63ms |
| Median | 42ms | 81ms |
| Average | 51ms | 94ms |
| 95th Perc. | 73ms | 164ms |
| Slowest | 343ms | 453ms |

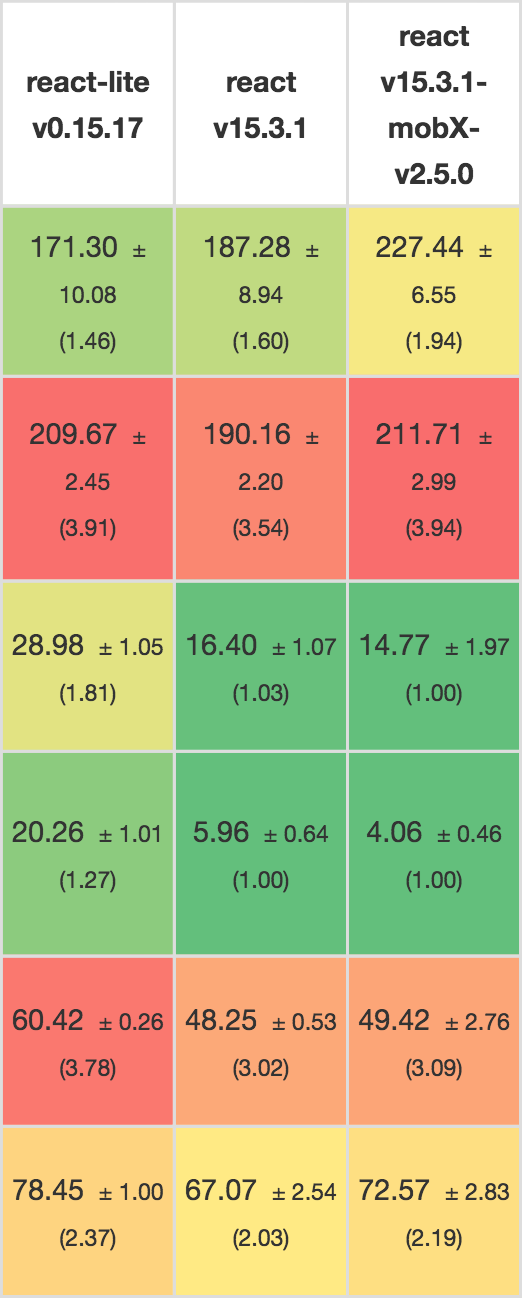
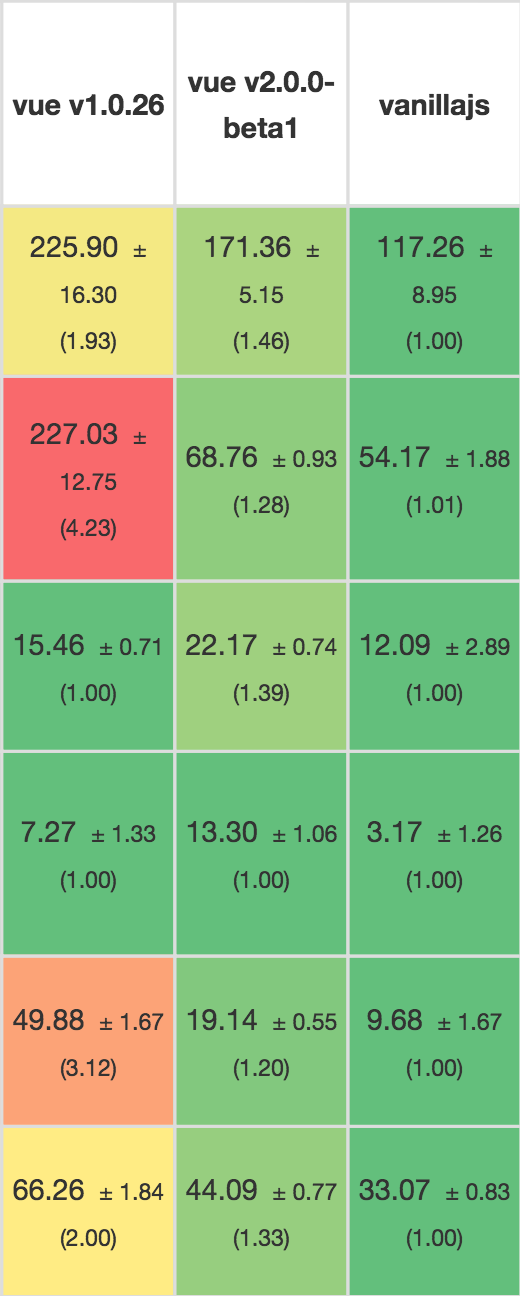
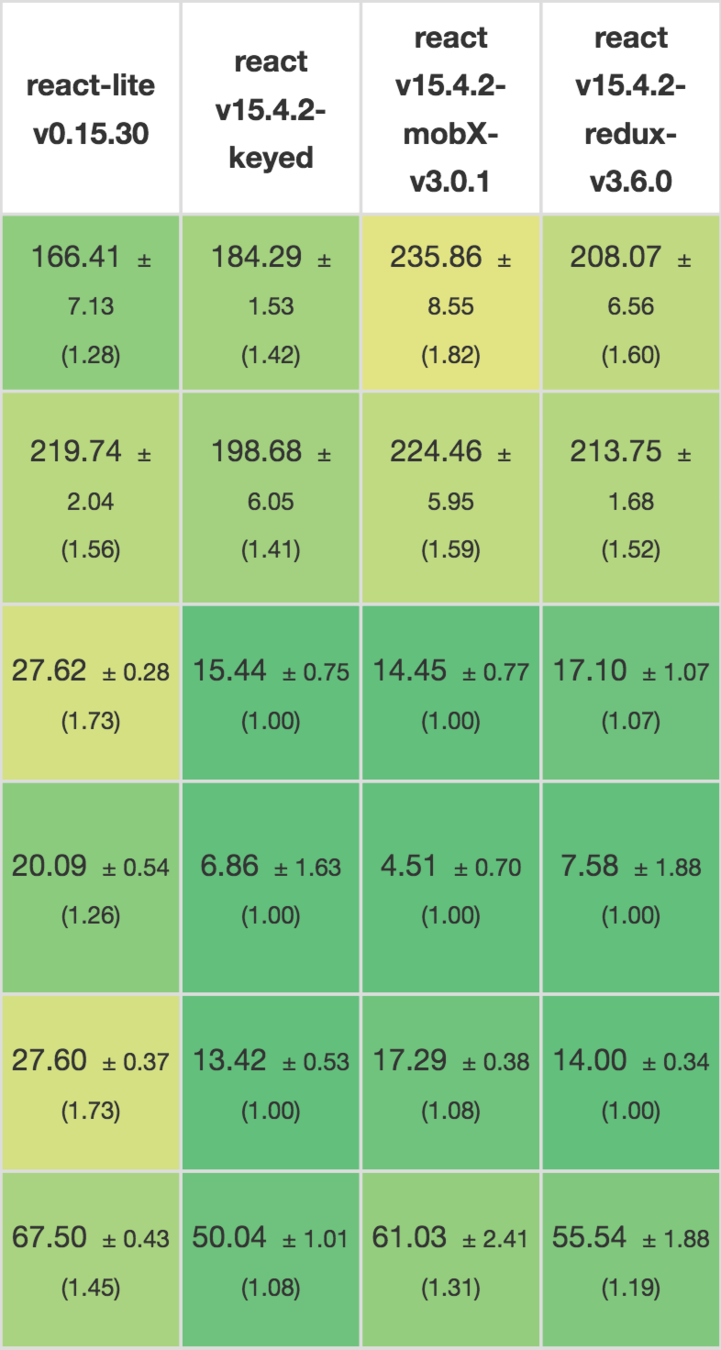
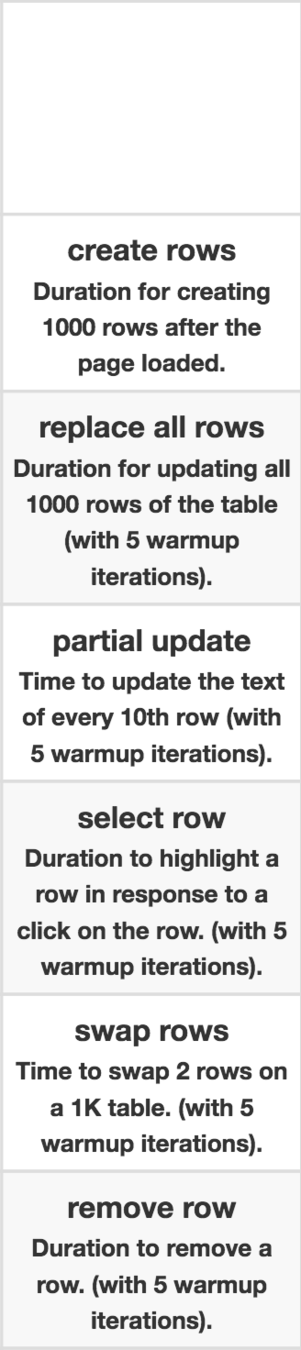
Vanilla JS
Ref.
Who chose Vue.js ?
- GitLab ( Why We Chose Vue.js )
- Laravel 5.3
- Weex
- urAD
終於開始了
其實還沒

MVVM

開始使用 Vue.js
Vue.js 不支援 IE8 及其以下版本,因為 Vue.js 使用了 IE8 不能模擬的 ECMAScript 5 特性。
CDN
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>Vue-cli
npm install vue-cli -g
vue init webpack my-vue-projectSingle file component
基礎使用
聲明式渲染
// HTML
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>// JS
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})
Hello Vue!Constructor
var vm = new Vue({
// options
})需要傳入一個 option object
Options
- el
- data
- methods
- computed
- template
el
- Type: string | HTMLElement
Provide the Vue instance an existing DOM element to mount on.
data
- Type: Object | Function
Vue will recursively convert its properties into getter/setters to make it “reactive”.
Update Data
Update Object
- return new Object
Update Array
- push()
- pop()
- splice()
- shift()
- unshift()
- sort()
- reverse()
methods
- { [key: string]: Function }
All methods will have their this context automatically bound to the Vue instance.
var vm = new Vue({
data : {
a: 1
},
methods : {
plus : function () {
this.a++
}
}
})
vm.plus()
vm.a // 2computed
- { [key: string]: Function | { get: Function, set: Function } }
All getters and setters have their this context automatically bound to the Vue instance.
var vm = new Vue({
data: { a: 1 },
computed: {
// 僅讀取,值只須為函數
aDouble: function () {
return this.a * 2
},
// 讀取和設置
aPlus: {
get: function () {
return this.a + 1
},
set: function (v) {
this.a = v - 1
}
}
}
})
vm.aPlus // -> 2
vm.aPlus = 3
vm.a // -> 2
vm.aDouble // -> 4template
- Type: string
模板將會替換掛載的元素。掛載元素的內容都將被忽略。
// HTML
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</div>
// JS
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
},
template: `
<div>
Hey, {{ message }}
</div>
`
})var vm = new Vue({
data: {
a: 1
},
created: function () {
// `this` points to the vm instance
console.log('a is: ' + this.a)
},
mounted: function() {
console.log('mounted')
}
})
// -> "a is: 1"Instance Lifecycle Hooks

注意事項
- data
- methods
- computed
- etc.
以上都不能使用 arrow function,否則 this 將不是 Vue instance
Directive
- v-bind
- v-if
- v-show
- v-for
- v-on
- v-model
帶有 v- 前綴的特殊屬性
預期值是單一 JavaScript 表達式( v-for 除外 )
v-bind
// HTML
<div id="app-2">
<span v-bind:title="message">
Hover your mouse over me for a few seconds
to see my dynamically bound title!
</span>
</div>
// JS
var app2 = new Vue({
el: '#app-2',
data: {
message: 'You loaded this page on ' + new Date()
}
})v-if
// HTML
<div id="app-3">
<p v-if="seen">Now you see me</p>
</div>// JS
var app3 = new Vue({
el: '#app-3',
data: {
seen: true
}
})v-show
// HTML
<div id="app-3">
<p v-show="seen">Now you see me</p>
</div>// JS
var app3 = new Vue({
el: '#app-3',
data: {
seen: true
}
})v-if vs v-show
- v-if 切換時的性能消耗較大
- v-show 初始渲染消耗較大
v-on
// HTML
<div id="app-5">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="reverseMessage">Reverse Message</button>
</div>// JS
var app5 = new Vue({
el: '#app-5',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue.js!'
},
methods: {
reverseMessage: function () {
this.message = this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})// HTML
<div id="demo">
<button v-on:click="show = !show">
Toggle
</button>
<transition name="fade">
<p v-if="show">hello</p>
</transition>
</div>
// JS
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
show: true
}
})// CSS
.fade-enter-active, .fade-leave-active {
transition: opacity .5s
}
.fade-enter, .fade-leave-active {
opacity: 0
}v-for
// HTML
<div id="app-4">
<ol>
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{{ todo.text }}
</li>
</ol>
</div>// JS
var app4 = new Vue({
el: '#app-4',
data: {
todos: [
{ text: 'Learn JavaScript' },
{ text: 'Learn Vue' },
{ text: 'Build something awesome' }
]
}
})1. Learn JavaScript
2. Learn Vue
3. Build something awesomev-model
// HTML
<div id="app-6">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div>// JS
var app6 = new Vue({
el: '#app-6',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})v-model
// HTML
<input v-model="something">// HTML
<input v-bind:value="something" v-on:input="something = $event.target.value">只是個語法糖衣
Shorthands
v-bind
<!-- full syntax -->
<a v-bind:href="url"></a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<a :href="url"></a>v-on
<!-- full syntax -->
<a v-on:click="doSomething"></a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<a @click="doSomething"></a>Component

Registration
// Define a new component called todo-item
Vue.component('todo-item', {
template: '<li>This is a todo</li>'
})<ol>
<!-- Create an instance of the todo-item component -->
<todo-item></todo-item>
</ol>聲明式 props
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// The todo-item component now accepts a
// "prop", which is like a custom attribute.
// This prop is called todo.
props: ['todo'],
template: '<li>{{ todo.text }}</li>'
})子組件不能夠修改 props
Vue.component('todo-item', {
props: ['todo'],
template: '<li>{{ todo.text }}</li>'
})
var app7 = new Vue({
el: '#app-7',
data: {
groceryList: [
{ text: 'Vegetables' },
{ text: 'Cheese' },
{ text: 'Whatever else humans are supposed to eat' }
]
}
})<div id="app-7">
<ol>
<!-- Now we provide each todo-item with the todo object -->
<!-- it's representing, so that its content can be dynamic -->
<todo-item v-for="item in groceryList" v-bind:todo="item"></todo-item>
</ol>
</div>
1. Vegetables
2. Cheese
3. Whatever else humans are supposed to eatOptions
el- data
- methods
- computed
- template
- props
Component 注意事項
- 不能有 el option
- data 必須是 function type
- data, methods, computed 都不能使用 arrow function,否則 this 將不是 Vue instance
<div id="app">
<app-nav></app-nav>
<app-view>
<app-sidebar></app-sidebar>
<app-content></app-content>
</app-view>
</div>Use Component
Slot
<!-- my-component's template -->
<div>
<h2>我是子組件的標題</h2>
<slot>
只有在沒有要分發的內容時才會顯示。
</slot>
</div><div>
<h1>我是父組件的標題</h1>
<my-component>
<p>這是一些初始內容</p>
<p>這是更多的初始內容</p>
</my-component>
</div><div>
<h1>我是父組件的標題</h1>
<div>
<h2>我是子組件的標題</h2>
<p>這是一些初始內容</p>
<p>這是更多的初始內容</p>
</div>
</div>多個 Slot
<!-- app-layout -->
<div class="container">
<header>
<slot name="header"></slot>
</header>
<main>
<slot></slot>
</main>
<footer>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</footer>
</div><app-layout>
<h1 slot="header">這裡可能是一個頁面標題</h1>
<p>主要內容的一個段落。 </p>
<p>另一個主要段落。 </p>
<p slot="footer">這裡有一些聯繫信息</p>
</app-layout><div class="container">
<header>
<h1>這裡可能是一個頁面標題</h1>
</header>
<main>
<p>主要內容的一個段落。 </p>
<p>另一個主要段落。 </p>
</main>
<footer>
<p>這裡有一些聯繫信息</p>
</footer>
</div>- 只能有一個匿名 slot
- 其他必須是具名 slot
Custom Events
- Listen to an event using $on(eventName)
- Trigger an event using $emit(eventName)
Custom Events
<div id="counter-event-example">
<p>{{ total }}</p>
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
</div>Vue.component('button-counter', {
template: '<button v-on:click="increment">{{ counter }}</button>',
data: function () {
return {
counter: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment: function () {
this.counter += 1
this.$emit('increment')
}
},
})
new Vue({
el: '#counter-event-example',
data: {
total: 0
},
methods: {
incrementTotal: function () {
this.total += 1
}
}
})使用自定義事件的表單輸入組件
<input v-model="something">
<input v-bind:value="something" v-on:input="something = $event.target.value">
// in component
<custom-input v-bind:value="something" v-on:input="something = arguments[0]"></custom-input>在組件中觸發父組件的 v-model
- 接受一個 value 屬性
- 在有新的 value 時觸發 input 事件
<currency-input v-model="price"></currency-input>Vue.component('currency-input', {
template: `
<span>
<input
v-bind:value="value"
v-on:input="updateValue($event.target.value)"
/>
</span>
`,
props: ['value'],
methods: {
// 不能直接更新值,而是使用此方法來對輸入值進行觸發 input event
updateValue: function (value) {
this.$emit('input', value);
}
}
})組件命名約定
<!-- 在HTML模版中始終使用kebab-case -->
<kebab-cased-component></kebab-cased-component>
<camel-cased-component></camel-cased-component>
<title-cased-component></title-cased-component>當註冊組件(或者 props )時,可以使用kebab-case ,camelCase ,TitleCase。
// 在組件定義中
components: {
// 使用kebab-case 形式註冊
'kebab-cased-component' : { /* ... */ },
// register using camelCase
'camelCasedComponent': { /* ... */ },
// register using TitleCase
'TitleCasedComponent': { /* ... */ }
}在 HTML 模版中,請使用 kebab-case 形式:
Local Registration
var Child = {
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
}
new Vue({
// ...
components: {
// <my-component> will only be available in parent's template
'my-component': Child
}
})有時間再講系列
Vue-router
Vuex
Vue.js 入門介紹
By 邱俊霖
Vue.js 入門介紹
- 491



