Understanding Role of Provenance in Bioinformatics Workflows and Enabling Interoperable Computational Analysis Sharing
PhD Completion Seminar
Presenter: Farah Zaib Khan
Supervisors: AProf. Andrew Lonie, Prof. Richard O. Sinnott
Chair: Prof. Adrian Pearce

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar

November 28th, 2018
Introduction - Context
-
Workflows
-
Role of Workflows in Bioinformatics
-
Why use workflows?
-
Provenance
-
Why should we care about Provenance?
-
Workflow Management Systems
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
Workflows
(Esp. scientific workflows)
"The description of a process for accomplishing a scientific objective, usually expressed in terms of tasks and their dependencies"
(Ludäscher et al. 2009)
- Automated mechanism to systematise a computational analysis and capture the methods
- Directed Acyclic Graphs
- Data-flow oriented

https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
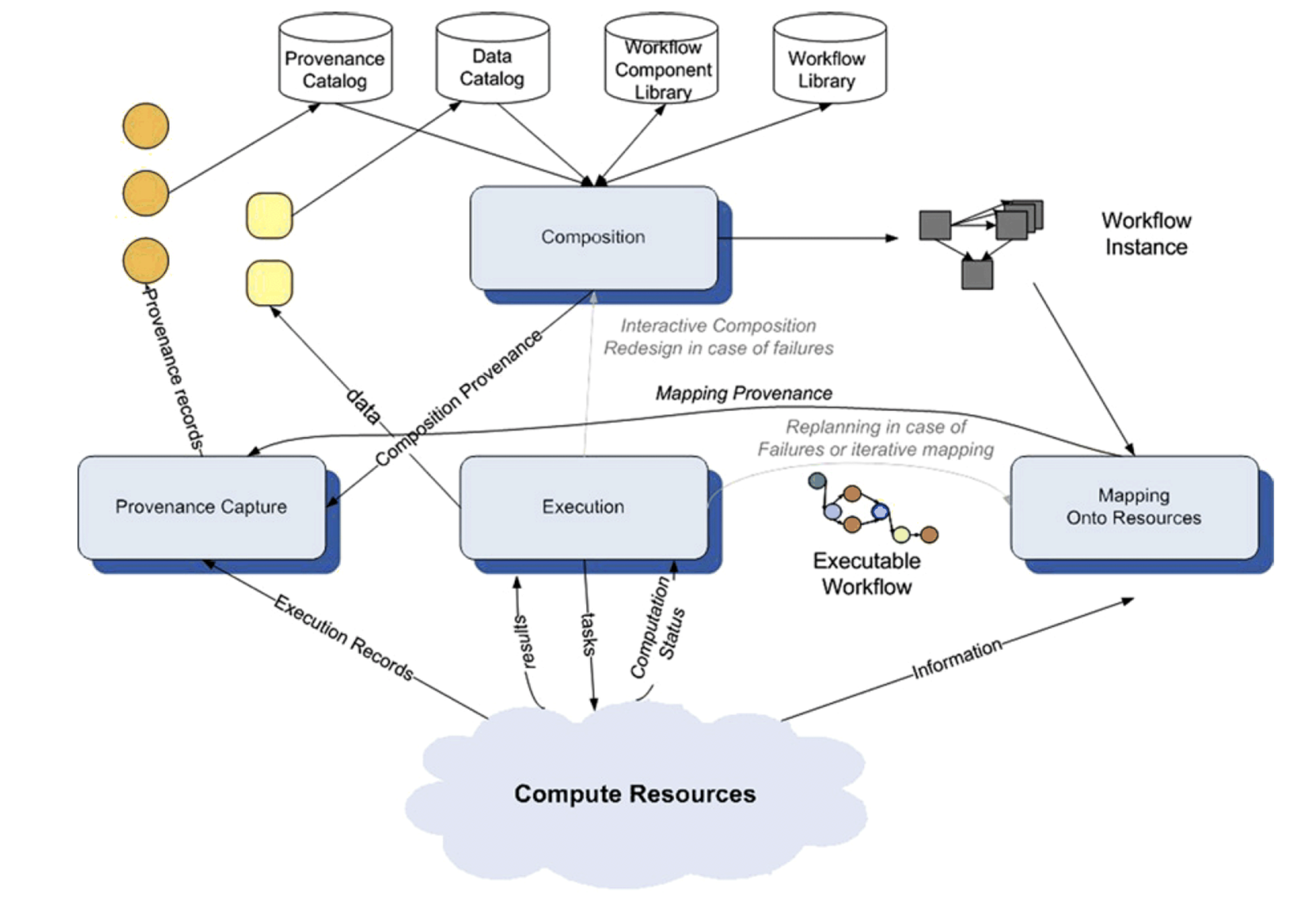
Workflow Life Cycle
4 Stages
-
Composition, Representation and Data Model
-
Mapping to Resources
-
Workflow Execution
-
Metadata and Provenance
Introduction - Context
-
Workflows
-
Role of Workflows in Bioinformatics
-
Why use workflow?
-
Provenance
-
Why should we care about Provenance?
-
Workflow Management Systems
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
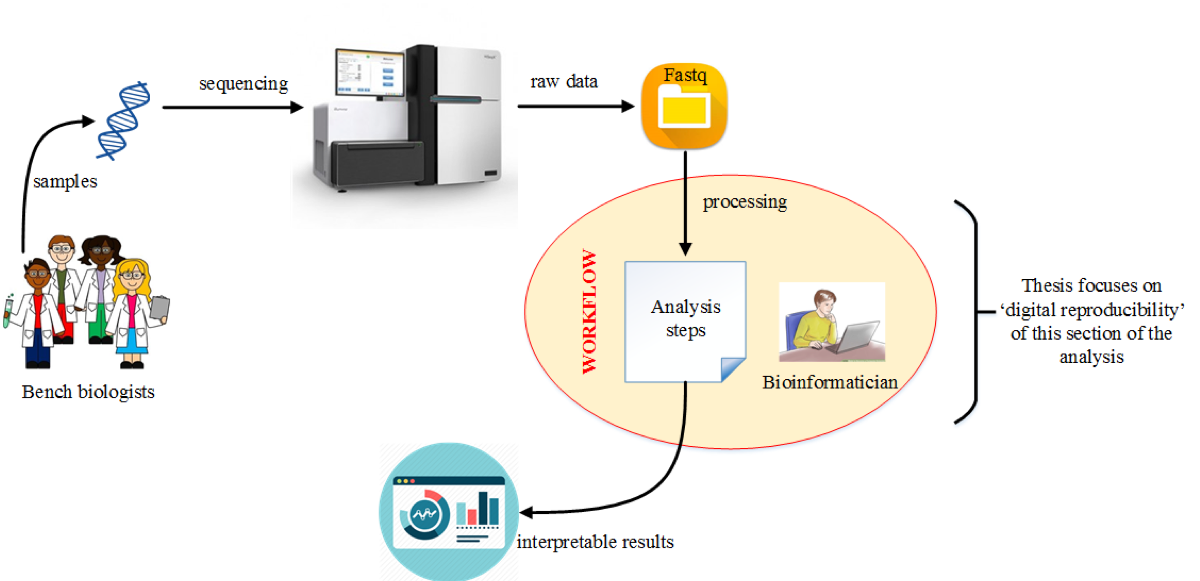
Exponential advances in the technologies and instruments
Declining sequencing cost ( From 2.7 billion USD to 1000USD)
- Ad hoc methods (scripts, manual steps etc.) are not enough to handle the volume of data.
- Computational Bioinformatics Workflows are employed to automate and record the steps performed.
Genomic data produced exponentially (tenfolds/year since 2002)
Now called four-headed beast...
Acquisition, Storage, Distribution, Analysis
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
Introduction - Context
-
Workflows
-
Role of Workflows in Bioinformatics
-
Why use workflow?
-
Provenance
-
Why should we care about Provenance?
-
Workflow Management Systems
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
Introduction - Context
-
Workflows
-
Role of Workflows in Bioinformatics
-
Why use workflow?
-
Provenance
-
Why should we care about Provenance?
-
Workflow Management Systems
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
Provenance
Information about entities, activities, and people involved in producing a piece of data or thing, which can be used to form assessments about its
Quality
Reliability
Trustworthiness

https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
Retrospective Provenance
The detailed record of the workflow execution including details of every process together with comprehensive information about the execution environment used to derive a specific data product.
All the details associated with a given workflow run
“Who enacted the workflow?”, “what was used to create a given data artefact?”, “when were the workflow and its processes enacted?”, “Where was the workflow enacted?”.
Prospective Provenance
The ‘recipes’ used to execute a computational task, e.g. the workflow specification.
Workflow Evolution
Tracking and capturing changes in workflow specifications, parameter setting, changes in the underlying software for a workflow step, or altering (adding/removing) a step
Introduction - Context
-
Workflows
-
Role of Workflows in Bioinformatics
-
Why use workflow?
-
Provenance
-
Why should we care about Provenance?
-
Workflow Management Systems
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
Who did this?
When did this happen?
Using what?
Provenance Applications
Attribution
Quality Assurance
Verification of Results
Debugging in case of failure/error
Reproducibility
Understandability
Reuse
Trust
Introduction - Context
-
Workflows
-
Role of Workflows in Bioinformatics
-
Why use workflow?
-
Provenance
-
Why should we care about Provenance?
-
Workflow Management Systems
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
- Systematising the representation and management of complex computational experiments comprised of various inter-dependent data analysis tasks.
- Efficient task scheduling, data management, modular methods and improved debugging.
-
Automated capture of provenance information (data) to document data dependencies and the derivation process.
Workflow Management Systems (WMSs)
Examples: Taverna, Galaxy, Kepler, WINGs, GenePattern, Pegasus, Vistrails, Knime...
Problem Statement
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
We have workflows ... with provenance collection as a major stage of workflow life cycle
We have WMS ... with provenance capture as an important attribute of such systems
What are the expectations from published research?
https://slides.com/farahzkhan/phd-seminar
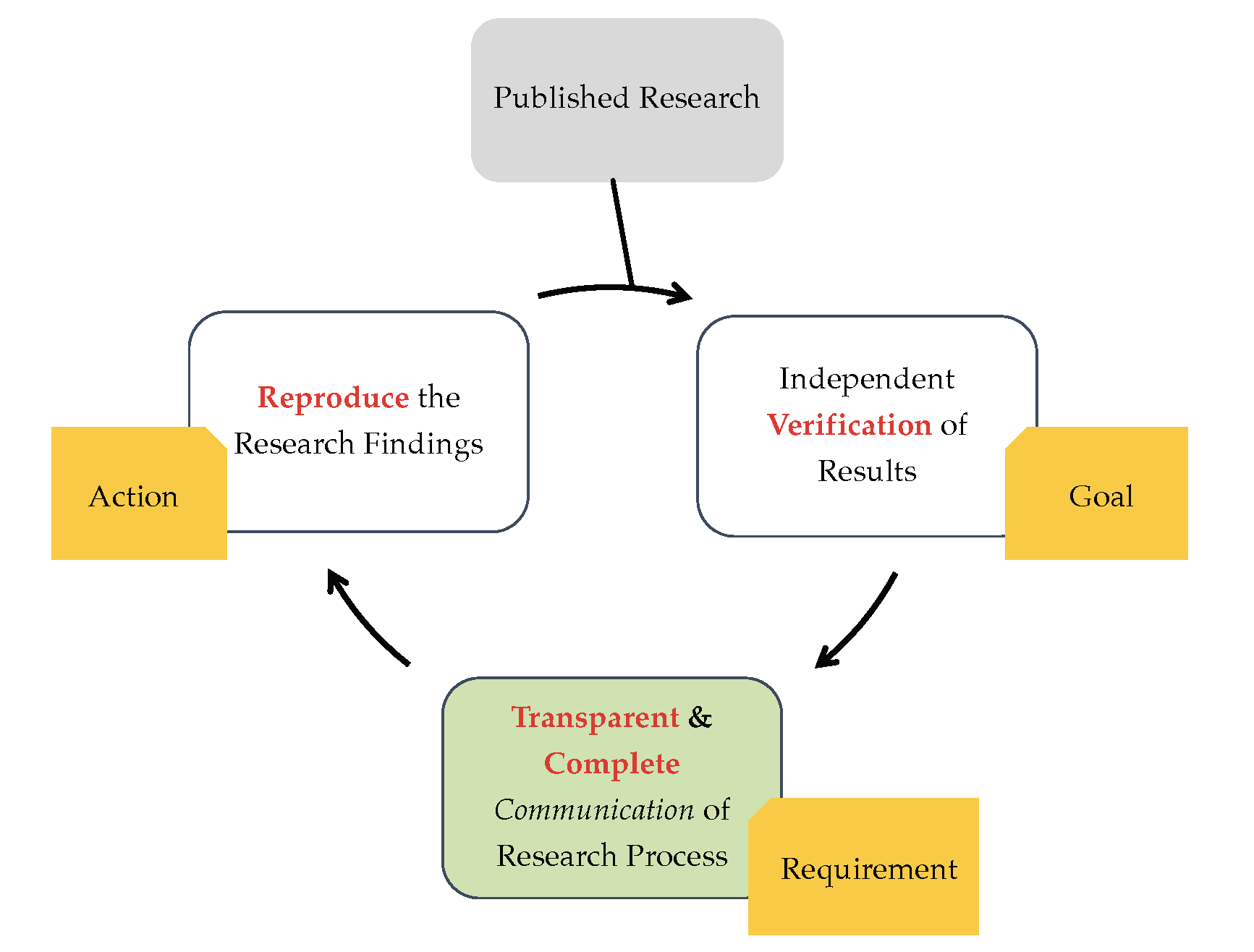
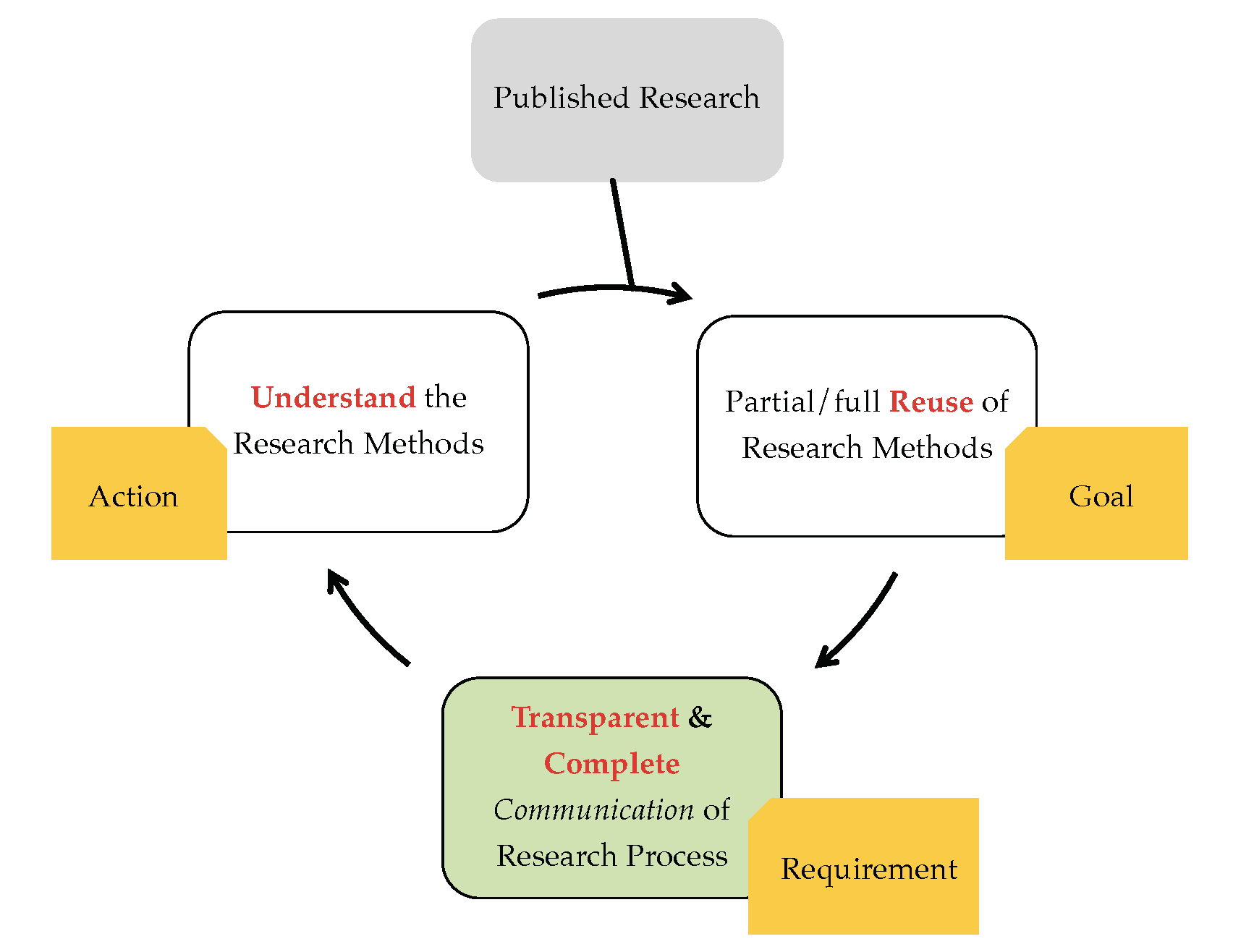
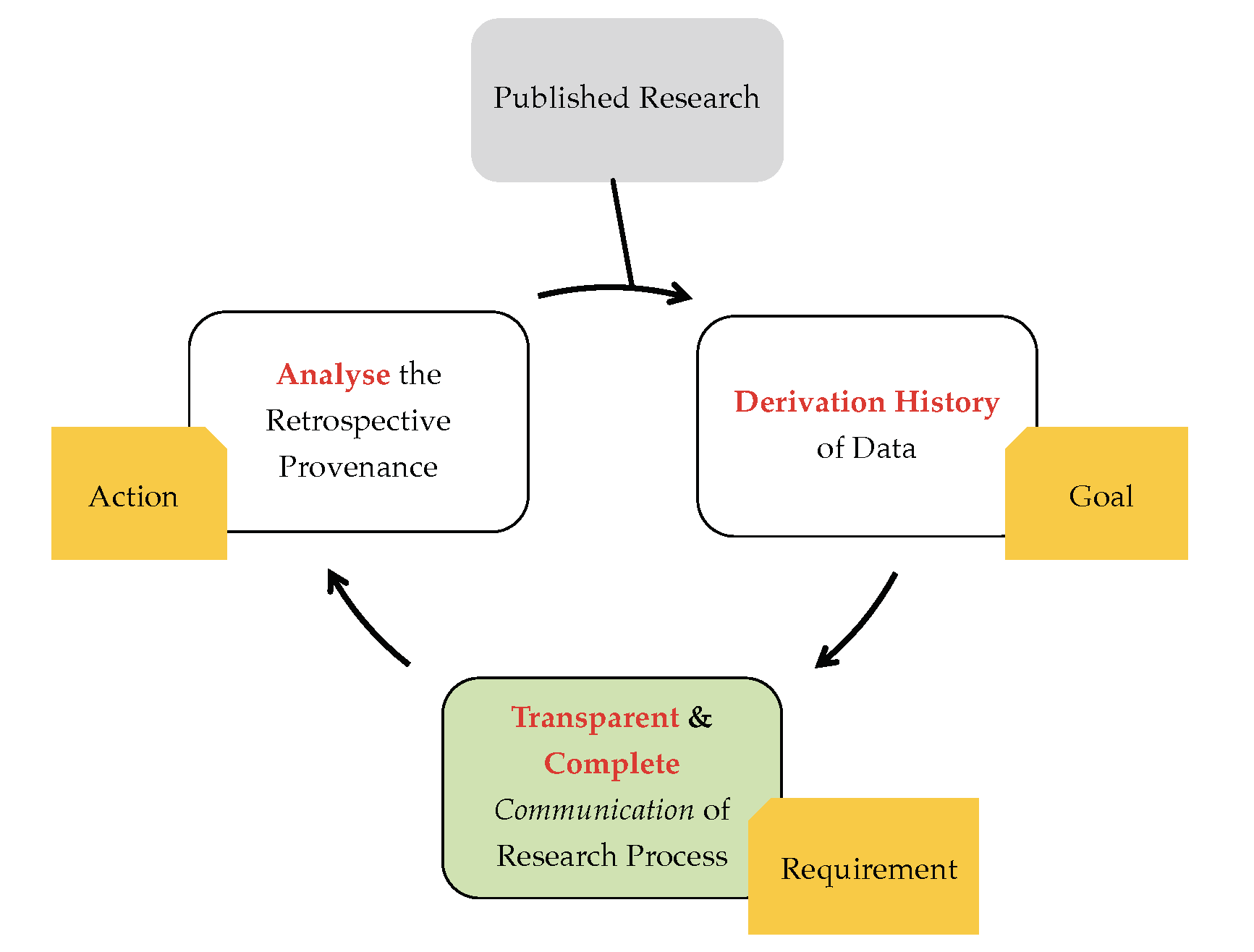
Expectation?
Published workflow-centric research end-users builds new research by exploiting sufficient provenance information including systematic methods and associated data documented in that paper.
Reality?
Different computing environment; Heterogeneous WMS; Incomplete Provenance; Limited/no access to data; Proprietary Software, Lack of standardisation, Poor understanding of provenance ...
Resulting in Workflow Decay
-
Limited understanding of Provenance factors and the associated artefacts - Leading to incomplete provenance
-
Heterogeneity in Workflow definition & Management - Heterogeneous Provenance capture, granularity & representation
-
Lack of standard Representation of Workflow-centric Analysis - Results in lack of understanding & interoperability between WMS and computing platforms
Open problems
The full "incomplete" list contains 232 entries...
And then we have many such lists.
WMS heterogeneity
What's wrong with having so many approaches??
Incomplete Provenance documentation;
Lack of interoperability;
Specific Solutions to workflow design and provenance capture;
Different Provenance Representations resulting in heterogeneity
Customised research-based pipelines supporting individual scenarios
Vendor Lock-In;
Aim & Scope of the Study
Aim of the Study
Facilitate bioinformatics workflow-centric research understanding and improve its reproducibility and re-use by analysing existing workflow definition approaches and identifying the fundamental elements of workflow provenance.
Building on this,
Devise techniques supporting Transparent & Complete Communication of Research.
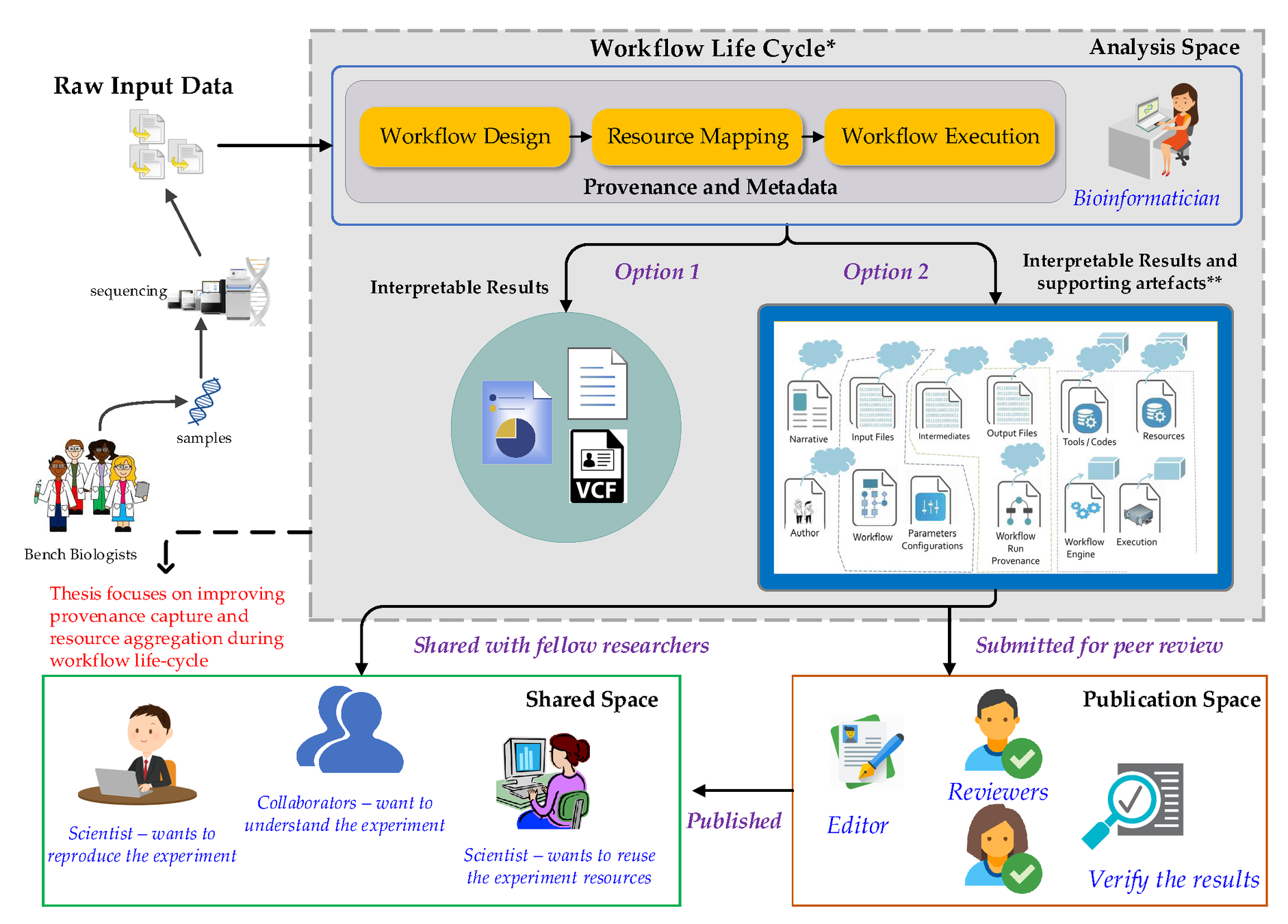
(*) The workflow life cycle is adapted from Deelman et al.
(**) The aggregation representation is adapted from these slides
Scope
-
Identification of Key Artefacts of Bioinformatics Workflow Provenance - To improve the understanding and ultimately capture of the provenance
-
Conceptual Provenance Framework applicable to all - To address the heterogeneity
-
Standardised Representation of Workflow Enactments - To ensure comprehensive analysis sharing including the resources associated with provenance and achieve interoperability
Three Major Lines of Work in this Thesis
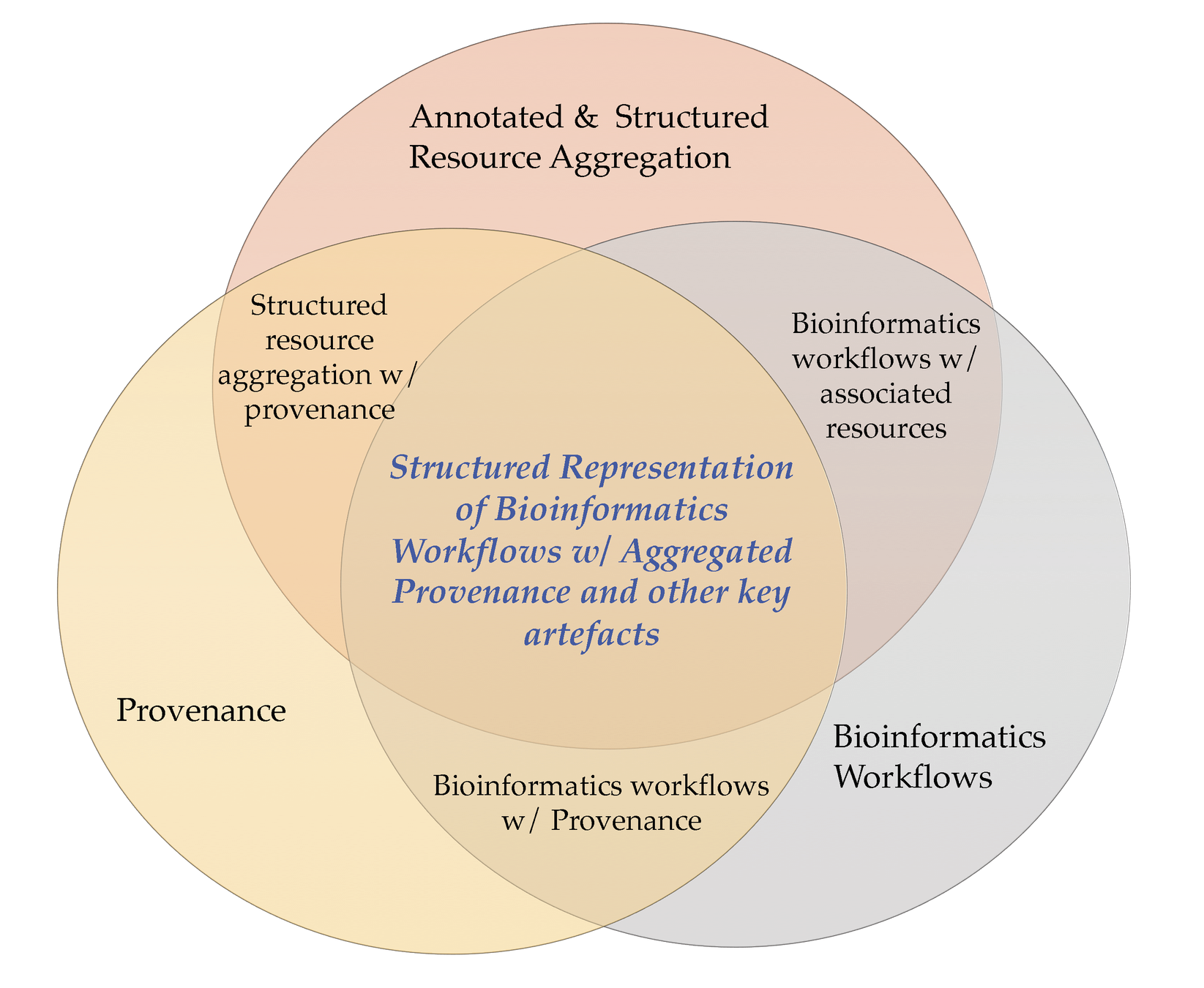
Dimensions explored:
-
Provenance
-
Bioinformatics Workflows
-
Annotated & Structured Resource Aggregation

Research Questions
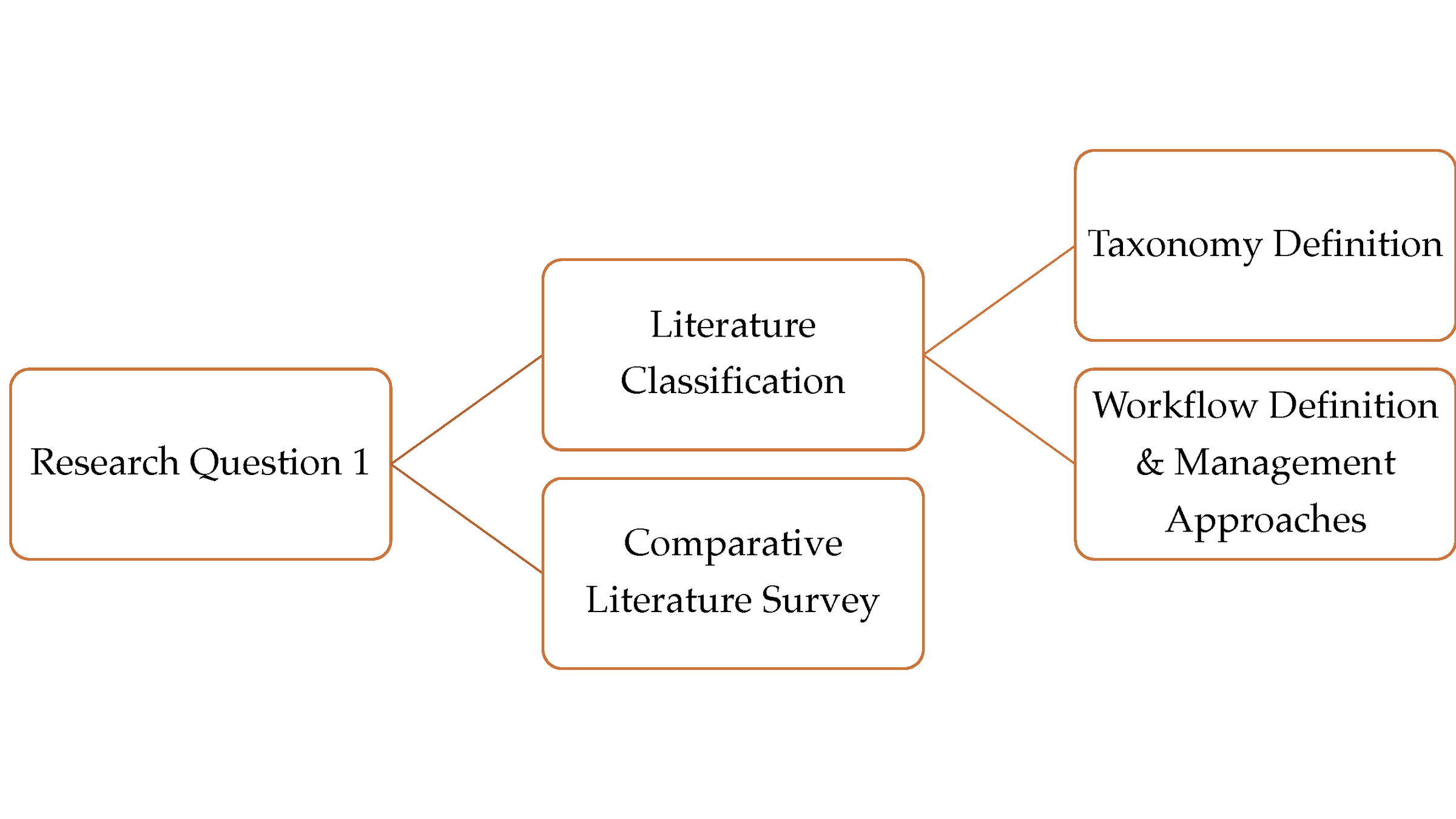
Research Question 1:
How are existing WMSs handling different aspects of provenance?
"different aspects of provenance"
"existing WMS"
Both classifications help in the evaluation of the existing WMSs with respect to their provenance capabilities.

Research Question 1:
How are existing WMSs handling different aspects of provenance?
"different aspects of provenance"
"existing WMS"
Provenance Taxonomy
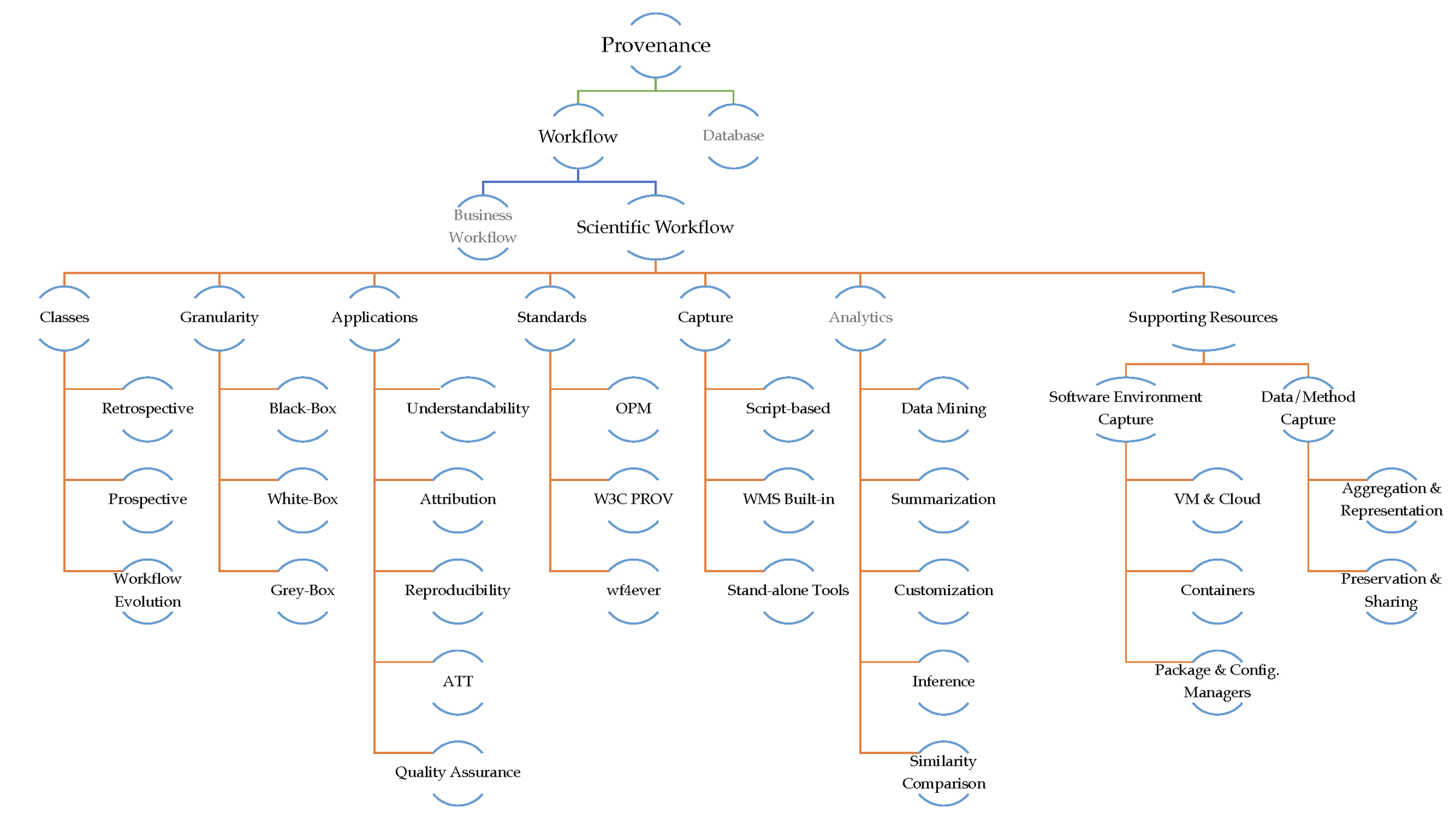

Provenance Aspects

Provenance Supporting Resources

Research Question 1:
How are existing WMSs handling different aspects of provenance?
"different aspects of provenance"
"existing WMS"
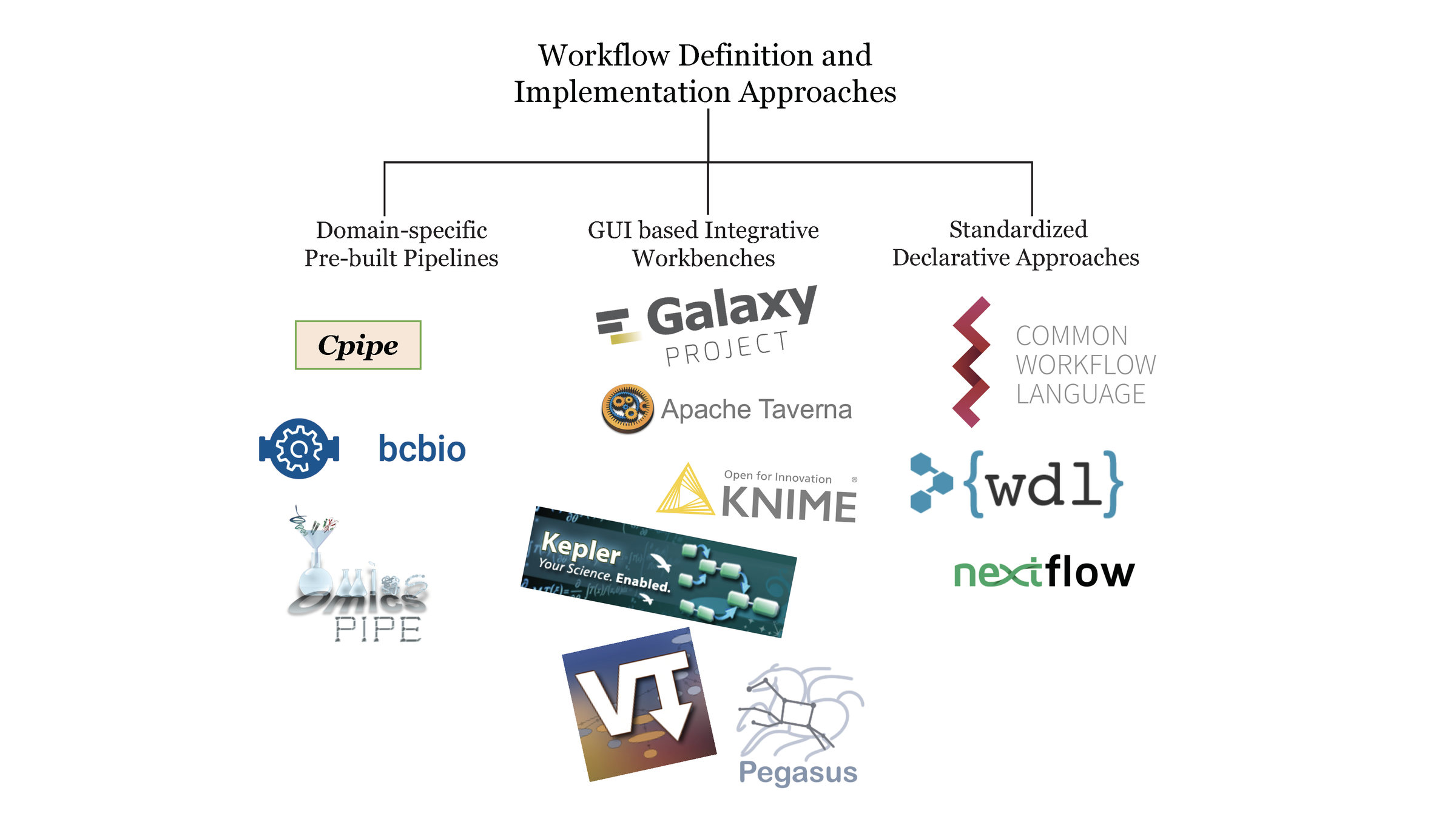
Workflow Approaches

Research Question 1:
How are existing WMSs handling different aspects of provenance?
"different aspects of provenance"
"existing WMS"
Both classifications help in the evaluation of the existing WMSs with respect to their provenance capabilities.

Common Trends
- No specific solution to provenance
- Dependent on execution platform for provenance capture
- Minimal information stored as provenance (as pdf document)
- Informal metadata captured
- Provenance elements are there but not always standardised
- Specific solutions such as HIstories and pages in Galaxy
- System specific workflows and methods
- Explicit declaration of resources facilitated
- Depends on the execution platform for provenance capture
Research Question 2: What are the key artefacts that must be documented for comprehensive provenance capture in bioinformatics workflows?

Research Question 2: What are the key artefacts that must be documented for comprehensive provenance capture in bioinformatics workflows?
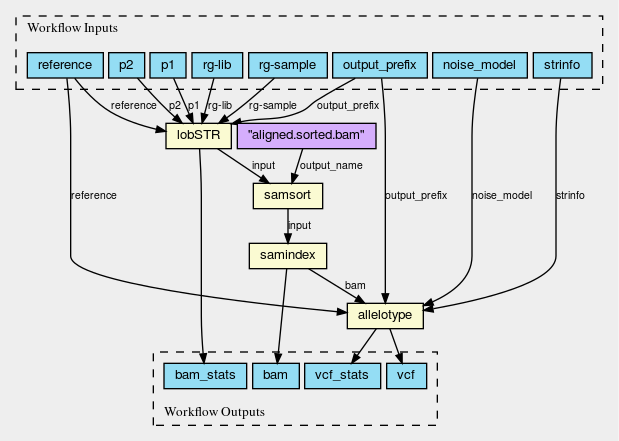
The Exemplar Systems


Variant Calling Workflow

Exemplar Workflow
Test Data (NA12878)
One from each Workflow Approach
This work in published and implementation details are available: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1747-0
Assumptions
What are assumptions?
Intricate details often considered needless to be documented by WMS or workflow authors
Note: Different workflow approaches have different assumptions; missing information varies
Why assumptions are not encouraged?
Assumptions result in lack of necessary details when an analysis is published
Heterogeneous & Incomplete provenance documentation
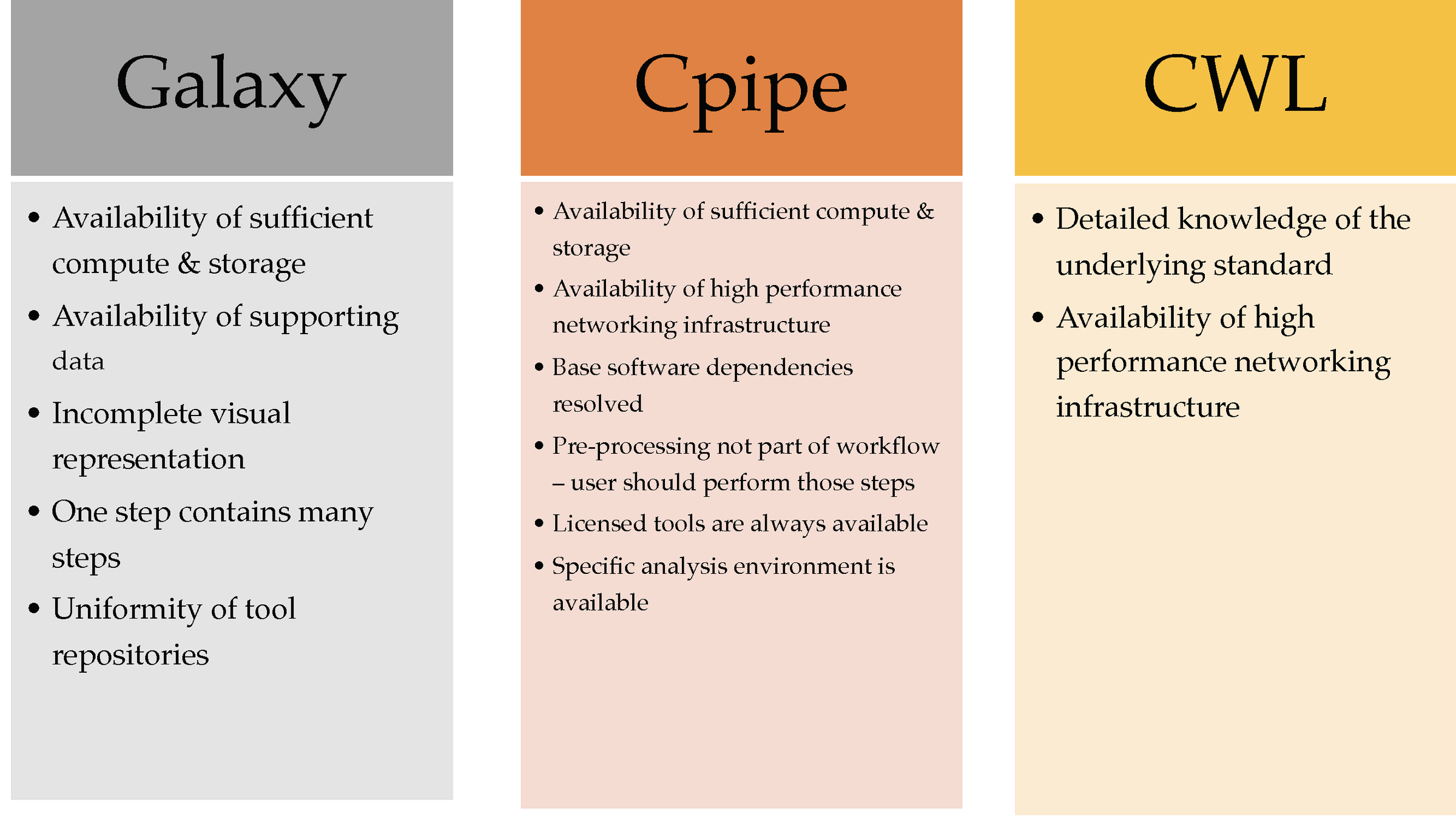
Identified Assumptions
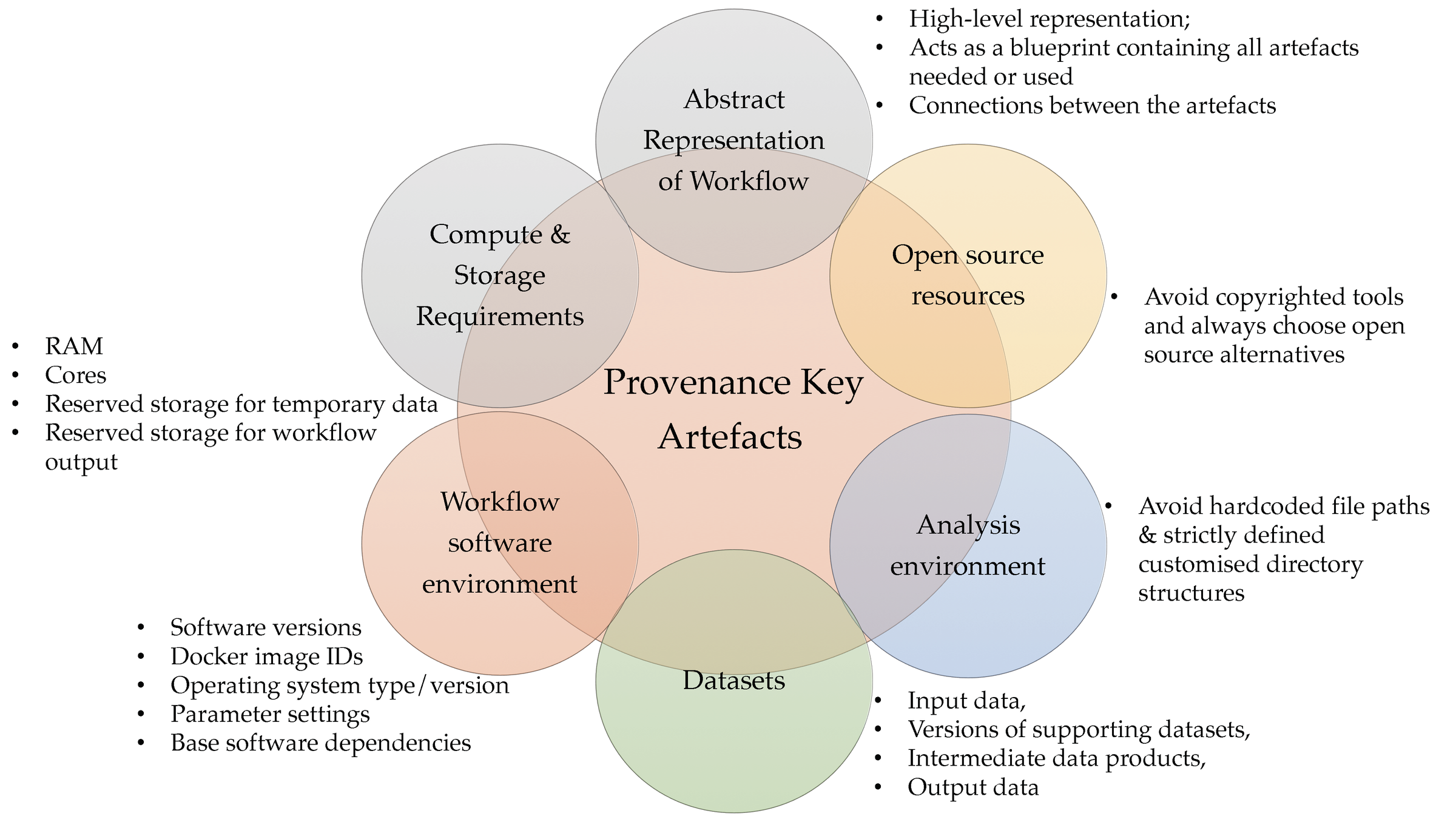
Factors out of control of an author
- Online third party resources
- Learning curve of new standards
Summary
-
The intricate underlying details associated with workflow implementation, considered needless to be stated (assumed to be known)
- Lead to various missing elements from the workflow provenance.
-
These implicit assumptions are identified through practical enactment of a complex workflow.
- Using one exemplar system from each workflow category
-
Declarative approaches are found better for workflow definition... why??
- Explicit nature
- A standard is followed to specify workflows
- Least assumptions
- Through the implicit assumptions, key artefacts of bioinformatics workflow provenance are identified.

Conclusions
Adhering to the following proposed recommendations along with an explicit declaration of workflow specification will result in fine-grained and complete provenance capture.
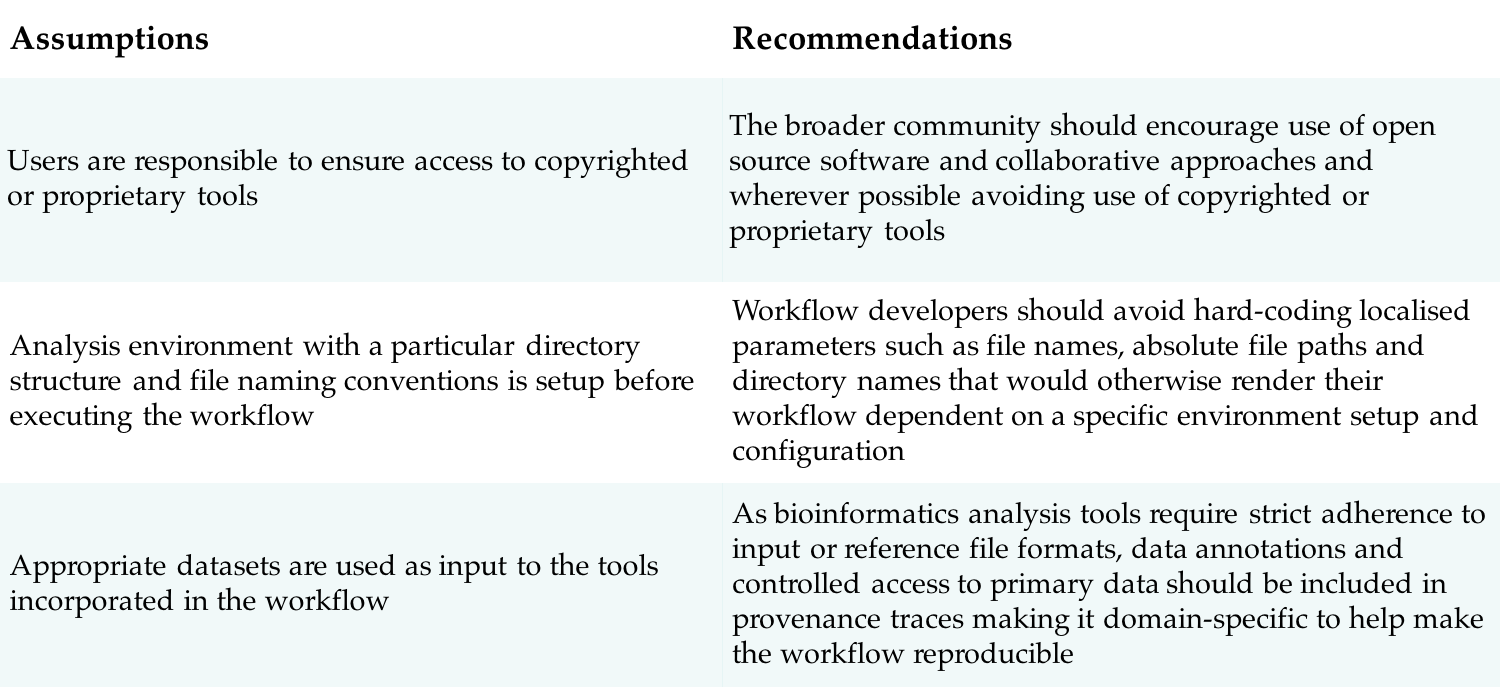
Conclusions
Adhering to the following proposed recommendations along with an explicit declaration of workflow specification will result in fine-grained and complete provenance capture.
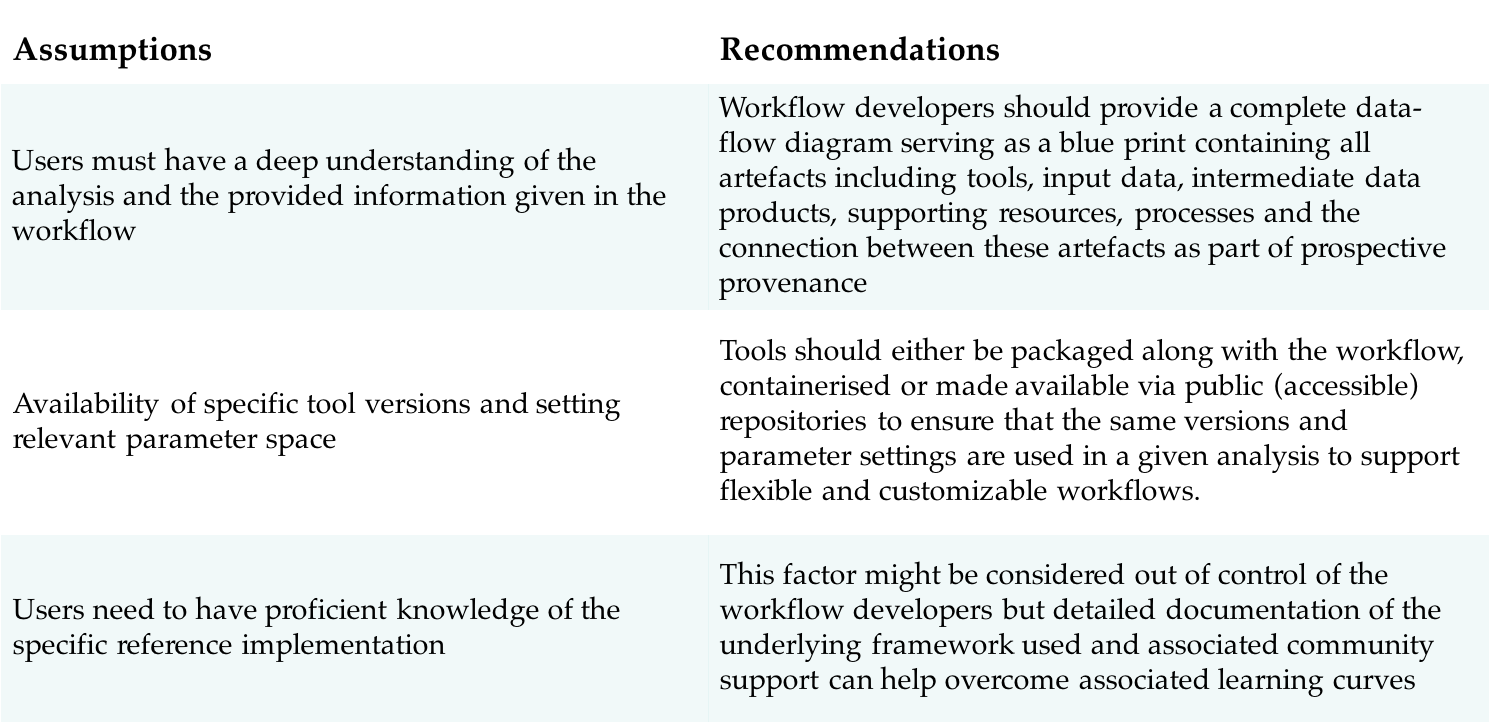
Conclusions
Adhering to the following proposed recommendations along with an explicit declaration of workflow specification will result in fine-grained and complete provenance capture.

Research Question 2: What are the key artefacts that must be documented for comprehensive provenance capture in bioinformatics workflows?
Common recommendations, best practices and standard approaches for
workflow design and workflow-centric analyses sharing
focused on improving the applications of provenance
Grouped these recommendations to identify fundamental artefacts and practices crucial for the capture of comprehensive provenance
and support the transparent sharing of workflow-centric studies.
Pragmatic Analysis of 15 prominent studies to extract 20 common recommendations
Literature
Method
Outcome
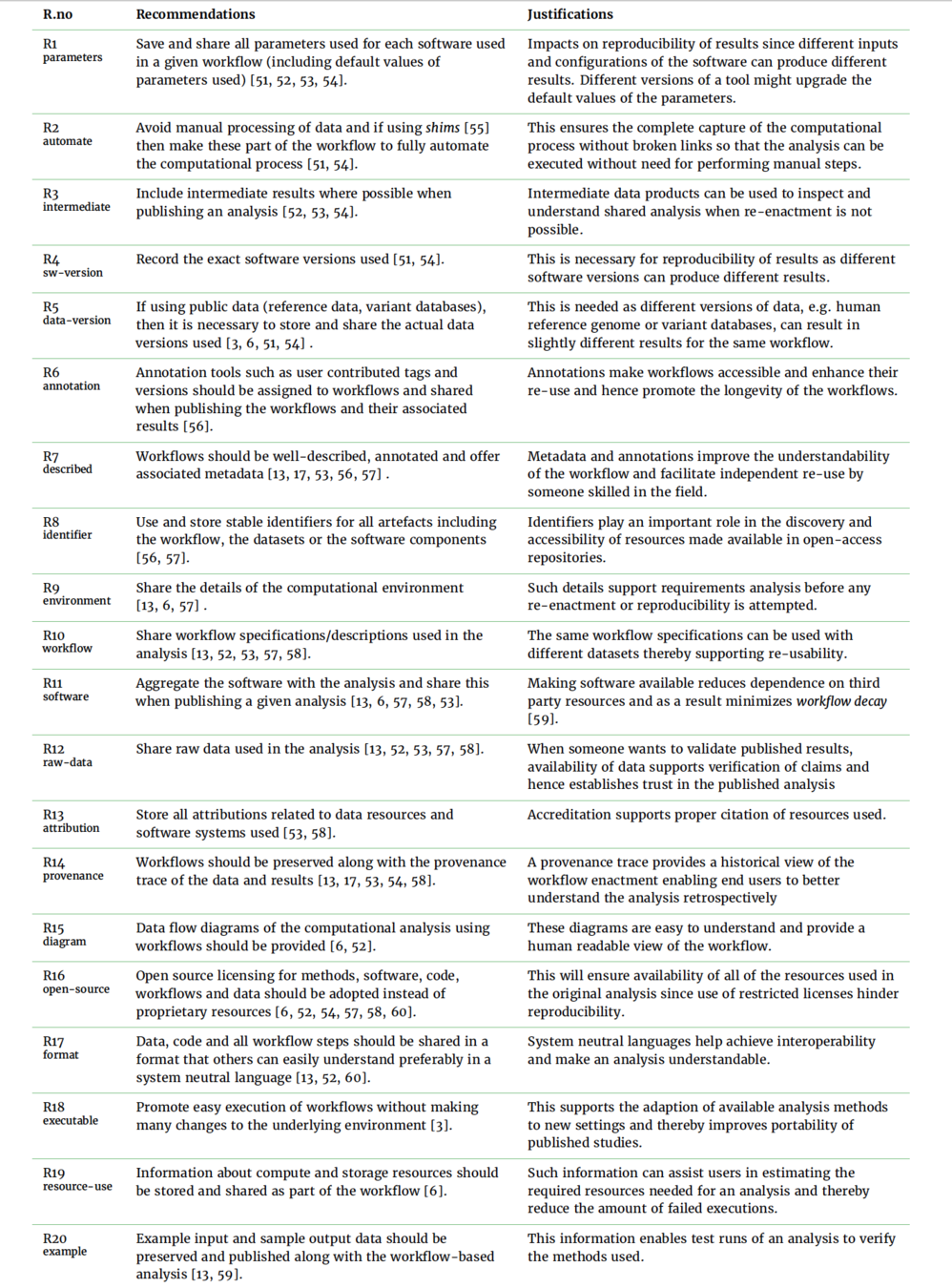
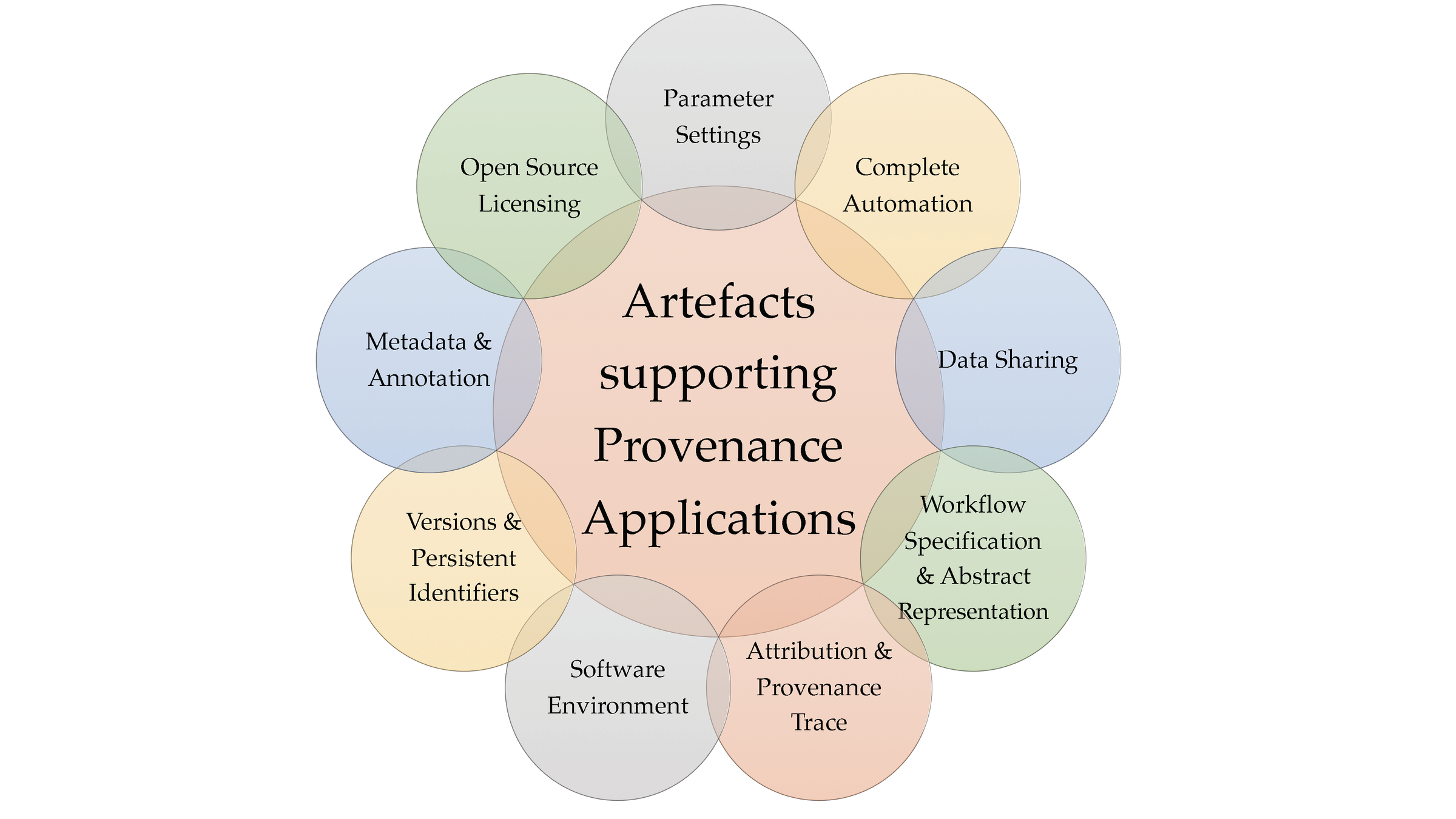
Findings
-
Improved understanding of
-
The crucial provenance artefacts that are required in case of bioinformatics workflows
-
Impact of these artefacts on different applications of provenance
-
Implications of incomplete documentation of provenance
-

Issues
- The sharing of “all artefacts” from a computational experiment or in other words following all the recommendations and best practices arbitrarily without any informed guidance is a demanding task.
-
Again "heterogeneity" resulting in varying
- Provenance documentation
- Provenance Granularity
- Provenance representation
- Sharing mechanisms of these artefacts
Research Question 3
How can we devise a hierarchical provenance framework encompassing community experiences that can serve as a guiding principle to determine the state of the provenance of a given published analysis designed using a particular workflow definition approach?

Issues
- The sharing of “all artefacts” from a computational experiment or in other words following all the recommendations and best practices arbitrarily without any informed guidance is a demanding task.
-
Again "heterogeneity" resulting in varying
- Provenance documentation
- Provenance Granularity
- Provenance representation
- Sharing mechanisms of these artefacts
Provenance Framework

Provenance Framework

Level 0 –Trust, Prospective Provenance & Reuse
Level 1 –Retrospective Provenance & Reproducibility
Level 2 –Towards White-box Enactment
Level 3 –Understandability & Specificity
Issues
- The sharing of “all artefacts” from a computational experiment or in other words following all the recommendations and best practices arbitrarily without any informed guidance is a demanding task.
-
Again "heterogeneity" resulting in varying
- Provenance documentation
- Provenance Granularity
- Provenance representation
- Sharing mechanisms of these artefacts
Solution
- Hierarchical & Generic Provenance framework as a guide
-
Again "heterogeneity" resulting in varying
- Each level will have same provenance elements
- The granularity of information will be similar given the level is same
- Provenance representation - Still an issue
- Sharing mechanisms of these artefacts - Still an issue
Summary
Research Question 4
How can we leverage existing abstraction and standardisation techniques to realise the provenance framework and demonstrate its utility?
Issues
- The sharing of “all artefacts” from a computational experiment or in other words following all the recommendations and best practices arbitrarily without any informed guidance is a demanding task.
-
Again "heterogeneity" resulting in varying
- Provenance documentation
- Provenance Granularity
- Provenance representation
- Sharing mechanisms of these artefacts
Solution
- Hierarchical & Generic Provenance framework as a guide
-
Again "heterogeneity" resulting in varying
- Each level will have same provenance elements
- The granularity of information will be similar given the level is same
- Provenance representation - Still an issue
- Sharing mechanisms of these artefacts - Still an issue
Research Question 4
How can we leverage existing abstraction and standardisation techniques to realise the provenance framework and demonstrate its utility?

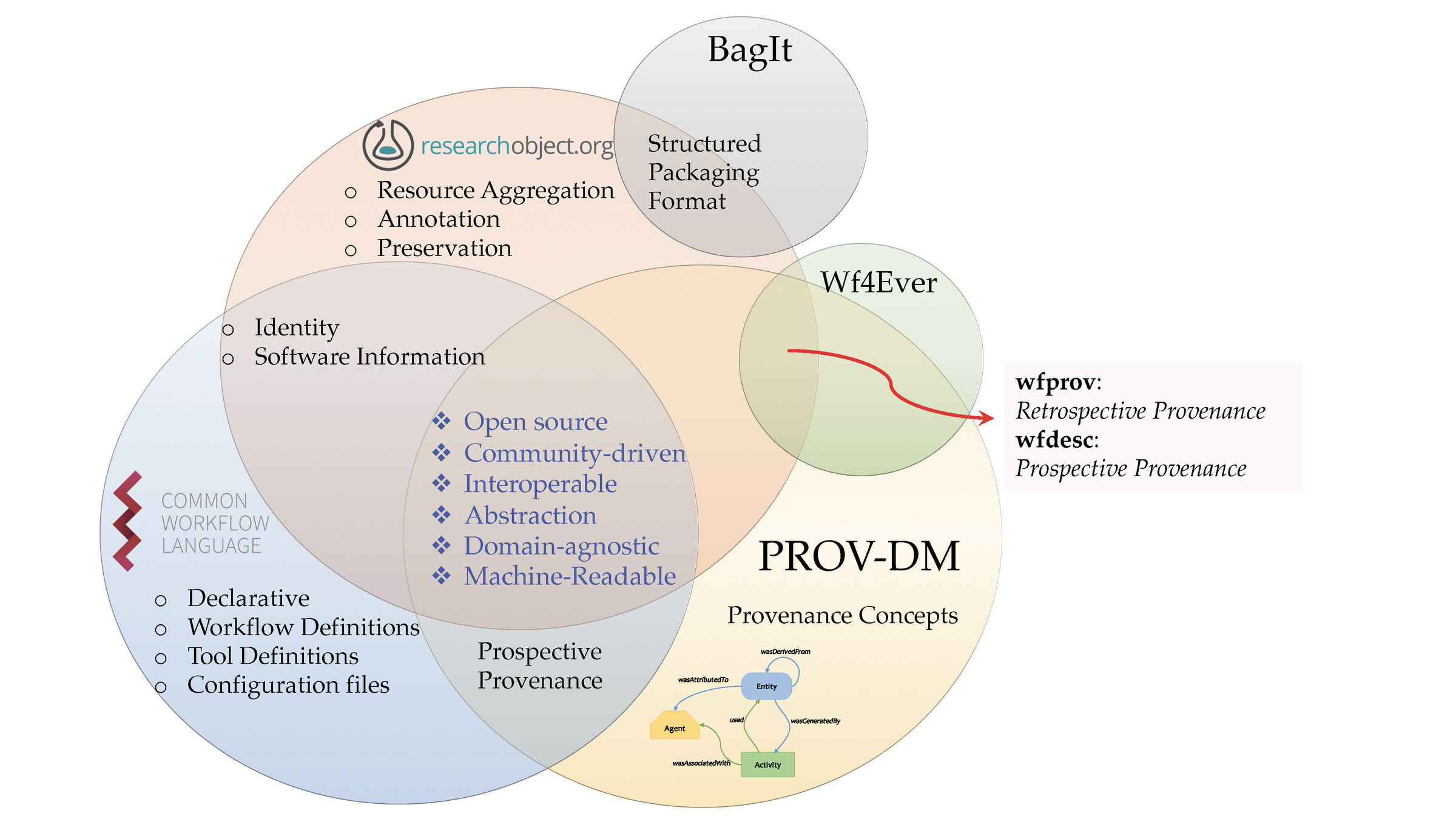
CWLProv
Standardised Format for the representation of a CWL workflow enactment, associated artefacts and the retrospective provenance


Provenance using PROV-Model
expanded with wfprov and wfdesc
Workflow specifications




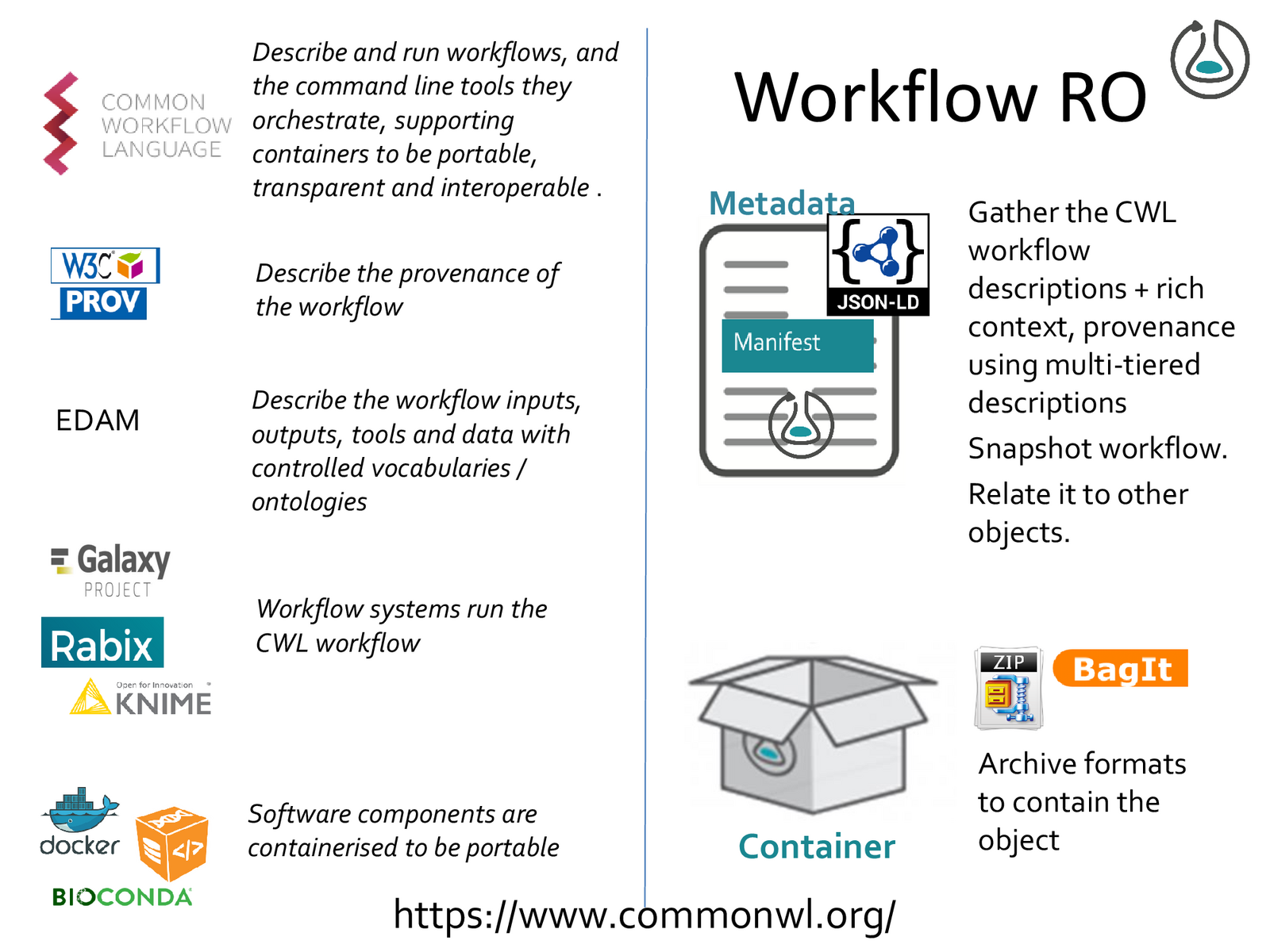
CWLProv Research Object
Adapted from:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1484286#page=8

Mechanism for serialization and transport consistency
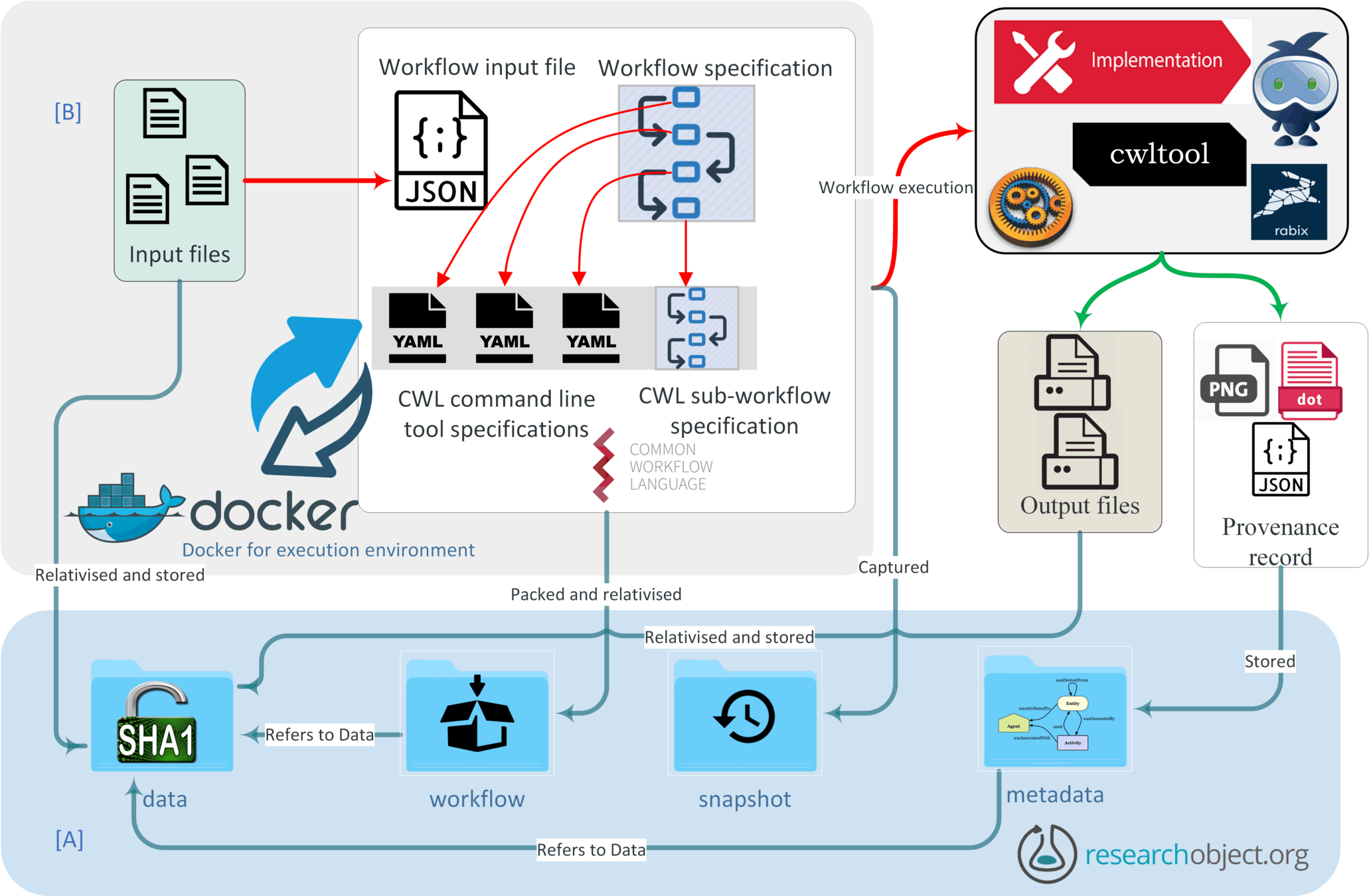

Research Question 4
How can we leverage existing abstraction and standardisation techniques to realise the provenance framework and demonstrate its utility?

Step one:
Choose a feature complete reference implementation of CWL
Ideal choice:
cwltool
- Feature complete implementation of CWL.
- Extensive validation of CWL files
- Comprehensive set of test cases to validate new modules introduced as extensions to the existing implementation
Why?
CWLProv is implemented as an optional module to cwltool and can be invoked if required
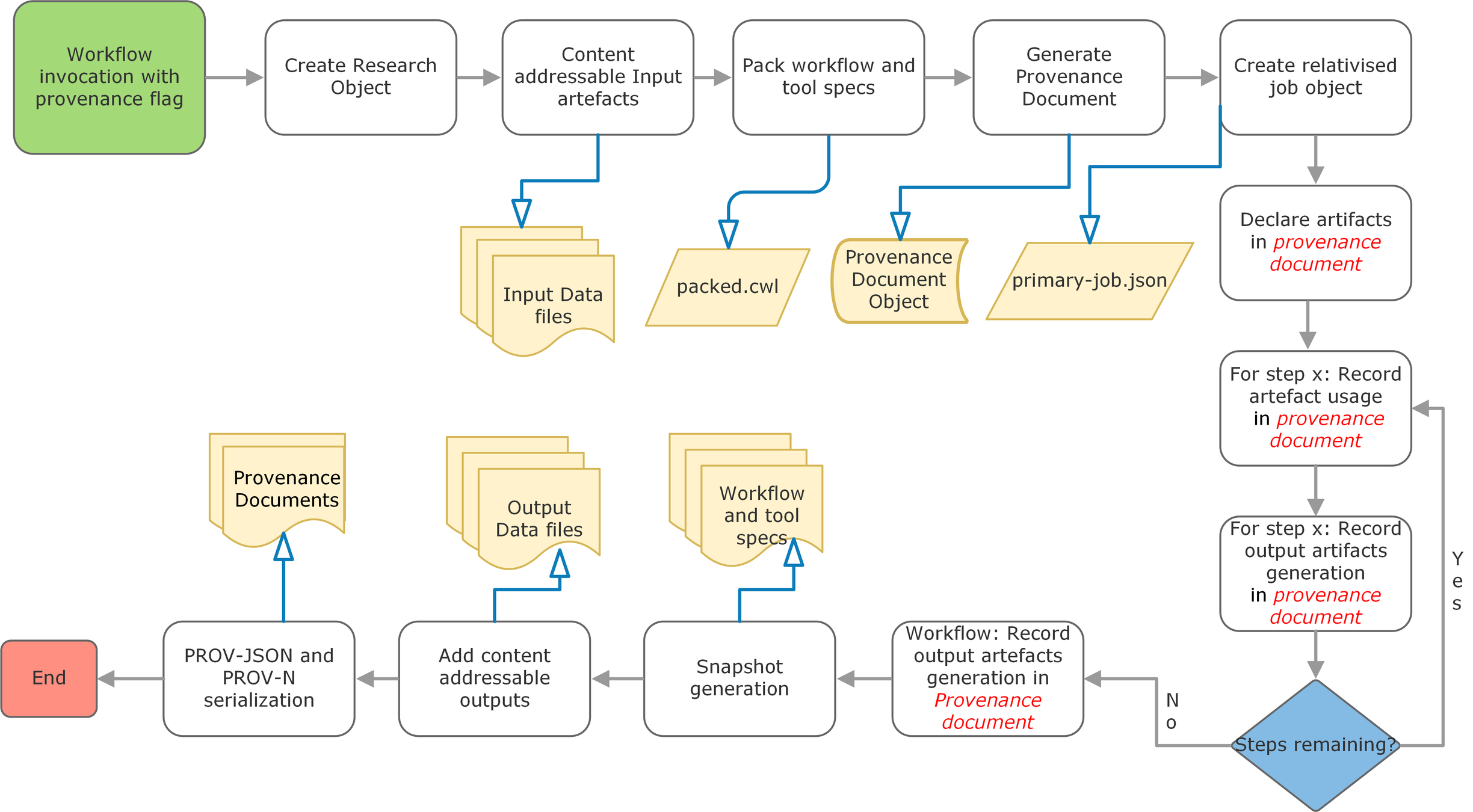
Process diagram for recording provenance
cwltool --provenance ROname workflow.cwl job.json
Research Question 4
How can we leverage existing abstraction and standardisation techniques to realise the provenance framework and demonstrate its utility?

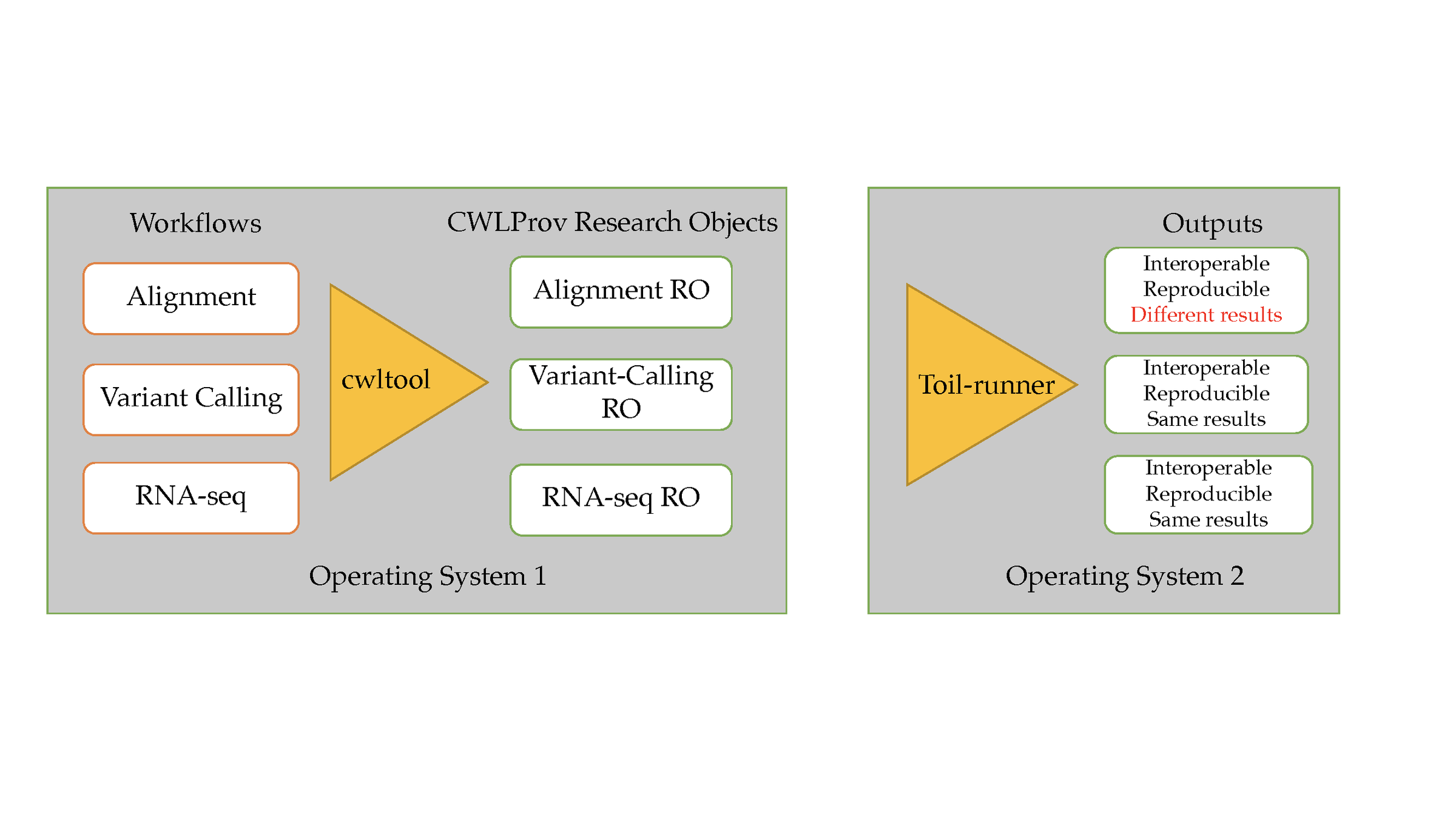
CWLProv Evaluation using workflows defined by independent research groups
Across computing platforms
Across executors

This workflow despite specified in standardised workflow definitions missed "explicit declaration"
non-deterministic algorithm: number of threads –t and the seed length –K
$ cwlprov --help
usage: cwlprov [-h] [--version] [--directory DIRECTORY] [--relative]
[--absolute] [--output OUTPUT] [--verbose] [--quiet] [--hints]
[--no-hints]
{validate,info,who,prov,inputs,outputs,run,runs,rerun,derived,runtimes}
...
cwlprov explores Research Objects containing provenance of Common Workflow
Language executions. <https://w3id.org/cwl/prov/>
commands:
{validate,info,who,prov,inputs,outputs,run,runs,rerun,derived,runtimes}
validate Validate the CWLProv Research Object
info show research object Metadata
who show Who ran the workflow
prov export workflow execution Provenance in PROV format
inputs list workflow/step Input files/values
outputs list workflow/step Output files/values
run show workflow Execution log
runs List all workflow executions in RO
rerun Rerun a workflow or step
derived list what was Derived from a data item, based on
activity usage/generation
runtimes calculate average step execution Runtimeshttps://slides.com/soilandreyes/2018-10-29-cwlprov#/13/2
Key Findings
- "Explicit is better than implicit" - Tim Peters
-
Workflow abstraction can address the heterogeneity of workflow specifications to improve their interoperability across different WMS and computing platforms
- Supported with the accompanying resources & provenance
- CWL called “future trend” and “lingua franca”
-
Provenance capture and subsequent use to support published research transparency and integrity should not be treated as an after-thought but rather as a standard practice of utmost priority.
-
The assumption of black-box provenance often associated with the workflows
and used to justify the coarse-grained provenance of workflow steps should not be encouraged
-
Summary of Contributions
- Taxonomy Definition
- Workflow Approaches Classification
- Identification of Implicit Assumptions
- A comprehensive set of recommendations
- Identification & Understanding of Provenance Artefacts
-
Conceptual Provenance Framework
-
CWLProv –Standard Format
-
Practical Implementation to generate CWLProv ROs
-
Interoperability Demonstration across different platforms
-
Supporting Tool Development - Provenance analytics
Impact of the Research
-
The empirical case study and its findings are already contributing in shaping recent research - https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5551
-
The conceptual hierarchical provenance framework and CWLProv format are now utilised as a guide by the Nextflow team to implement research object support for the nextflow pipelines - 10.5281/zenodo.1323830
-
A recent effort focused on extending toil-runner has commenced which will provide support for CWLProv RO generation after workflow enactment.
Thank you
Questions?



PhD Completion Seminar
By Farah Z Khan
PhD Completion Seminar
Understanding Role of Provenance in Bioinformatics Workflows and Enabling Interoperable Computational Analysis Sharing
- 1,580



