Coding a Real-World App Using Purely Functional Techniques in

Ernesto Chero
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING?
Functional programming is based on a simple premise with far-reaching implications: functions that have no side effects.
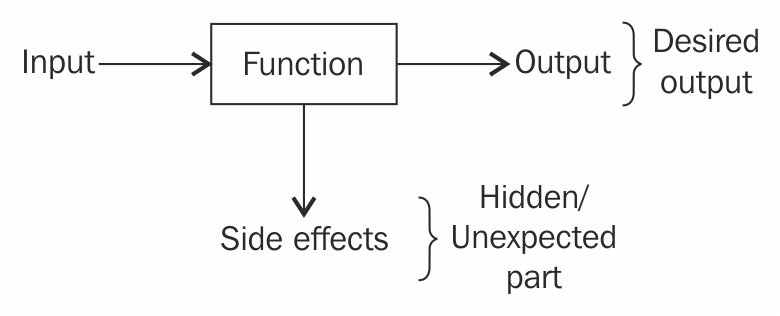
-
Modifying a variable -
Modifying a data structure in place -
Setting a field on an object -
Throwing an exception or halting with an error -
Printing to the console or reading user input -
Reading from or writing to a file -
Drawing on the screen
What are the side effects?

What is a pure function?
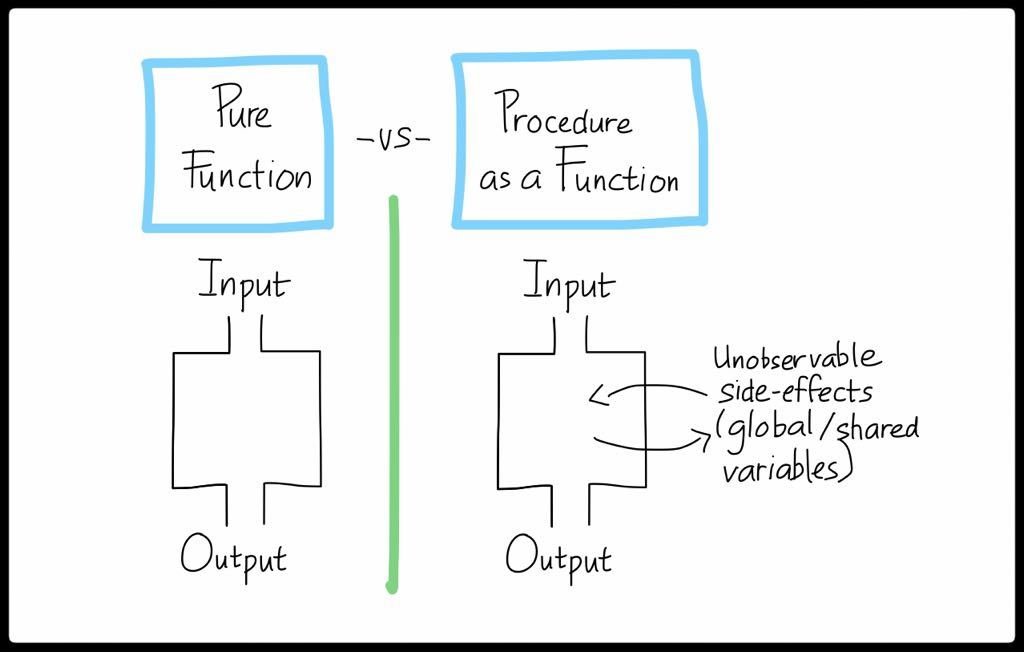
A pure function is side-effect free, plus the result does not depend on anything other than its inputs.
More about pure functions
For a given input, the only effect of a pure function is the output it produces—there are no other effects.
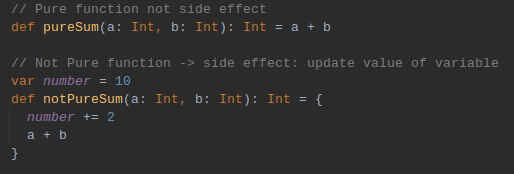
Why pure functions?
Benefits of pure funtions:
-
They're easier to reason about
- They're easier to combine
- They're easier to test
- They're easier to debug
- They're easier to parallelize
val x = f(a)
val y = g(b)
val z = h(c)
val result = x + y + zEVERYTHING IS A TYPE
Algebraic Data Types(ADTs)
- They are a way to structuring data and work well with the pattern matching
- An algebraic data type is any data that uses the product and sum pattern
Sum Types
- define a type which can assume different values
- A sum type is a type that is composed of different possible values and value shapes
// sum Type [Either, sealed trait, CoProduct]
sealed trait VehicleType
case object Car extends VehicleType
case object Moto extends VehicleType
// 2 VehicleTypes
sealed trait Colour
case object Red extends Colour
case object Yellow extends Colour
case object Blue extends Colour
// 3 ColoursProduct Types
- A product type is essentially a way of sticking multiple values inside of one - a Tuple, or something that’s very similar to one. Case classes are the prototypical product type:
case class Vehicle(vehicleType: VehicleType, colour: Colour, isUsed: Boolean)
- how many vehicles? if 2 VehicleTypes and 3 Colours and 2 Boolean types
- result => 12 vehicles
Function Types
- a function is a type in Scala, it represents an exponential operation
type Like = Colour => Boolean
How many implementations?
2*2*2 = (2)^3 = 8
Red -> {true, false}
Yellow -> {true, false}
Blue -> {true, false}WHERE CAN I START
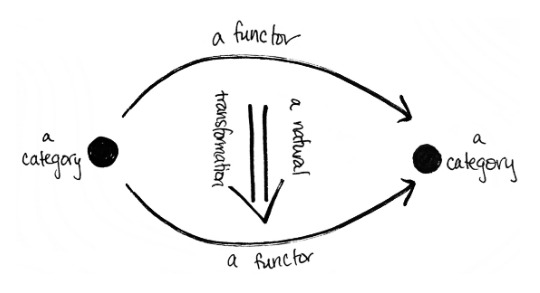
- Category Theory - Basic concepts
- Semigroup
- Monoid
- Functor
- Monad
- Applicative
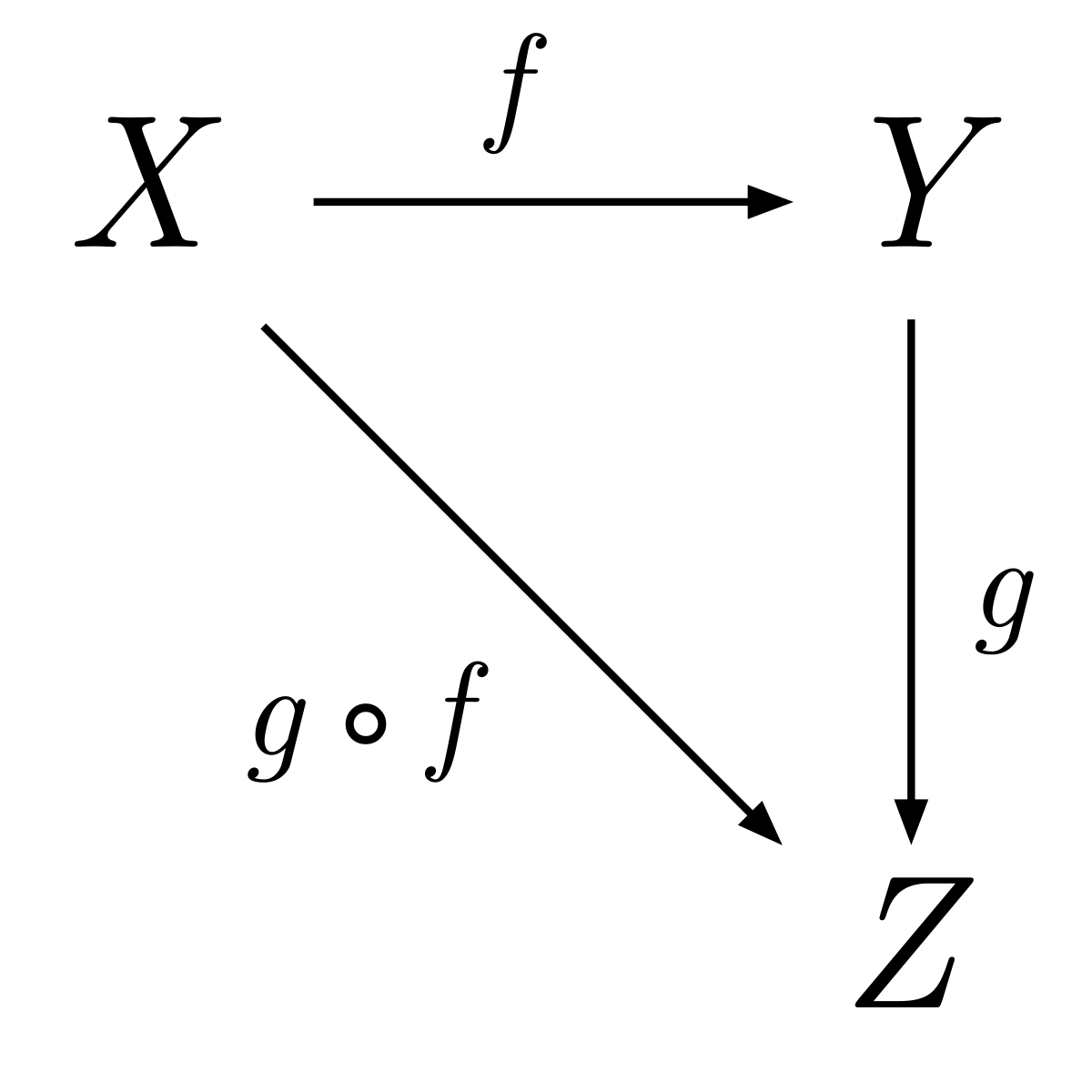
Cats FP Hierarchy
Semigroup
Monoid
Foldable
Semigroupal
Traverse
Functor
Apply
MonadError
Monad
Applicative
FlapMap
ApplicativeError
CODING A REAL-WORLD APP
Use Case : - Build a Spark Job to process data from different Json files and transform them so it could be sent to an external resource. [for example API, GraphQL, Store on DB, etc]
INPUTS
file: bands.json
{"id":1,"name":"AC/DC","hometown":"Sydney","year":1973}
{"id":0,"name":"Led Zeppelin","hometown":"London","year":1968}
{"id":3,"name":"Metallica","hometown":"Los Angeles","year":1981}
{"id":4,"name":"The Beatles","hometown":"Liverpool","year":1960}
file: guitars.json
{"id":0,"model":"EDS-1275","make":"Gibson","guitarType":"Electric double-necked"}
{"id":5,"model":"Stratocaster","make":"Fender","guitarType":"Electric"}
{"id":1,"model":"SG","make":"Gibson","guitarType":"Electric"}
{"id":2,"model":"914","make":"Taylor","guitarType":"Electric"}
{"id":3,"model":"M-II","make":"ESP","guitarType":"Electric"}
file: guitarsPlayers.json
{"id":0,"name":"Jimmy Page","guitars":[0],"band":0}
{"id":1,"name":"Angus Young","guitars":[1,2],"band":1}
{"id":2,"name":"Eric Clapton","guitars":[1,5],"band":2}
{"id":3,"name":"Kirk Hammett","guitars":[1,3],"band":3}EXPECTED OUTPUT
file: output.json
{
"id":1,
"name":"Angus Young",
"guitars":[
{
"id":1,
"model":"SG",
"make":"Gibson",
"guitarType":"Electric"
},
{
"id":2,
"model":"914",
"make":"Taylor",
"guitarType":"Electric"
}
],
"band":{
"id":1,
"name":"AC/DC",
"homeTown":"Sydney",
"year":1973
}
}
// more records below
...GRAPHIC REPRESENTATION
read
SOURCE
send
transform
Success
Failure
LET'S GO TO CODE

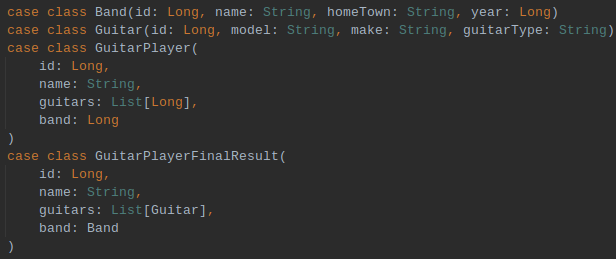
Defining types
Defining case classes [product type]
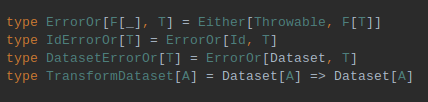
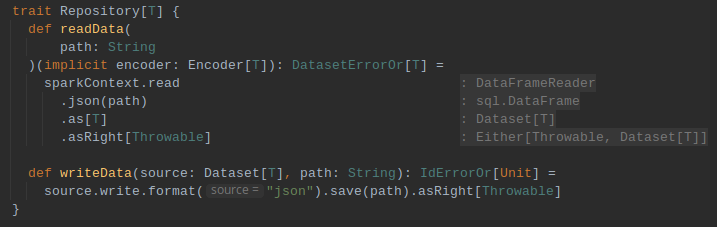
Spark Context Provider
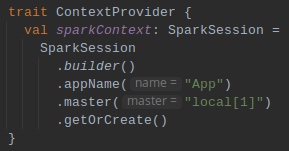
A common trait Repository
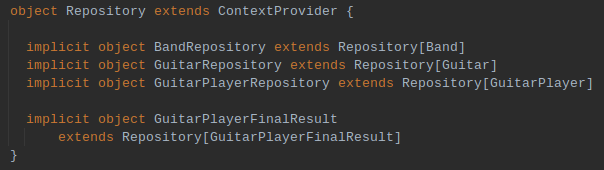
Repository Implementation
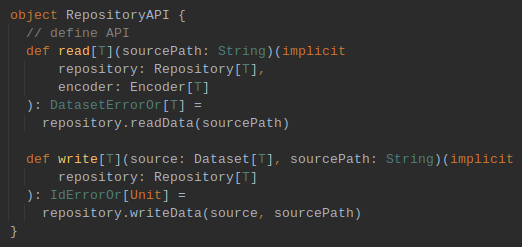
Defining API
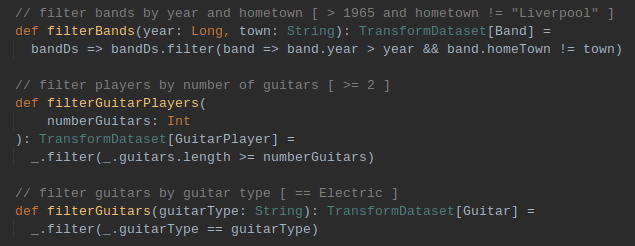
Transform Data [ filters ]
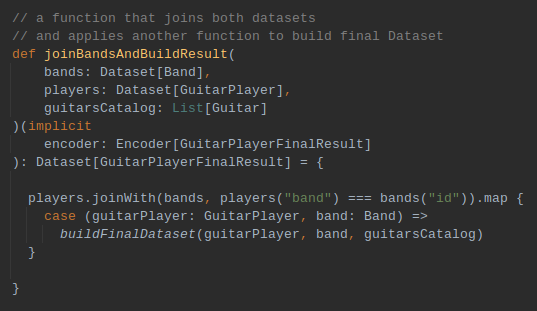
Transform Data [ joins ]
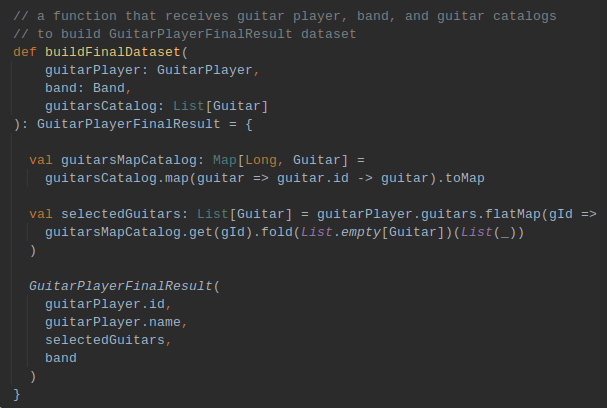
Transform Data [ transformations ]
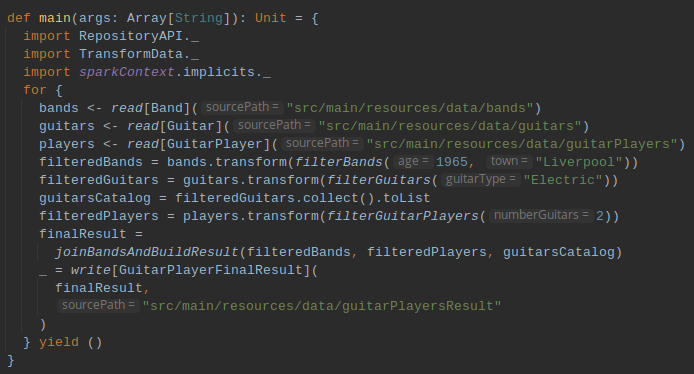
Put all together
Thank You!
-
https://blog.knoldus.com/scala-best-practices-pure-functions/ -
http://alvinalexander.com/scala/fp-book/benefits-of-pure-functions/ -
https://livebook.manning.com/book/functional-programming-in-scala/chapter-1/ -
https://kubuszok.com/2018/kinds-of-types-in-scala-part-1/ -
https://alvinalexander.com/scala/fp-book/algebraic-data-types-adts-in-scala/
References :
GitHub Repository
https://github.com/ernestochero/sparkRealApp
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMING
By Ernesto Chero
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMING
- 89
