Data Visualization with D3
David Leonard
March 10th, 2016
David Leonard
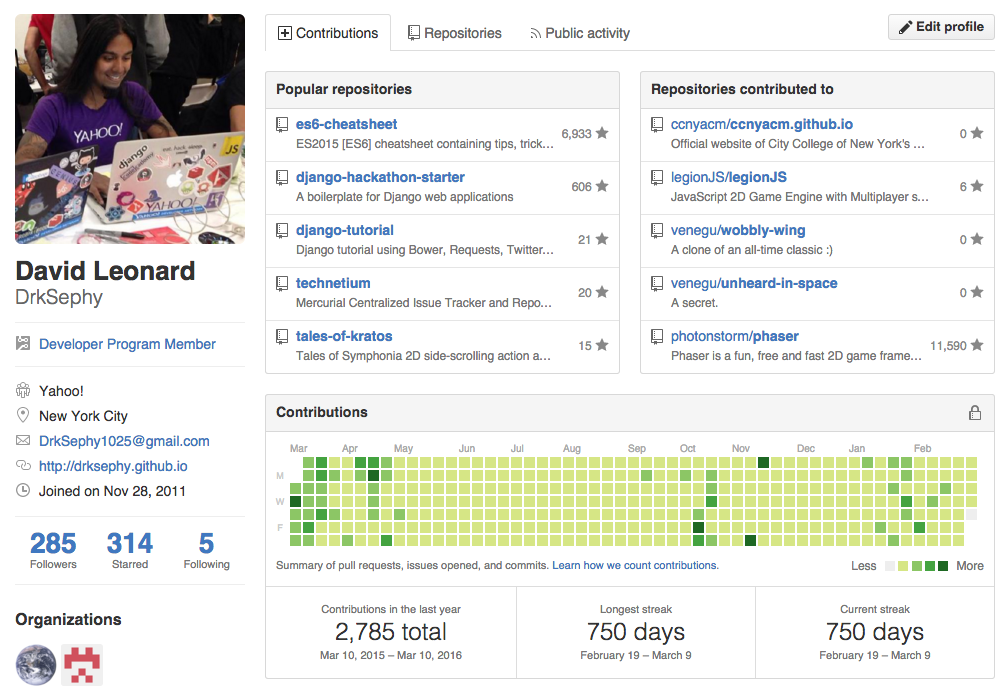
David Leonard
What I do:
Grad Student
Dev Games
Yahoo!



What is D3?
Data
- Driven
Documents
HTML

Hyper
Text
Markup
Language
<tagname>content</tagname>
HTML
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>

HTML Attributes
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id='someID'>My First Heading</h1>
<p class='someClass'>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
DOM Tree

Document Object Model
CSS

Cascading
Style
Sheets
p { color: red; font-size: 10px; }
CSS
css selector
property
value
CSS
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
<style type='text/css'>
p {
color: red;
}
</style>

External CSS
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
p {
color: red;
}
styles.css
<link rel='stylesheet' href='styles.css'/>
CSS ID Selector
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id='someID'>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
#someID {
color: red;
}
styles.css
<link rel='stylesheet' href='styles.css'/>
CSS Class Selector
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class='someClass'>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
.someClass {
color: red;
}
styles.css
<link rel='stylesheet' href='styles.css'/>
JavaScript
What can JavaScript do?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM Manipulation example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>JavaScript is magic.</p>
</body>
</html>
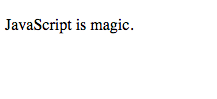
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM Manipulation example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>JavaScript is magic.</p>
</body>
</html>
<script type='text/javascript'>
var paragraphs = document.getElementsByTagName('p');
for(var i = 0; i < paragraphs.length; i++) {
paragraphs[i].style.color = 'red';
}
</script>

JavaScript is pretty cool!

...right?

Interactive Stories
credit: http://www.dangersoffracking.com/

Awesome Browser Games

Interactive Visualizations



EcmaScript
EcmaScript
Language Specification


EcmaScript 2016 (ES6)
Latest Version of JavaScript
Classes
Modules
Let / Const
Scope
EcmaScript 2016 (ES6)



JavaScript Crash Course
Functions
function multiply(x, y) { return x * y; }
Function constructor
var multiply = function(x, y) { return x * y; };
Anonymous Function
var multiply = function func_name(x, y) { return x * y; };
Function in variable
Scope
var snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
if (food) {
var snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// undefined
// undefined
Scope
var snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
var snack;
if (food) {
snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
Hoisting!
(A)
(B)
Scope Continued
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
});
}
Object Property
// Cannot read property 'name' of undefined
Scope Continued
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
var that = this;
return arr.map(function (character) {
return that.name + character;
});
};
// Store this
Arrow Functions (ES6)
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map((character) => this.name + character);
}
Arrow Functions (ES6)
return arr.map(function (character) {
return that.name + character;
});
return arr.map((character) => this.name + character);
Objects
Just a collection of key / value pairs
var person = {
firstName:'David',
lastName:'Leonard',
age:25,
eyeColor:'brown'
};
> person.firstName // 'David' > person.eyeColor // 'brown
Method Chaining
var obj = {
first: function() { alert('first'); return obj; },
second: function() { alert('second'); return obj; },
third: function() { alert('third'); return obj; }
}
obj.first().second().third();
JavaScript is Aysnchronous!
Sync vs Async
var users = [];
$.get('/users', function(data) {
users = data;
});
renderUsersOnPage(users);
Asynchronous Call
Callback Functions
$.get('/users', (data) => {
var users = data;
renderUsersOnPage(users);
});
Callback Hell
func1(function (value1) {
func2(value1, function (value2) {
func3(value2, function (value3) {
func4(value3, function (value4) {
func5(value4, function (value5) {
// Do something with value 5
});
});
});
});
});
Promises
new Promise(resolve => resolve(data))
.then(result => console.log(data));
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
reject(new Error('Failed to fufill Promise')))
.catch(reason => console.log(reason));
Promises








Promises
var userData = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.get('/users', (data) => {
if (data) {
resolve(data);
} else {
reject(new Error('Failed to fetch data'));
}
});
});
renderUsersOnPage(userData);
D3 Fundamentals
Selections
var paragraphs = document.getElementsByTagName('p');
for(var i = 0; i < paragraphs.length; i++) {
paragraphs[i].style.color = 'red';
}
.selectAll( )
d3.selectAll('p').style('color', 'red');
.select( )
d3.select('body').append('p').text('New paragraph!');
var body = d3.select('body');
var p = body.append('p');
p.text('New paragraph!');
Binding Data
d3.selectAll('p')
.data([4, 8, 15, 16, 23, 42])
.style('font-size', function(d) { return d + 'px'; });
Virtual Selections
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="d3.v2.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html
var dataset = [ 1, 2, 3 ]
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('p')
.text('hello');
Virtual Selections
.enter( )
.update( )
.exit( )
Virtual Selections
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
Virtual Selections
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('p')
Virtual Selections
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('p')
.text('hello')
Virtual Selections
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('p')
.text('hello')
console.log(p);
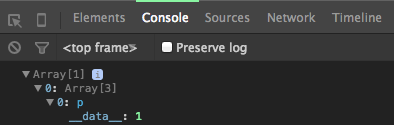
Virtual Selections
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('p')
.text( function (d) { return d; } );
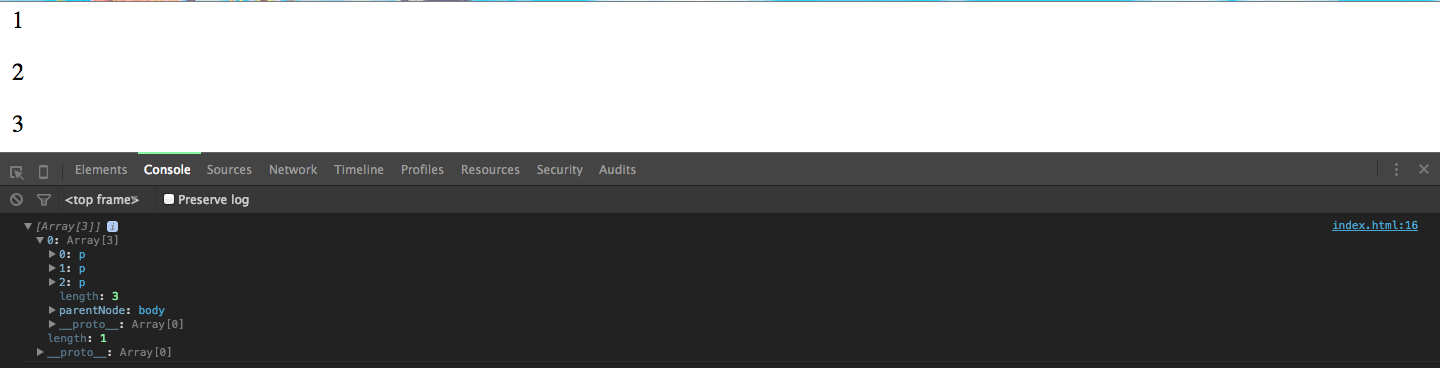
Virtual Selections
var p = d3.select('body').selectAll('p')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('p')
.text( function (d, i) { return 'd=' + d + ' , i= ' + i ; } );
console.log(p);
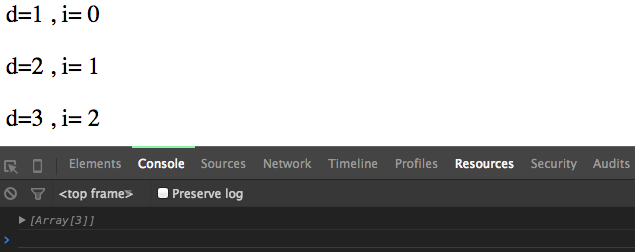
Update and Exit
var numbers = [15, 8, 42, 4];
<div id="chart">
<div class="bar" style="height: 15px; margin-top: 85px;"></div>
<div class="bar" style="height: 8px; margin-top: 92px;"></div>
<div class="bar" style="height: 42px; margin-top: 58px;"></div>
<div class="bar" style="height: 4px; margin-top: 96px;"></div>
</div>
function update() {
var selection = d3.select('#chart')
.selectAll('.bar').data(numbers)
}
Update and Exit
function update() {
var selection = d3.select('#chart')
.selectAll('.bar').data(numbers)
}
.style('height', function(d) {
return d;
})
.style('margin-top', function(d) {
return 100 - d;
})
.on('click', function(e, i) {
numbers.splice(i, 1);
update();
});
Update and Exit
function update() { ... };
selection.enter()
.append('div').attr('class', 'bar')
.style('height', function(d){
return d;
})
.style('margin-top', function(d){
return 100 - d;
})
.on('click', function(e, i){
numbers.splice(i, 1);
update();
});
selection.exit().remove();
Update and Exit
d3.select('#add-btn').on('click', function(e) {
numbers.push(Math.round(Math.random() * 100));
update();
});
Update and Exit

Scales
Scales are functions that map from an input domain to an output range.
Mike Bostock
Scales
var dataset = [ 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 ];
What if we had larger numbers?
Linear Scales
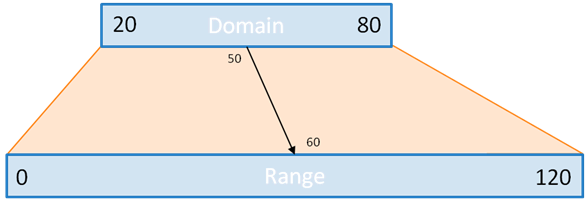
credit: http://www.jeromecukier.net/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/d3scale1.png
Linear Scale Construction
var scale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([100, 500])
.range([10, 350]);
> scale(100); // Returns 10
> scale(300); // Returns 180
> scale(500); // Returns 350
Scalable Vector Graphics
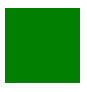
SVG Rectangle
<svg width='50' height='50'>
<rect x='0' y='0' width='50' height='50' fill='green' />
</svg>
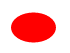
SVG Circle
<svg width='50' height='50'>
<circle cx='25' cy='25' r='25' fill='purple' />
</svg>

SVG Ellipse
<svg width='50' height='50'> <ellipse cx='25' cy='25' rx='15' ry='10' fill='red' /> </svg>
SVG Lines
<svg width='50' height='50'>
<line x1='5' y1='5' x2='40' y2='40' stroke='gray' stroke-width='5' />
</svg>

SVG Paths
<svg width='100' height='100'> <path d=' stroke='red' stroke-width='2' fill='none' />
</svg>
M 10 25
L 10 75
L 60 75
L 10 25'
SVG Groups
<svg width='200' height='200'>
<circle cx='20' cy='20' r='20' fill='green' />
<circle cx='70' cy='70' r='20' fill='purple' />
<rect x='110' y='110' height='30' width='30' fill='blue' />
<rect x='160' y='160' height='30' width='30' fill='red' />
</svg>
<g>
<g>
<g/>
<g/>
Axes
Constructing Axes
var svgContainer = d3.select('body').append('svg')
.attr('width', 400)
.attr('height', 100);
var axisScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, 100])
.range([0, 400]);
var xAxis = d3.svg.axis()
.scale(axisScale);
var xAxisGroup = svgContainer.append("g")
.call(xAxis);
Constructing Axes
Constructing Axes
var width = 500;
var height = 300;
var padding = 30;
var dataset = [
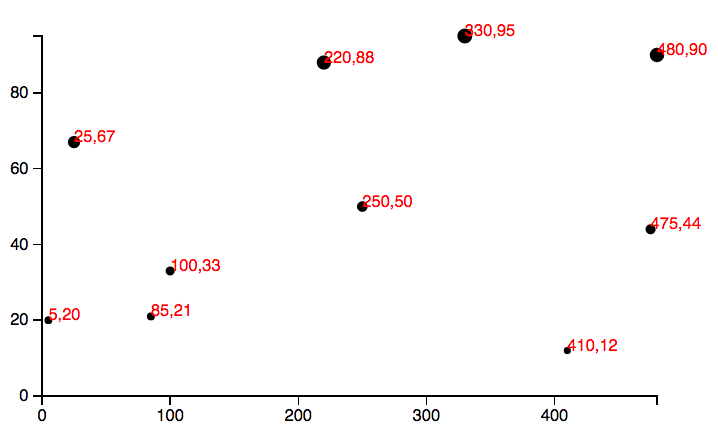
[5, 20], [480, 90], [250, 50], [100, 33], [330, 95],
[410, 12], [475, 44], [25, 67], [85, 21], [220, 88]
];
Constructing Axes
var xScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, d3.max(dataset, function(d) { return d[0]; })])
.range([padding, width - padding * 2]);
var yScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, d3.max(dataset, function(d) { return d[1]; })])
.range([height - padding, padding]);
var rScale = d3.scale.linear()
.domain([0, d3.max(dataset, function(d) { return d[1]; })])
.range([2, 5]);
Constructing Axes
var xAxis = d3.svg.axis()
.scale(xScale)
.orient('bottom')
.ticks(5);
var yAxis = d3.svg.axis()
.scale(yScale)
.orient('left')
.ticks(5);
Constructing Axes
var svg = d3.select('body')
.append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height);
Constructing Axes
var svg = d3.select('body')
.append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height);
Constructing Axes
svg.selectAll('circle')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('circle')
.attr('cx', function(d) {
return xScale(d[0]);
})
.attr('cy', function(d) {
return yScale(d[1]);
})
.attr('r', function(d) {
return rScale(d[1]);
});
Constructing Axes
svg.selectAll('text')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('text')
.text(function(d) {
return d[0] + ',' + d[1];
})
.attr('x', function(d) {
return xScale(d[0]);
})
.attr('y', function(d) {
return yScale(d[1]);
})
.attr('font-family', 'sans-serif')
.attr('font-size', '11px')
.attr('fill', 'red');
Constructing Axes
svg.append('g')
.attr('class', 'axis')
.attr('transform', 'translate(0,' + (height - padding) + ')')
.call(xAxis);
svg.append('g')
.attr('class', 'axis')
.attr('transform', 'translate(' + padding + ',0)')
.call(yAxis);
Constructing Axes
Thanks!
Github: https://github.com/DrkSephy
ES6 Cheatsheet: https://github.com/DrkSephy/es6-cheatsheet
Dashing D3: https://www.dashingd3js.com/
D3 Resources
Scott Murray: http://alignedleft.com/tutorials/d3
D3 Blocks: https://bl.ocks.org/
D3 Slides: https://bost.ocks.org/mike/d3/workshop/#0
Data Visualization with D3
By David Leonard
Data Visualization with D3
A brief dive into HTML / CSS / JS along with a deep dive into D3.js.
- 7,717



