Is registration of births/deaths mandatory?
- Registration of Deaths and Still births in India is mandatory as per Registration of Births and Death Act (RBD Act), 1969
- It is done as per place of occurrence of the event
Responsible person for informing the fact of “death” to the designated Registrars
| Place of death | Informant |
|---|
| 1)Hospital, nursing home, etc. | Medical Officer in-charge (M.O. I/c) or any person authorized by the M.O. I/c |
| 2)Other institutions |
| a)Hotel, hostel, dharamshala, etc. | Person in-charge |
| b)Jail | Jailor in-charge |
| 3)Home |
| a)In village | Head of the household or other relative to ANM/ASHA/AWW* |
| b)In town, city, etc. | Head of the household or other relative to Municipal Health Officer/ Registrar in-charge |
Responsible person for informing the fact of “death” to the designated Registrars
| Place of death | Informant |
|---|
| 4)Moving vehicle |
| a)Ambulance | Driver |
| b)Other vehicle (airplane, ship, tonga, etc.) | Person in-charge of the moving vehicle |
| 5)Plantation | Superintendent/ Manager |
| 6)Public place (eg road, bus-stand, etc.) | Head of the household or other relative to ANM/ASHA/AWW* |
| a)In village | Panchayat (village) head |
| b)In town, city, etc. | Officer-in-charge of local police station |
| * ANM = Auxiliary Nurse & Midwife; ASHA = Accredited Social Health Activist; AWW = Anganwadi worker (all three are village level government workers) |
Additional information
| Prescribed period for notification of death/still-birth to Registrar of Births/Deaths |
|---|
| 21 Days |
| Official document that will be handed over to the family by the Registrar |
|---|
| the 'Death Certificate’ (this will state the date and place of death but not the cause-of-death) (FORM 6) |
| Fee to be charged by the Registrar for issuing the official government 'Death Certificate' |
|---|
| Nil (=zero) |
| Can late registration be done beyond 21 days after death? And if so, how? |
|---|
| 21 to 30 days --> on payment of Rs. 2/- fine 31 days to 1 year --> on approval by Officer on payment of Rs. 5/- fine After 1 year --> on approval by a First Class Magistrate and on payment of Rs. 10/- fine |
Form 6 - Government issued death certificate

When to fill the MCCD form?
-
From the previous slides, it is now clear that when the death occurs in the hospital, the Superintendent or Medical Officer in-charge is bound to notify the Government registrar about the fact of death. In addition, the cause-of-death must also be intimated. This depends on whether it is a natural death or a medico-legal case, as determined below from the manner of death
| Manner of death |
|---|
| Natural (=biomedical) |
| Accident/ suicide / homicide /undetermined intent (=medico-legal) |
When to fill the MCCD form?
-
If it is a medico-legal case, the final cause-of-death form can be submitted after the enquiry is over; but if it is a natural cause of death, then the cause-of-death form (Form 4 or 4A) must also be submitted to the government registrar by the hospital superintendent along with the notification of the fact of death
-
Hence the attending physician must certify the Cause-of-death soon after death
Who should fill the MCCD form - ordinary cases?
| Death in Hospital | Who is to certify? |
|---|
| 1. Ward, OPD, ICU, Operating theatre, etc | - attending physician of the hospital |
| 2.Emergency Room (ER) | - attending physician in E.R. (based on whatever information is available; can fill MCCD form immediately if natural death and can fill later if medico-legal case) |
Who should fill the MCCD form - ordinary cases?
| Death outside hospital and brought dead | Who is to certify? |
|---|
| For eg Death in ambulance or at home or on the way |
1)If medico-legal case – wait for final autopsy/enquiry report 2)If natural death – a)If patient of the hospital discharged/taken discharge due to poor prognosis or while referring out to another hospital, then ER physician can fill Form 4A in consultation with the attending physician b)If brought dead as a fresh case, Form 4A needs to be filled by the usual family physician or physician assigned by the Civil registrar |
What is to be handed over to the relatives?
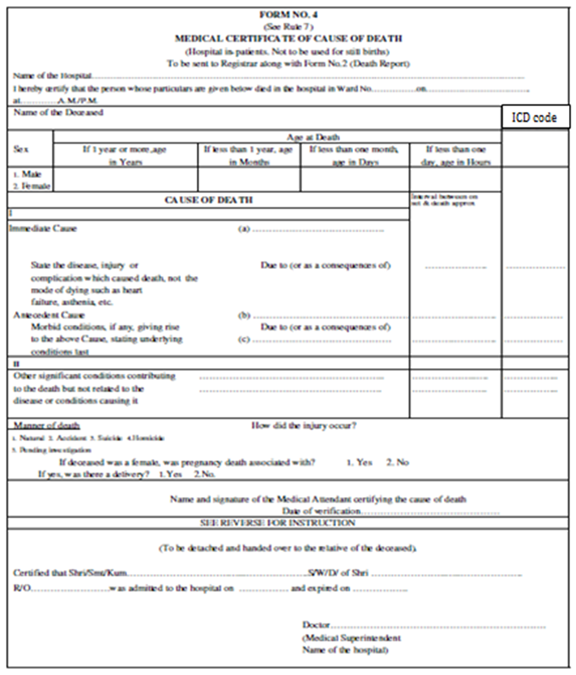
Only this bottom tear-off portion of the MCCD Form 4 (for hospital death)
What is to be handed over to the relatives?
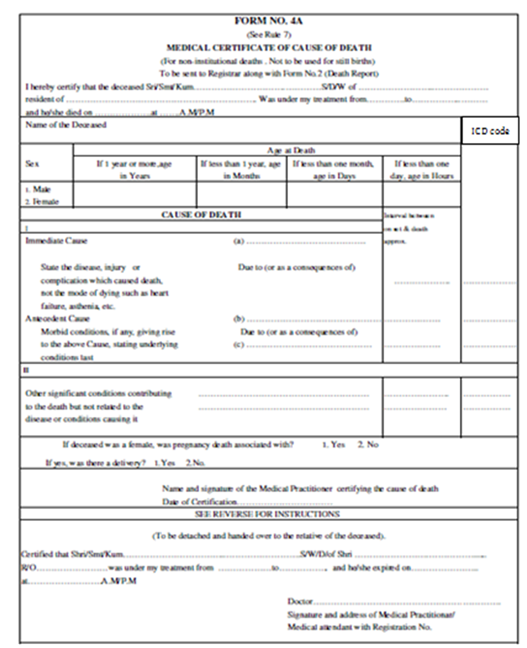
Only this bottom tear-off portion of the MCCD Form 4A (for out-of-hospital death)
What will the relative do with the tear-off portion? And what is its use?
2)Show at government registrar office to get the Govt death certificate (form 6)
The relative will use the tear-off portion for 2 main uses:
1)Produce at cemetery/ crematorium for burial/ cremation
What will the relative do with the tear-off portion? And what is its use?
Government Death Certificate (Form 6) by the Government office is issued to the relative only when Form 4 or 4A tear-off portion and Form 2 is submitted together by the relative to the Government office

Form 6

What to do for Home Deaths
| For event notification according to time period | <30 days | 31 days to 1 year | > 1 year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1)For fact of death | ≤21 days free 22-30 on payment of Rs. 2/- fine |
- with affidavit by notary public or other authorized officer (eg revenue officer) & - payment of Rs. 5/- fine |
- By magistrate of 1st class after verification & - Payment of Rs. 10/- fine |

What to do for Home Deaths
| For event notification according to time period | <30 days | 31 days to 1 year | > 1 year |
|---|
| 2)For cause-of-death | Form 4A by medical officer from PHC (or) family physician (or) medical officer authorized by the municipality/corporation (or) from hospital (where patient was last being seen for terminal illness) |
Probable medico-legal cases…
• any suicide
• any accident
• any death by drowning
• any death by burning, scalding, fire or explosion
• certain deaths of children - any sudden death in
infancy, any death due to suffocation, any death of a foster child
Probable medico-legal cases…
• death arising out of the use of a vehicle including a bus, lorry, train, aircraft. etc
• death involving fault or neglect on the part of another
• any death due to violent, suspicious or unexplained cause
• any death due to poisoning or suspected poisoning, including by prescription or non- prescription drugs, other substances, gas or solvent fumes
Probable medico-legal cases…
• any death as a result of medical mishap
• any death in legal custody
e-MCCD M3U2S1 final
By drkavya1
e-MCCD M3U2S1 final
- 187



