Virtualization
vs
Cloud Computing

Virtualization
What is it?
Software that manipulates hardware. It separates physical infrastructures to create dedicated resources.
Resources that are allocated on-demand include memory, CPU, network and storage.
Virtualization
Difference
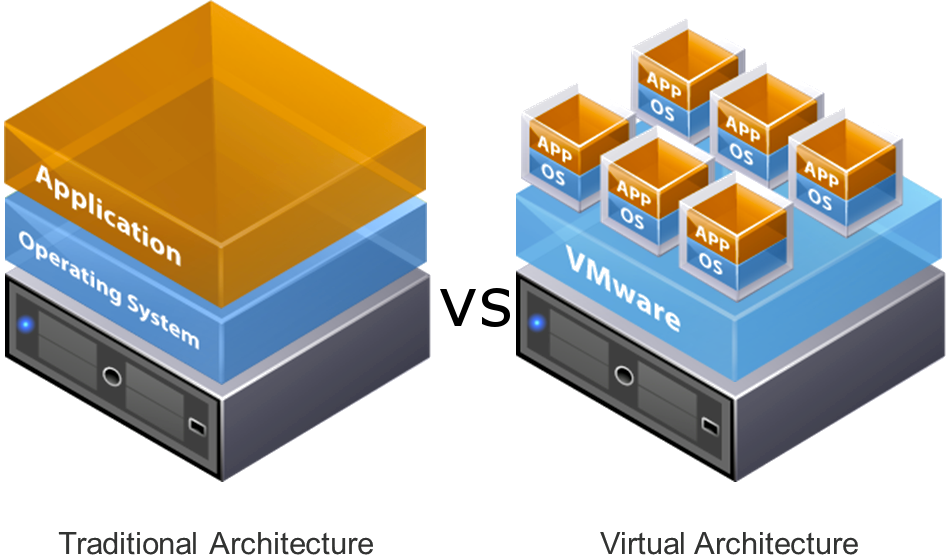
Virtualization
Different types
Virtualization technology is categorized as the following:
- Application virtualization
- Desktop virtualization
- User virtualization
- Storage virtualization
- Hardware virtualization
Virtualization
Application
This type of virtualization allows the user to access the application from a remotely located server.
It stores all personal information and other characteristics of the application, but can still run locally on the user's workstation.
Virtualization
Desktop
Allows user's OS to be remotely stored on a server in the data center, where the user can access it virtually from any location.
VDI, similarly to HW virtualization, logically separates the desktop from the physical machine.
Virtualization
User
It allows the user to maintain a fully personalized virtual desktop even when they get off the company’s network.
This is very useful because users can login even from a tablet or smartphone using a BYOD policy.
Virtualization
Storage
The concept of pooling of the physical storage from multiple network storage devices into what appears to be a single storage device that is managed from a central console.
Helps admins perform backups, archiving, and recovery more easily.
Virtualization
Hardware
The concept here is to make one processor act like there are several different ones.
Users leverage this type to run multiple OS on the same hardware. A hypervisor (VM manager) is needed in this case.
Virtualization
vCenter Server

Cloud Computing
What is it?
Delivery of services to organizations using the Cloud as a medium. Cloud, is the idea of having many computers together acting as a single computing environment.
Here, computing is treated as a utility rather than a specific product or technology.
Cloud Computing
The Cloud
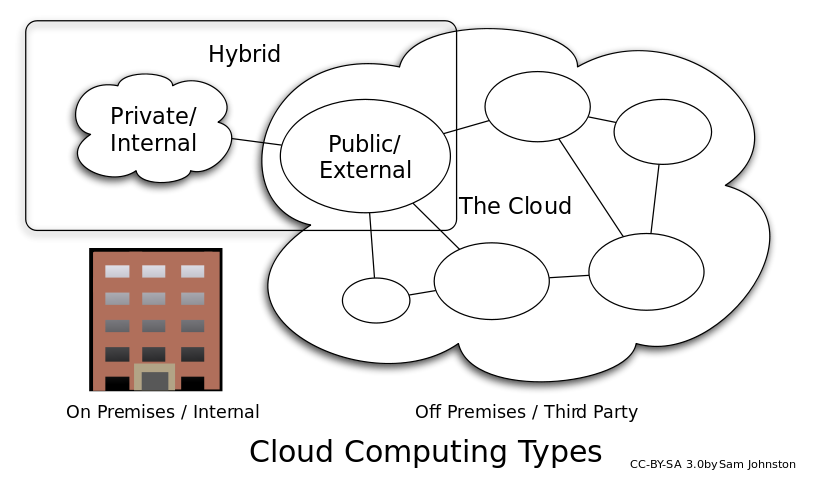
Cloud Computing
The Cloud
Private is when the infrastructure is operated by a single organization, internally or by a third-party, and is hosted either internally or externally.
Public is when the services are rendered over a network for public use. Most of the services here are free.
Hybrid is when the infrastructure is a combination of private and public.
Cloud Computing
Services
Cloud computing offers the following:
- Software-as-a-service (SaaS)
- Platform-as-a-service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS)
Cloud Computing
Services

Cloud Computing
SaaS
SaaS runs on distant computers in the cloud connect users via internet. Provides accessibility for the app development.
Software is managed from a central location and delivered in a one-to-many model.
Can be dynamically scaled based on the needs of end user.
Cloud Computing
PaaS
PaaS provides a cloud-based environment that supports the complete lifecycle of building and delivering web-based applications.
The ability to develop, test, deploy, host and maintain new apps in the same IDE.
Offers built-in scalability of deployed software including load balancing and failover features.
Cloud Computing
IaaS
IaaS provides computing resources including servers, networking, storage and data center space on a pay-per-use basis.
No need to invest in hardware as the resources are distributed as a services.
Can scale on-demand dynamic workloads and be very flexible for the working environment.
Virtualization
Software product that allows for the pooling of storage, network and compute resources that can be allocated on-demand.
Benefits:
- diverse systems
- budget integration
- resource maximization
Cloud Computing
Service delivery to organization depending on their needs. Services such as SaaS, PaaS and IaaS via the Cloud.
Benefits:
- outsourced IT
- pay-as-you-go model
- high scalability
Conclusion
Q&A

Virtualization vs Cloud Computing
By Ernest Stratoberdha
Virtualization vs Cloud Computing
Seminar in Networking
- 1,030
