Fondamentals of Machine Learning
Nicolas Rochet
2025
A brief summary
Definition
Machine learning is a field of artificial intelligence that uses statistical techniques to give computer systems the ability to "learn" (e.g., progressively improve performance on a specific task) from data, without being explicitly programmed
From Arthur Samuels (source : Wikipedia)
Definition
"A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E"
From Tom M,Mitchel
Learning categories
Supervised learning
Semi-supervised learning
Unsupervised learning
Reinforcement learning
Transfert learning
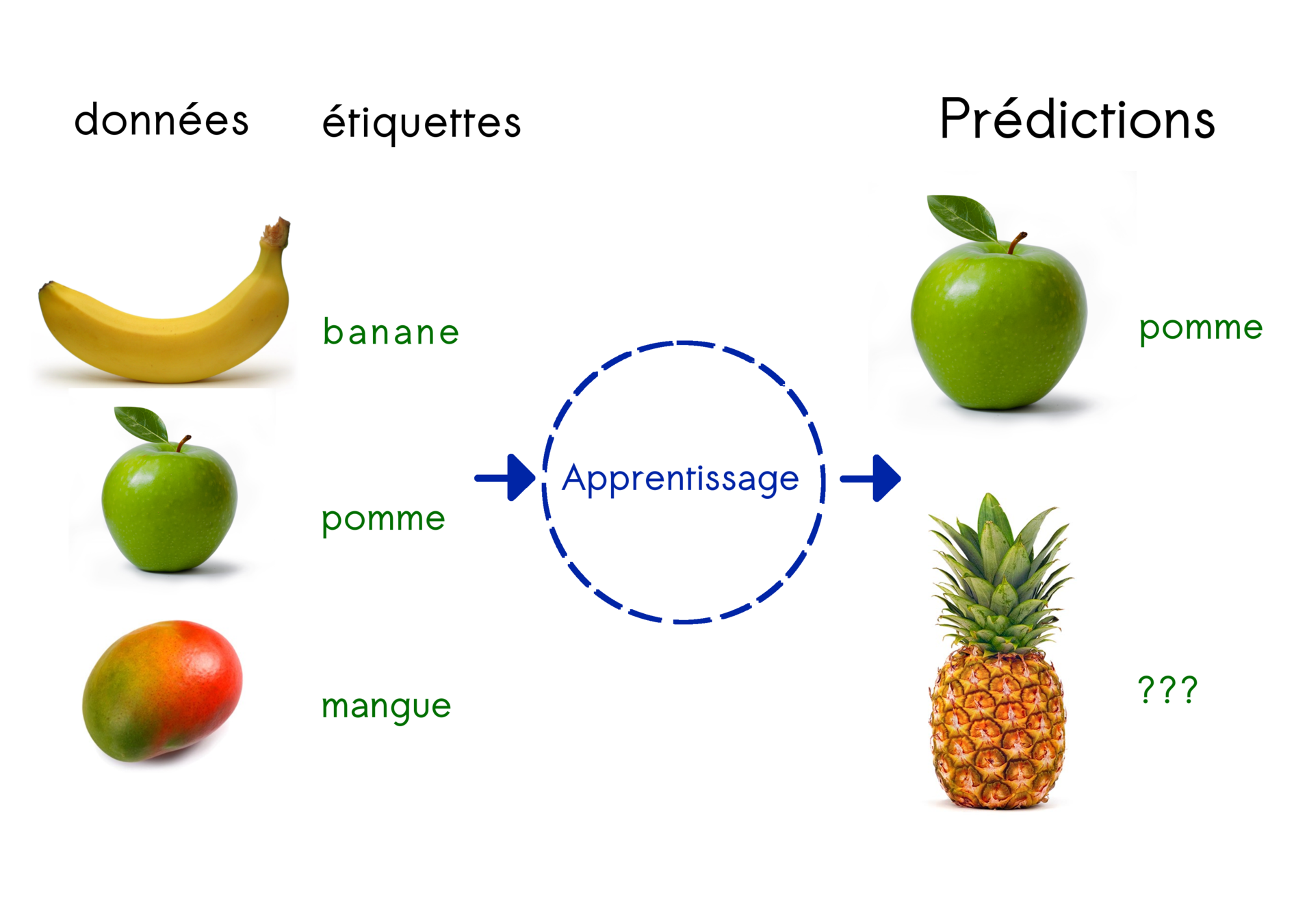
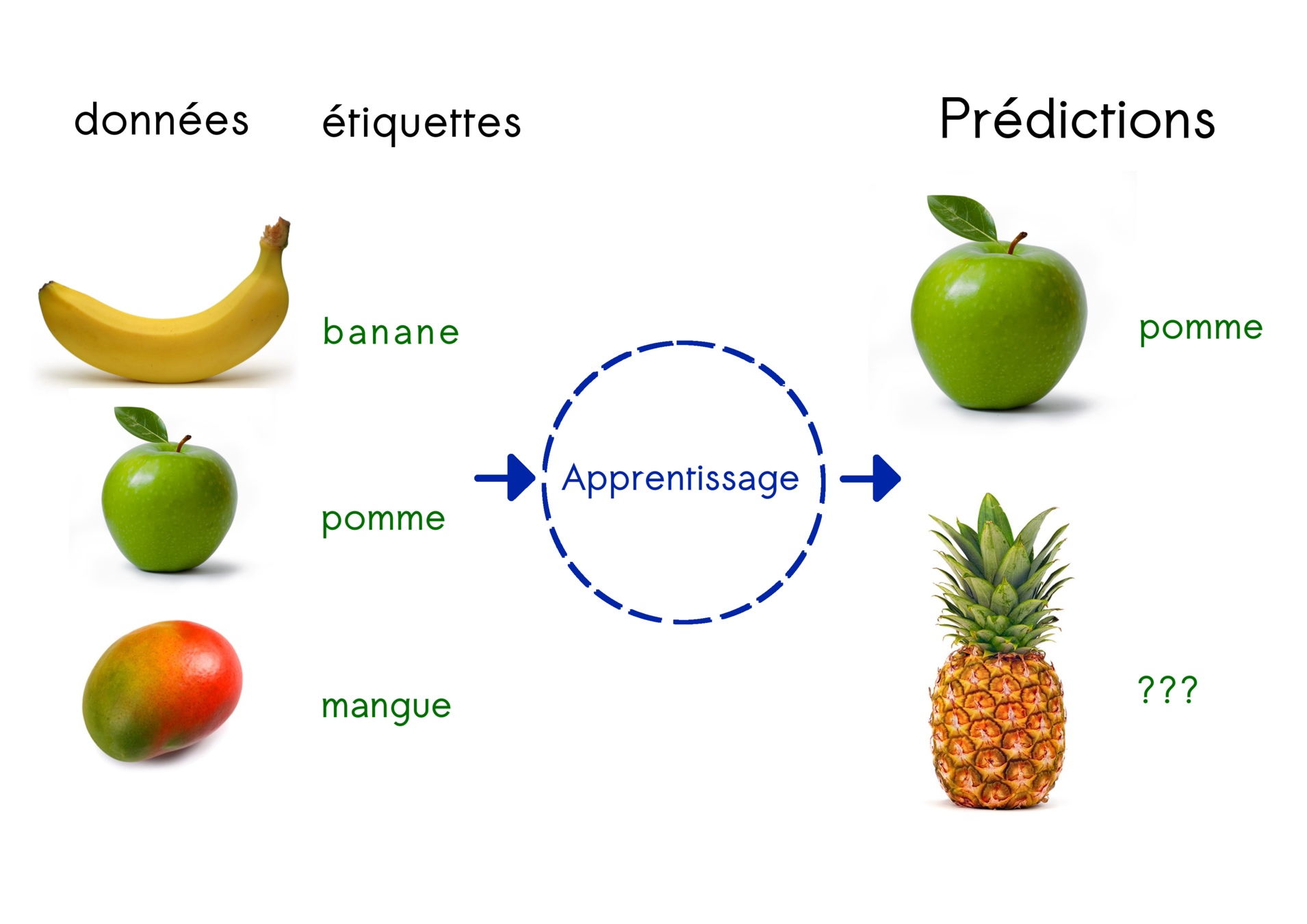
Supervised learning
Principle :
Find the general rule that links data and labels
Unsupervised learning
Principe :
find a structure in data
Clsutering
Estimate the distribution of data
Estimate covariance in the data
Identify outlier data
Reduce the number of variables
...
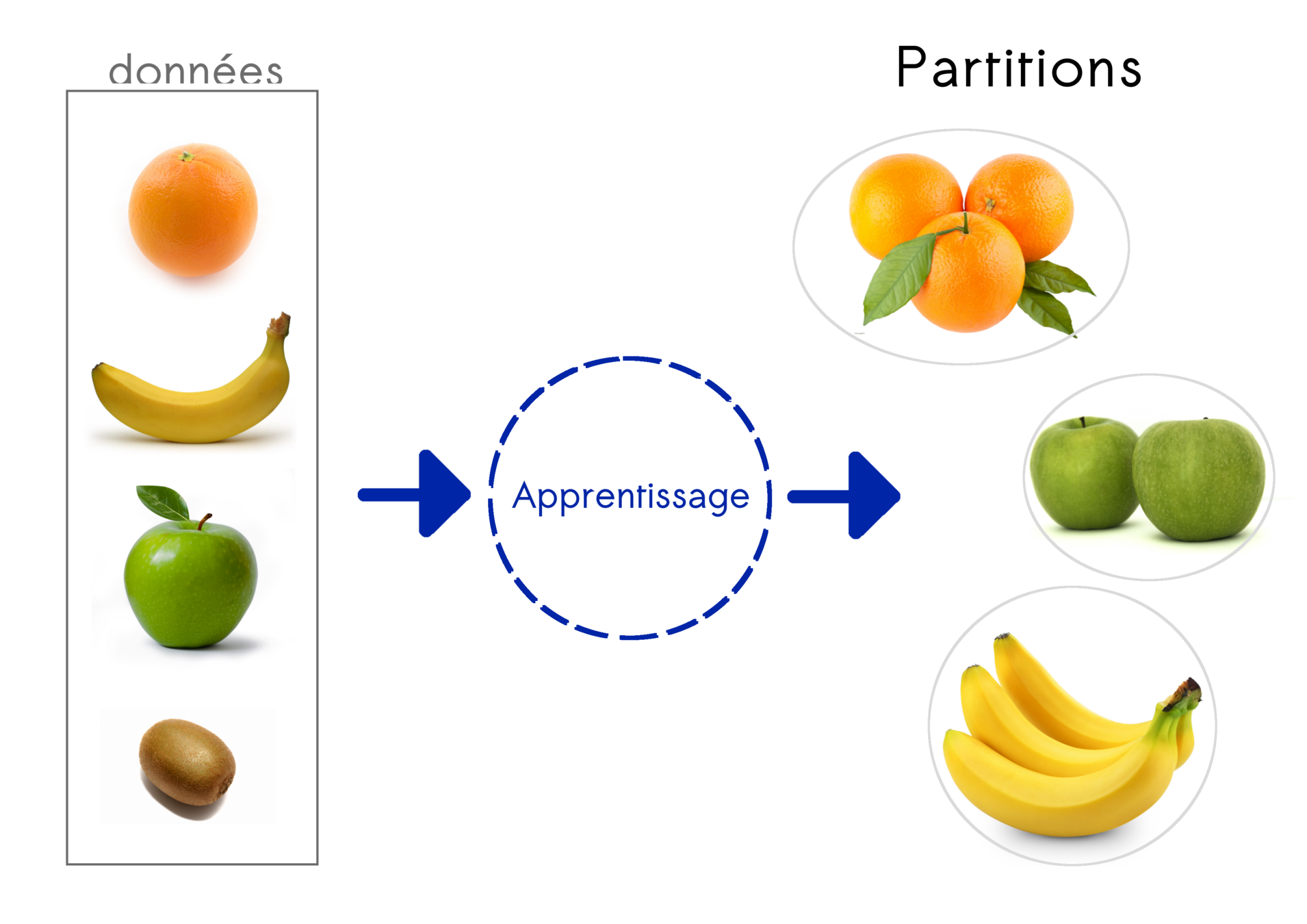
Unsupervised learning
Clustering
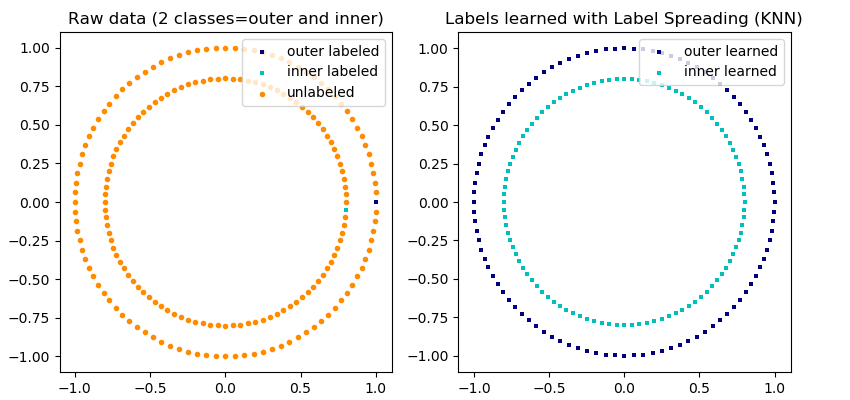
Semi-supervised Learning
Principle: find a structure in the data but with a large amount of unlabeled data
Active learning
Principle:
Procedure in which the algorithm can query the supervisor to obtain new data

from sckit-learn
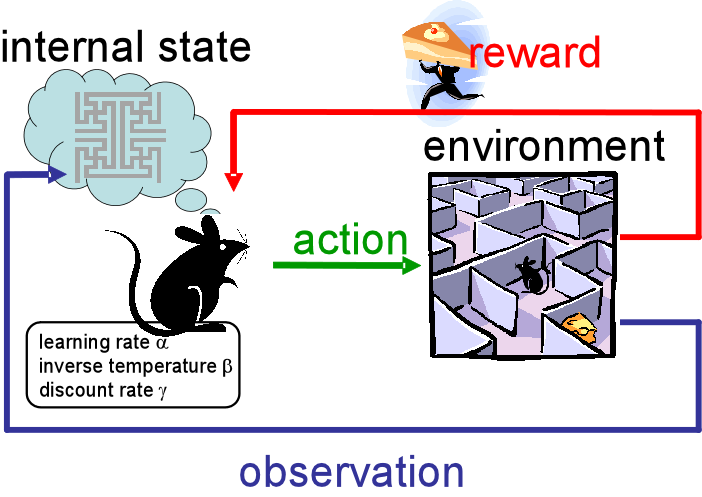
Reinforcement learning
Principle:
An agent learns the actions to perform on its environment by maximizing a reward
Transfert learning
Principle:
Apply knowledge learned on a previous task to new tasks
The main tasks of machine learning
Classification
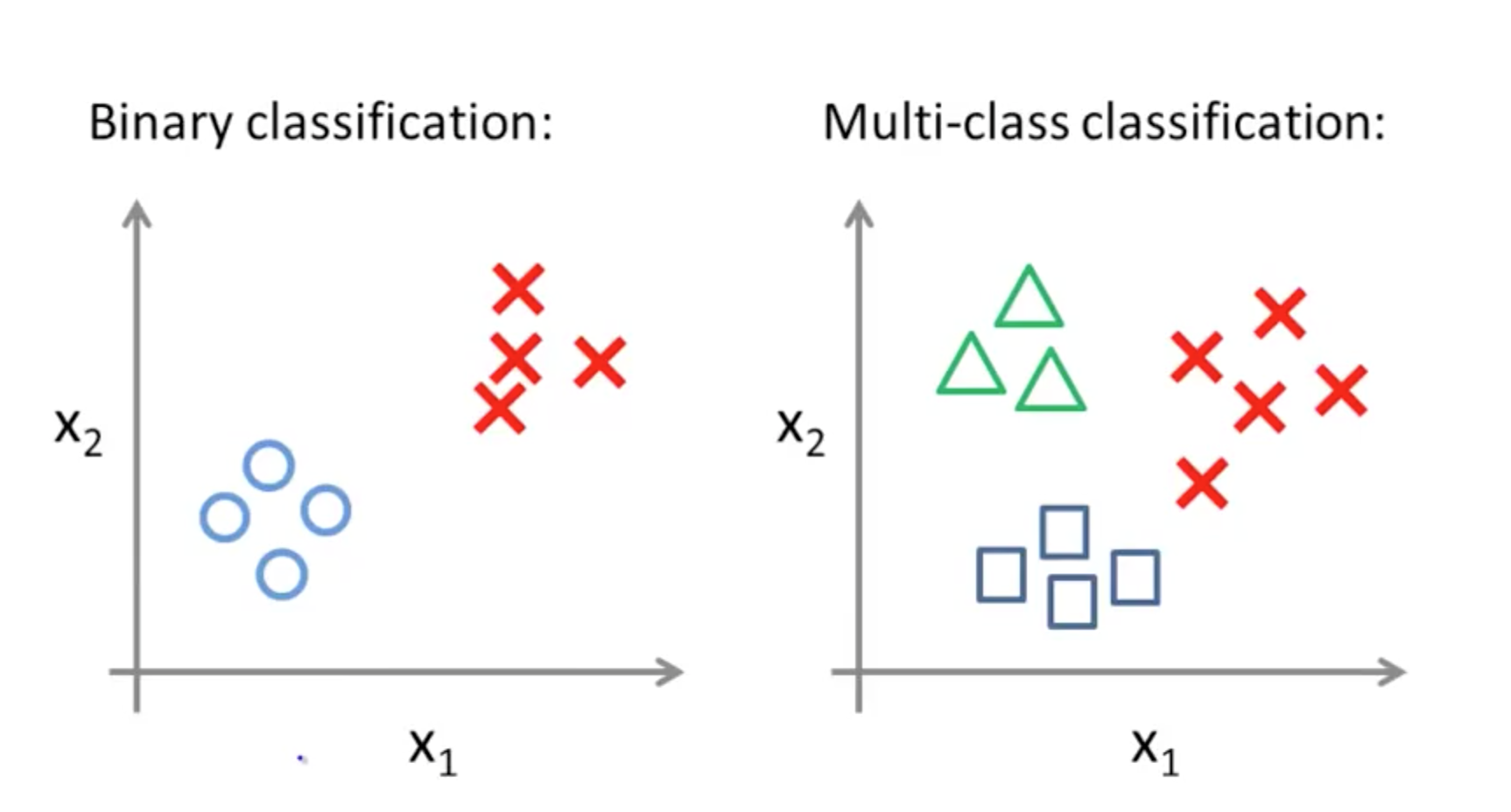
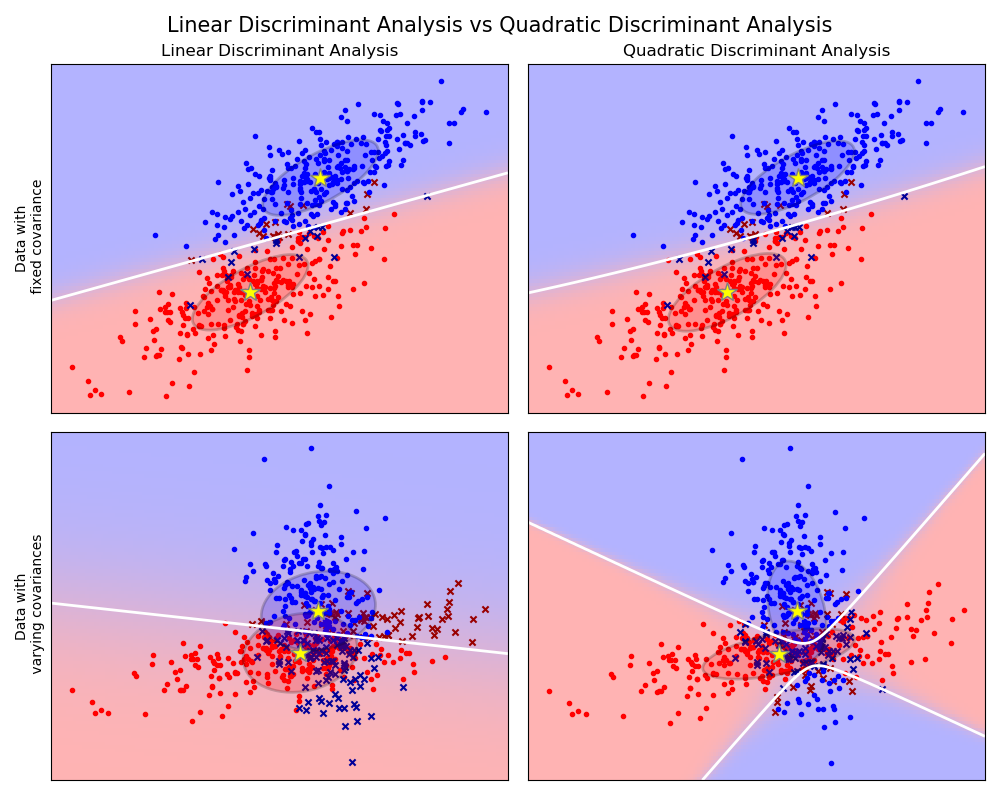
Regression
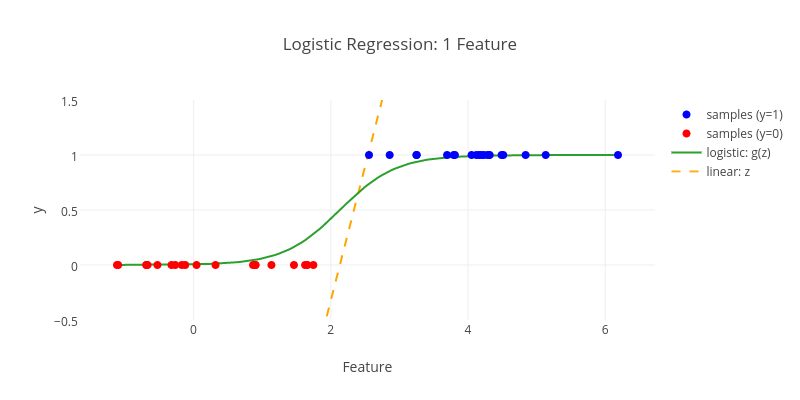
From Wikipedia
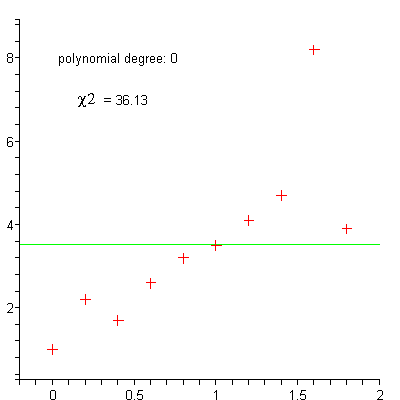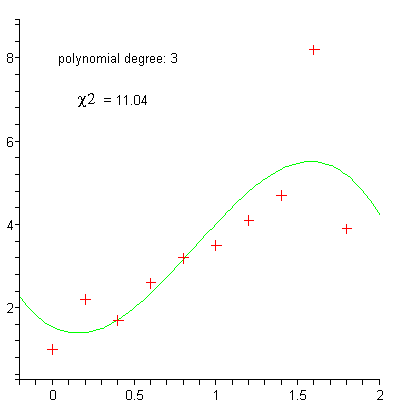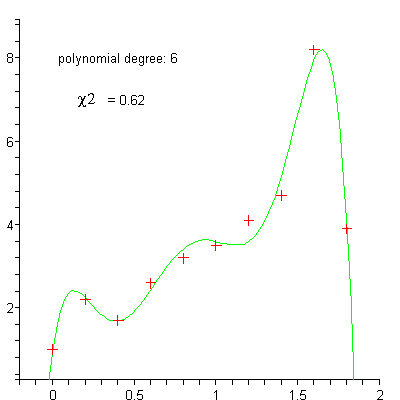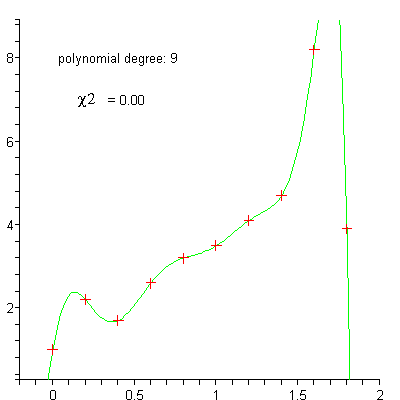
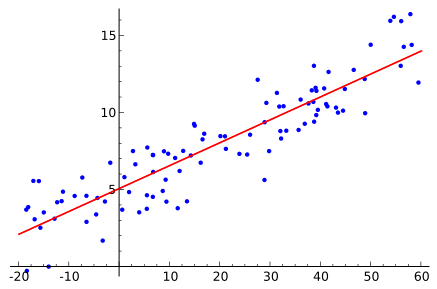
linear
logistic
polynomial
Clustering
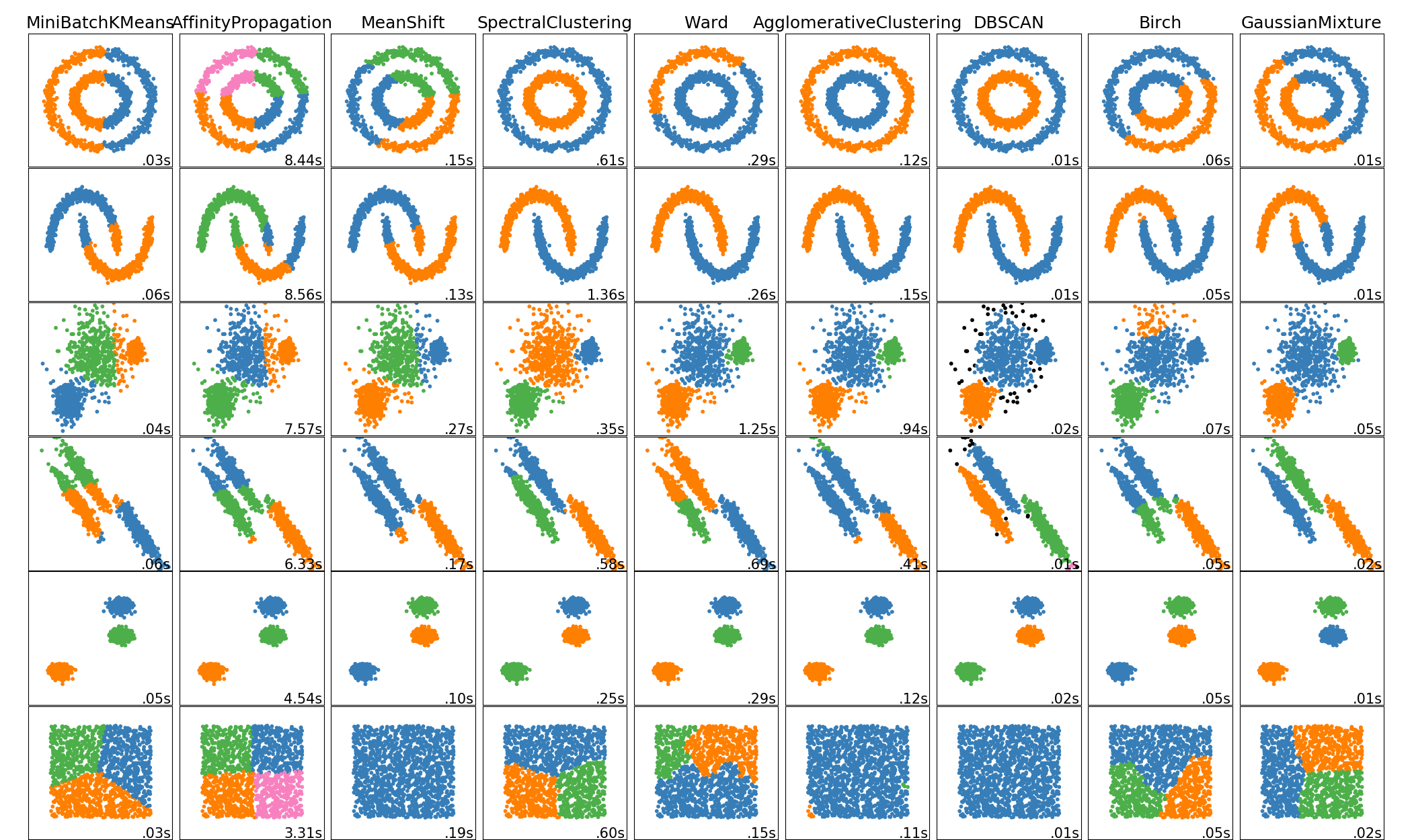

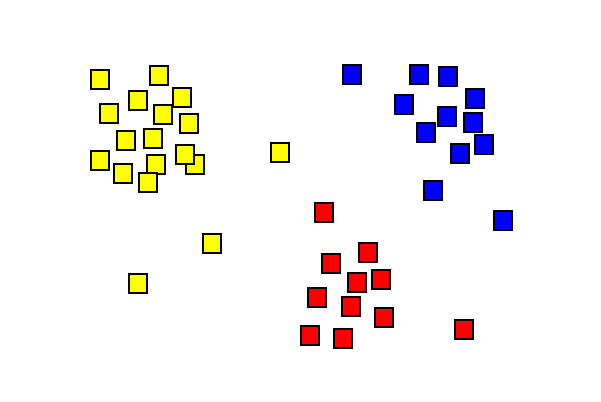
Fondamental principles
Data science:
data preparation
Management of missing data
Management of outliers
Normalisation
Data formatting (matrices)
Reduction of dimensionality
...
Optimisation of
paramers
Almost all machine learning algorithms have internal parameters to adjust in order to give good results!
"tuning"
Objective: minimize a cost/error function
parameters vs hyper parameters
Parameters
Hyper parameters
Their values are learned
Their values are fixed before learning
Ex: coefficients of a régression
Ex: number K of clusters K-means
Almost all machine learning algorithms have internal parameters to adjust in order to give good results!
Objective: minimize a cost/error function
Some optimization methods are quite specific:
...
least squares
regression
gradient descent
neural network
boosting methods
Almost all machine learning algorithms have internal parameters to adjust in order to give good results!
Objective: minimize a cost/error function
Without preconceived assumptions, use generalized methods:
Grid Search
Random Search
Bayesian Search
Evolutionnary Search
Gradient-based Optimisation
...
More details ici
Evaluation metric
Quantify the result of a model
accuracy
F1 score
precision &
recall
area uner ROC curve
mean squared error
percentage of variance explained
mutual infomation
...
limitations of machine learning
biais / variance tradeoff
The problem consists in "tuning" the algorithm so that it learns with sufficient accuracy while keeping good performances on data it has never encountered (its ability to generalize its results)
biais / variance tradeoff
Expected error calculated on the test set
Variance of the estimator of f
Square of the bias of the estimator of f
irreducible error
"gap between model and data reality"
"ability to estimate f with the least variability when the dataset changes"
biais / variance tradeoff
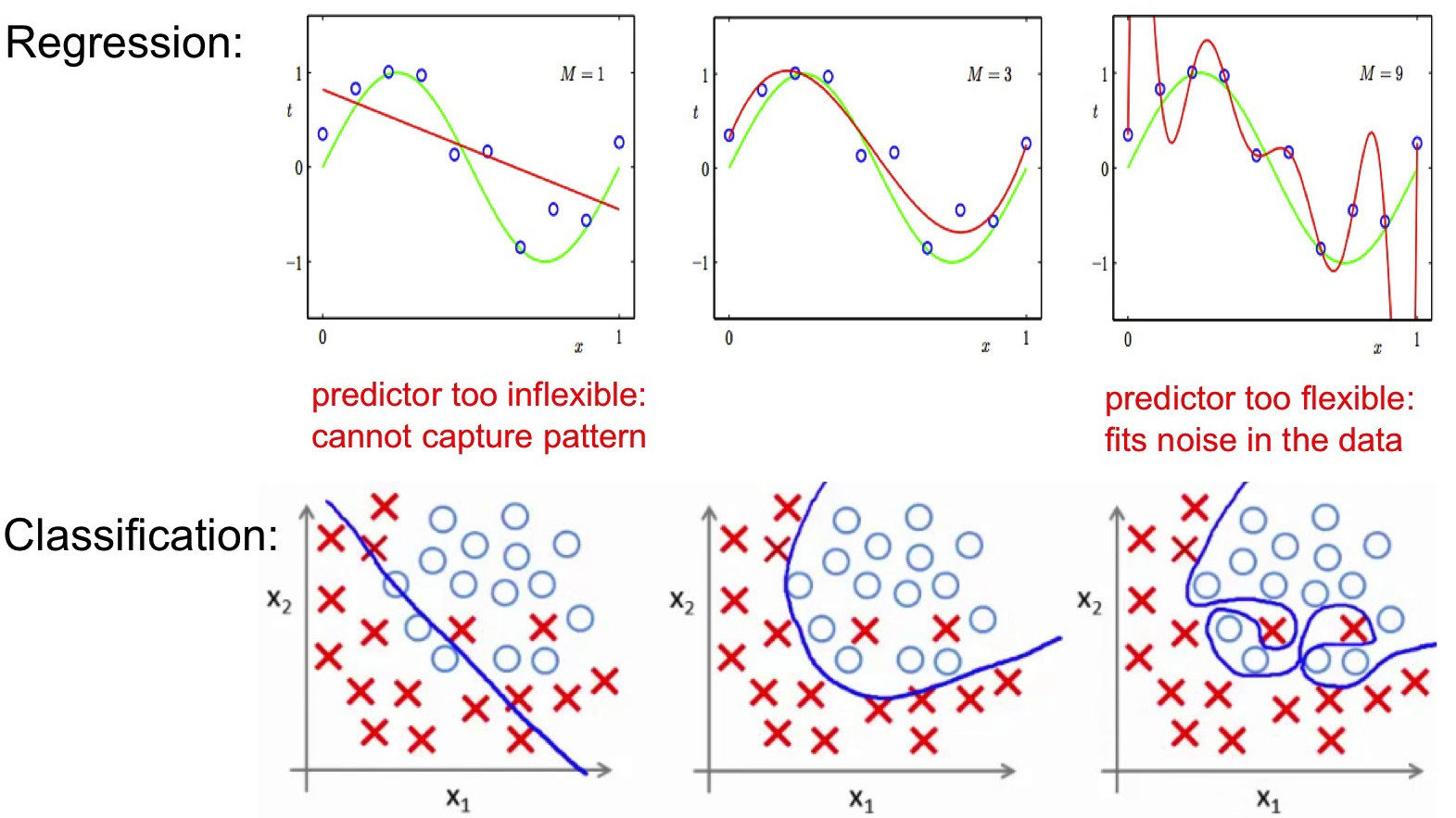
biais / variance tradeoff
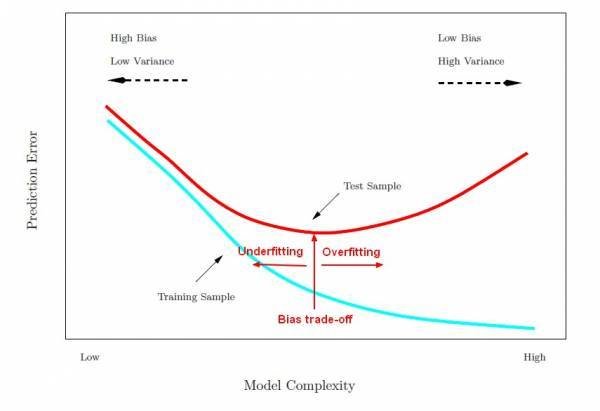
learning curves as fonction of model complexity

In practice we often observe a double gradient descent with an error peak in the middle
Curse of dimensionality
Problem that appears when our dataset contains many variables compared to the number of observations
...
...
...
variables
observations
Curse of dimensionality & k-NN
"A space almost empty of points"
No free lunch theorem in supervised learning
Under certain conditions, the performance of all algorithms is identical on average
Consequence: there is no "ultimate" algorithm that would always give the best performance for a given dataset
Non computable problems
Class of problems that cannot be solved in a reasonable time, i.e. that have a high algorithmic complexity
Some solutions to this limitations
Data split
Problem: evaluate the generalization performance of a model while avoiding over fitting
We sample the data in three parts:
data set
test
training & validation
validation
test
training
Cross validation
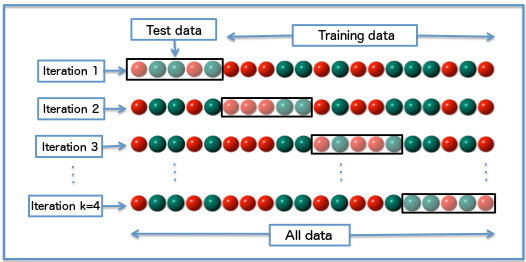
Problem: evaluate the generalization performance of a model while avoiding over fitting
Feature selection
Principle : Select from the dataset the minimum number of features that contribute the most to good performance
Threshold Methods
...
Intrinsic methods
Objectif : reduce model complexity
Wrapper methods
correlations
information gain
...
threshold methods
recursive feature elimination
hierarchical selection
LASSO
Ridge
...
Domain knowledge
Feature selection
Only applies to the training set, not to the test set --> risk of data leakage
Pitfalls to avoid:
To be applied during each fold of the cross-validation at the same time as the model training !

Regularisation
Idea: constrain coefficient values to limit their variation
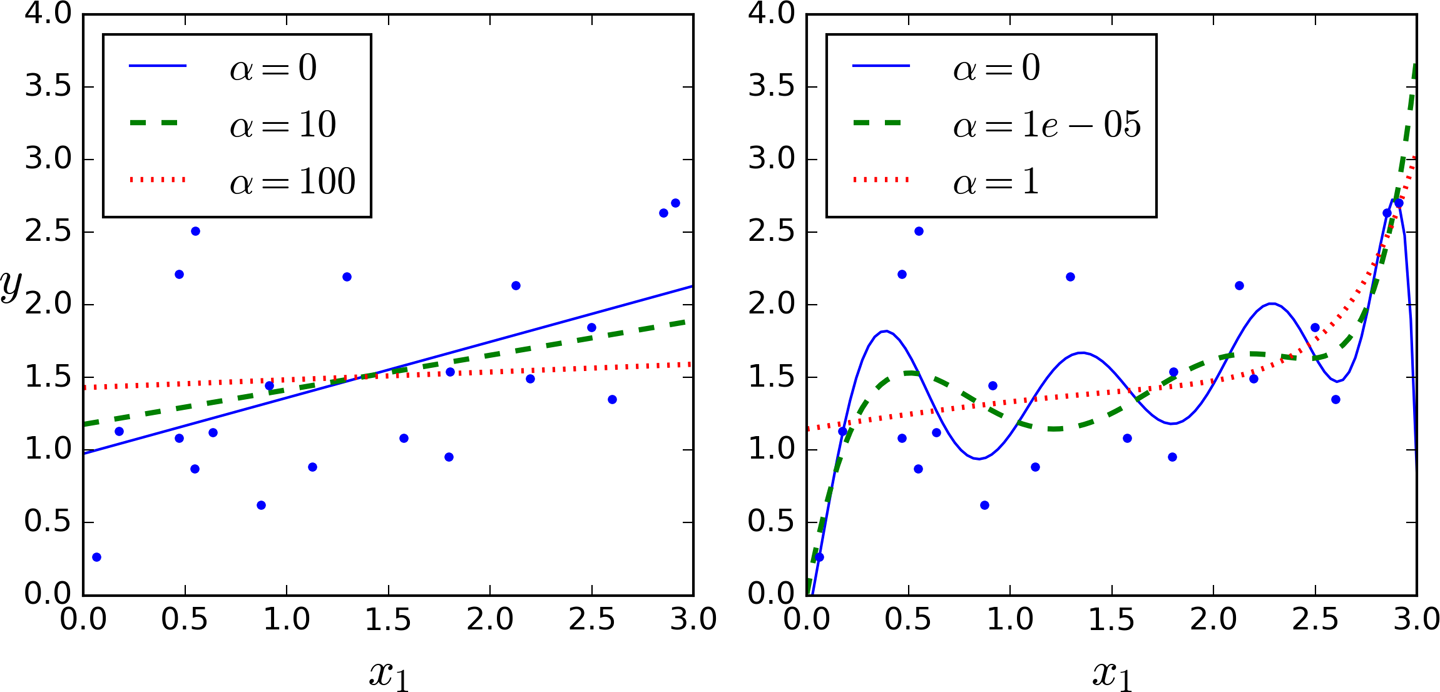
linear regression
polynomial regression
Data augmentation
Transform or enrich existing data
Add more données (volume & variety)
business data, open data, scraping ...
Feature engineering :
create new variables
enrichment (annotations, metadata, ...)
transformations (image deformations, ...)
The end
Thanks for trying to minimize your error function :)
[Summary] Fondamentals of ML
By Nicolas Rochet
[Summary] Fondamentals of ML
Revisions Cours 2020 - 2021 Masters Data Science & IA
- 63



