INFORMATIK I
Übung 11 : Liste, Stack und Queue
14. Mai 2014
Daniel Hentzen
dhentzen@student.ethz.ch

Übung 10 : Klassen
Rationale Zahlen
Binomialkoeffizient
Operatoren
Theorie
- Listen
- Queues
- Stacks
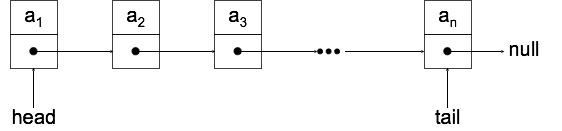
Linked Lists
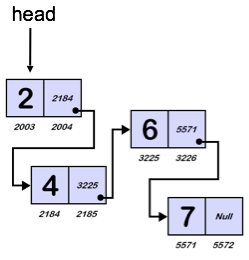
- Ansammlung von Knoten
- Zwei Komponenten pro Knoten :
- ein Wert
- eine Adresse (Pointer) zum nächsten Knoten
- Erster Knoten hat einen head pointer
- Letzter Knoten ohne pointer
- Implementierung als struct :
struct nodeType{
int data;
nodeType *next;
};
nodeType *head;Liste erstellen (backwards)
//Liste initialisieren
nodeType *head;
nodeType *newNode;
int num;
head = NULL;
// Liste erstellen (backwards)
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << "Enter number : ";
cin >> num;
newNode = new nodeType; //Pointer auf neuen Node
newNode->data = num;
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}Linked Lists Operationen
Liste durchlaufen
nodeType *current;
current = head; //Start
while (current != NULL)
{
cout << current->data << " ";
current = current->next; //nächster Knoten
}Element finden
nodeType *current;
current = head; //Start
int element = 12;
while (current != NULL)
{
if (current->data == element)
break;
current = current->next; //nächster Knoten
}
//Resultat : current zeigt auf gefundenes ElementNeuen Knoten einsetzen
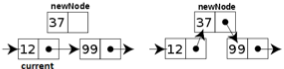
//neuer Knoten :
nodeType *newNode;
newNode = new nodeType;
newNode->data = 37;
//Einsetzen :
newNode->next = current->next;
current->next = newNode;Knoten löschen
nodeType *deleteNode;
deleteNode = current->next;
current->next = deleteNode->next;
delete deleteNode;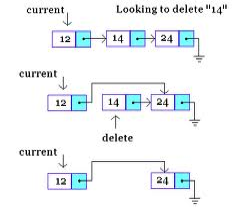
Doubly linked Lists
- Jeder Knoten hat 2 pointers
- next
- previous
- --> Liste kann rückwärts durchlaufen werden
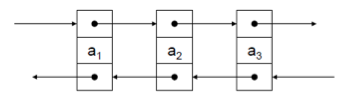
struct nodeType {
int data;
nodeType *next;
nodeType *prev;
};
nodeType *head;Queues
- neue Elemente am Ende einfügen
- Elemente am Anfang löschen
struct Node { int value; struct element *next; };Node *head = NULL; //pointer auf 1. Element Node *tail = NULL; //pointer auf letztes Element
Element hinzufügen (am Ende)

Node *v = new Node;
tail->next = v;
tail = v;
v->next = NULL;Element löschen (am Anfang)
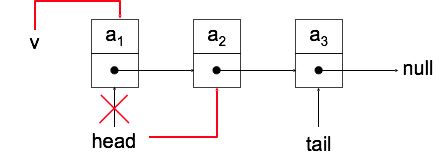
Node *v = head;
head = head->next;
delete v;Stacks
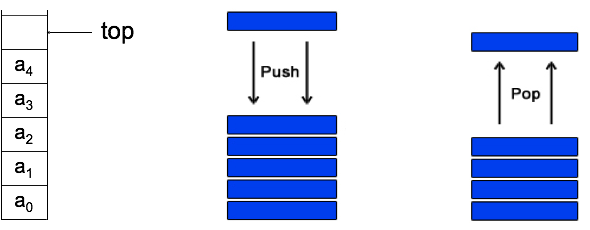
- "one-sided queues"
- von oben hinzufügen : push
- von oben löschen : pop
Element hinzufügen : push
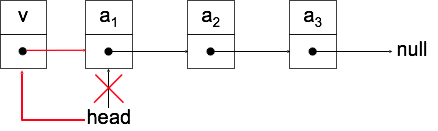
Node *v = new Node;
v->next = head;
head = v;
Element löschen : pop
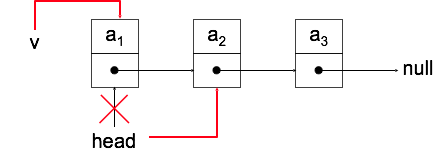
Node *v = head;
head = head->next;
delete v;Stacks vs Queues
Queues:
Work in FIFO (first-in-first-out) fashion
Store two pointers
Add/removal using different pointers
Operating systems: Jobs wait in a queue for CPU time
Printers: Incoming jobs end up in a queue
Stacks:
Work in LIFO (last-in-first-out) fashion
Store only one pointer
Add/removal from top only
Evaluating Arithmetic Operations
Function calls: They are put in a stack by the compiler
Aufgabe 1 : Liste
Aufgabe 2 : Stack
//"stack.h"
struct Node
{
int value;
Node *next;
};
class Stack
{
public:
Stack();
~Stack();
void push(int value);
int pop();
private:
Node *m_stack;
}
Aufgabe 3 : Queue
Übung 11 : Liste, Stack und Queue
By Daniel Hentzen
Übung 11 : Liste, Stack und Queue
- 834



