Web Design
The Web
| HTML | Meaning and Content |
| CSS | Presentation & Style |
| JavaScript & jQuery | Scripting, manipulating the DOM |
Excellent resource: W3 Schools
Styling and Layout with CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheet)
- Style sheet language
- Associates style rules with HTML elements
- Reusable
- Styles "cascade", or have known order of precedence
- 2 Parts: selection of elements to apply style property values
(w3schools)
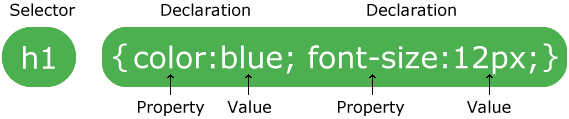
Syntax
- Each rule has one or more selectors and a declaration block
- Declaration block contains a set of properties with their values
body {
font-family: Arial, Verdana, sans-serif;
font-size: 12px;
color: #6605AA;
}body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 20px;
}Selectors
How to access specific elements
/* Select specific elements, here all <h1>, <h2> and <h3>
(using grouping syntax) */
h1, h2, h3 { }
/* Select all elements where class attribute has value
* "questions" */
.questions { }
/* Select all <p> elements where class attribute has value
* "questions" */
p.questions { }
/* Select all elements where id attribute has value
* "topstory" */
#topstory { }id Attribute
A global attribute. Used to uniquely identify an element (from CSS or Javascript).
Common use of id attribute
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#myHeader {
background-color: lightblue;
color: black;
padding: 40px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="myHeader">My Header</h1>
</body>
</html>
Output from the id attribute code
class Attribute
Used to make this element a member of a named class. Also a global attribute.
Common use of class attribute
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.city {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
border: 2px solid black;
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="city">
<h2>London</h2>
<p>London is the capital of England.</p>
</div>
<div class="city">
<h2>Paris</h2>
<p>Paris is the capital of France.</p>
</div>
<div class="city">
<h2>Tokyo</h2>
<p>Tokyo is the capital of Japan.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Output from the class attribute code

| Selector | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| #id | #firstname | Selects the element with id="firstname" |
| .class | .intro | Selects all elements with class="intro" |
| element.class | p.intro | Selects only <p> elements with class="intro" |
| * | * | Selects all elements on a page |
| element | p | Selects all <p> elements |
| element,element,.. | div, p | Selects all <div> elements and all <p> elements |
Properties
Just about anything you can think of. Properties for:
- Colors
- Fonts, font weight
- Borders
- Spacing, position, margins, alignment
- Layout of elements and flow
CSS Colors
Colors can be applied using:
name ->
<h1 style="background-color:DodgerBlue;">Hello World</h1>
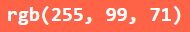
rgb value ->
<h1 style="background-color:rgb(255, 99, 71);">rgb(255, 99, 71)</h1>
hex value ->
<h1 style="background-color:#065535;">#065535</h1>

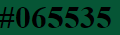
Where to put it?
- In the element
- In the head of the document
- In a separate file, "imported" via a link element
Precedence (Cascading)
When two or more selectors match an element, the rule closest to the element is applied.
In most cases:
Inline style - will be closest.
<h2 style="color: red;">This text will be red always</h2>
In the header - will be next.
<head>
<style type="text/css">
h2{
style="color: blue;"
}
</style>
In an external style sheet will be furthest. Two rules in the same style sheet - the one furthest down (it is closer)
h2{
style="color: purple;" }
<!--index.html-->>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet"href="css/styles.css">
</head>
In the element
<p style="font-family:tahoma"> Lorem ipsum dolor sit
amet consectetur adipisicing
<span style="vertical-align:sub;border-style:dotted;
border:3px dotted rgb(255, 0, 212);border-radius:20px;
font-size:120%;font-family:Impact, sans-serif">elit.</span>
</p> 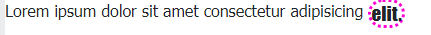
In the head of the document
<head>
<style type="text/css">
body {
background-color: silver;
color: white; }
</style>
</head>
In a separate file
/* File: css/styles.css */
body {
background-color: purple;
color: white;
}
ul li {
list-style-type: square;
}
<!--index.html-->
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/styles.css">
</head>
Bootstrap
-
Get Bootstrap - include via CDN (Content Delivery Network)
- We will copy the links under
- We will focus on the grid system
- Easy to use, implemented with basic HTML and CSS knowledge
- There are a lot of examples with code

What is Bootstrap?
- A framework that makes layout design easy
- Makes responsive design automatic
- Many copy and paste elements, but you need to know what you are doing ;)
As always, an excellent resource: W3 Schools
Constructing a Grid Layout
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Start with basic HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- Latest compiled and minified CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/jquery@3.6.4/dist/jquery.slim.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Add the links to the CDN (Content Delivery Network)
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/jquery@3.6.4/dist/jquery.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/popper.js@1.16.1/dist/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
Next Create the Grid Structure (showing just the content of the body tag)
<body>
<!--First create the container, it holds the grid.
The container can also be fluid-->
<div class="container">
<!--Inside the container there are 1 or more rows that stack-->
<div class="row">
<!--Inside the rows there are columns dividing the width of the row-->
<div class="col">This is</div>
<div class="col">my fancy</div>
<div class="col">layout.</div>
</div>
<!--Inside the container there are 1 or more rows that stack-->
<div class="row">
<!--Inside the rows there are columns dividing the width-->
<div class="col">Again I</div>
<div class="col">am soooo</div>
<div class="col">fancy.+</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>CS Web Design - CSS
By drmorgan
CS Web Design - CSS
- 16



