Rocket
Elle Cheng
Victoria Chen
Background ➟ History of Rocket
- Wooden bird principel of action-reaction
- Chinese Fire Arrows real rocket born
- "Step Rocket" higher altitudes
- More powerful rocket heavier
- Spin stabilization gases placed at bottom
- Fly to higher altitudes and become lighter
- V-2 rocket small and powerful
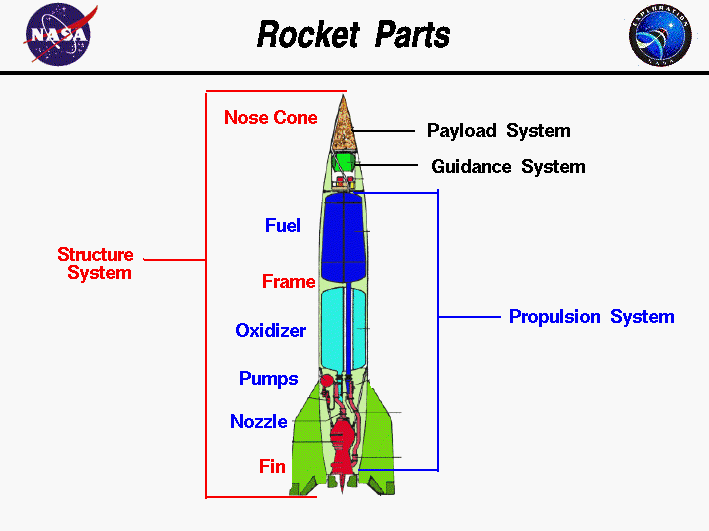
Parts of Rocket

Physics Concepts
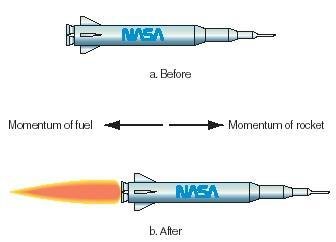
1. Conservation of momentum ➟
The of the fuel becomes the thrust of the rocket, therefore, the momentum is conserved the of the fuel becomes the thrust of the rocket, therefore, the momentum is conserved
the of the fuel becomes the thrust of the rocket, therefore, the momentum is conserved
Sample Calculation
0 =Mr • Vr↾+Mf • Vf⇂
2. Conservation of energy ➟
Backward force of the gases =
Forward forces of the rocket

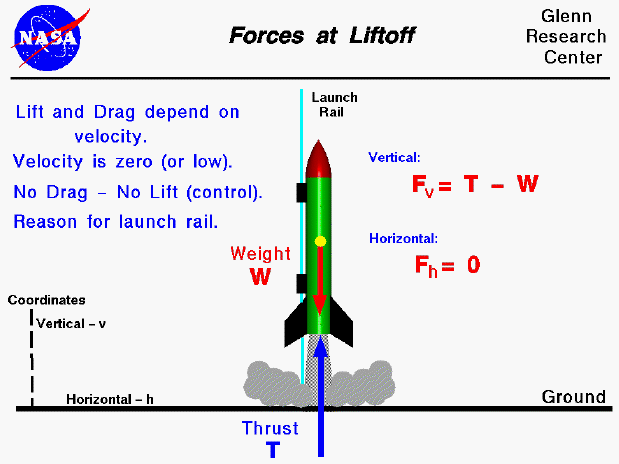
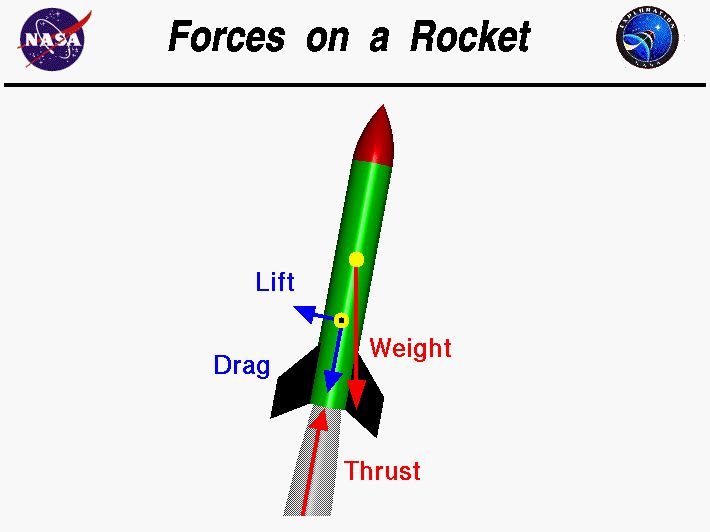
3. Force ➟
a large force must be apply in order for the rocket to accelerate.
Sample Calculation
4. Velocity ➟
The speed and the direction of motion for an object.
5. Acceleration ➟
When the fuel thrust out of the rocket, it has a huge force that pushes down, and so the acceleration occurs.
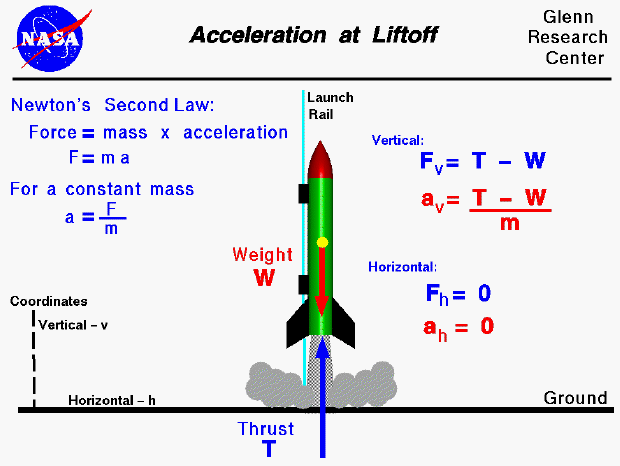
Sample Calculation
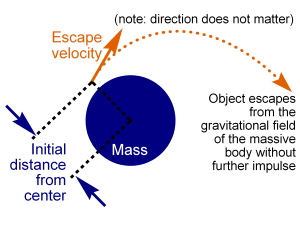
6. Escape speed ➟
a critical starting speed that permits a projectile to outrun gravity and to escape Earth.
References
"Force and Momentum." Rocket Principles. Web. 1 Jan. 2015.
Web. 3 Jan. 2015<http://www.philsrockets.org.uk/physics.pdf>.
"Brief History of Rockets." Brief History of Rockets. Web. 3 Jan. 2015<http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/k12/TRC/Rockets/history_of_rockets.html>.
NASA. NASA. Web. 3 Jan. 2015. <http://www.nasa.gov>.
"Presenting the Wonders of the Universe." Presenting the Wonders of the Universe. Web. 3 Jan. 2015. <http://www.guidetothecosmos.com>.
Web. 3 Jan. 2015. <http://www.real-world-physics-problems.com/rocket-physics.html >.

Copy of physics mid project
By Elle Cheng
Copy of physics mid project
- 172