Data Persistence Layer
Architecture
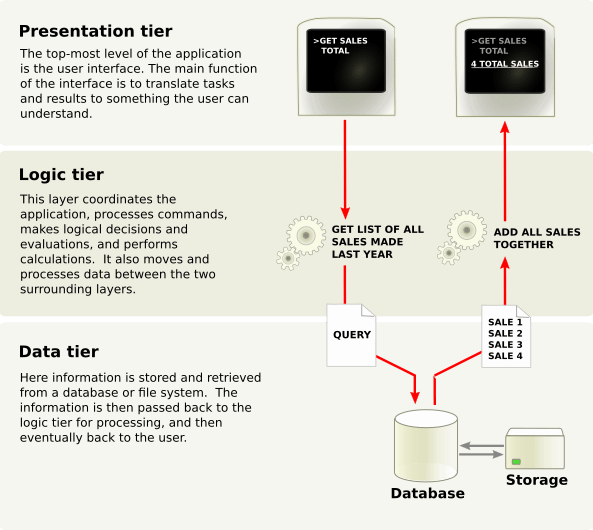
N-Tier “Application”
“N-tier data applications are data applications that are separated into multiple tiers. Also called “distributed applications” and “multitier applications,” n-tier applications separate processing into discrete tiers that are distributed between the client and the server. When you develop applications that access data, you should have a clear separation between the various tiers that make up the application.”
Stack view
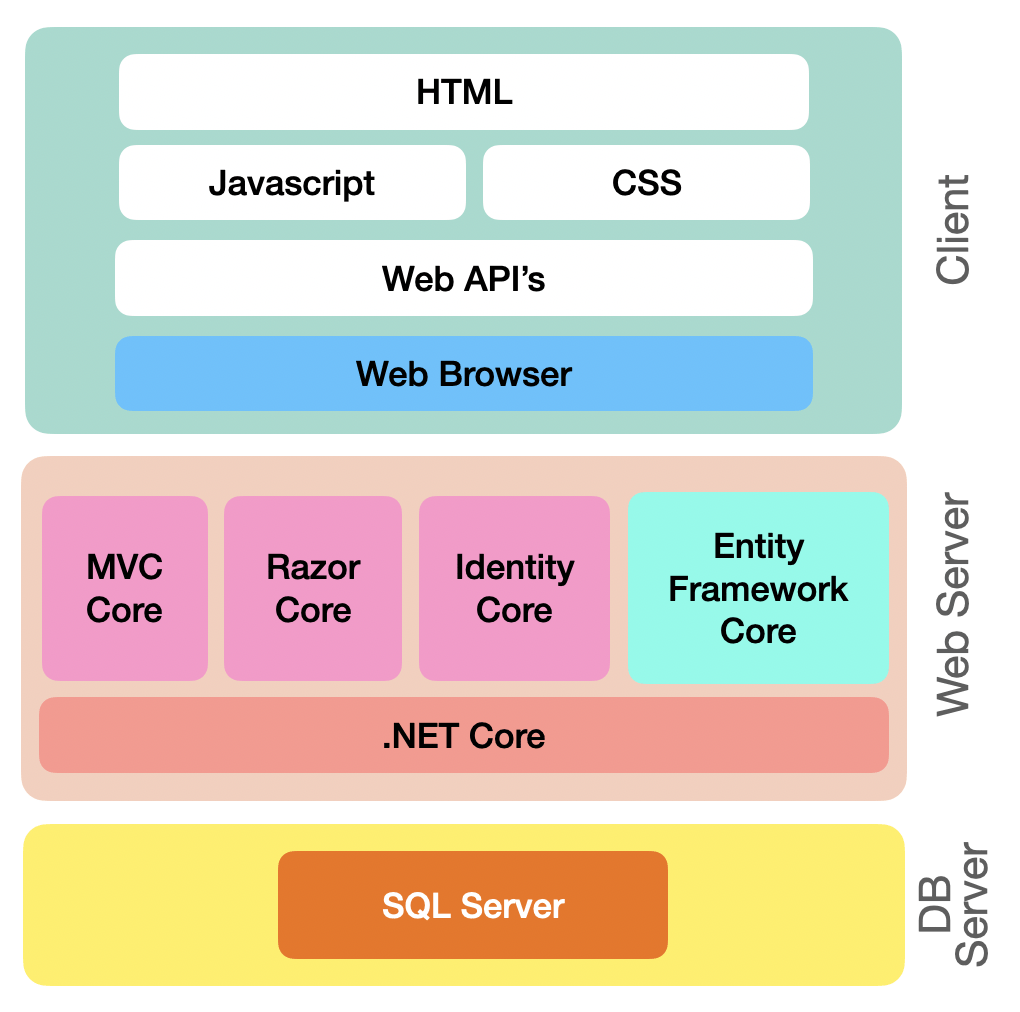
You've already worked top-down, now we'll do bottom-up and connect the two. two.
“Network” view
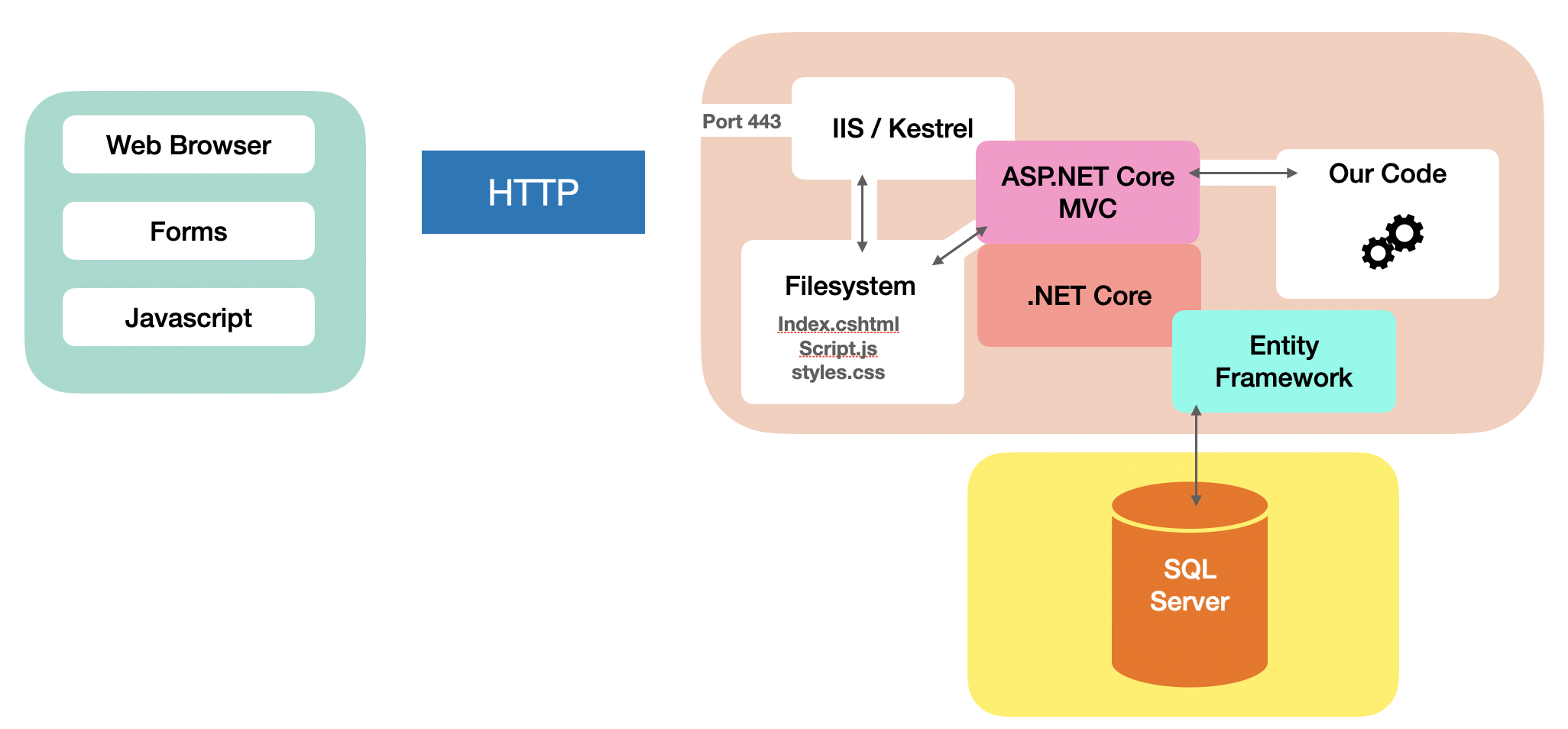
Database
Other possibilities
- NoSQL data stores
- Other DBMS
- File storage, including image stores
- ?
Why MS SQL Server?
- Free
- Integrates well with ASP.NET Core MVP
- Easy to use, configure, and maintain
- Cross Platform
- Lots of Documentation
- Is one you are likely to see
- Deploys easily
Create local SQL Server databases on any platform
- Practice: go make a new one now
Agile Data
Think about a real project...
- What data do you already have?
- What data will you need?
- How will the data be used?
- What needs to be built?
- How will it work?
- ⟶ Requirements
In Reality
- Requirements are hard and messy
- they start fuzzy and ambiguous,
- they change, at any time.
- Solutions are numerous
- can be hard to understand,
- and change frequently.
Agile Data
We need a process such that
- Everyone can clearly understand the current data model at any time
- and compare it with past data models
- See who made changes, why, and when
- Supports versioning
- Easily and with no errors, deploy/update the data model for development/testing/production
- Fully supports automation
- Preferably does not lock you into one brand or toolset
- Supports "Greenfield" or blank slate development
- without an existing database
- but can be translated to
- development with existing db and legacy code
What supports all this?
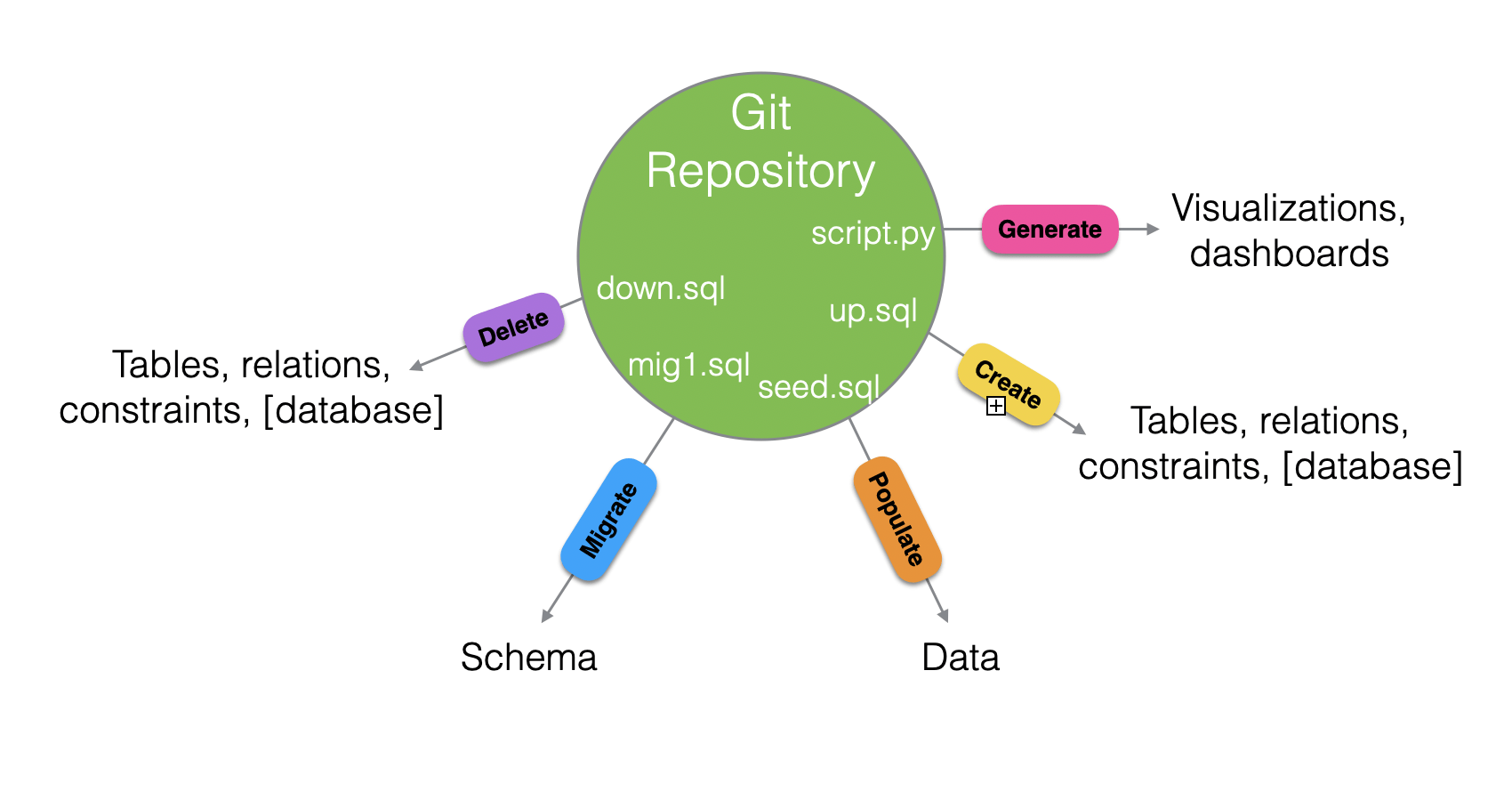
Our Agile Data Process
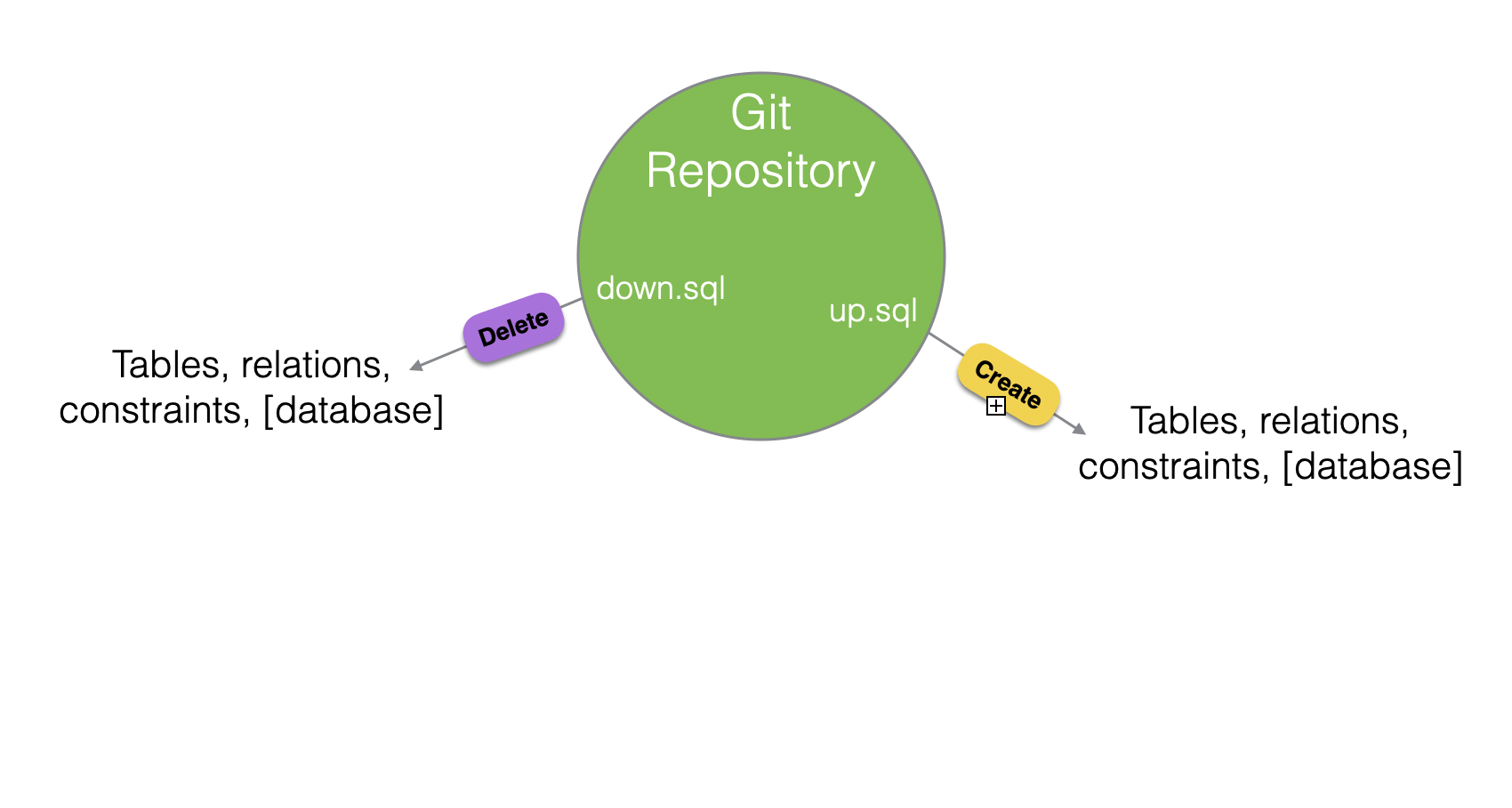
Example
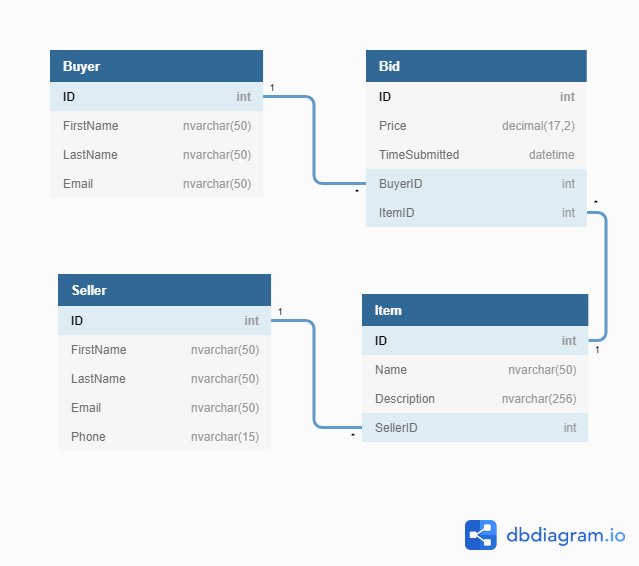
An auction business
- A person can put items up for bid
- A person can bid on items and potentially buy them
- It should be possible to search for items
- We need to be able to distinguish between people who are buying and those selling
- An auction can take place where the highest bidder wins the item
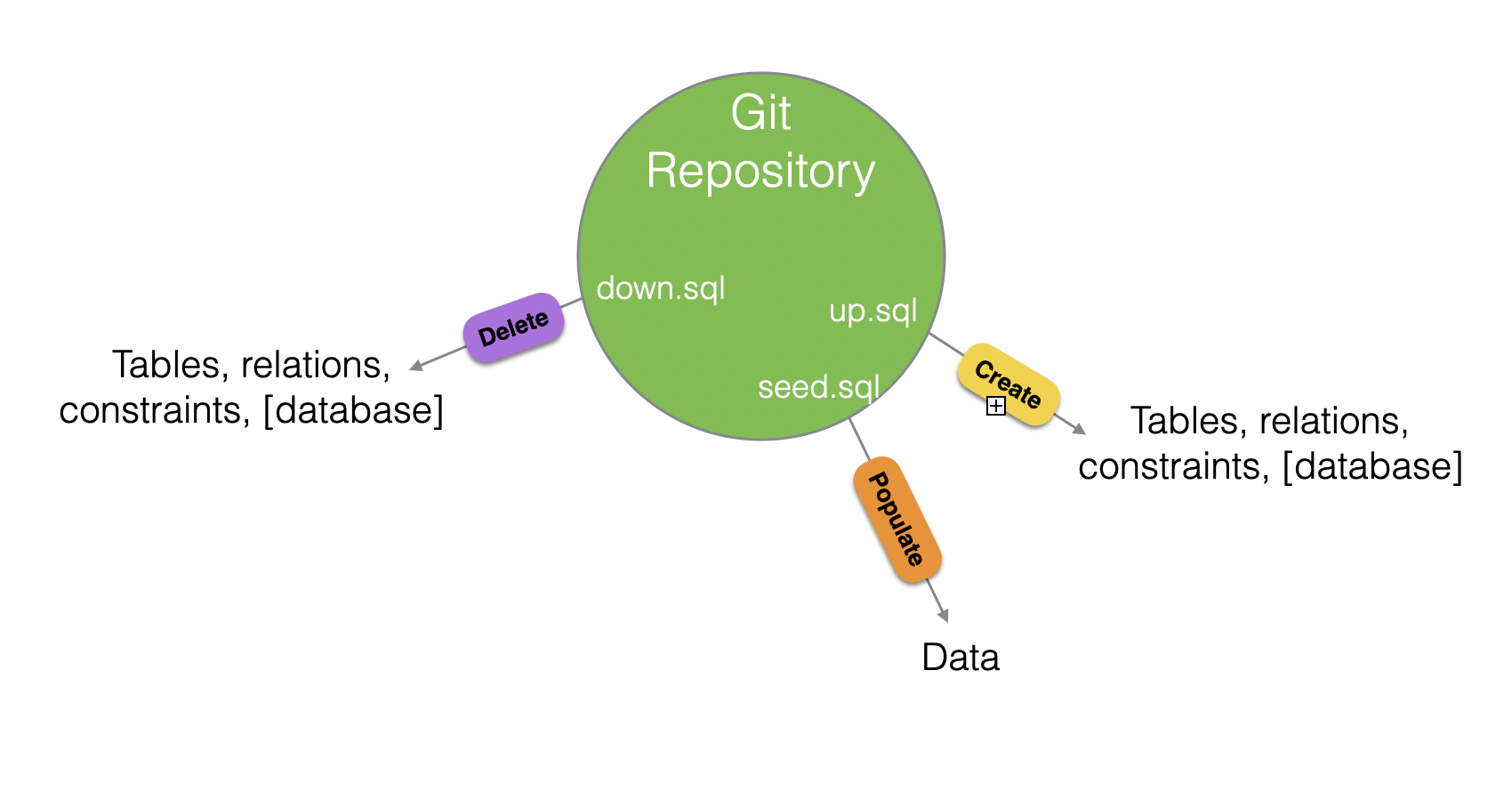
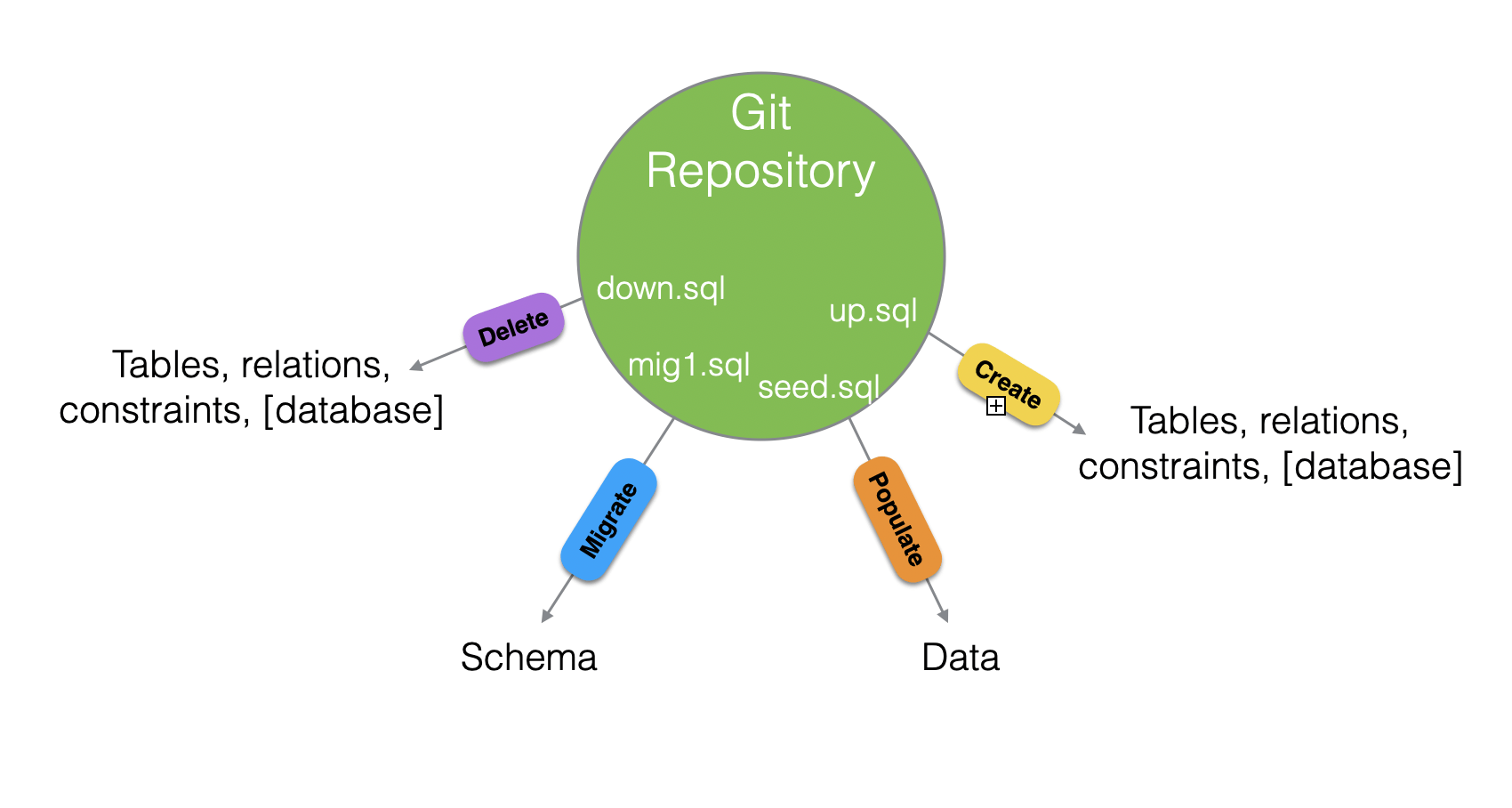
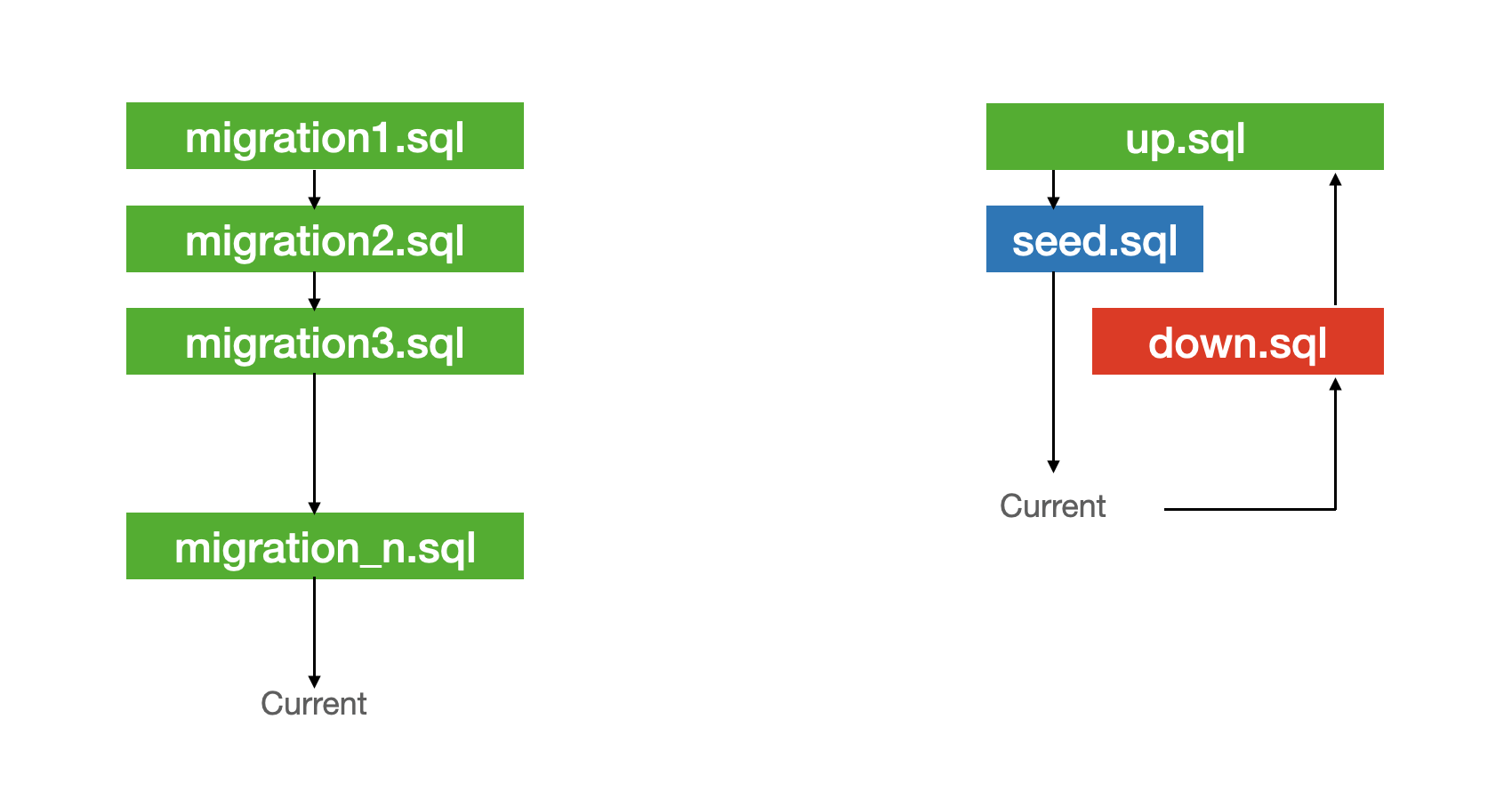
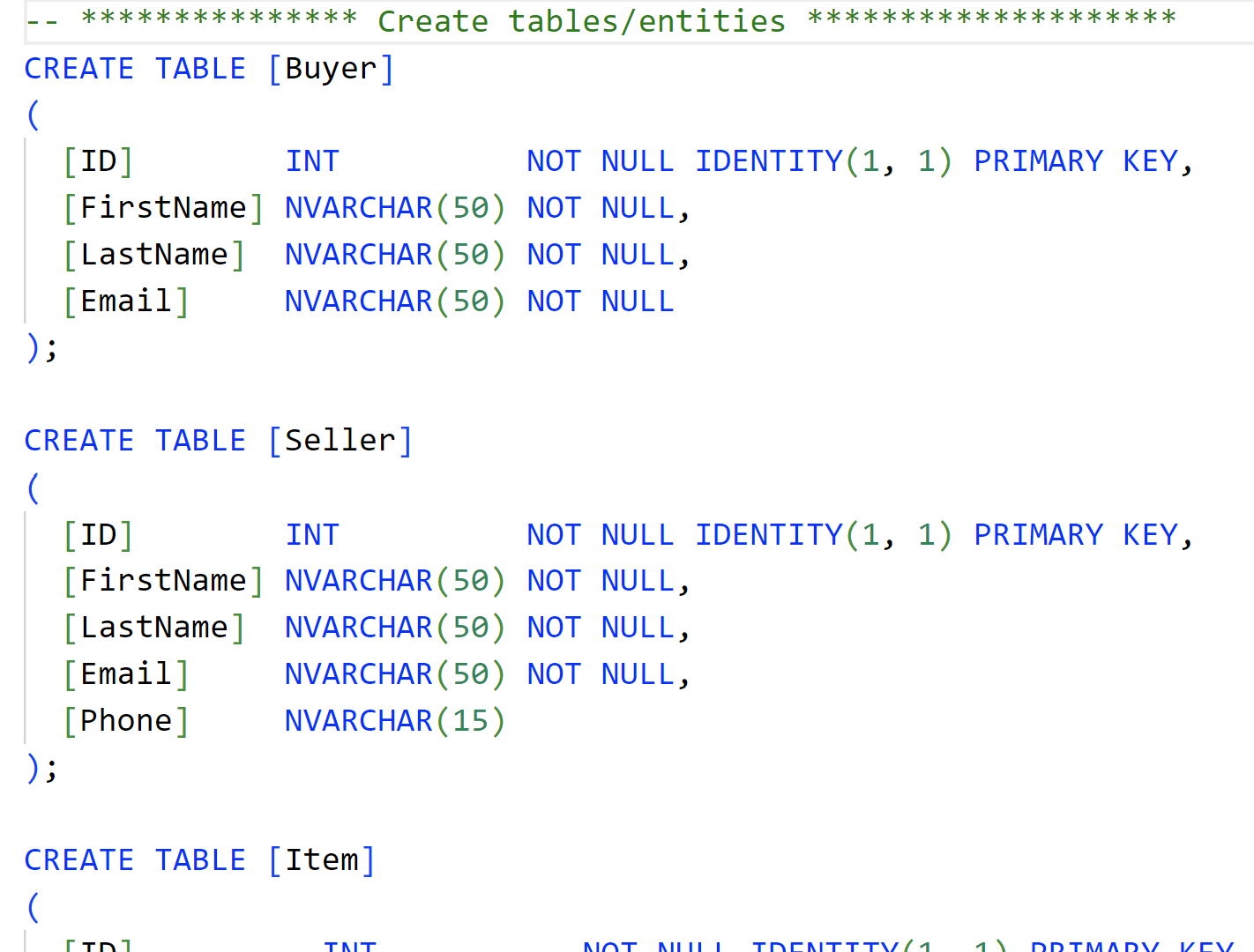
up.sql
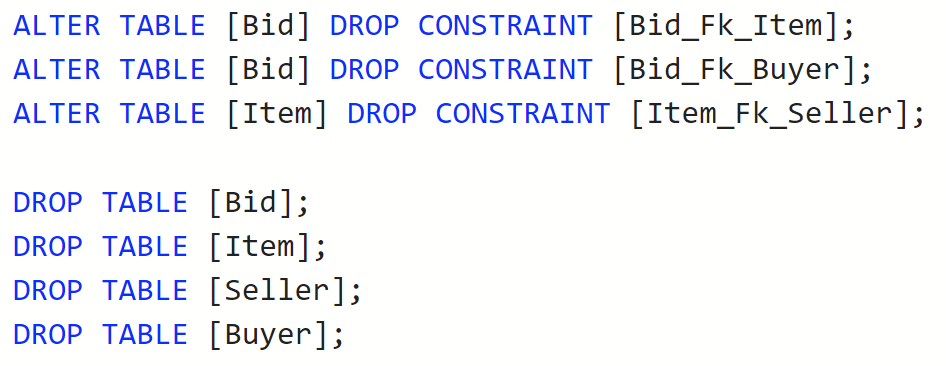
down.sql
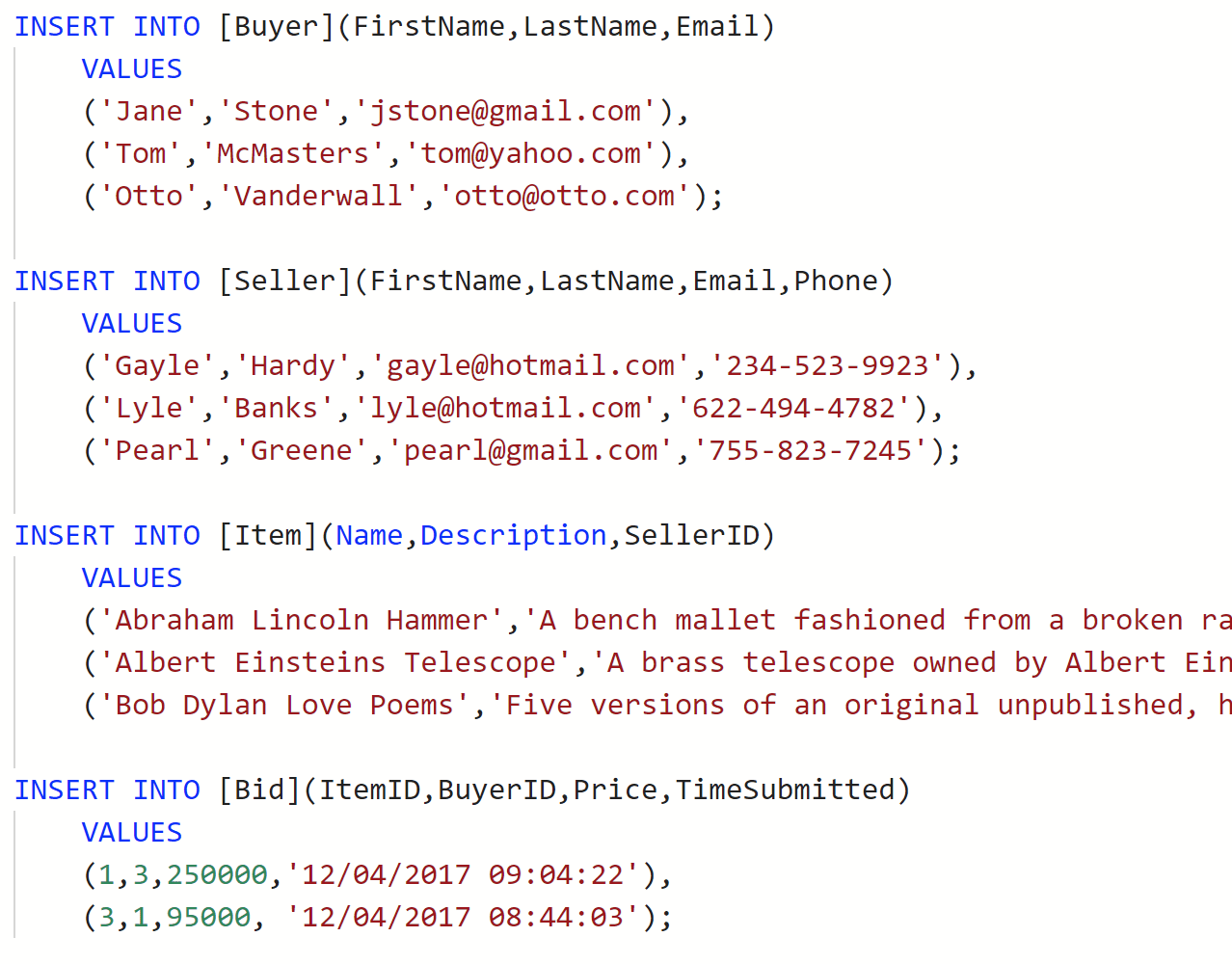
seed.sql
Let's run these
Demonstrations
Now you try one
zyBooks
- Instructors need to be able to create assignments,
- and students complete then before the due date.
- Assignments are made up of content, which can be participation activities, challenge activities, or labs.
Modeling activities
- Identify entities
- Add attributes to entities
- Determine relationships required to support features
- Draw it on a whiteboard or on paper
- Go over needs and features to think if the model supports them, if not:
- Add/remove/change relationships
- Turn an attribute into a relationship or vice versa
- Split or merge entities
- Go back to step 1 and repeat until it is good for now
- Use a tool such as dbdiagram.io to make it formal (especially if this is the first time)
- Export it as SQL Server code and write your up script
- Write down and seed scripts
Data Persistence Layer
By drmorgan
Data Persistence Layer
- 20



