Intro to Command Line
vs
Synonymous with....
- Shell
- bash ('Bourne-Again shell', although I've haven't heard that used recently)
- Command Line
- Text Terminal
- DOS Prompt (on windows machines)
- SSH (on remote machines)
- Bourne Shell
- csh
- ksh
- sh
- UNIX Shell
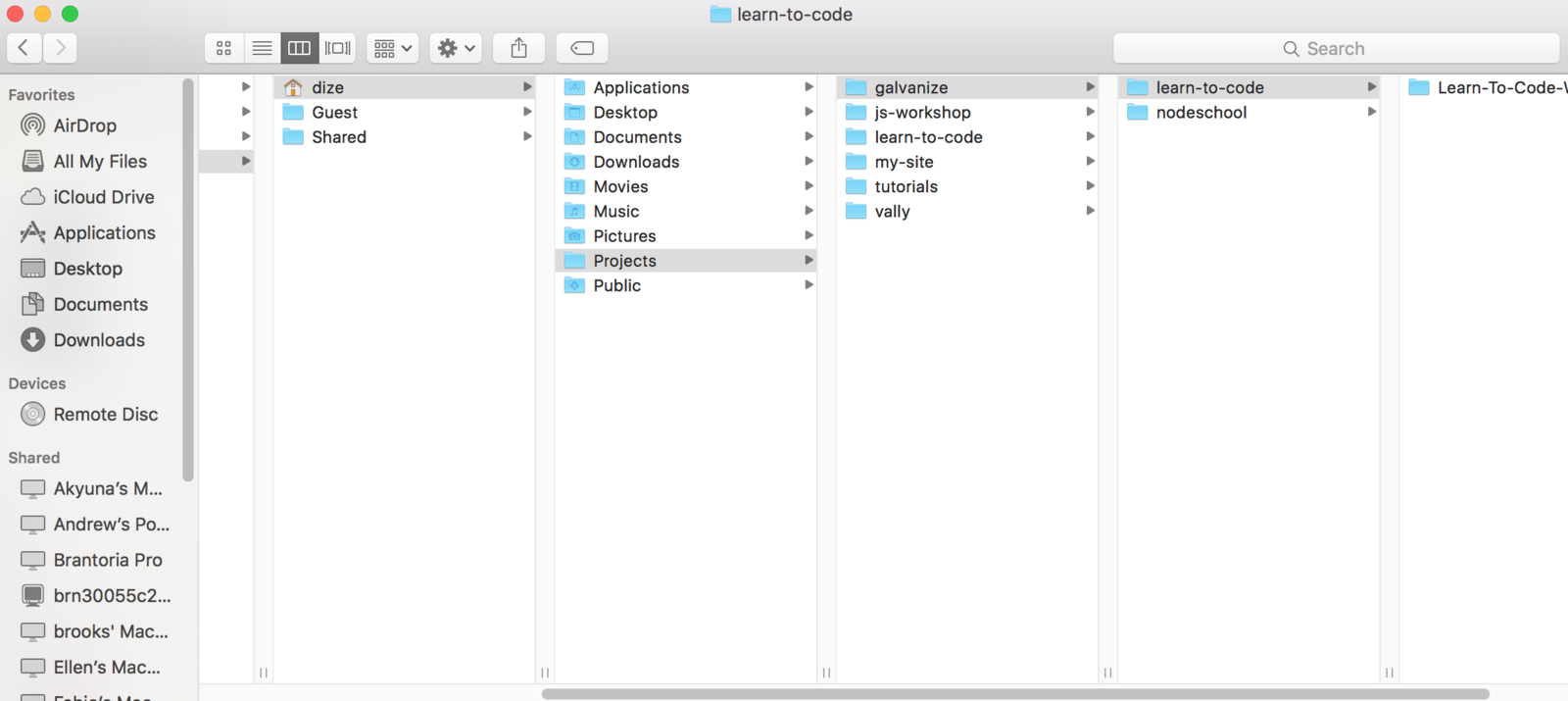
Navigate file system using command line
Learning Objectives
- use cd to change working directory
- pwd to print working directory
- ls to list files in a directory
- -a flag to show hidden files
- -l flag to see file details
- . and .. to refer to the current directory and parent directory
- ~ to refer to the home directory
- use both absolute and relative paths
- use TAB for Autocompletion
Let's try some out!
cd
pwd
ls -l
ls -a
. vs ..
~
Absolute
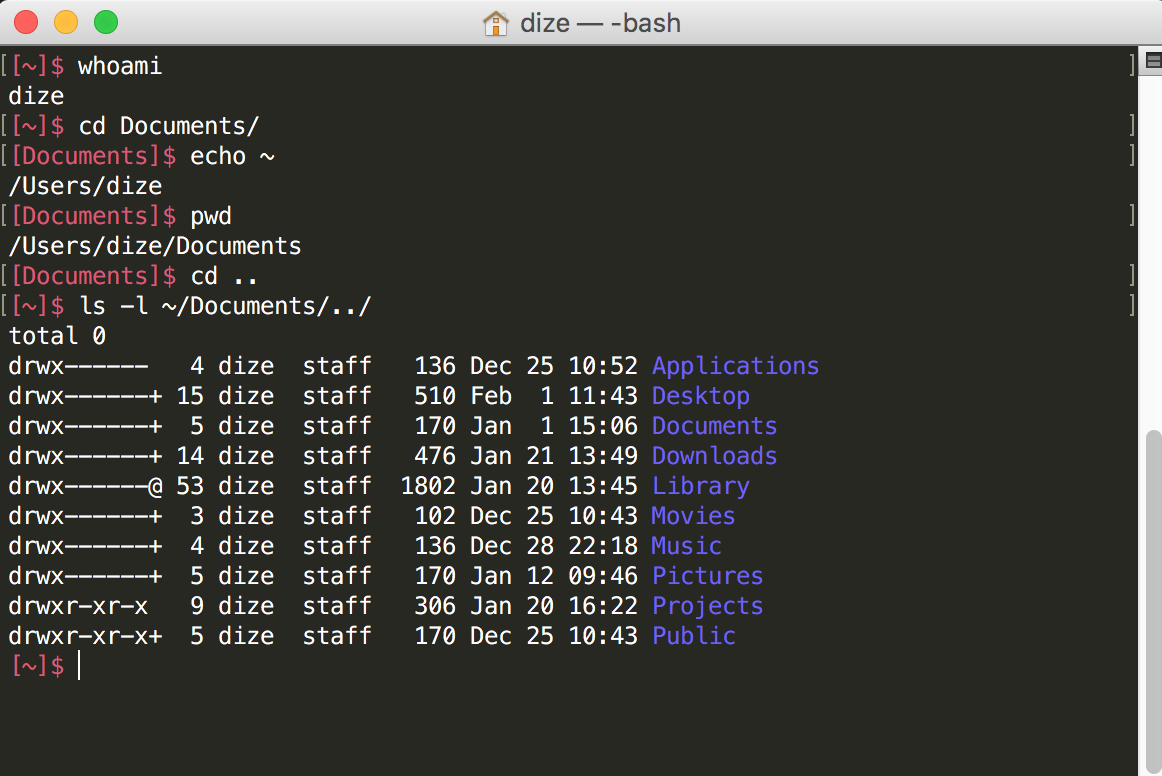
Relative
Any path that doesn't start with a / is relative to your current working directory
- Any path that starts with /
- Start at the root directory and work your way down the tree.
- Your home directory has an absolute path of /Users/[yourAccountName]
Take 7 minutes to look up the difference between absolute and relative paths, then answer these questions:
When accessing a file using its relative path, the file path starts in
When accessing a file using its absolute path, the file path starts in
.
.
the current/working directory
the root folder (~)
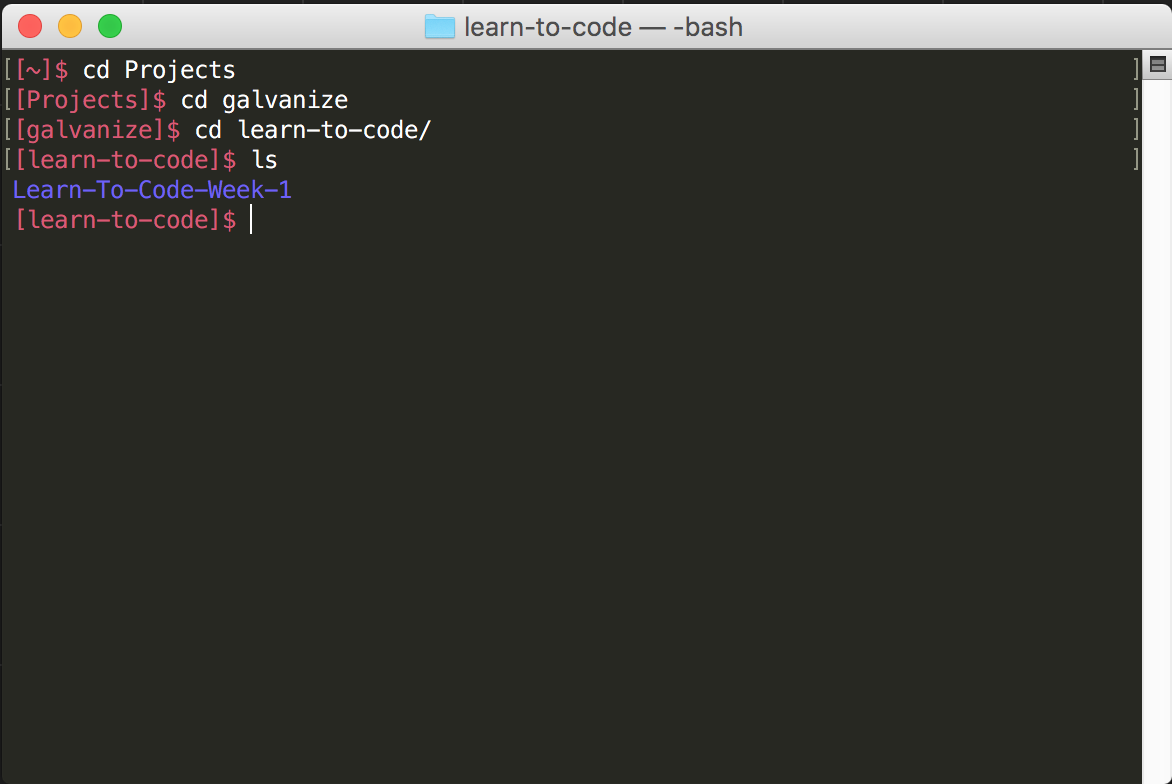
$ cd ~
$ ls ~/Documents
$ ls Documents
$ ls /
$ ls ../..Absolute vs Relative
What do you think
$ ls -l ~/Documents/../
will do?
Tab is your new BFF
-
Tab Autocompletes stuff
-
Type $ ls then double tap tab!
-
Type $ ls L then single tap tab
- now double tap tab!
Did we get it?
- use cd to change working directory
- pwd to print working directory
- ls to list files in a directory
- -a flag to show hidden files
- -l flag to see file details
- . and .. to refer to the current directory and parent directory
- ~ to refer to the home directory
- use both absolute and relative paths
- use TAB for Autocompletion
- store folders in your $PATH so you can execute files contained in them from anywhere
Let's practice!
Grab a buddy and practice:
Exercise: 5 minutes in Pairs
-
Using Finder: Pick a directory somewhere under the /Users directory on your partner's computer
-
Your Task: Navigate to that directory in a single command from your home directory using a relative or absolute path
-
Help your partner if they are having trouble and use Tab Completion
Learning Objectives
- > to redirect standard output to a file (overwrite)
- >> to redirect standard output to a file (append)
- | to redirect the standard output of one command into the standard input of another command
- && to chain a series of commands (only continues if the previous command executes successfully)
- ; to chain a series of commands
- Pipe input through grep to filter
Complete "File Manipulation" section of Command Line LE
Manage files on the command line
Learning Objectives
- ___ for moving and renaming files
- ___ for copying files
- ______ to create files
-
___ to remove files and directories
- -__to force
- -__ for directories
- ___ to show file contents
- _____ to search and filter file contents
- _____ to read file contents
mv
cp
touch
rm
f
r
cat
grep
less
mv
cp
touch
rm -rf
cat
grep
less
intro to command line
By Dize Hacioglu
intro to command line
- 161



