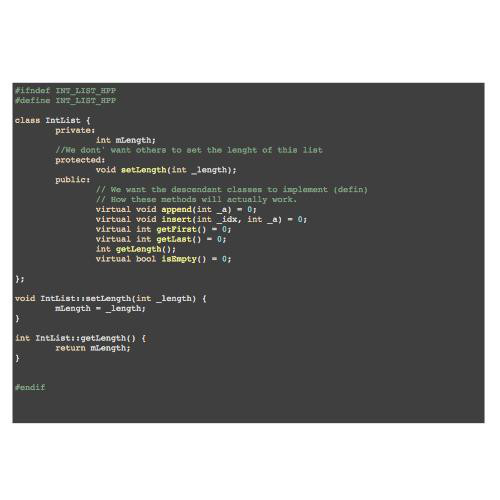
Programming Paradigms
Procedural
int[5] input = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[5] output = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (input[i] % 2 == 0) {
output[i] = input[i] * 2;
} else {
output[i] = input[i];
}
}Procedural
- Functions (procedures)
- GOTO is evil
- variables and control flow
Object Oriented
// Java
class Car {
public:
int _km = 0;
void ride(km) {
_km += km;
}
}
Car myCar = new Car();
myCar.ride(123);
// JavaScript
var myCar = {
km: 0
ride: function(km) {
this.km += km;
}
};
myCar.ride(123);Object Oriented
- Classes or at least objects
- Methods rather than functions
Functional
// Java
List<int> myList =
Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
myList
.stream()
.map(n -> n % 2 == 0 ? n * 2 : n)
// JavaScript
var myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
myArray.map(n => n % 2 == 0 ? n * 2 : n);Functional
- First class function
- Try to avoid control flow
- Try to avoid mutation
Pure Functional
factorial :: int -> int
factorial 0 = 1
factorial n = n * factorial (n - 1)
quicksort :: (Ord a) => [a] -> [a]
quicksort [] = []
quicksort (x:xs) =
let smallerSorted = quicksort [a | a <- xs, a <= x]
biggerSorted = quicksort [a | a <- xs, a > x]
in smallerSorted ++ [x] ++ biggerSorted
Pure Functional
- No control flow
- No side-effects
- No mutations
Programming Paradigms
By eggdice
Programming Paradigms
- 644