Digital Media
Representational Theory
48120 Fall 2016 Analog and Digital Media
Online version:
In Review
- Assignment 10: Rhino III
- Assignment 11: Vray
In Review
- Assignment 10: Rhino III
- Assignment 11: Vray

Midterm Exam this Wednesday
Digital Hiatus
"Hybrid" Assignments November
Coming up..
Technical Tip
- Keep Vray texture images in the same folder as the Rhino file, and know how to package materials if you lose track of them. As always, keep your models clean. If you change computers to render on Vray, the images must accompany the Rhino file in order for the textures to properly load.
Housekeeping
- Get extra help Saturdays, 1-on-1 help if necessary (Talk to Carolina)
- Be mindful of TAs and fellow SoA upper class students' time
- Exhaust research methods you can pursue on your own first before reaching out for help (e.g. instructions, Google, software documentations, etc.)
- Submit to the correct folder (i.e. in-class submission vs. re-submission)
- Assignment grading rubric clarification:
- 3 - Flawless even upon close inspection
- 2 - Good for most steps, with one or two steps missing
- 1 - Missing significant steps, poor attention to detail
- 0 - Missing most or all steps, fail
Midterm Exam
- Everything covered in the lecture slides and workshops; not too much into detail for the Wikipedia articles
- Should be able to make categorical associations with image and names
- Multiple choice, questions randomized
- Will be administered via Blackboard with IP address tracking (you must take the exam in person)
- We will start 10:30am sharp at CFA 214
- Bring your computers fully charged
- Use of computer other than taking exam on Blackboard not allowed.
- Use of messaging in any form (e.g. Facebook, SMS, iMessage, IRC, etc.) not allowed
- Use of phones not allowed
Assignments 10 & 11
Open Critique

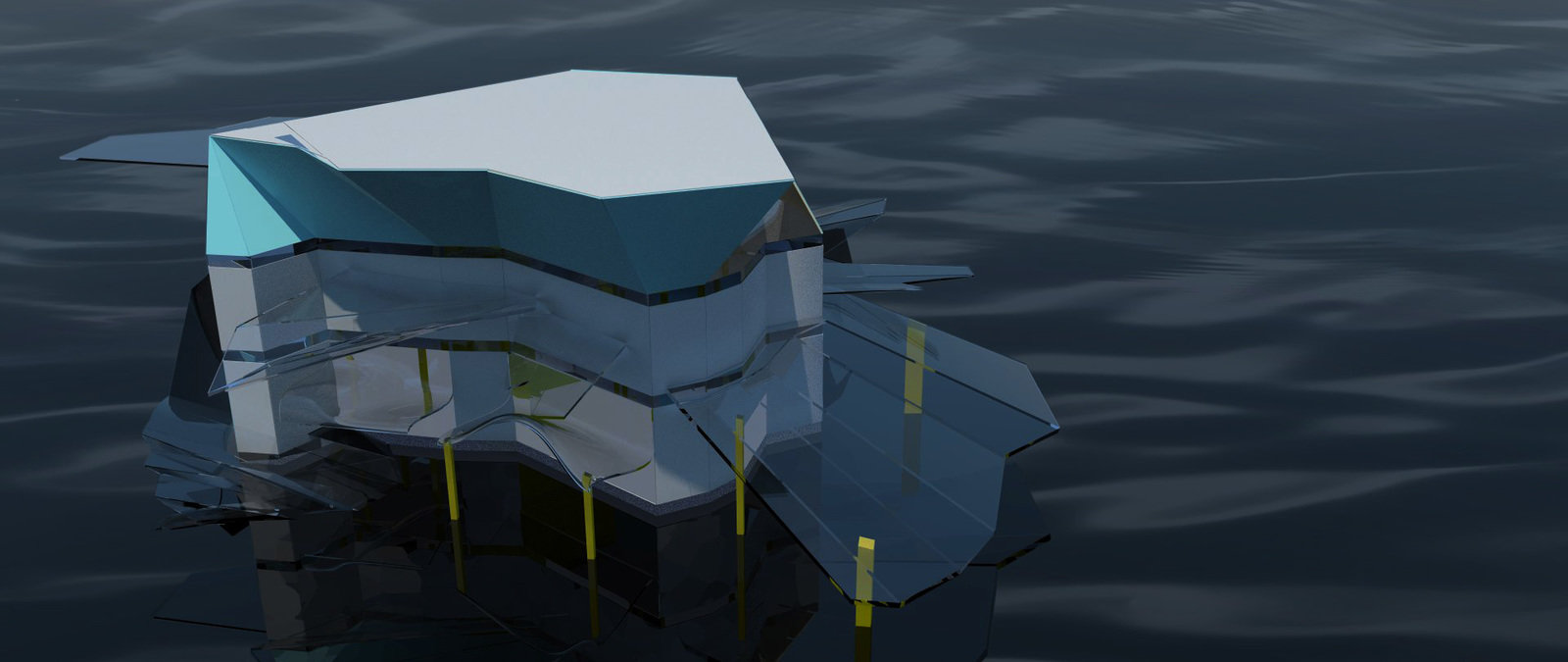
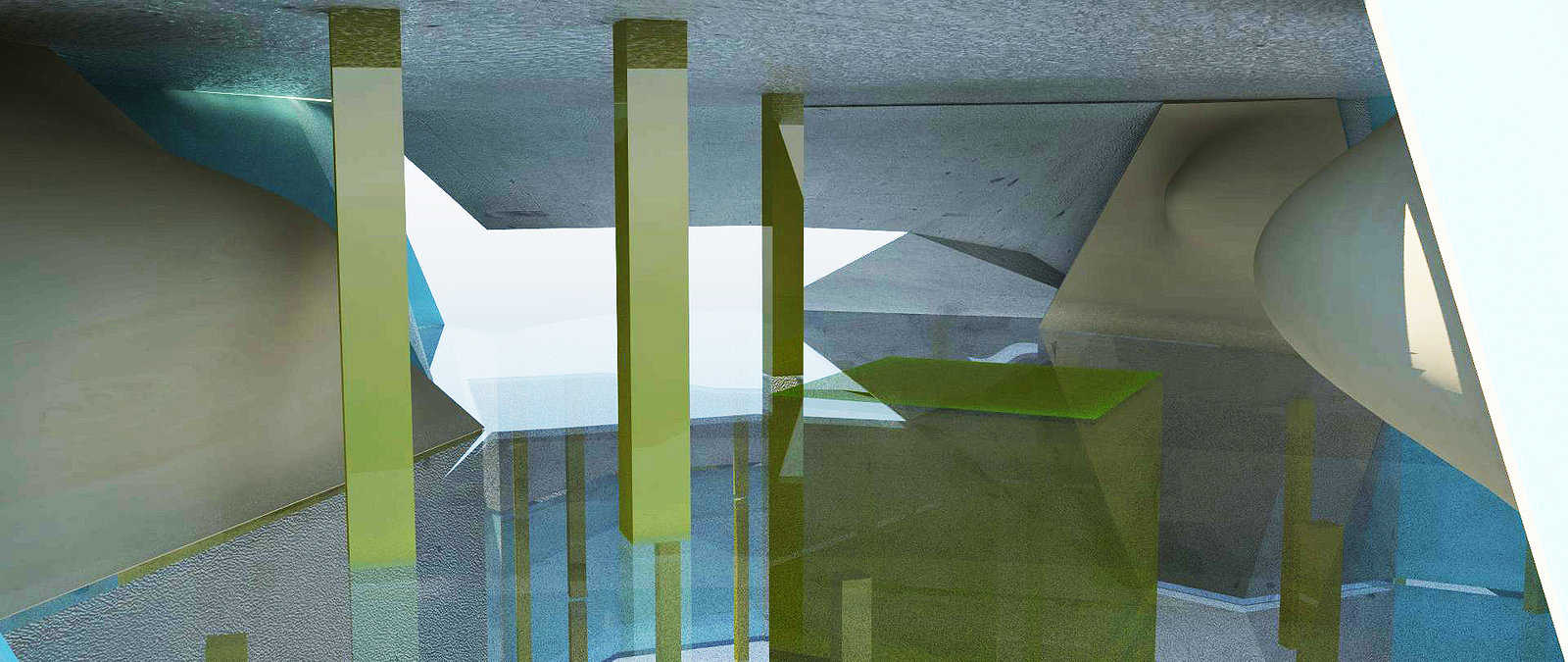
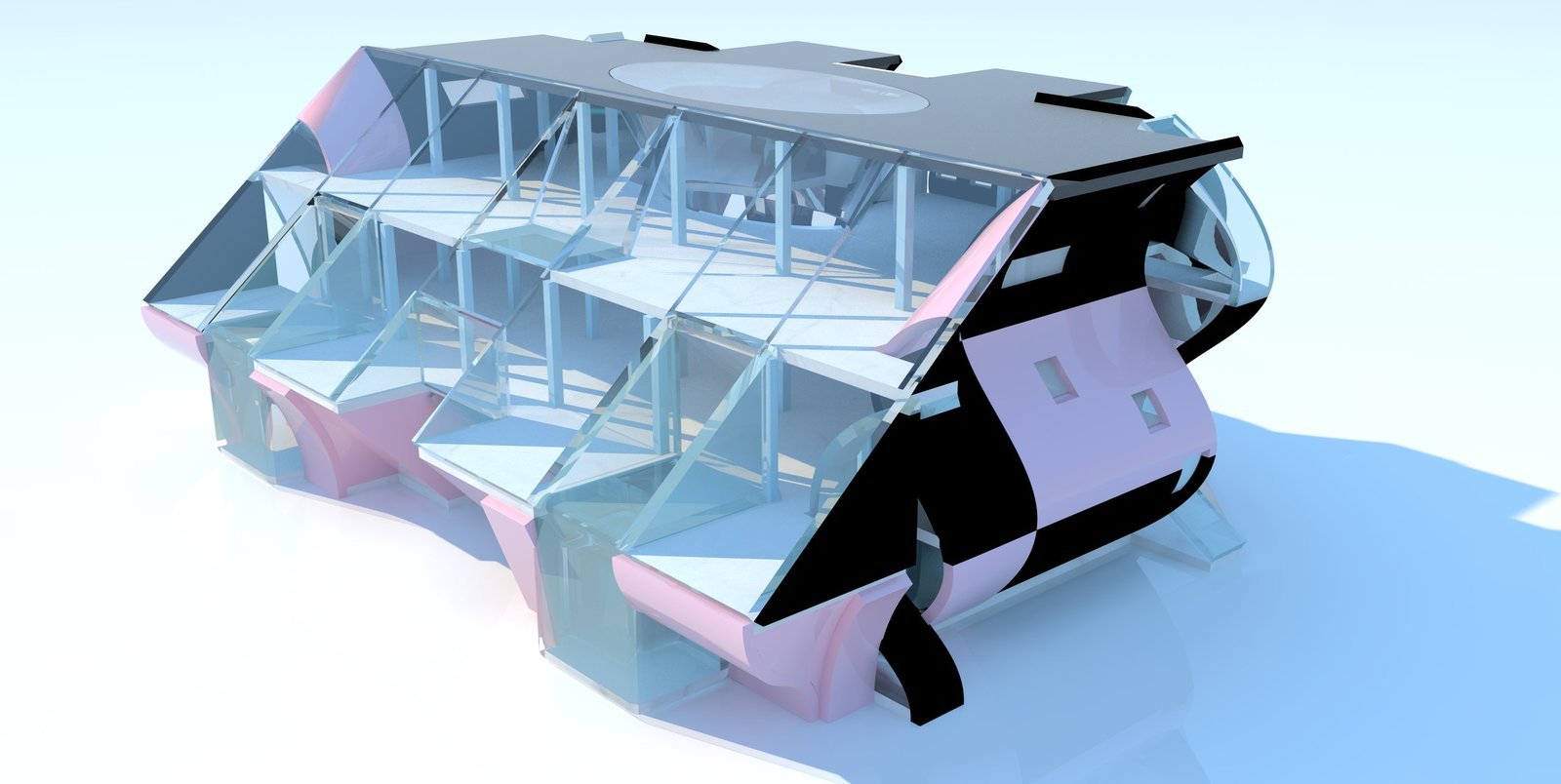

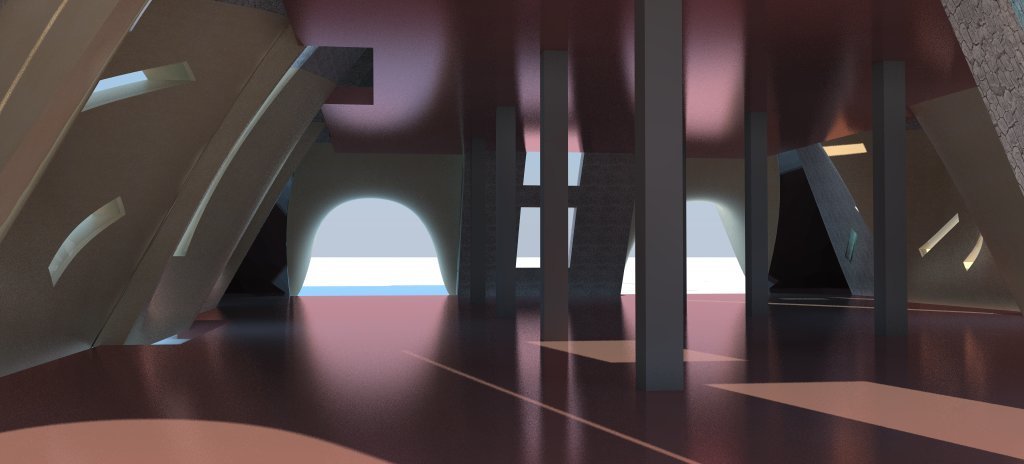
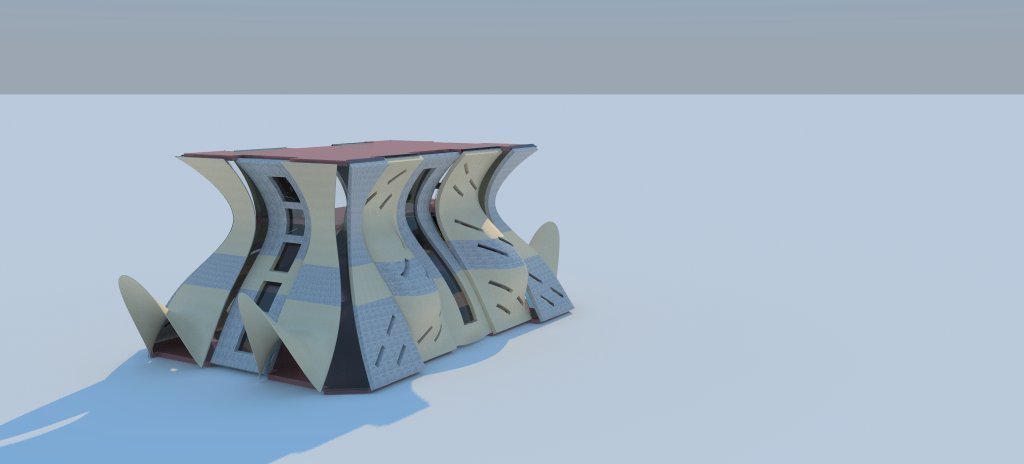
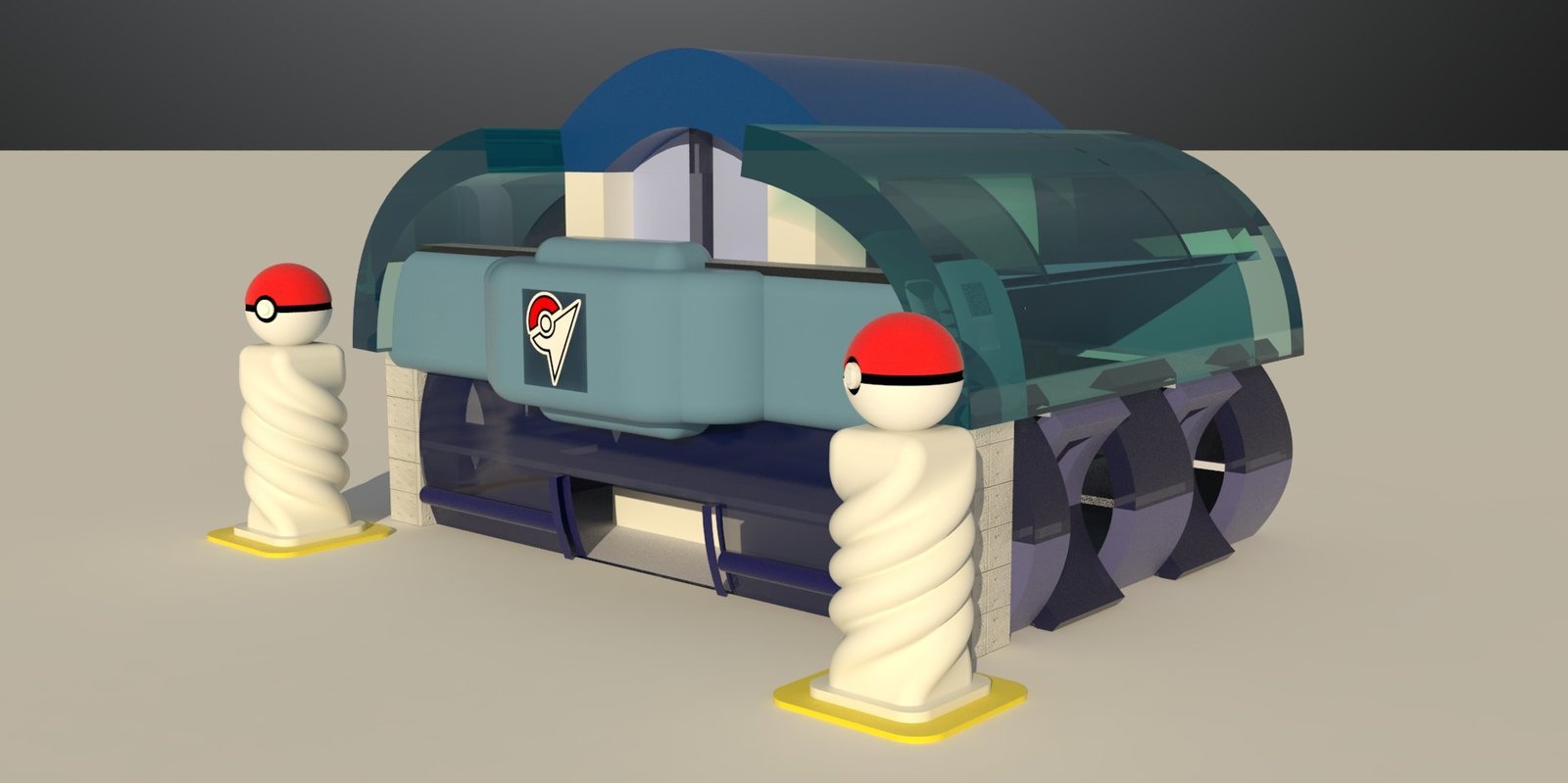


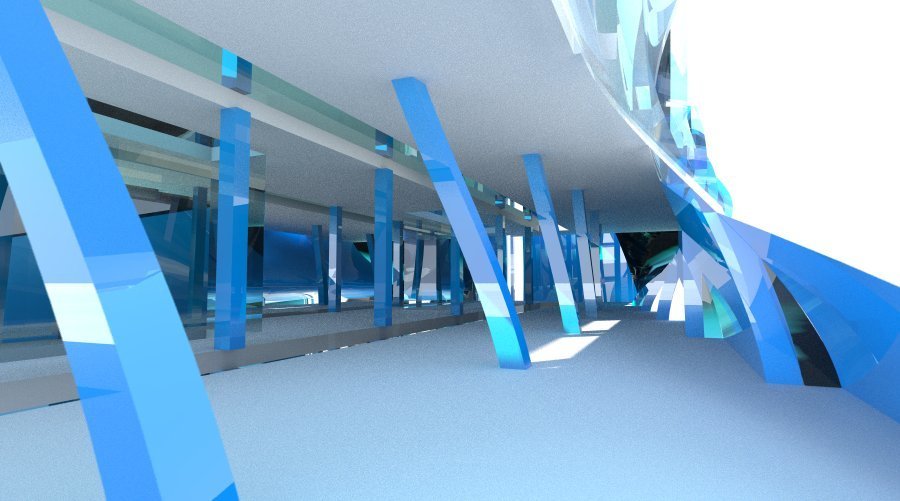

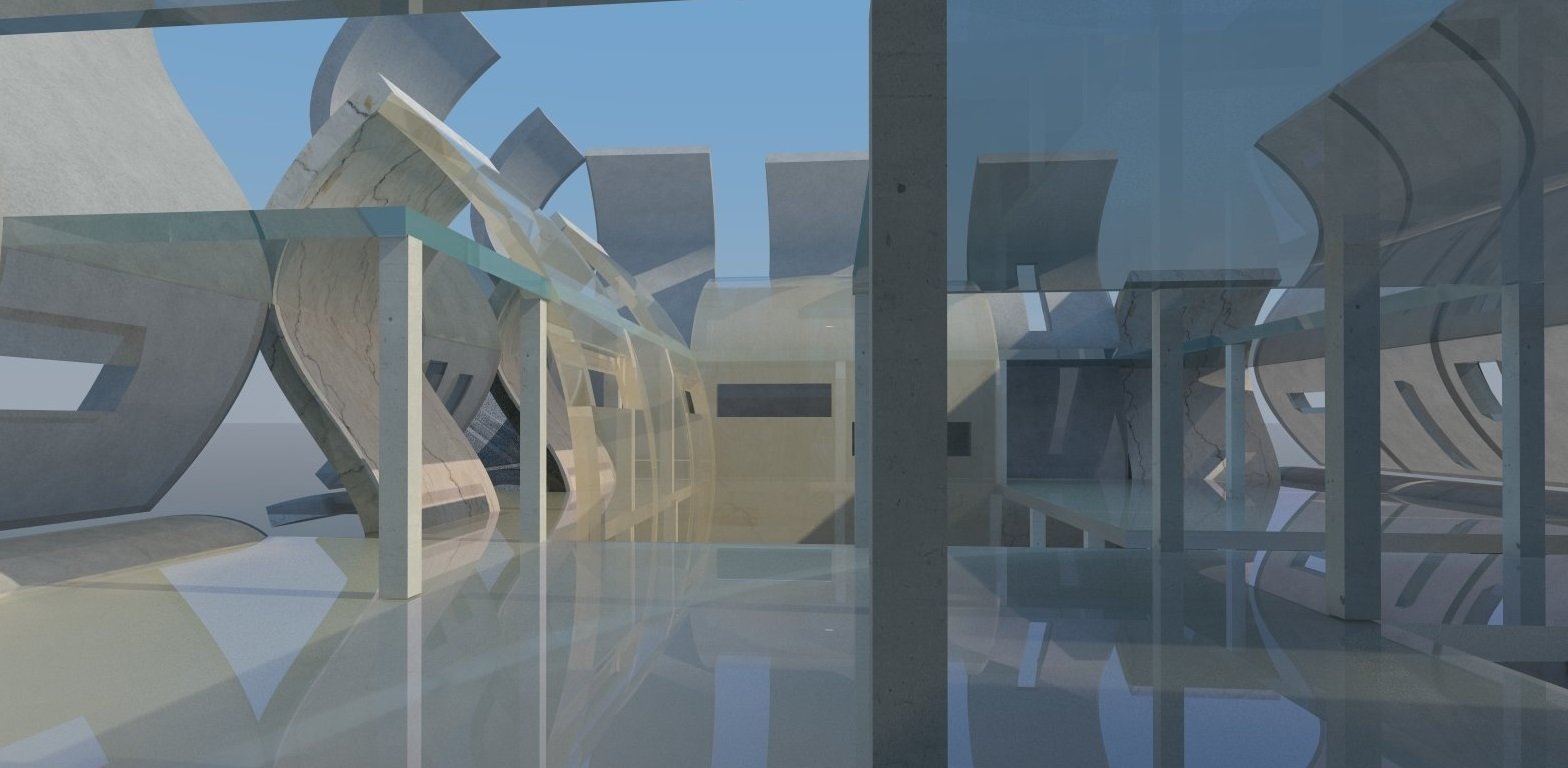
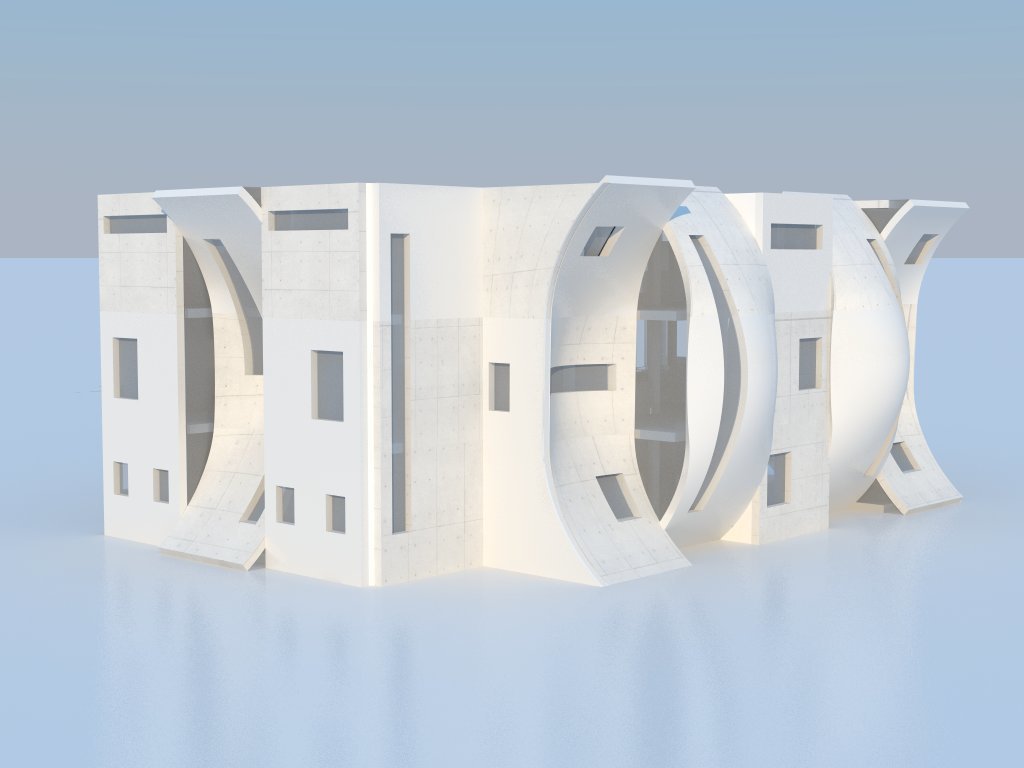
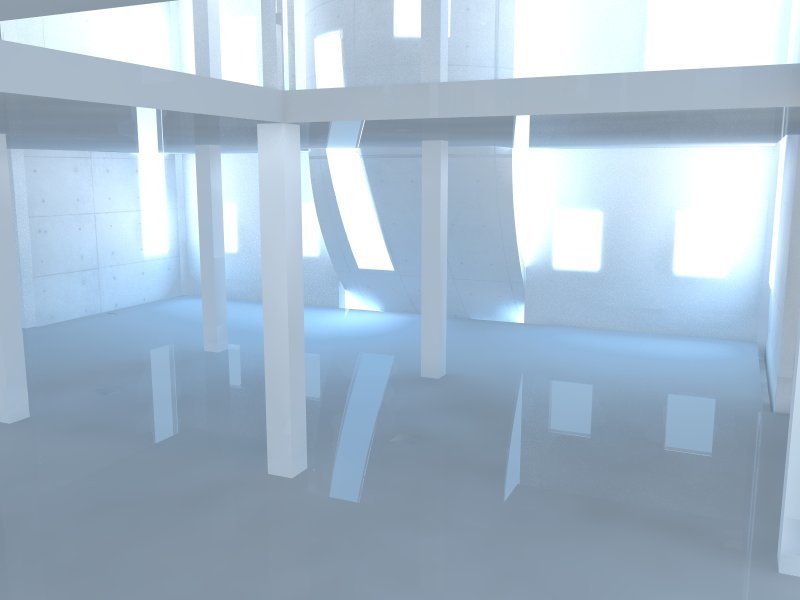





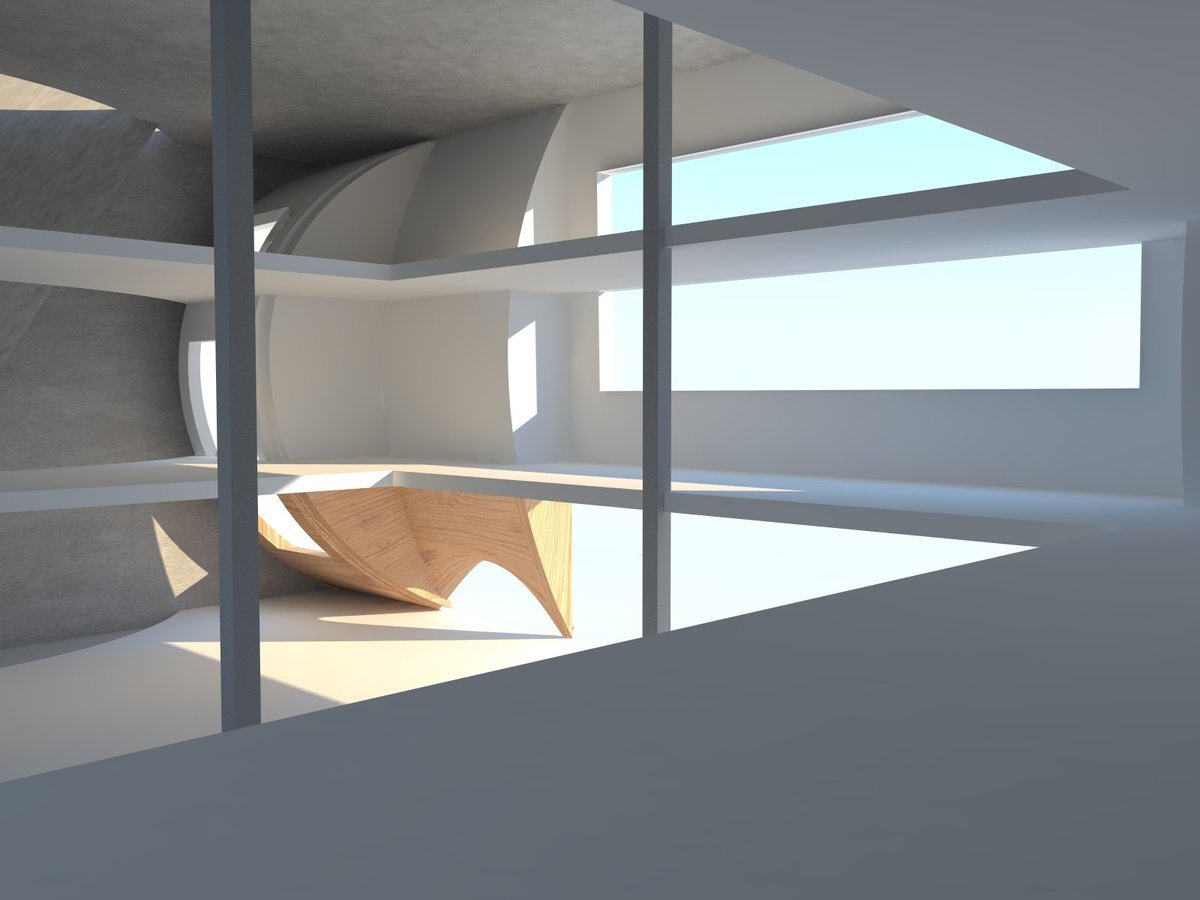





Representational Theory
(Architectural Drawing)
What I believe is that whether it be a question of sculpture or of painting, it is in fact only drawing that counts. One must cling solely, exclusively to drawing. If one could master drawing, all the rest would be possible.
Alberto Giacometti
MEDIA
- Line
- Render
- Mixed Media
TYPES
- Sketches
- Diagrams
- Plans
- Sections and elevations
- Axonometric and isometric projections
- Perspectives
MEDIA - Line
Coop Himmelb(l)au

MEDIA - Line
Perry Kulper

MEDIA - Line
Owen Dore

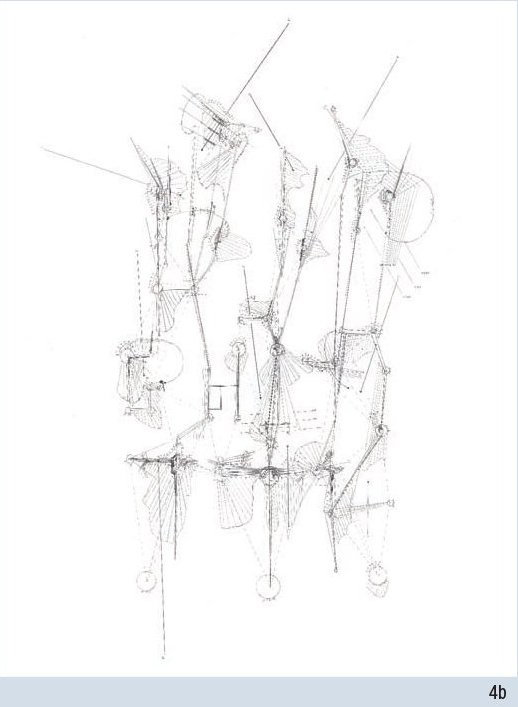
MEDIA - Line
Archi-Tectonics

MEDIA - Line
Lebbeus Woods
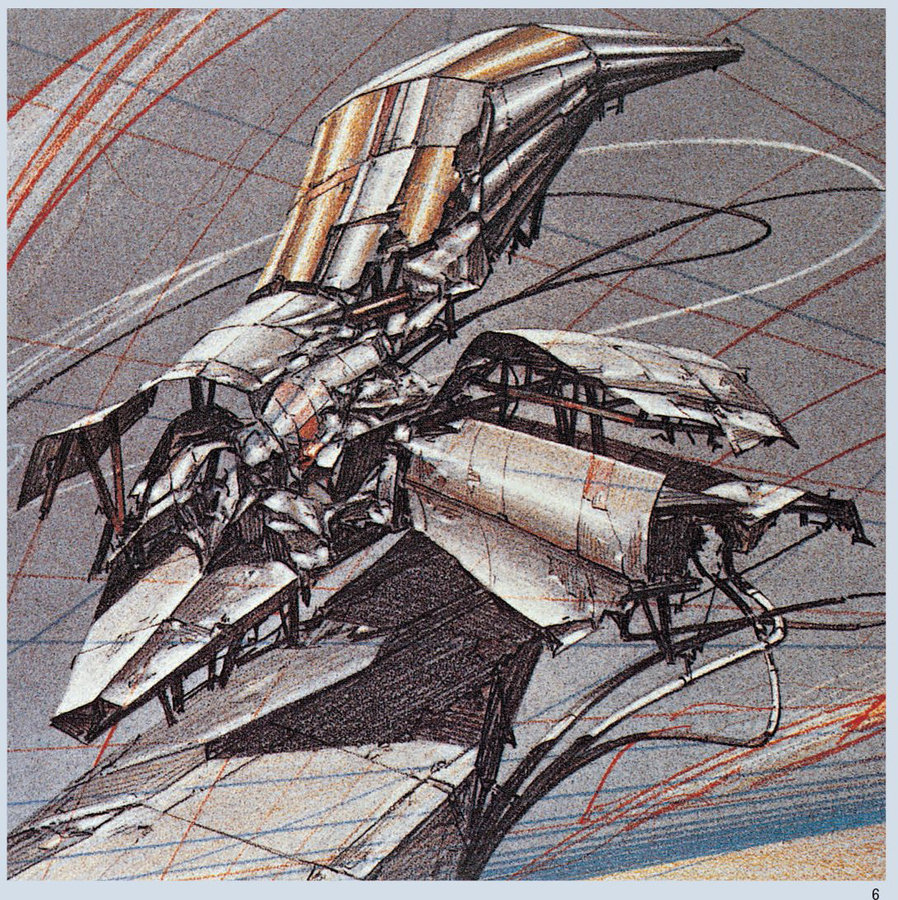
MEDIA - Line - Pencil
MEDIA - Line - Charcoal

MEDIA - Line - Ink

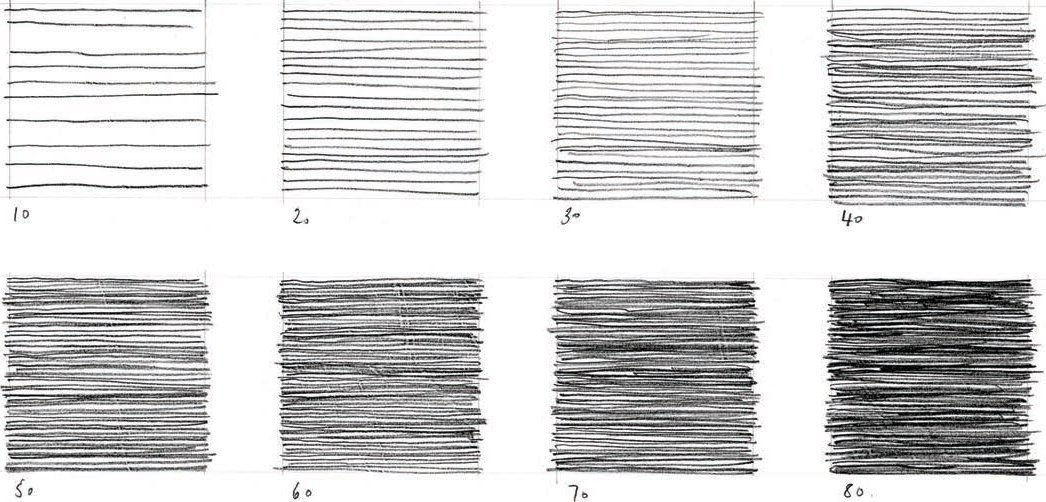
Lines are the most vital components of almost any drawing. Great drawings are read through the character of individual lines and lines come together to define the spatiality of the drawing: lines are like boundaries and as such open up spatial relationships on a page.
The immediacy of a line is the most direct way to visualize thought and observation and as a line drawing evolves, and line weights differentiate, it can express a spatial depth and also define gradations of light and shadow.
David Dernie
MEDIA - Render
MEDIA - Render - Linocut Print
Anne Desmet

MEDIA - Render - Woodcut Print
Anne Desmet

MEDIA - Render - Colored Pencil and Crayon
Eric Parry
MEDIA - Render - Watercolor
Elizabeth Day

MEDIA - Render - Hybrid
Yakim Milev

MEDIA - Render - Hybrid
David Dernie

MEDIA - Mixed Media
Saraben Studio

MEDIA - Mixed Media
David Dernie
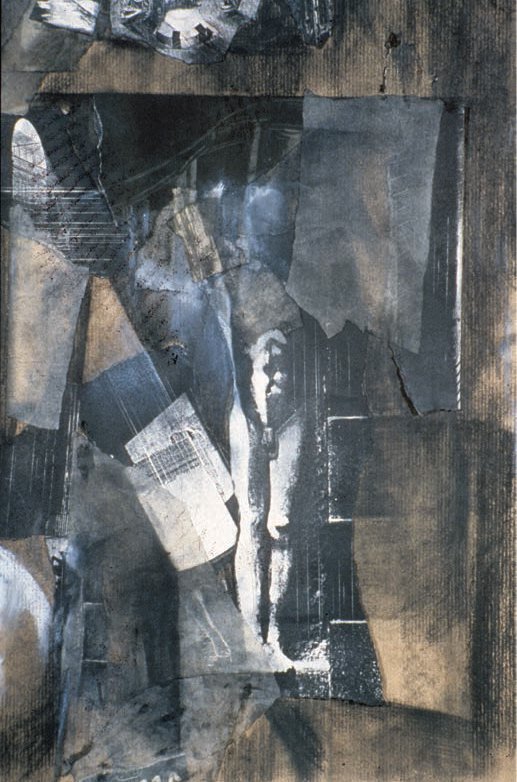
MEDIA - Mixed Media
David Dernie

MEDIA - Mixed Media
David Dernie

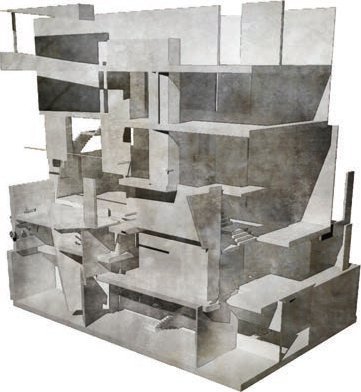
MEDIA - Mixed Media
Kenny Tsui

TYPES - Sketch
Eric Parry
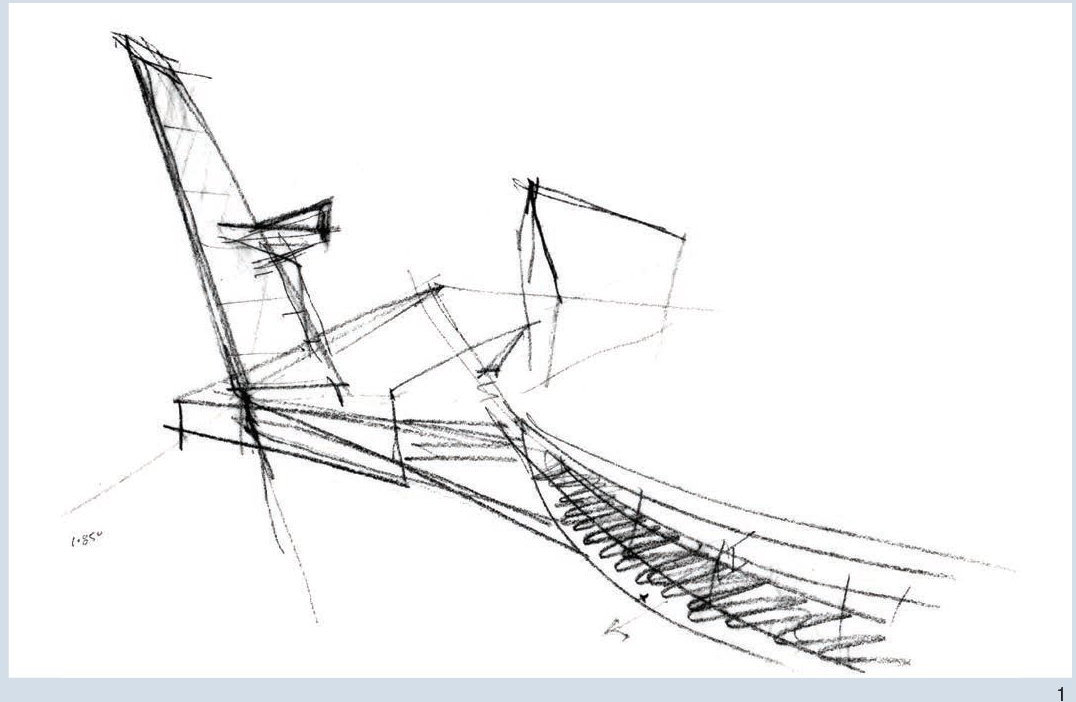
TYPES - Sketch
Eduardo Souto de Moura

TYPES - Sketch
Ian Simpson
TYPES - Sketch
David Dernie
TYPES - Diagrams
Patkau Architects
TYPES - Diagrams
OMA
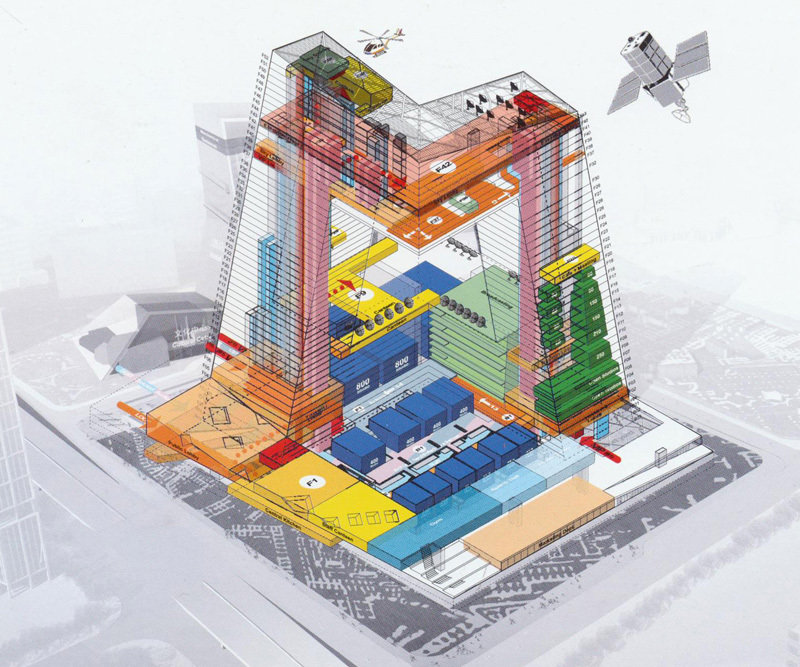
TYPES - Diagrams
MVRDV
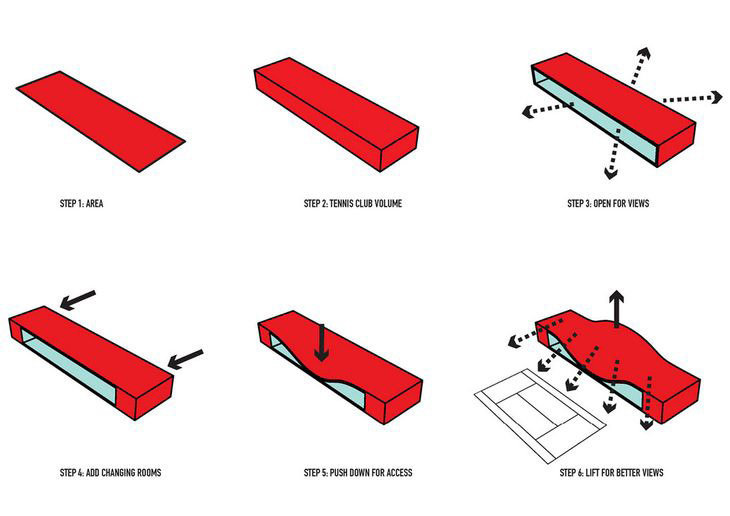
TYPES - Diagrams
David Dernie
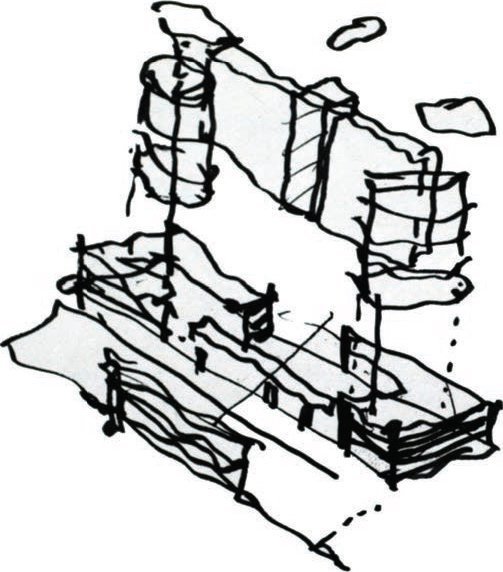
TYPES - Diagrams
Sophia Cole


TYPES - Diagrams
David Dernie
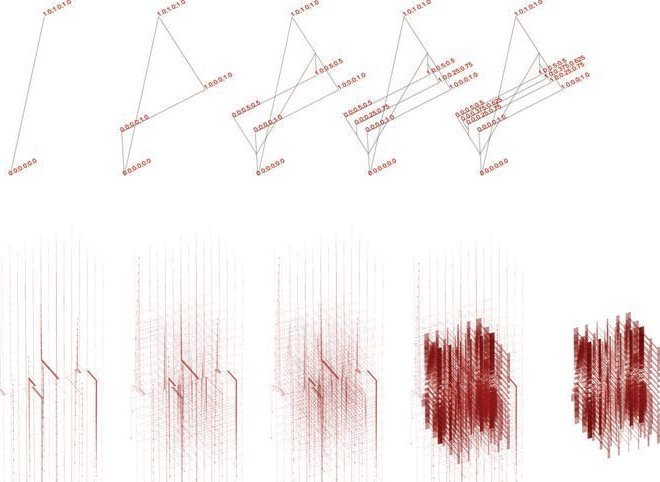
While for some architects diagramming has become an essential mode of designing, diagrams are generally not used as a singular mode of representation, but as a drawing type they may help us to clarify a design at various stages of its development. Diagrams can be freehand, digital or hybrid; drawing technique will depend on the nature of the thinking or analysis that the diagram is articulating.
Diagrams can help us to understand essential components of a scheme and can be used at all stages of a building, from site analysis to initial design ideas to analysis of a building itself. Diagrams can be useful because they reduce complex architectural ideas to their composite elements. They can freeze otherwise shifting relational conditions, emphasizing clarity of communication of a singular aspect of a proposal or given condition.
David Dernie
TYPES - Plans
David Dernie
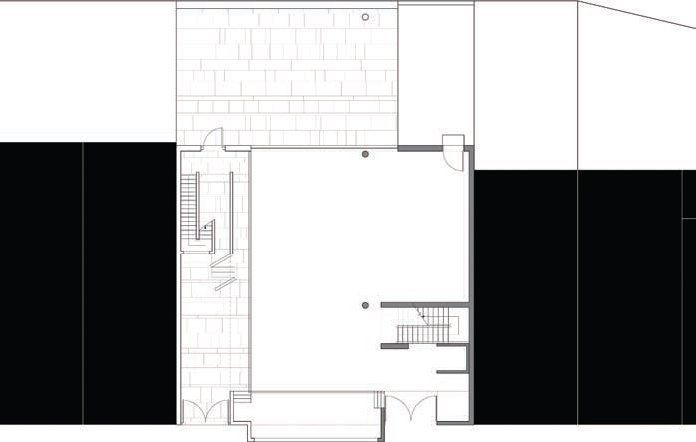
TYPES - Plans
David Dernie
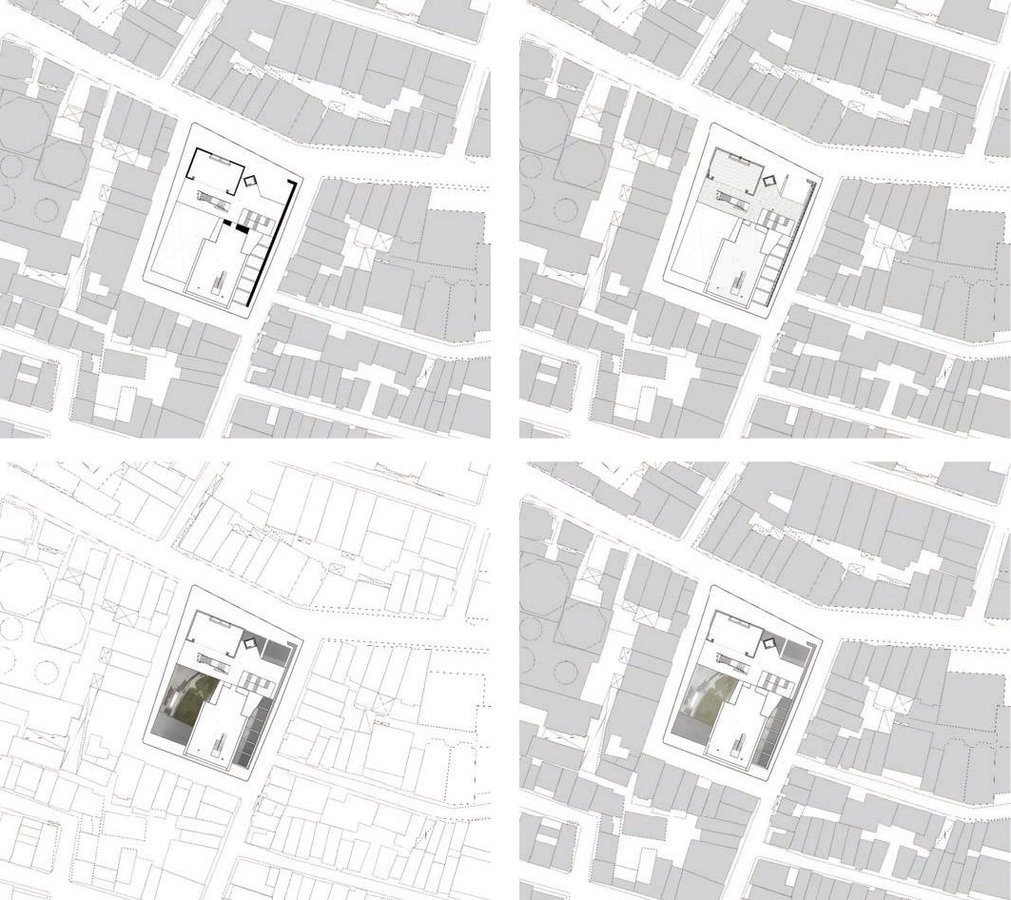
TYPES - Plans
Philip Meadowcroft
TYPES - Plans
Philip Meadowcroft

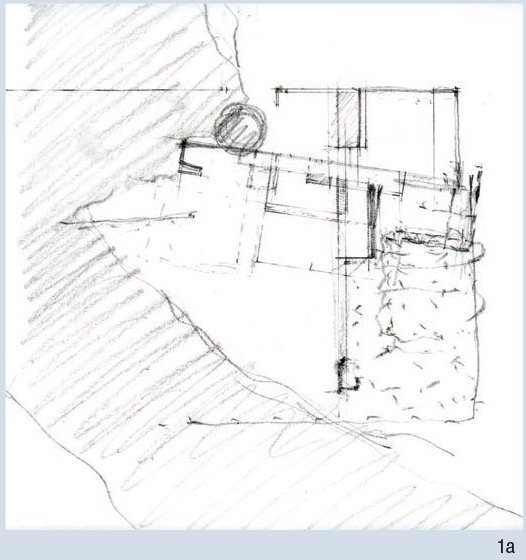
TYPES - Plans
Archi-Tectonics
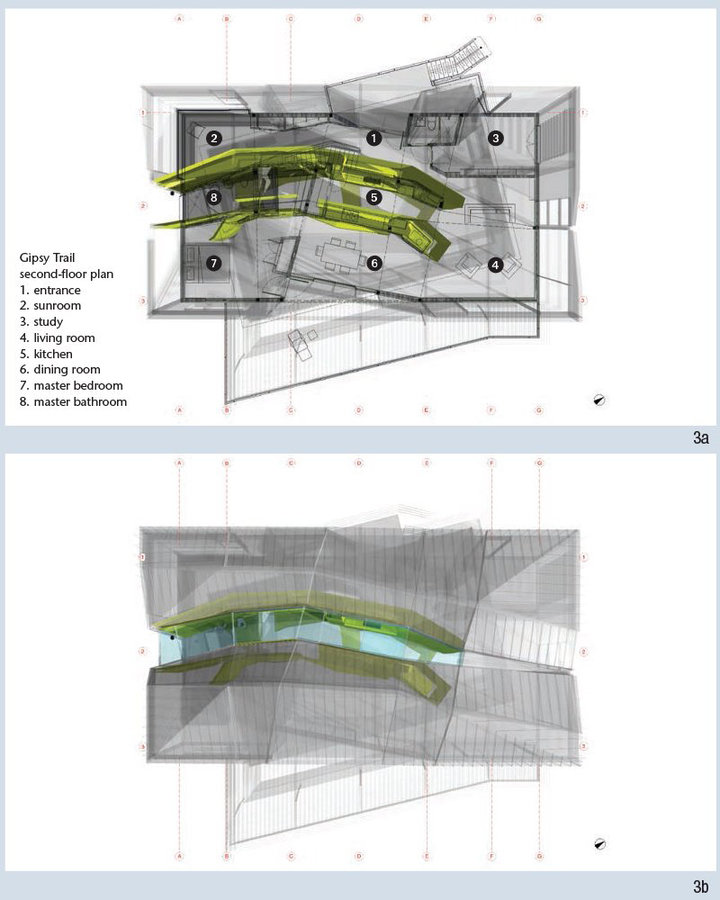
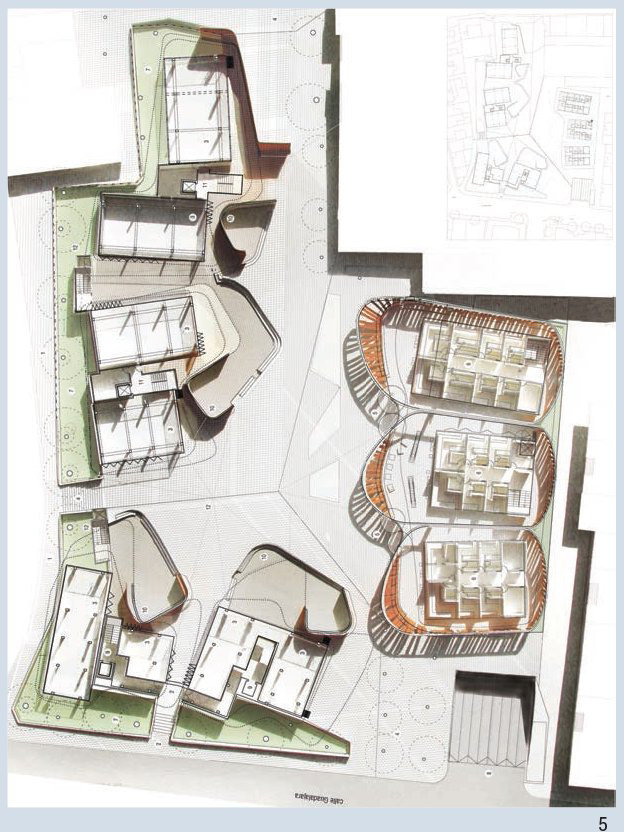
TYPES - Plans
Saraben Studio
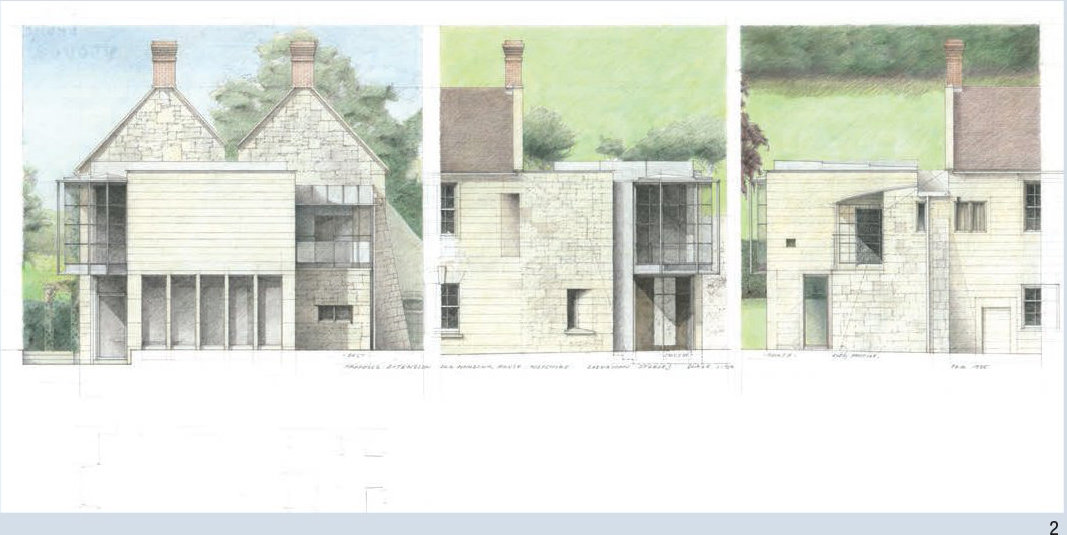
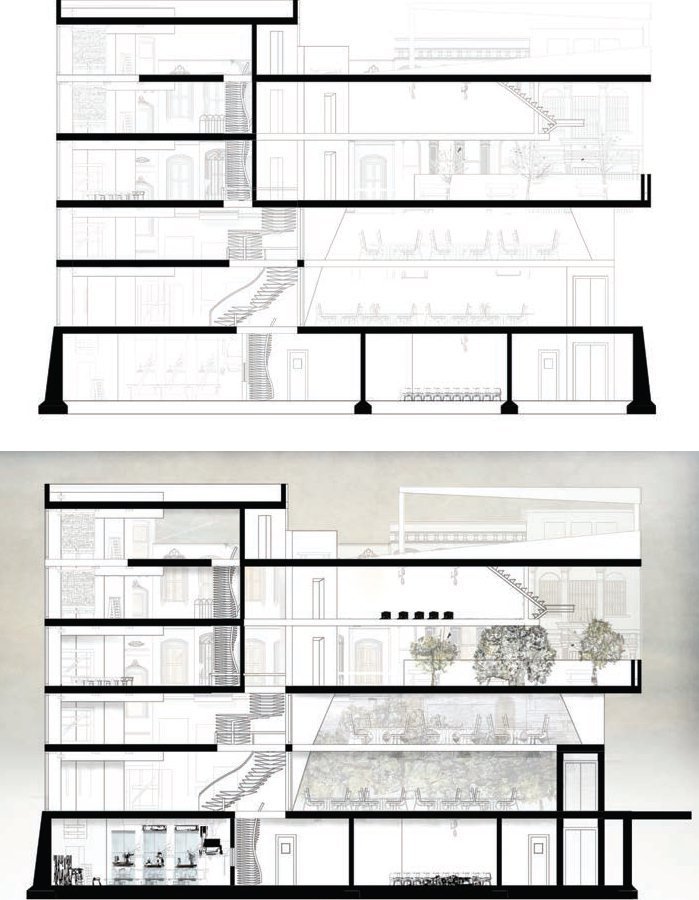
TYPES - Sections and Elevations
David Dernie
TYPES - Sections and Elevations
David Dernie
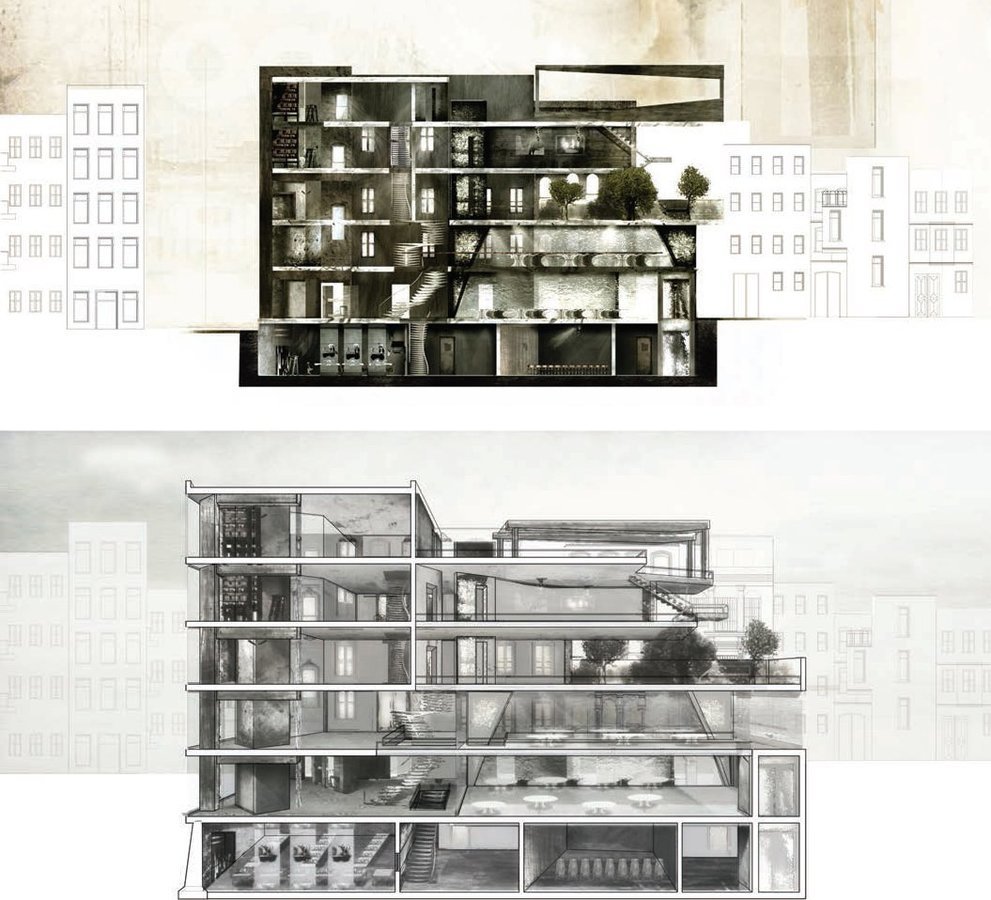
TYPES - Sections and Elevations
Philip Meadowcroft
TYPES - Sections and Elevations
Buschow Henley

TYPES - Sections and Elevations
Stephenson Bell

TYPES - Sections and Elevations
Hodder Associates

TYPES - Sections and Elevations
Saraben Studio

TYPES - Sections and Elevations
LTL Architects

TYPES - Sections and Elevations
Atelier Bow-wow
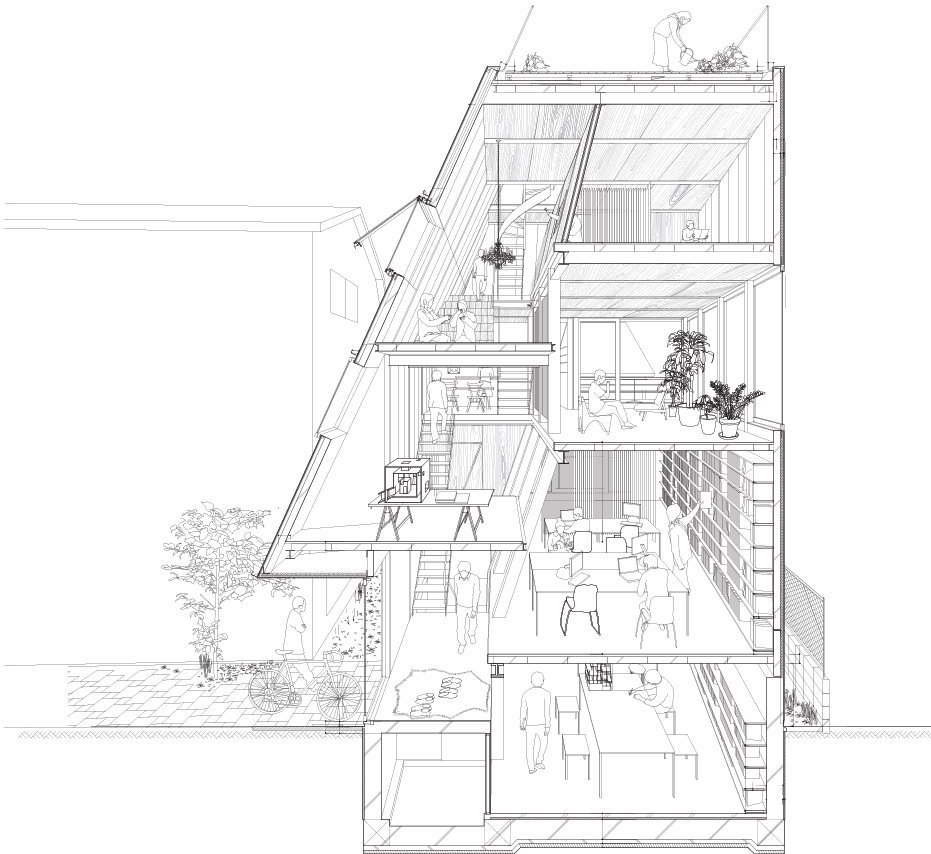
TYPES - Axonometric and Isometric Projections
David Dernie
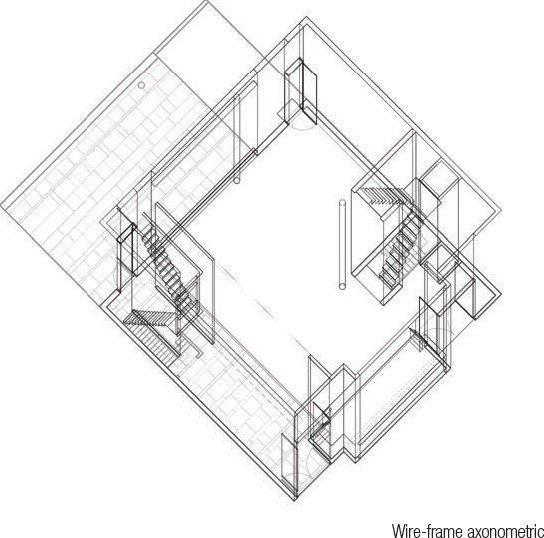
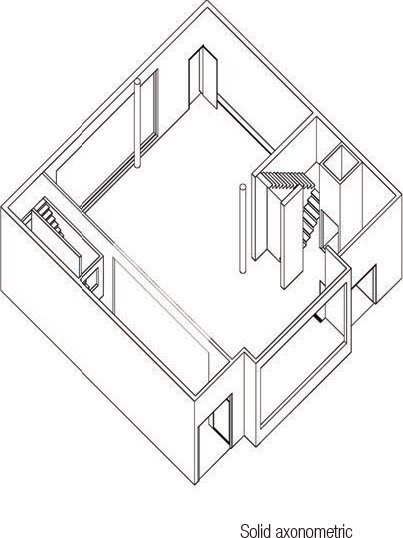
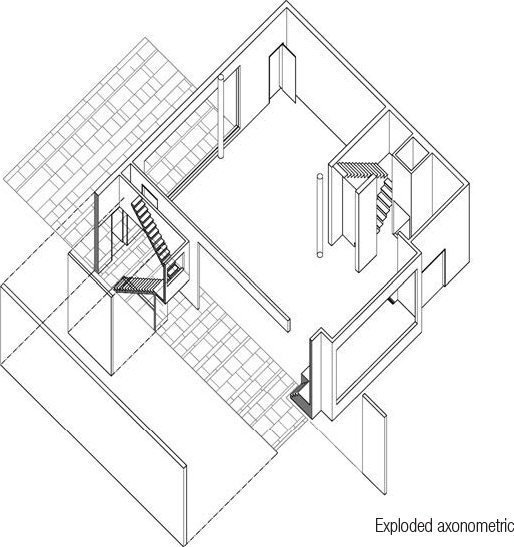
TYPES - Axonometric and Isometric Projections
Gary Butler
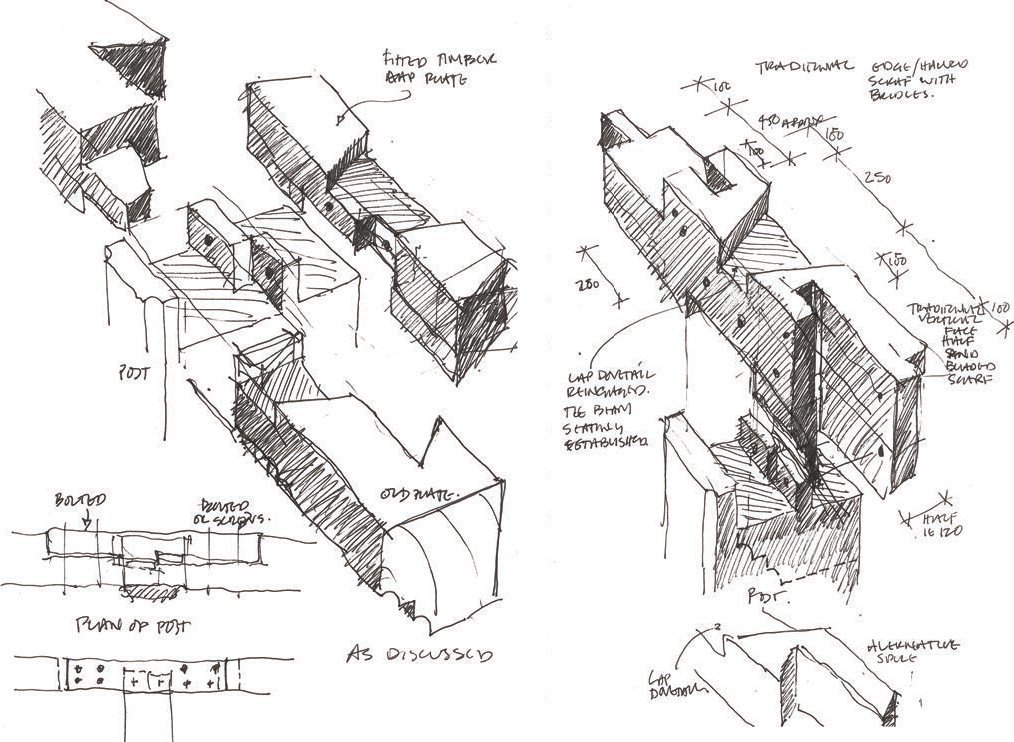
TYPES - Axonometric and Isometric Projections
Sophia Cole
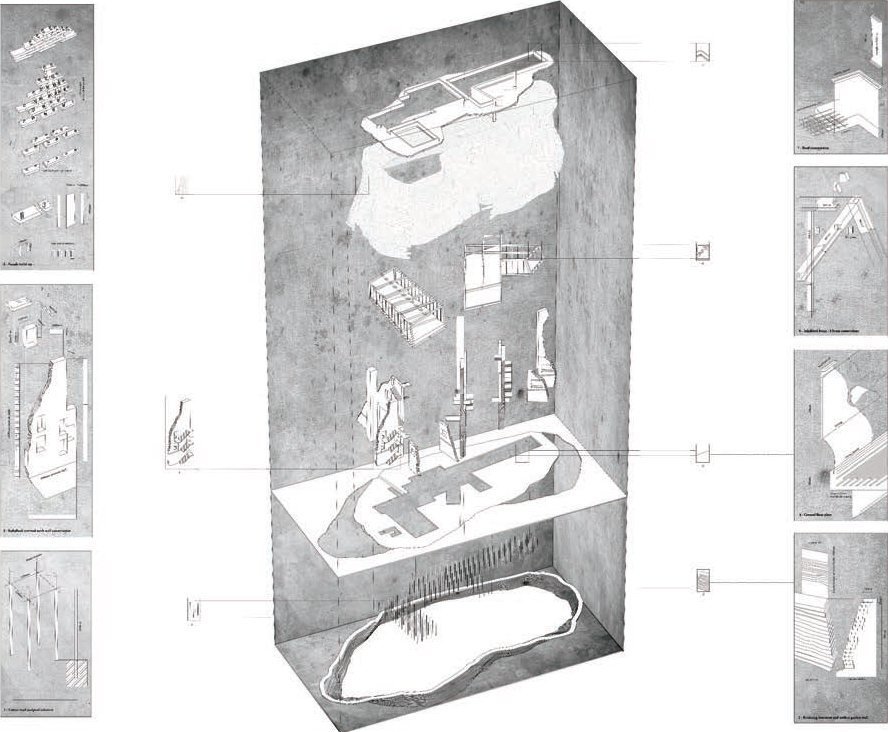
TYPES - Perspectives
Alberto Campo Baeza
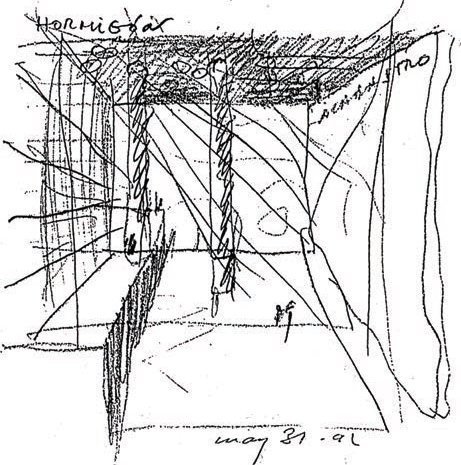
TYPES - Perspectives
Kyle Henderson

TYPES - Perspectives - One Point
David Dernie
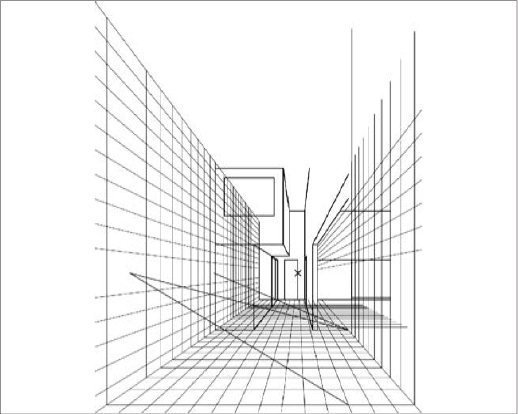
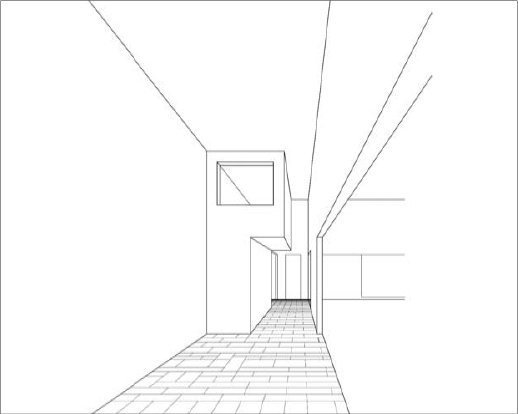
TYPES - Perspectives - Two Point
David Dernie
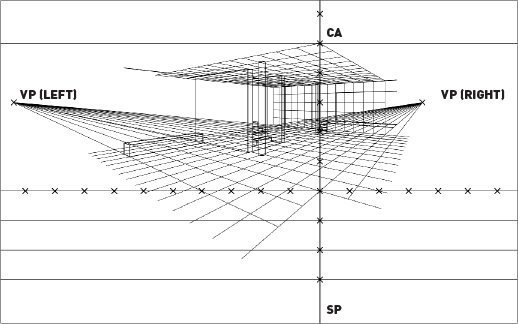
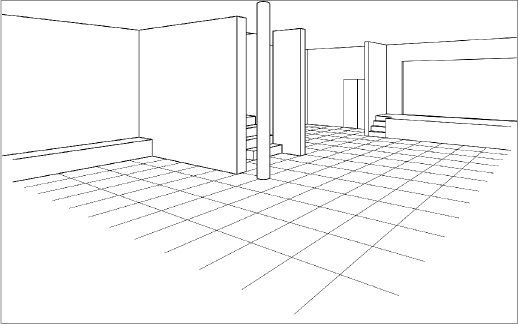
TYPES - Perspectives
Meadowcroft Griffin

TYPES - Perspectives
Neil Denari

Let's dig deeper..
Representational Theory
(Visual Arts and Design)
Composition (visual arts)
Composition (visual arts)
In the visual arts—in particular painting, graphic design, photography, and sculpture—composition is the placement or arrangement of visual elements or ingredients in a work of art, as distinct from the subject of a work. It can also be thought of as the organization of the elements of art according to the principles of art.
Design Elements
Line — the visual path that enables the eye to move within the piece
Shape — areas defined by edges within the piece, whether geometric or organic
Color — hues with their various values and intensities
Texture — surface qualities which translate into tactile illusions
Tone — Shading used to emphasize form
Form — 3-D length, width, or depth
Space — the space taken up by (positive) or in between (negative) objects
Depth — perceived distance from the observer, separated in foreground, background, and optionally middle ground
Wikipedia
Design Principles
Unity / Harmony — A good balance between unity and variety must be established to avoid a chaotic or a lifeless design.
Balance — It is a state of equalized tension and equilibrium, which may not always be calm.
Hierarchy — A good design contains elements that lead the reader through each element in order of its significance.
Scale / Proportion — Using the relative size of elements against each other can attract attention to a focal point.
Dominance / Emphasis — Dominance is created by contrasting size, positioning, color, or shape.
Similarity and Contrast — Too much similarly is boring but without similarity important elements will not exist and an images without contrast is uneventful so the key is to find the balance between similiarity and contrast.
Wikipedia
Design Principles - Unity / Harmony
Methods
- Perspective: sense of distance between elements.
- Similarity: ability to seem repeatable with other elements.
- Continuation: the sense of having a line or pattern extend.
- Repetition: elements being copied or mimicked numerous times.
- Rhythm: is achieved when recurring position, size, color, and use of a graphic element has a focal point interruption.
Wikipedia
Design Principles - Balance
Types
- Symmetrical balance
- Asymmetrical balance produces an informal balance that is attention attracting and dynamic.
- Radial balance is arranged around a central element. The elements placed in a radial balance seem to 'radiate' out from a central point in a circular fashion.
- Noisy balance: Overall is a mosaic form of balance which normally arises from too many elements being put on a page. Due to the lack of hierarchy and contrast, this form of balance can look noisy but sometimes quiet.
Wikipedia
Design Principles - Similarity and Contrast
Similar environment
- Build a unique internal organization structure.
- Manipulate shapes of images and text to correlate together.
- Express continuity from page to page in publications using a template. Items to watch include headers, themes, borders, and spaces.
- Develop a style manual and adhere to it.
Wikipedia
Design Principles - Similarity and Contrast
Wikipedia
-
Space
- Filled / Empty
- Near / Far
- 2-D / 3-D
-
Position
- Left / Right
- Isolated / Grouped
- Centered / Off-Center
- Top / Bottom
-
Form
- Simple / Complex
- Beauty / Ugly
- Whole / Broken
-
Direction
- Stability / Movement
-
Structure
- Organized / Chaotic
- Mechanical / Hand-Drawn
-
Size
- Large / Small
- Deep / Shallow
- Fat / Thin
-
Color
- Grey scale / Color
- Black & White / Color
- Light / Dark
-
Texture
- Fine / Coarse
- Smooth / Rough
- Sharp / Dull
-
Density
- Transparent / Opaque
- Thick / Thin
- Liquid / Solid
-
Gravity
- Light / Heavy
- Stable / Unstable
Contrasts
Gestalt Principles
Learn how to visually identify all the elements and principles visual representation.
See you Wednesday @ CFA 214
48120_F16_3
By Eddy Man Kim
48120_F16_3
10/9/2016 Lecture on Representational Theory
- 1,759



