Web Design
The Web
| HTML | Meaning and Content |
| CSS | Presentation & Style |
| JavaScript & jQuery |
Scripting, manipulating the DOM |
Excellent resource: W3 Schools
JavaScript Can Change HTML Content
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello JavaScript";
JavaScript Can Change HTML Styles (CSS)
document.getElementById("demo").style.fontSize = "35px";
JavaScript Can Hide HTML Elements
document.getElementById("demo").style.display = "none";
JavaScript Can Show HTML Elements
document.getElementById("demo").style.display = "block";
The Beginnings
- Types
- Variables
- Operations
- Functions
Primitive Types
- Number (64 bit floating point)
- String (16 bit Unicode)
- Boolean
- BigInt
- Symbol
- undefined
- null (sort of)
JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript strings are for storing and manipulating text.
-
A JavaScript string is zero or more characters written inside quotes.
-
Strings are very robust and we can manipulate them in a variety of ways. For simplicity we will stick to the basics.
-
Let's play with strings demo
The Beginnings
- Types
- Variables
- Operations
- Functions
Text
Variables
Declaration-> let age = 61
reassign -> age = 24
Operations -> let nextAge = age + 1
The Beginnings
- Types
- Variables
- Operations
- Functions
Mathematical Operators
- addition + (also see Strings)
- subtraction -
- multiplication *
- division /
Boolean Logical Operators
- and &&
- or ||
- not !
Comparison operators
- equal to ==
- equal value and equal type ===
- greater than >
- less than <
- greater than or equal to >=
- less than or equal to <=
The Beginnings
- Types
- Variables
- Operations
- Functions
What is a function?
A function is a block of reusable code written to perform a specific task. A function consists of a set of statements but executes as a single unit. In JavaScript, we have some browser built-in functions like alert(), prompt(), and confirm()
function nameOfFunction() {
//some code here....
}A function consists of:
- Function keyword
- The name of the function
- Parentheses (which can take in parameters, or also be empty)
- The body of the function (wrapped in curly braces).
function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello world");
}Here’s how to call the function:
sayHello();
//output: Hello world
Another example with parameters
function sum(num1, num2){
return num1 + num2;
}To invoke this function, we call it like this:
sum(1, 2);
//output: 3Use the name of the function ->
<- Pass in values for the parameters
in the parentheses
Changing HTML with JavaScript
JavaScript Can Change HTML Content
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello JavaScript";
JavaScript Can Change HTML Styles (CSS)
document.getElementById("demo").style.fontSize = "35px";
JavaScript Can Hide HTML Elements
document.getElementById("demo").style.display = "none";
JavaScript Can Show HTML Elements
document.getElementById("demo").style.display = "block";
Each of these examples start with document.
What is being referred to?
Each browser Window object has the following:
Window object has:
- Document (DOM)
- History
- Location
- Screen
- Storage
- Console
- GlobalEventHandlers
- ...
This is what we are interacting with ->
This and the following pages use information from W3 Schools. There is a link to the content on the last slide of this section :)
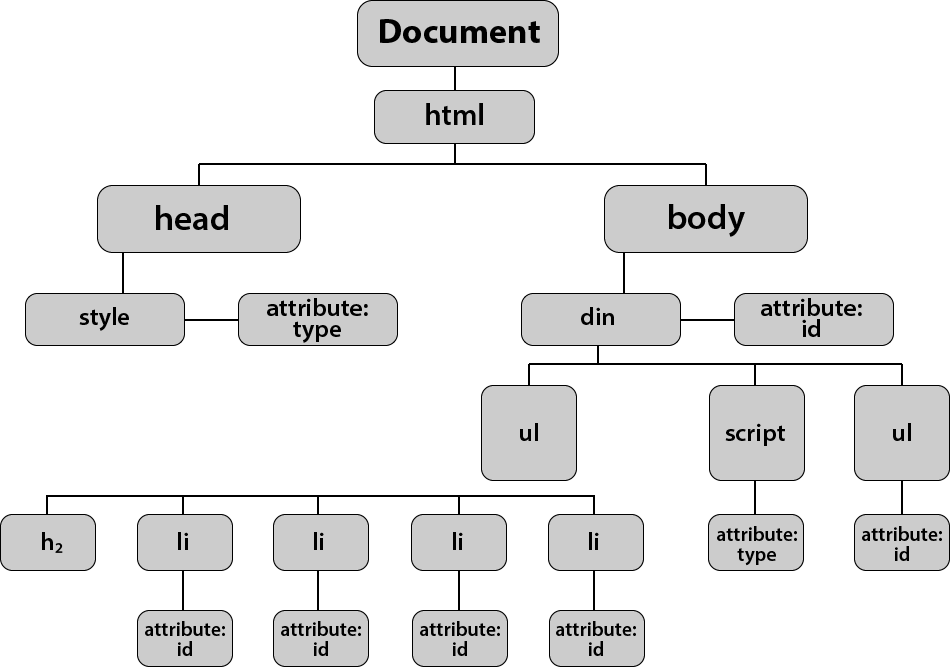
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page. The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects:
The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, change, add, or delete HTML elements.
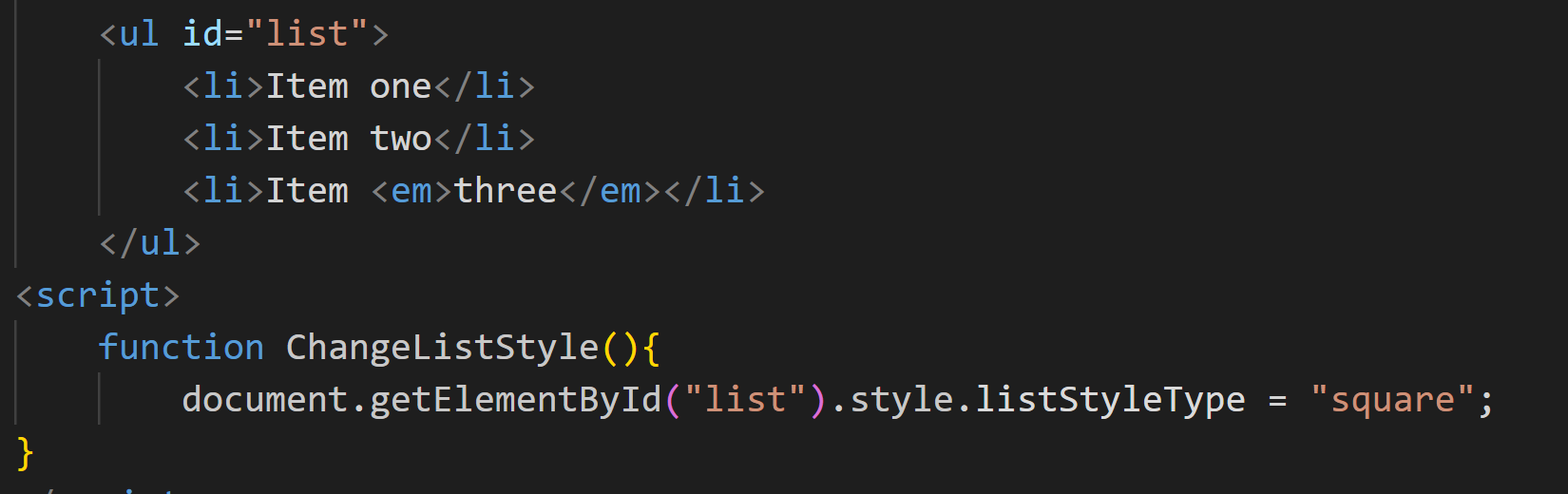
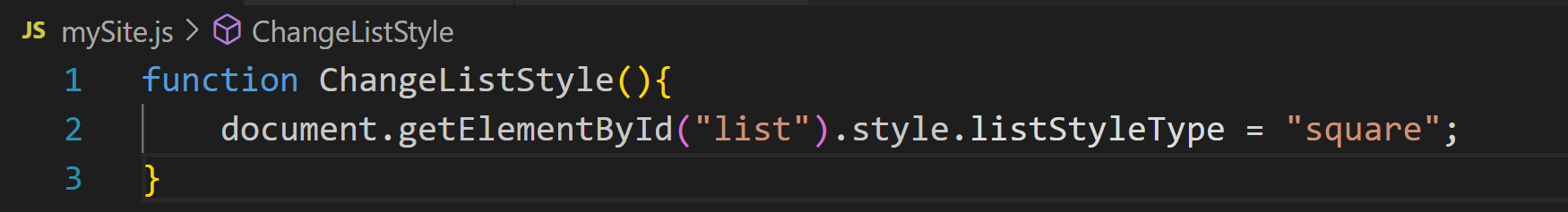
document.getElementById("list").style.listStyleType = "square";
id="list"
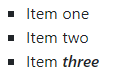

Before
After
- HTML DOM methods are actions you can perform (on HTML Elements).
- HTML DOM properties are values (of HTML Elements) that you can set or change.
- The HTML DOM can be accessed with JavaScript (and with other programming languages).
- In the DOM, all HTML elements are defined as objects.
- The programming interface is the properties and methods of each object.
- A property is a value that you can get or set (like changing the content of an HTML element).
- A method is an action you can do (like add or deleting an HTML element).
Accessing Elements
HTML
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>getElementById example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id="para">Some text here</p>
<button onclick="changeColor('blue');">blue</button>
<button onclick="changeColor('red');">red</button>
</body>
</html>JavaScript function changeColor(newColor) { const elem = document.getElementById("para"); elem.style.color = newColor; }

ResultIn this example getElementById() is a method and elem.style.color accesses a property
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| document.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| document.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
Finding HTML Elements
Changing HTML Elements
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| element.innerHTML = new html content | Change the inner HTML of an element |
| element.attribute = new value | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
| element.style.property = new style | Change the style of an HTML element |
| Method | Description |
| element.setAttribute(attribute, value) | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
We can also add and delete elements, however we will not cover that this week. You can find more information about adding and deleting elements in your JavaScript & jQuery book :)
Online resources include:
How do we include JavaScript code?
You don't have to get or download JavaScript. JavaScript is already running in your browser on your computer, on your tablet, and on your smart-phone. JavaScript is free to use for everyone.
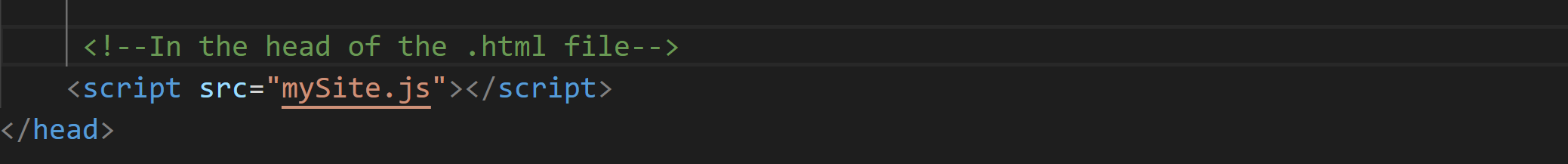
We do however need to reference our code in our files. Much like CSS, you can put a script within the body, in the head of the page or in a separate JavaScript file using the .js extension.
In most cases:
In the body
In the header
In an external .js file
CS Web Design - JavaScript
By drmorgan
CS Web Design - JavaScript
- 8



