C黑魔法
whoami
-
fallnight
-
資工二甲
-
113屆 儲備會長
-
特選仔
-
女婕思
outline
-
C黑魔法是啥
-
小試身手 - 判斷奇偶
-
運算子的優先順序
-
for-loop 的各種寫法
-
區域 & 全域變數
-
Random (亂數)
-
C的安全問題
C黑魔法是什麼?
C黑魔法是什麼?
-
你平時寫程式不會注意的小細節
-
遇到特定的測資就會出錯
-
可能沒學過的酷酷的寫法
-
遇到沒寫完善的code就可以鑽它的漏洞做壞壞的事(x
判斷奇偶
寫個可以判斷輸入的整數是奇數還是偶數的程式吧
if(n % 2 == 1)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數if(n % 2 != 0)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數哪一個比較準確?
直接丟個負數給它試試吧 你會知道誰比較好的
結果竟然不一樣?!

#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("請輸入n: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n % 2 != 0)
{
printf("%d是奇數\n",n);
}
else
{
printf("%d是偶數\n",n);
}
return 0;
}#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
printf("請輸入n: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n % 2 == 1)
{
printf("%d是奇數\n",n);
}
else
{
printf("%d是偶數\n",n);
}
return 0;
}
再試試看這個
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf(" 5 %% 2 = %d\n" , 5 % 2);
printf("-5 %% 2 = %d\n" , -5 % 2);
printf(" 5 %% -2 = %d\n" , 5 % -2);
return 0;
}第三行輸出怪怪的??
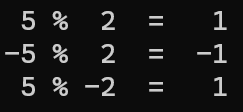
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf(" 5 %% 2 = %d\n" , 5 % 2);
printf("-5 %% 2 = %d\n" , -5 % 2);
printf(" 5 %% -2 = %d\n" , 5 % -2);
return 0;
}不賣關子了
解答時間~
C怎麼定義取餘數 %
a = (a / b) * b + a % b
=> (a % b) = a - (a / b) * b
整數型態的 a 等於 (a / b) * b + a % b
移項得知
a 除以 b 的餘數是 (a % b) = a - (a / b) * b
代入數字就清楚了
(a % b) = a - (a / b) * b
// a=-5, b=2
-5 % 2 = -5 - (-5 / 2) * 2
= -5 - (-2) * 2
= -5 - (-4)
= -5 + 4
= -1
// a= 5, b=-2
5 % -2 = 5 - (5 / -2) * (-2)
= 5 - (-2) * (-2)
= 5 - 4
= 1
if(n % 2 == 1)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數if(n % 2 != 0)
// 奇數
else
// 偶數所以比較準確的是?
if(n % 2 == 0)
// 偶數
else
// 奇數這樣寫也可以💯
驗證環節

#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
while(1)
{
printf("請輸入n: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n % 2 == 0)
{
printf("%d是偶數\n",n);
}
else
{
printf("%d是奇數\n",n);
}
}
return 0;
}運算子的優先順序
一樣先來個小試身手時間!
它會輸出什麼?
int a = -1, b = 1, c;
c = a+++b;
printf("a, b, c = %d, %d, %d\n", a, b, c);解答時間 ! 答案是...
int a = -1, b = 1, c;
c = a+++b;
printf("a, b, c = %d, %d, %d\n", a, b, c);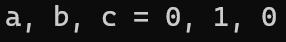
C的運算子優先順序
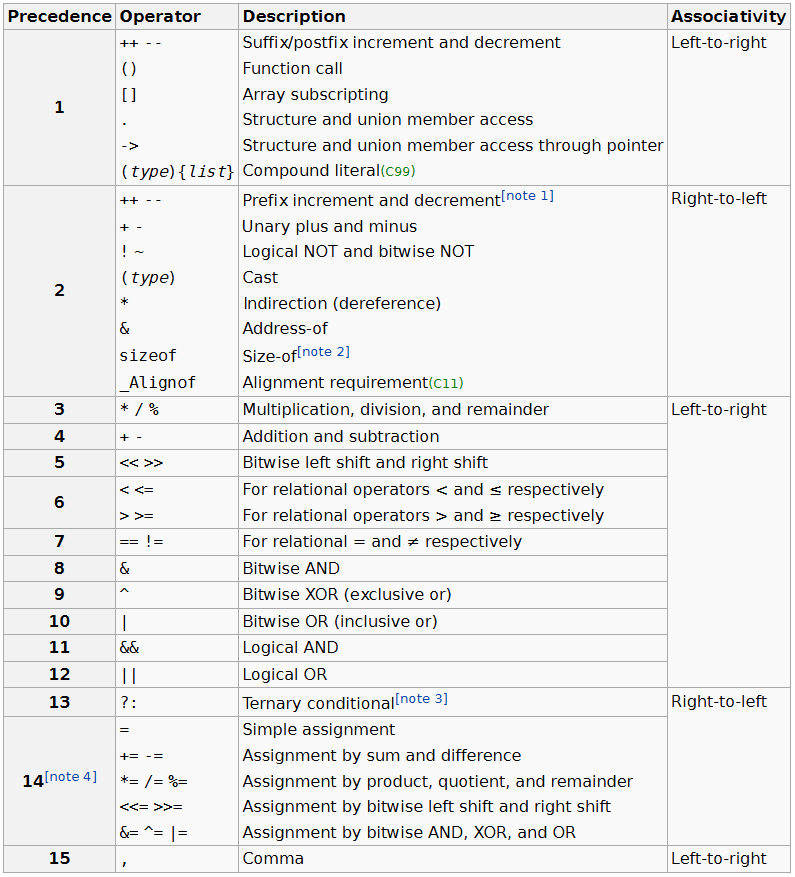
圖片來源: https://en.cppreference.com/w/c/language/operator_precedence
-
Operator Precedence
-
如果遇到同一種運算子就由左往右
再看回頭看一次
int a = -1, b = 1, c;
c = a+++b;
printf("a, b, c = %d, %d, %d\n", a, b, c);c = a+++b
=> c = (a++)+b
=> c = -1 + 1 = 0
=> a = a+1 = -1 + 1 = 0
=> b = 1
=> a = 0, b=1, c=0
它會輸出什麼?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i=1;0<i<10;i++){
printf("NISRA");
}
return 0;
}無限迴圈?!

解答時間 ! 原因是...
for(int i=1;0<i<10;i++){
printf("NISRA");
}0 < i < 10
=> (0 < i) < 10
因為 i 的初始值直接從大於 0 的 1 開始,所以 0 < i 永遠是True = 1
=> 1 < 10
所以迴圈的條件判斷永遠都是True,造成無限迴圈
改良方案
for(int i=1;0<i && i<10;i++){
printf("NISRA");
}0 < i < 10
=> 0 < i && i < 10
//i = 10
=> True && False
=> False,迴圈結束
它會輸出什麼?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 30;
if (c > b > a)
printf("True\n");
else
printf("False\n");
}解答時間 ! 答案是...
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 30;
if (c > b > a)
printf("True\n");
else
printf("False\n");
}
c > b > a
=> (c > b) > a
=> (30 > 20) > 10
=> (True) > 10 = 1 > 10
=> False
改良方案
int a = 10, b = 20, c = 30;
if (c > b > a)
printf("True\n");
else
printf("False\n");c > b > a
=> c > b && b > a
=> 30 > 20 && 20 > 10
=> True && True
=> True
for-loop的各種寫法
又一樣先來個小試身手時間!
請寫個for迴圈,印出以下結果
複習一下,迴圈是如何運作的?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 9; i >= 0; i--){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}- 先宣告初始值 i = 9
- 給個條件判斷迴圈何時終止
- 告訴程式結束一次迴圈之後要如何改變 i
1
3
2
還可以怎麼寫?
就是一些沒什麼意義但看起來很厲害的寫法
for-loop的黑魔法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10; 0 <= --i;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}for-loop的黑魔法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10; 0 <= --i;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}- 先宣告初始值 i = 10
- --i -> i 會先做 i = i - 1
- 最後進行條件判斷 0 <= i
1
3
2
for-loop的黑魔法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10;i-->0;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}for-loop的黑魔法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10;i-->0;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}- 先宣告初始值 i = 10
- i-->0 其實就是 i-- > 0
先取 i 的值做條件判斷,再做 i = i - 1
1
2
for-loop的黑魔法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10; 0 <= ~~ --i;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}for-loop的黑魔法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for(int i = 10; 0 <= ~~ --i;){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}- 先宣告初始值 i = 10
- ~ 是取反運算符,會把每一個 bit 取反,例如: 1010 取反變成 0101
所以 0 <= ~~ --i 跟 0 <= --i 是一樣的意思
1
2
如果要寫出這樣的結果呢?
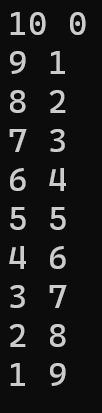
可以這樣寫
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 10, j = 0; i > 0 && j < 10; i--, j++){
printf("%d %d\n",i,j);
}
}- 先宣告兩個變數的初始值 i = 10, j = 0
- i、j的條件用&&相連,也就是只有i、j同時符合條件,迴圈才能繼續
- i 做 i--,j 做 j++,用逗號相連就可以一次做多個動作
1
3
2
珍惜生命,不要亂寫噁心別人
By 歷屆學長姐的留言
區域變數? 全域變數?
又又一樣先來個小試身手時間!
x會回傳多少?
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
return x;
}
}變數的可視範圍
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
return x;
}
}-
由下往上、由內到外,遇到的第一個
-
所以 x 會回傳1214
如果想跳過區域變數呢?
int x=0;
int getNum(){
int x=1214;
{
extern int x;
return x;
}
}x會回傳多少?
int main(){
{
int x=0;
}
printf("%d\n",x);
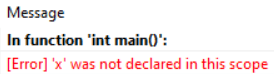
}報錯了?
int main(){
{
int x=0;
}
printf("%d\n",x);
}
-
跟 printf 相同的{ }內沒有 x 被宣告,所以出現錯誤
隨機亂數真的隨機嗎?
終於沒有小試身手了(x
Random ?
-
產生亂數的函式
-
但亂數並不是隨機產生
-
而是由一個亂數種子,透過複雜的數學演算法算出很像亂數的數值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // C 的亂數標頭檔
/* #include <cstdlib>
如果是C++則是引入這個標頭檔 */
int main(){
int x = rand(); //產生亂數
printf("x = %d\n",x);
return 0;
}多輸出幾次試試
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("%d\n",rand());
}
}每次執行結果都一樣??
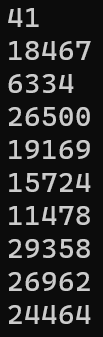
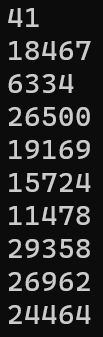
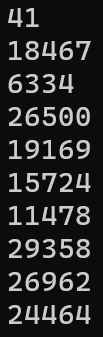
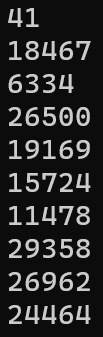
Random怎麼生成亂數的?
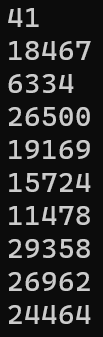
-
基於一個亂數種子,透過複雜的數學演算法算出很像亂數的數值
-
因為沒有特別去設定這次的亂數種子是什麼,所以執行結果都一樣
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
printf("%d\n",rand());
}
}怎麼設定亂數種子?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h> // C 的時間相關的標頭檔
/* #include <ctime>
如果是C++則是引入這個標頭檔 */
int main(){
srand(time(NULL)); //初始化時間種子
printf("%d\n",rand());
return 0;
}-
利用srand()函式設定
-
可以設定成以當下時間為種子去做亂數計算
C的安全問題
交作業都來不及了誰還會想到安全問題
這有什麼問題嗎?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}input沒有限制輸入長度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}限制? 怎麼加? 為什麼要加?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char input[10];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%9s", input);
printf("%s\n", input);
return 0;
}-
%s -> %9s
-
如果沒有限制,輸入過大的值會覆蓋到其他變數原本的值 -> Buffer Overflow
為什麼長度限制是9 ?
-
input字元陣列的宣告長度是10
-
但字串結尾要有結束符號 \0
-
所以是 9 個字元 + 1 個結束符號 = 10個陣列元素
| N | I | S | R | A | B | L | A | B | \0 |
|---|
input[10]
9
結尾
Buffer Overflow
-
緩衝區溢位
-
輸入的內容超過預先留好的記憶體大小
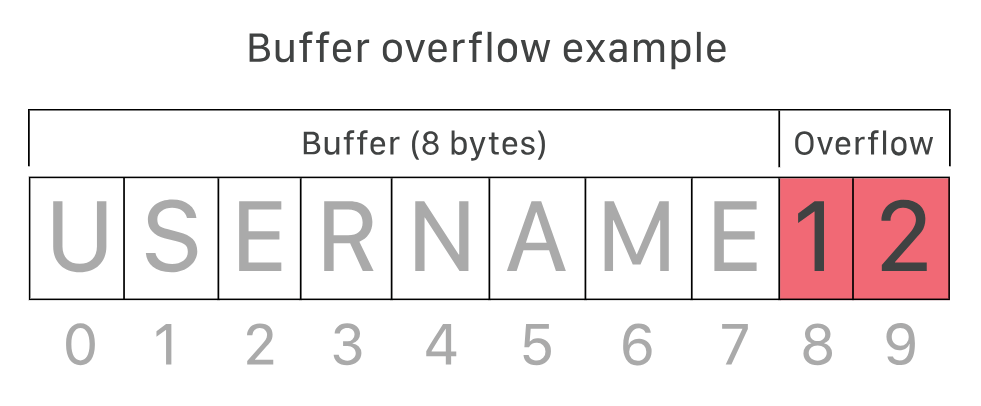
圖片來源: https://www.cloudflare.com/zh-tw/learning/security/threats/buffer-overflow/
讓我們鬼轉進入組語的世界
記憶體怎麼儲存輸入的變數內容?
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
簡易的記憶體佈局(Memory Layout)的示意圖
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
高位址
低位址
Memory Layout
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 程式碼區段(code section)
- 又稱為 text section
高位址
低位址
Memory Layout
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 存放著程式的全域變數
- 已初始化 / 未初始化
高位址
低位址
Memory Layout
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
-
動態分配的空間
-
C
-
malloc / free
-
-
C++
-
new / delete
-
-
高位址
低位址
Memory Layout
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 區域變數
高位址
低位址
Memory Layout
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
- 系統保留的空間
高位址
低位址
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
#include <stdio.h>
int global = 87; // data
int main()
{
int a = 10; // stack
}Memory Layout
高位址
低位址
Registers of x86
Register ?
-
暫存器
-
是一個臨時儲存區域
-
用於儲存指令、變數和變數的值、計算後的結果
- 方便CPU需要時可以快速存取,不用每一次都從記憶體找
x86 ?
-
x86是intel發明的指令集,我們的電腦處理器就會去執行x86的這些指令
Registers of x86
-
EIP
-
Instruction Pointer
-
下一個執行的 instruction 之位址
-
-
ESP
-
Stack Pointer
-
儲存 Stack 頭位址
-
-
EBP
-
Base Pointer
-
儲存 Stack 基底(base)位址
-
Memory Layout & Register of x86
kernel space
stack
data
heap
code
系統保留
區域變數
動態分配
程式全域變數
程式碼
EBP
ESP
EIP
舉個栗子
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[4];
scanf("%4s",&a);
printf("%s",a);
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | ???? |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
舉個栗子
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[4];
scanf("%4s",&a);
printf("%s",a);
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
舉個栗子
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[4];
scanf("%4s",&a);
printf("%s",a);
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
a [ ]
輸入 abcd
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[4];
scanf("%4s",&a);
printf("%s",a);
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | dcba |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
a [ ]
輸出 abcd
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a[4];
scanf("%4s",&a);
printf("%s",a);
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | dcba |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP

Lab Time
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}在不改動程式碼的前提下
輸入 input
印出 "Yes you pass it!"
~解答時間~
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | ???? |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | ???? |
| EBP-0x8 | ???? |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | 0x00000041 |
| EBP-0x8 | 0x5253494E |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00A |
| EBP-0x8 | RSIN |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
為什麼是A RSIN
Endian
-
位元組存放順序(byte ordering)
-
資料在記憶體中放的順序
e.g. 0x12345678 -
little-endian \x78 \x56 \x34 \x12
-
big-endian \x12 \x34 \x56 \x78
低位址
高位址
LSB
MSB
為什麼反過來 ? 為什麼一次只放4個 ?
-
x86 是 little-endian
-
一個字元等於 1 byte
-
1 byte = 8 bits
-
Register 是 32-bit = 4 byte
-
NISRA 存在EBP內,所以一行只能容納 4 個字元
A
R S I N
低位址
高位址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00A |
| EBP-0x8 | RSIN |
| EBP-0xC | ???? |
| EBP-0x10 | ???? |
EIP
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00n |
| EBP-0x8 | imda |
| EBP-0xC | bbbb |
| EBP-0x10 | aaaa |
EIP
如果輸入aaaabbbbadmin
覆蓋到 pwd[]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char pwd[8] = "NISRA";
char input[8];
printf("Give me some input: ");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(pwd, "admin") == 0)
printf("Yes you pass it!\n\n");
else
printf("No, keep trying.\n\n");
return 0;
}| index | value |
|---|---|
| EBP+0x8 | ... |
| EBP+0x4 | ... |
| EBP | EBP |
| EBP-0x4 | \x00\x00\x00n |
| EBP-0x8 | imda |
| EBP-0xC | bbbb |
| EBP-0x10 | aaaa |
EIP
input [ ]
pwd [ ]
參考資料
-
https://blog.gtwang.org/programming/c-cpp-rand-random-number-generation-tutorial-examples/#google_vignette
-
https://hackmd.io/@Ben1102/B1gfGLT3u
-
https://ithelp.ithome.com.tw/articles/10188599
-
https://hackmd.io/@mushding/assembly_language
-
https://www.eagletek.com.tw/post/register-in-cpu?srsltid=AfmBOooF2MVABCyP1Rfk334LJCFAkoybJTZpVatjJceDhXFcchuolNQb
-
https://www.ithome.com.tw/tech/56880
C黑魔法
By fallnight
C黑魔法
- 121



