Nodejs
Training
Program
- Javascript course Basic and Advanced
- Nodejs core & Libraries
- Modejs Ecosystem, Framwork and Application
Day 1 : Javascript course Basic and Advanced
- Basic
- Native method
- Naming
- Workshop based on Nodeschool.io
- Heritage
- this
- bind, call and apply
- Wrokshop
Les 3 vies du Javascript
Dans les année 90 : DHTML (Dynamic HTML), servait à faire des "petits effets" sur les page web. (Netscape, IE 5.5, ...)
Dans les année 2000 : JQuery, propose des effets compatible sur tous les navigateurs. Une révolution !
A partir des 2010 : Google crée V8, le nouveau moteur d'interprétation du JS.
Javascript : Assignment
var i = 10;
var str = 'Hello';
var ing = 'word';i += 1;
i -= 1;
i++;
i--;
++i;
--i;var string = str;
string += ing;
string = str + ing;
string += ", How is it going ?"'Javascript : Expression
Loops
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
...
}var i = 0;
while (i < 10) {
...
i++;
}var i = 0;
do {
i++;
...
} while (i < 10);For
While
Do while
Javascript : Expression
Loops
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i % 2) continue;
...
}var i = 0;
while (true) {
if (i > 10) break;
...
i++;
}Continue
Break
Javascript : Type of value
Native
var foobar;
typeof foobar
// "undefined"undefined
var isTrue = true;
var isFalse = false;
typeof isTrue
// "boolean"
typeof isFalse
// "boolean"boolean
var age = true;
typeof age
// "number"number
var name = "Edouard";
typeof name
// "string"string
Javascript : Type of value
Object
var object1 = null;
typeof object1
// "object"
object1
// nullNull
var object2 = ['cat', 'dog'];
typeof object2
// "object"
object2
// ['cat', 'dog']Array
var object3 = {flowers: 'roses'};
typeof object3
// "object"
object3
// Object {flowers: 'roses'}Object
Javascript : RegExps
Syntaxe
var myTest = /^Hel.*rld$/;
myTest.test("Bonjour monde");
// false
myTest.test("Hello world");
// trueTest
var str = "Hello world";
var myTest = /^Hel(.*)rld$/;
myTest.exec(str);
// ["Hello world", "lo wo"]Exec
Javascript : Function
Syntaxe
var myFunction = function () {
console.log("Hello word");
}
myFunction()
// Hello wordAnonymous
var hello = "Hello word"
var myFunction = function (message) {
console.log(message);
}
myFunction(hello)
// Hello wordArguments
function myFunction() {
console.log("Hello word");
}
myFunction()
// Hello wordBasic
Javascript : Function
Syntaxe
var myFunction = function () {
return("Hello word");
}
console.log(myFunction());
// Hello wordReturn
var myFunction = function (i, message) {
console.log(arguments);
}
myFunction(10, "Hello word")
// { '0': 10, '1': 'Hello word' }Arguments
Javascript : Function
Scopes
var message = "Hello word"
var myFunction = function () {
console.log(message);
}
myFunction()
// Hello wordVariable are passing through anonymous function
var message = "Hello word"
var myFunction = function () {
var mySecondFunction = function () {
console.log(message);
}
mySecondFunction();
}
myFunction()
// Hello wordAs long as you stay in the same file (= module)
var myFunction = function () {
console.log(message);
}
var message = "Hello word"
myFunction()
// Hello wordStill works if variable message is set after
Javascript : Objects
var object1 = {};
var object2 = {"cat": {}, "dog": "wouf"};
var object3 = {cat: {}, dog: {}};
var object4 = {cat: {number:3, totalWeight: 21}, dog: {number:5, totalWeight: 104}};Self declared
var object5 = { cat: { noise: function () { console.log("meow") } }
, dog: { noise: function () { console.log("wouf") } }
};
object5.cat.noise();
// meow
object5.lion = { noise: function () { console.log("grraou") };
object5.cat.noise();
// meow
object5.lion.noise();
// grraouobject5.cat.parent = object5;
object5.cat.parent.cat.parent.cat.noise();
// meow
console.log(object5);
// { cat: { noise: [Function], parent: [Circular] }, dog: { noise: [Function] } }Javascript : Objects
var Animal = function () {
var race;
this.setRace = function (lRace) {
race = lRace;
};
this.noise = function (m) {
var noise;
if (race == 'cat') {
noise = 'meow';
} else if (race == 'dog') {
noise = 'wouf';
} else {
noise = 'Error: Race need to be set';
}
console.log(noise);
};
}
var animal = new Animal();
animal.setRace('cat')
animal.noise();
delete animal; // Only remove reference
animal = undefined;new / delete
Javascript : Objects
var Animal = function (race) {
this.noise = function () {
var noise;
if (race == 'cat') {
noise = 'meow';
} else if (race == 'dog') {
noise = 'wouf';
} else {
noise = 'Error: Race need to be set';
}
console.log(noise);
};
}
var animal = new Animal('cat');
animal.noise();
delete animal;
animal = undefined;constructor
Javascript : Objects
Heritage
Later ;-)
Javascript : Native method
String
var str = "good morning";
str.replace("morning", "after noon");
// good after noonreplace
var str = "good morning";
str.split(' ');
// [ 'good', 'norning' ]replace
var str = "good morning";
str.indexOf("morning");
// 6
str.indexOf("o");
// 1indexOf
You want more ? http://www.w3schools.com/jsref/jsref_obj_string.asp
Javascript : Native method
Array
var mArray = [1, 2, 3, "cat", "dog"];
// [ 1, 2, 3, 'cat', 'dog' ]
Create / push / pop / indexOf / splice
mArray.push("lion");
// [ 1, 2, 3, 'cat', 'dog', 'lion' ]push
mArray.pop(); // return lion
// [ 1, 2, 3, 'cat', 'dog' ]
pop
mArray.splice(mArray.indexOf('cat'), 1);
// [ 1, 2, 3, 'dog' ]indexOf / splice
Object
- instance
- map
- record
- array
- list
- stack
Naming
Variable
- parameter
- closure
- property
function
- constructor
- lambda
- method
- callback
- recursive
Let's train
javascripting
Install nodejs
Install javascripting
bash $> sudo npm install -g javascriptingJavascript training
Begin
bash $> javascriptingVerifying
bash $> javascripting verify file.jsLet's train
power_iter / power_rec
javascript
heritage
Javascript : heritage
Remember
var cat = {
message: "meow"
, talk : function() { console.log(message) }
};
console.log(cat.message); // meow
cat.talk(); // meowObject inline declared
var Cat = function () {
var message = "meow";
this.talk = function () {
console.log(message);
};
}
var cat = new Cat();
console.log(cat.message); // undefined
cat.talk(); // meow Object self-declared
Javascript : heritage
Remember
var Cat = function () {
var message = "meow";
this.talk = function () {
console.log(message);
};
}
var felix = new Cat();
var lili = new Cat();
console.log(felix == lili); // falseEach new create a new instance.
There are not sharing their value or method
Javascript : heritage
Constructor and prototype
var Cat = function () {};
console.log(Cat.prototype); // {}
Cat.prototype.talk = function () { console.log("meow"); };
var felix = new Cat();
var lili = new Cat();
felix.talk(); lili.talk(); // meow meow console.log(felix.talk == lili.talk); // true Cat.prototype.talk = function () { console.log("graou"); }
felix.talk(); lili.talk(); // graou graou Create prototype
Instance share same prototype
If you change the prototype, both instances get the changement
Javascript : heritage
Constructor and prototype
felix.constructor.prototype.talk(); // graouYou can still access to the prototype
felix instanceof Cat; // trueEven if set a method, the instance is still from considering from the Object
felix.talk = function () { console.log("twit"); };
felix.talk(); lili.talk(); // twitt graouBut you can replace the prototype by set directly a method.
Javascript : heritage
Heritage overview
var Maincoon = function () {};
Maincoon.prototype = Cat.prototype;Never do :
var Cat = function () {};
Cat.prototype.talk = function () {console.log("meow") };
var Maincoon = function () {};
for (var proto in Cat.prototype) {
Maincoon.prototype[proto] = Cat.prototype[proto];
}
Maincoon.prototype.getWeight = function () {
console.log(12);
};
var symba = new Maincoon();
symba.talk();
symba.getWeight();Copy prototype
Javascript : heritage
Heritage overview
var Cat = function () {};
Cat.prototype.talk = function () {console.log("meow") };
var Maincoon = function () {};
for (var proto in Cat.prototype) {
Maincoon.prototype[proto] = Cat.prototype[proto];
}
Maincoon.prototype.getWeight = function () {
console.log(12);
};
var symba = new Maincoon();
symba.talk();
symba.getWeight();
Cat.prototype.lick = function () { console.log("slurp !"); };
var cat = new Cat();
cat.lick(); // slurp !
symba.lick(); // TypeError: Object [object Object] has no method 'lick'Hum, damned
console.log(symba instanceof Maincoon); // true
console.log(symba instanceof Cat); // falseCopy prototype : The limit !
Javascript : heritage
Heritage overview
var Cat = function () {};
Cat.prototype.talk = function () {console.log("meow") };
var Maincoon = function () {};
var Surrogate = function () {
this.constructor = Maincoon;
};
Surrogate.prototype = Cat.prototype;
Maincoon.prototype = new Surrogate();
Maincoon.prototype.getWeight = function () {
console.log(12);
};
var symba = new Maincoon();
symba.talk();
symba.getWeight();
Cat.prototype.lick = function () { console.log("slurp !"); };
var cat = new Cat();
cat.lick(); // slurp !
symba.lick(); // TypeError: Object [object Object] has no method 'lick'Chained prototype
Javascript : heritage
Heritage overview
var Class = function() {
this.initialize && this.initialize.apply(this, arguments);
};
Class.extend = function(childPrototype) { // defining a static method 'extend'
var parent = this;
var child = function() { // the child constructor is a call to its parent's
return parent.apply(this, arguments);
};
child.extend = parent.extend; // adding the extend method to the child class
var Surrogate = function() {}; // surrogate "trick" as seen previously
Surrogate.prototype = parent.prototype;
child.prototype = new Surrogate;
for(var key in childPrototype){
child.prototype[key] = childPrototype[key];
}
return child; // returning the child class
};Chained prototype : real case
The same method is use by angular, backbone, ...
Javascript : heritage
Heritage overview
Chained prototype : real case
var Cat = Class.extend({
initialize : function () {
this.noise = 'meow';
}
, talk: function () { console.log(this.noise) }
});
var Maincoon = Cat.extend({
getWeight: function () { console.log(12) }
});var symba = new Maincoon();
symba.talk();
symba.getWeight();var cat = new Cat();
console.log(Maincoon instanceof Cat);Cat.prototype.lick = function () { console.log("slurp !"); };
symba.lick();Let's try !
Heritage
Create a main object
Method
- getType()
Creates Moto inherits Vehicle
Properties
- this.type = 'moto'
Creates Car inherits Vehicle
Properties
- this.type = 'car'
Heritage
Let's train
merge_object
Day 2
Nodejs core & Libraries
Nodejs core & Libraries
- Runtime introduction: V8, callbacks, non-blocking IO, event-loop
- Module system: require, package.json, npm, node_modules
- EventEmitter
- Useful core modules
- Error handling: Exceptions, CPS, stack traces, try/catch, trycatch
- Asynchrony contracts: callbacks, promises and async generators
- Control-flow: stepup, async, q/bluebird
- Module lifetime: require, configure, initialize
- Assisted Nodeschool.io Workshops
NodeJS
2009 : Created by Ryan Dahl
NodeJS use V8 engine to execute the js code
2011 : NPM is created to publish and share libraries to the community
Windows work with on NodeJS to make it windows compliant
2012+ : Developpement of framework : Express.js, socket.io, ...
NodeJS : Technical
Threading : Node.js operates on a single thread, using non-blocking I/O calls, allowing it to support tens of thousands of concurrent connections without incurring the cost of thread context-switching
V8 is the JavaScript execution engine built for Google Chrome, open-sourced by Google in 2008. Written in C++, V8 compiles JavaScript source code to native machine code instead of interpreting it in real time.
npm is the pre-installed package manager for the Node.js server platform
Event Loop : Node.js registers itself with the operating system so that it is notified when a connection is made. When a connection is made, the operating system will issue a callback.
NodeJS
Callbacks
Nodejs : Callbacks
var callback = function () {
console.log("Callback called");
}
setTimeout(callback, 1000);var request = require('request');
console.log("Begin code");
var callback = function (error, response, body) {
console.log("Awnser received, length : ", body.length);
console.log(body.substr(0, 40));
};
request('http://www.google.com', callback);
console.log("Finish code");
Example 1
Example 2
NodeJS
non-blocking IO
Blocking pathern
Download file 1
wait download finish
Download file 2
wait download finish
Download file 1
Download file 2
wait download finish file 1 and 2
Non-blocking pathern
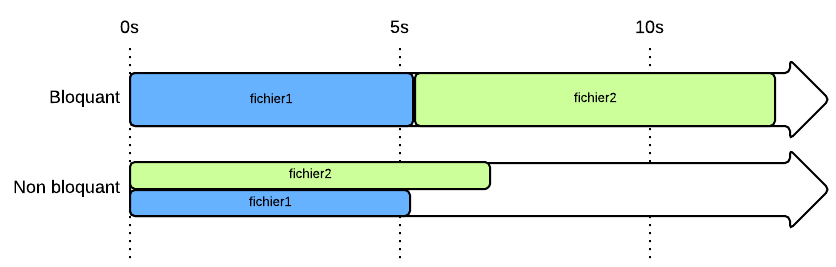
NodeJS : Non-blocking IO
console.log("Begin code");
setInterval(function () {
console.log("Bonjour");
}, 1000);
setInterval(function () {
console.log("Hello");
}, 2000);
console.log("Finish code");Example 1
NodeJS : Non-blocking IO
NodeJS : Event Loop
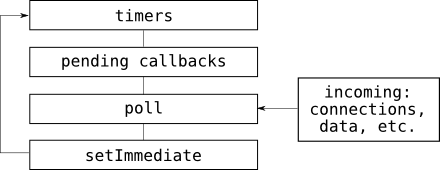
NodeJS is mono-thread !
NodeJS is synchrone !
And yes, NodeJS can handle millions of events
NodeJS : Event Loop
console.log("Begin code");
function tick() {
console.log('tick');
}
setInterval(tick, 1000);
console.log('End code');Example 1
console.log("Begin code");
setInterval(function () {
console.log("tick");
}, 1000);
while (1) { };
console.log("End code");Example 2
NodeJS : Event Loop
function asyncFake(data, callback) {
if(data === 'foo') callback(true);
else callback(false);
}
asyncFake('bar', function(result) {
// this callback is actually called synchronously!
});Using callback != synchrone
V8 Event Loop is based on epool (man 2 epool)
- epool watch a fd
- The event loop check return (man 2 epool_wait)
- Asynchrone work only with fd
Nodejs
Module system
NodeJS : Module system
Modules are libraries :
- Core library
- Community library
- Code library
Project module are manage by package.json
$ROOT/package.jsonNodeJS : Module system
Modules are libraries :
- Core library
- Community library
- Code library
Project module are manage by package.json
$ROOT/package.jsonNodeJS : Module system
npm
npm is the package manager of NodeJs
npm is driven by the package.json
Let's create our first project
mkdir first_project
npm initCreate a new directory and npm init
Answer question :
- Name : default (first formation)
- Version 1.0.0 (default)
- Description : This is my first project
- entry point : node index.js
- test command : (leave blank)
- keyword : first project init npm
- author : Your Name
- License : (ISC, MIT, ...)
- Yes !
First http server
Bash $> node test_2.jstest_2.js
var http = require('http');
console.log("Set new http server");
var server = http.createServer(function(req, res) {
res.writeHead(200);
res.end('Good morning !');
});
server.listen(8080);
console.log("Server listening on http://localhost:8080");
Take your web browser and test it : http://localhost:8080
First use
Read-Eval-Print-Loop (REPL)
Bash $> node
> console.log("hello word");
hello word
undefined
Bash $> node
> var string = "hello world"
undefined
> console.log(string);
hello world
undefined
Express and socket io
example
Create a new project
npm install express-generator -g
express -hexpress
cd . && npm installbin/wwwTo launch project
Let's create a chat
var io = require('socket.io').listen(app.listen(port));io.sockets.on('connection', function (socket) {
socket.emit('message', { message: 'welcome to the chat' });
socket.on('send', function (data) {
io.sockets.emit('message', data);
});
});Dans bin/www
Front-end
window.onload = function() {
var messages = [];
var socket = io.connect('http://localhost:3700');
var field = document.getElementById("field");
var sendButton = document.getElementById("send");
var content = document.getElementById("content");
var name = document.getElementById("name");
socket.on('message', function (data) {
if(data.message) {
messages.push(data);
var html = '';
for(var i=0; i<messages.length; i++) {
html += '<b>' + (messages[i].username ? messages[i].username : 'Server') + ': </b>';
html += messages[i].message + '<br />';
}
content.innerHTML = html;
} else {
console.log("There is a problem:", data);
}
});
sendButton.onclick = function() {
if(name.value == "") {
alert("Please type your name!");
} else {
var text = field.value;
socket.emit('send', { message: text, username: name.value });
}
};
}public/chat.js
Front-end
doctype html
html
head
title= title
link(rel='stylesheet', href='/stylesheets/style.css')
script(src='/chat.js')
script(src='/socket.io/socket.io.js') body
block content
views/layout.jade
extends layout
block content
#content(style='width: 500px; height: 300px; margin: 0 0 20px 0; border: solid 1px #999; overflow-y: scroll;')
.controls
| Name:
input#name(style='width:350px;')
br
input#field(style='width:350px;')
input#send(type='button', value='send')views/index.jade
"dependencies": {
"eventemitter3": "^1.1.1"
}nodejs-training
By Doud Ferrari
nodejs-training
- 1,176

