Phylogenomic and population genomic insights on the evolutionary history of Coffee Leaf Rust within the rust fungi
Diogo Nuno Proença Rico Silva


Doctoral dissertation
Advisors:
Dr . Dora Batista
Prof. Dr. Octávio S. Paulo
a
Introduction
Chapter I
Emerging fungal diseases | on the rise

Fungi responsible for ~30% of emerging diseases in plants
The threat has been heightened by:
- Resource rich agricultural practices
- Globalization
Genomics to the rescue!
Better understand the evolutionary history and potential of pathogen populations
Include eco-evolutionary principles in disease control measures
- Climate change
Fisher et al. 2012
The rust fungi

Stem rust
Puccinia graminis

Poplar rust
Melampsora spp.

Wheat leaf rust
Puccinia triticina

Soybean rust
Phakopsora spp.
Faba bean rust
Uromyces viciae-fabae
Coffee leaf rust
Hemileia vastatrix

Top 3

Top 3

Top 10

Phylogenomics
Population genomics
-
Studies evolutionary patterns above the species level
-
Provides insights on how taxonomic groups evolved
-
Data usually consists of DNA or protein sequences from unrelated taxa
-
Studies evolutionary patterns below the species level
-
Unravels the evolutionary history of populations within a species
-
Data usually consists of DNA sequences or SNPs from closely related taxa
How can it contribute:
How can it contribute:
Macro-evolutionary patterns of genetic diversity that correlate with functional innovations
Mechanisms of adaptation and population divergence in pathogens
Objectives
Chapter II: Phylogenomics
Chapter III: Population genomics
Chapter IV: Software development
- Evaluate the role of positive selection on the evolutionary origin of the rust fungi using complete genomes and EST data
- Investigate the evolutionary history and potential of the rust pathogen, Hemileia vastrix, using RAD sequencing
- The development of fast and efficient bioinformatic tools to gather, process and visualize large data sets in phylogenomics and population genomics
Phylogenomics
Genomic patterns of positive selection at the origin of rust fungi
Silva et al. 2015 PLOS One, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143959
Chapter II
The rust fungi
Life style:
Genomic characteristics:
Obligate biotrophy
Expansion of gene families resulting in high number of genes
Absence or loss of genes involve in nutrient uptake
Larger repertoire of small secreted proteins
Proliferation of transposons (mobile genetic elements)
"Big" genomes
Forgot how to survive outside the host (oops)
Excel at nullifying the host's defenses
Really, "big" genomes
What?
Phylogenomics | objectives
- Identify single-copy orthologs among 67 Basidiomycota and Ascomycota genomes and EST
- Detect episodic positive selection on the origin of the rust fungi
- Check for functional classes enriched for positively selected genes
What was the role of genetic adaptive variation on genes shared by rusts and other basidiomycota
Phylogenomics | methods
48 complete genomes
+
21 EST data sets
Ortholog assembly
(OrthoMCL + HaMSTr)
Pre-alignment QC
Alignment of putative orthologs
Post-alignment QC
Removal of saturated alignments
Removal of outlier alignments
Missing data filtering and file conversion
Data set creation
(3093 orthologs)
Ortholog assembly workflow







~ 50 scripts
~ 5000 lines of code
9 months
Phylogenomics | results
Maximum Likelihood reconstruction using RAxML
3093 genes - 67 taxa

Detection of positive selection at the root branch of the rust fungi
Phylogenomics | results
Episodic positive selection using branch-site model (PAML)
531 genes (nucleotide) - 37 taxa
104 genes (19.6%) with signatures of positive selection
Profiling selected amino acid sites:


Rusts
Non rusts
Unique
Strict
Relaxed
Diversifying
Strict
Relaxed
Phylogenomics | results
Functional annotation according to 21 KOG classes
Enrichment of several transport and metabolism classes
Genomic changes of nutrient transport and uptake
Enrichment of secondary metabolite biosynthesis
Possible triggers of plant defenses


Phylogenomics | Conserved class
Episodic positive selection using branch-site model (PAML)
531 genes (nucleotide) - 37 taxa
71 sites (24%) across 45 genes with signatures of positive selection on conserved amino acid sites.

Most prevalent class per gene
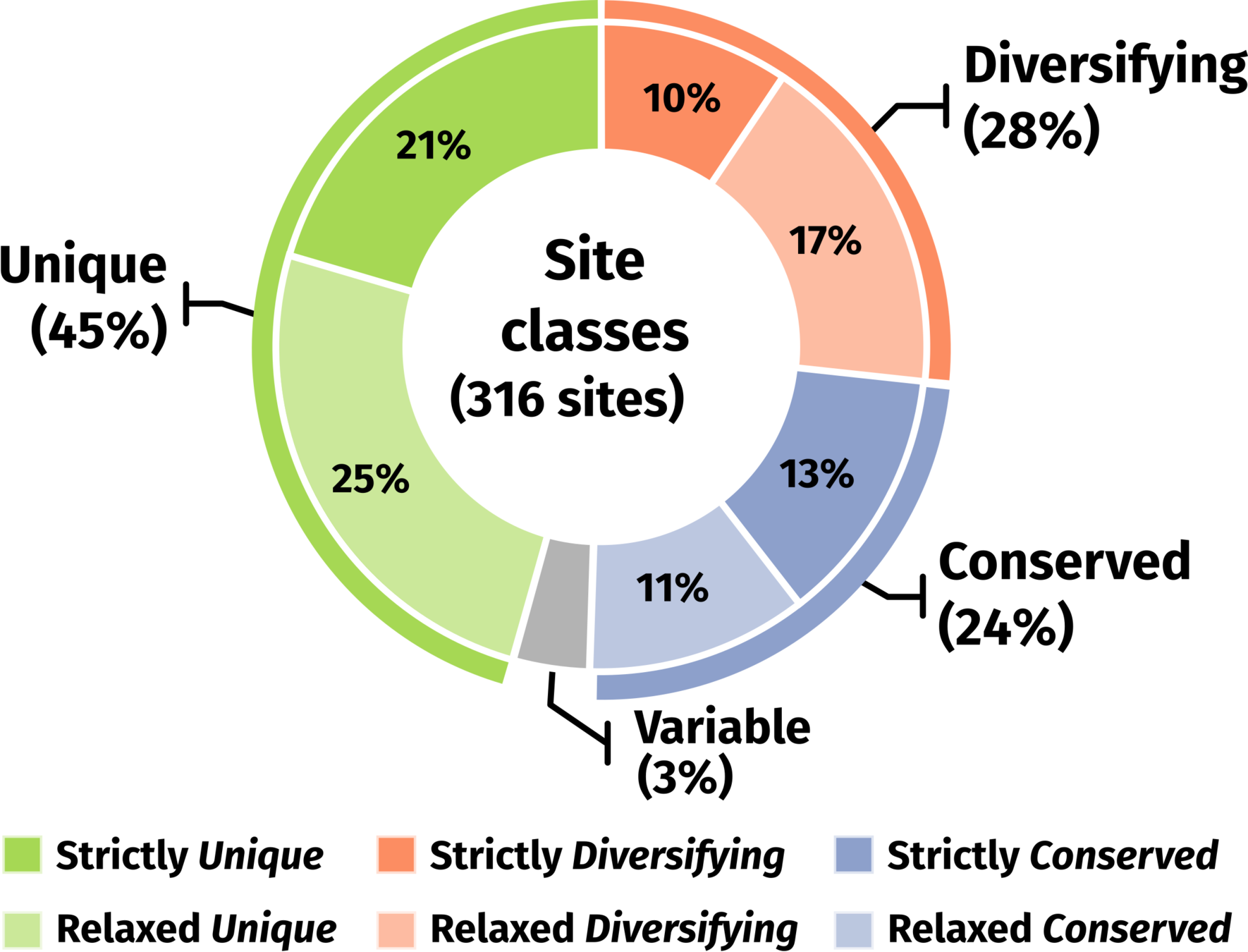
Phylogenomics | Conserved class
Episodic positive selection using branch-site model (PAML)
531 genes (nucleotide) - 37 taxa
Transition from AGY to TCN requires at least 2 non-synonymous mutations to maintain the same amino acid.
Substantial shift in codon usage between rusts and non-rusts for these amino acids.
Why?
- Role of positive selection?
- Purely neutral mechanisms?

Phylogenomics | conclusion
- Identifying important evolutionary transitions using positive selection detection
- Positive selection on codon usage may have bigger role than previously considered
- Transition to obligate biotrophy required significant adaptive changes in conserved genes
- Severe lack of bioinformatic tools for this studies
Population genomics
Population genomic footprints of host adaptation, introgression and recombination in Coffee Leaf Rust
Silva et al. 2018 Molecular Plant Pathology, DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12657
Chapter III
Pop genomics | introduction

Hemileia vastatrix:
... Hemicyclic with urediniospores as functional propagules
... causes Coffee Leaf Rust with losses up to 30%
... infects C. arabica (tetraploid) and C. canephora (diploid)
... Since 1861 (Lake Victoria) has spread worldwide
... more than 50 pathotypes/races
Literature state of the art?
Diversity
- Low
- Moderate
- High
Clonality
- Most evidence points to clonality
- Recombination in some regions
- Suggestion of cryptosexuality
No differentiation
Structure
... by geography
... by pathotype
... by host
Pop genomics | objectives
- Produce thousands of high quality SNPs for H. vastatrix using RAD-sequencing and technical replicates
- Investigate the genetic structure of H. vastatrix, with focus on how it impacts the evolutionary potential
- Test the clonality (or not) of H. vastatrix
Pop genomics | sampling

38 isolates (29 unique + 9 replicates):
- Pathotypes: 20
- Sampling time: 1954-2013
-
Hosts:
- 9 diploids (C. canephora)
- 21 tetraploids (C. arabica, HDT, inter-specific hybdrids)
Pop genomics | results
Maximum Likelihood reconstruction using RAxML (~20k SNPs)

1. Evidence of population structure according to host
2. Near absent structure among C3 isolates
3. Ladder-like pattern at the base of the C3 group
Pop genomics | results
Population structure and differentiation

Diploid hosts
Tetraploid hosts
Almost complete population differentiation

Structure
Principal Component analysis
Pop genomics | results
Introgression
Putative introgressed isolates

Supports the scenario of hybridization and introgression

Substantial allele sharing
Excess of heterozygosity
C2 > C3
C3 > C2
Pop genomics | results
Emergence of the C3 group

Could the C3 group be the result from a recent introduction from diploid coffee hosts?
Divergence bewteen C2 and C3 groups
Diversification of the C3 group
Pop genomics | results
Recombination within the C3 group

Sexual
Clonal
Association index: Measures linkage disequilibrium between SNPs and compares with expected distribution under equilibrium
Significant evidence of recombination occurring within the C3 group
Pop genomics | conclusions
- H. vastatrix as a complex of cryptic species
- Allele sharing between lineages > possibility of exchanging virulence factors
- H. vastatrix isolates in tetraploid hosts as a recent introduction followed by a specialization process
- Recombination as a source of genetic variation in H. vastatrix
TriFusion
Streamlining phylogenomic data gathering, processing and visualization
Chapter IV
TriFusion | description
Orthology
Process
Statistcs
Search orthologs...
Filter orthologs...
Graphical exploration
Export as protein/ DNA sequences
Complete proteomes
Sequence alignments
Convert/Concatenation
Collapse, filter, code gaps, creates consensus
Partition schemes
substitution models
+10 popular alignment formats
Fast and efficient
Summary statistics
Dozens of graphs
Detect outlier taxa/genes
Fast plot switching
Publication ready figures
TriFusion | benchmarks
Concatenation
Less is better

8 data sets:
- 40-376 taxa
- 2-52k alignments
- 17-567Mb in size
5 software:
- TriFusion
- SCaFoS
- FASconCAT.G
- SequenceMatrix
- BuddySuite
TriFusion | integrations
- Continuous integration with Travis CI with a suite of more than 220 tests using unittest.
- Extensive API and code documentation automatically built using sphynx and readthedocs.



- Step by step animated tutorials for all functionalities
TriFusion


Makes the home page and a featured project by the Kivy framework
TriFusion | conclusions
- TriFusion requires no bioninformatics experience to gather, process and visualize large phylogenomic data
- Comprehensive suite of complex and computationally intensive operations
- Opens phylogenomic studies to wider community by removing the requirements for programming expertise
Final remarks
- Bigger role of natural selection on shared genetic material
Phylogenomics
- Bigger role for positive selection on codon usage
Population genomics
- Hemileia vastatrix as a complex of hybridizing cryptic species
- Recent host-shift event with host specialization in Arabica crops
Software development
- TriFusion as a feature rich and accessible tool for genomic data processing.
Thank you for your attention

Acknowledgements:
CIFC
CoBiG2








PhD grant: SFRH/BD/86736/2012
Project grant: PTDC/AGR-GPL/119943/2010

Thesis defense
By Diogo Silva
Thesis defense
- 1,146



