Modern Approach
in
Web Application
Abdullah Fathi Bin Muhamad Azmi

Website
VS
Web Application
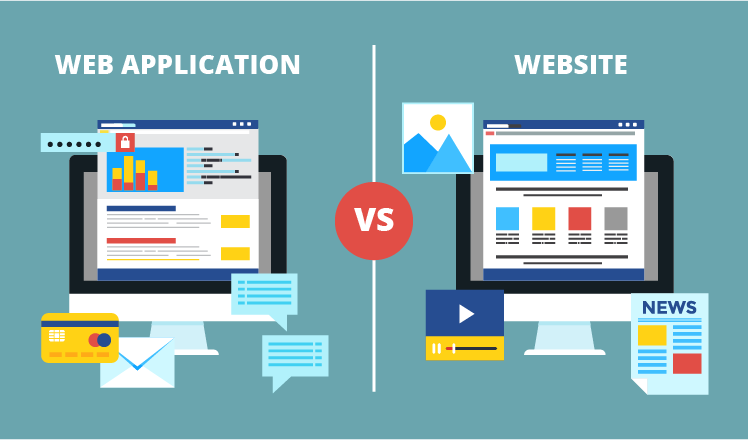
Website
Informational in nature
(Blogs, News site, etc)

Web Application
A software program that runs in an Internet browser, on or through a web page
Similar to a software program that runs on a computer desktop or desktop application, a web application allows for user interaction and can be designed for a variety of uses
Web applications are usually created using a combination of
programming languages
and
web application frameworks
Websites are meant for providing information and Web Applications are meant to solve a problem or satisfy a desire
Key Differences
1) Interactivity
2) Integration
3) Authentication
Web App
Special Names
Web Portals
Online Stores
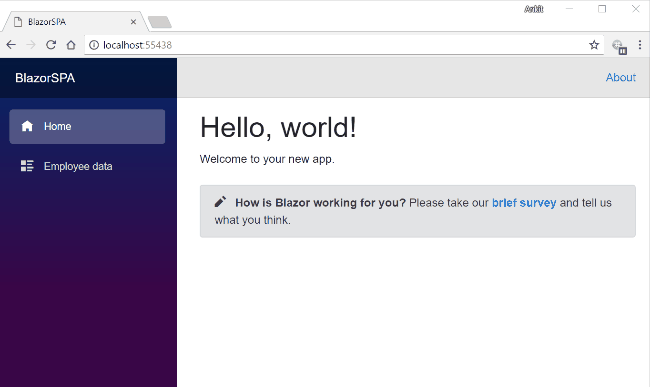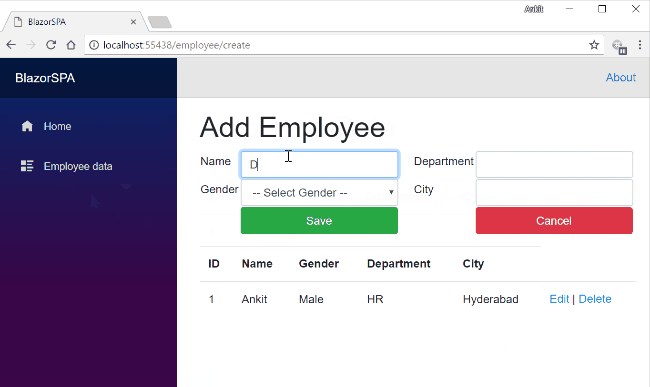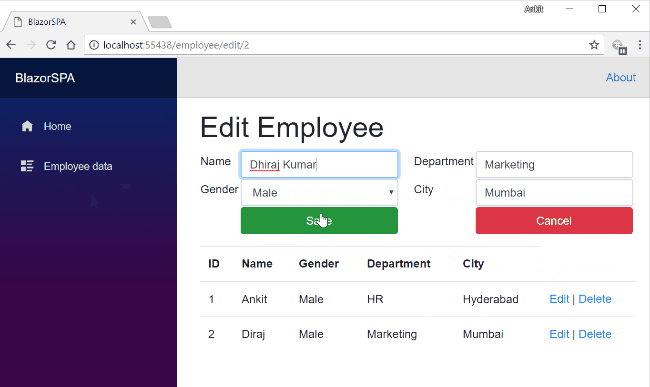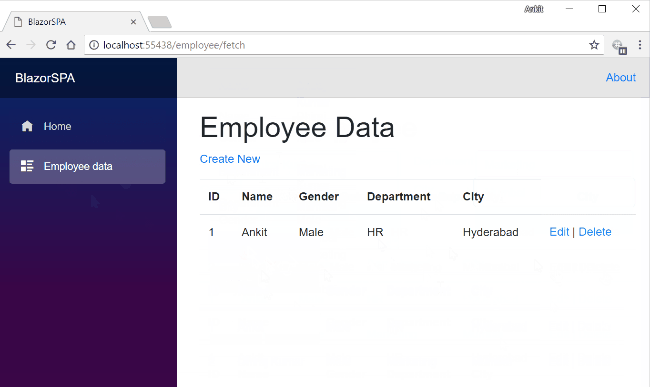
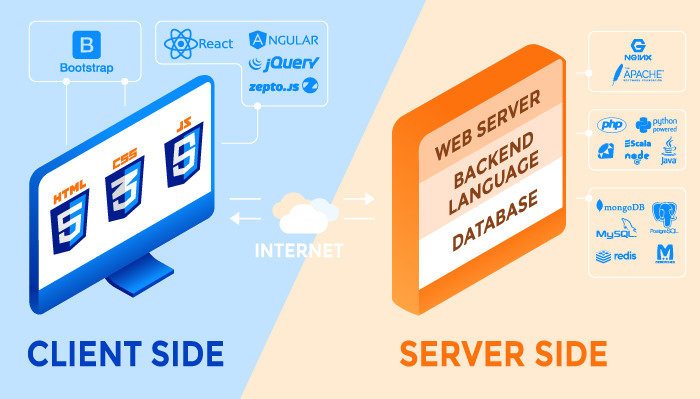
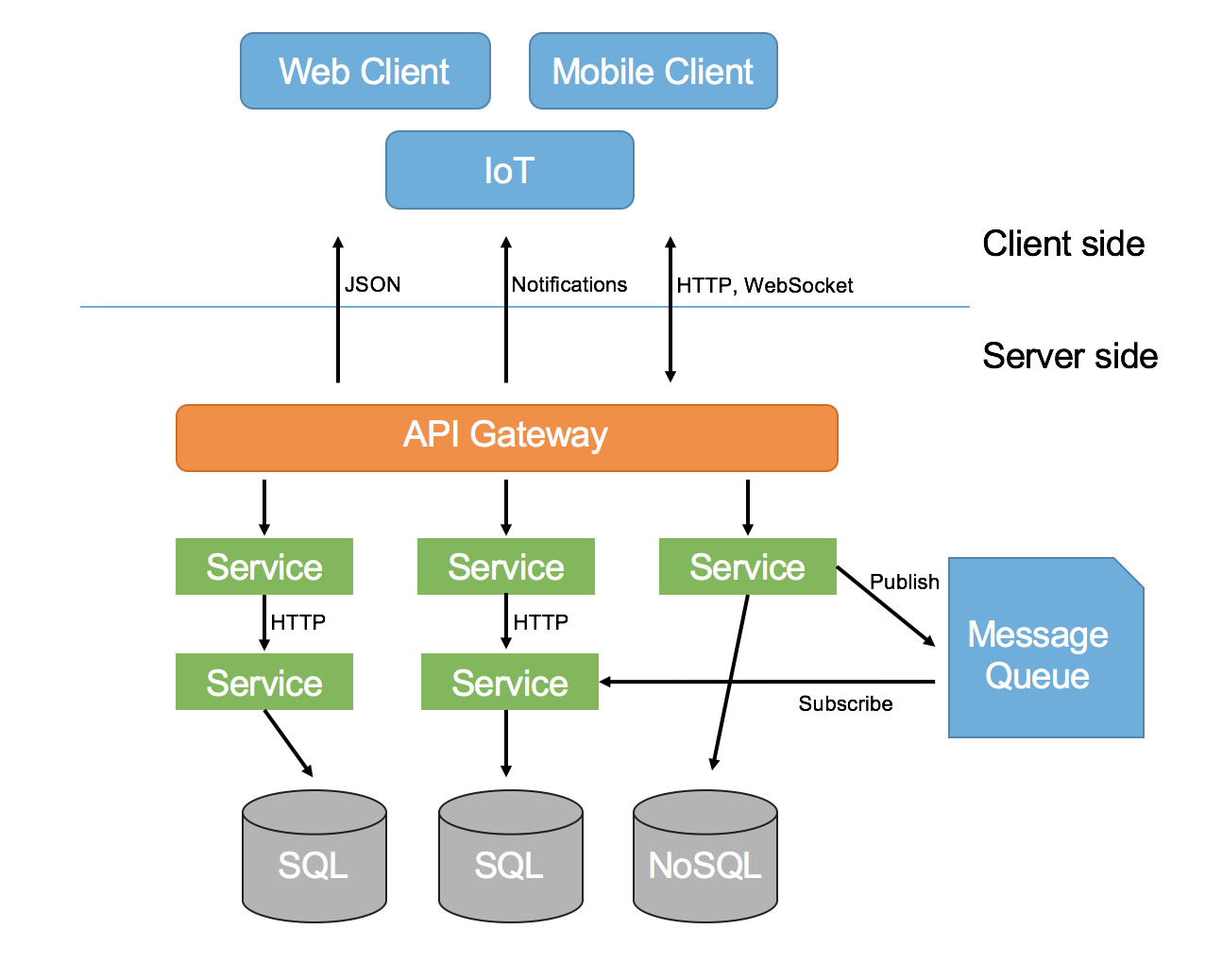
What does a web application consist of?
OS
Database
Web Server
Server Side Code
Browser
Client Side
Code
How Web Apps Works
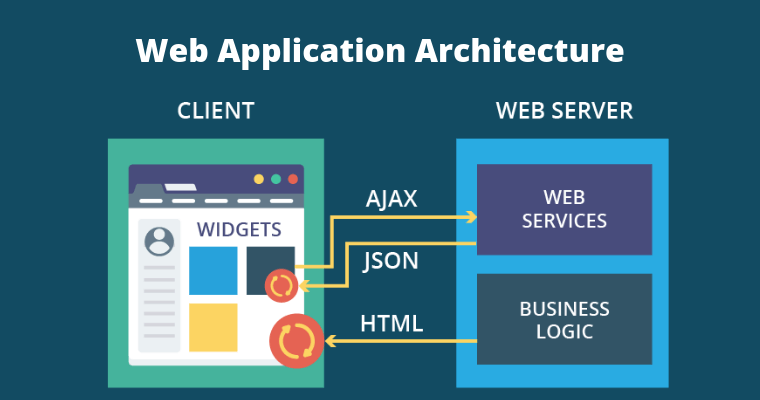
Multi Page Application (Traditional Web Apps)
- Perform most of the
application logic on the server - Each request sent to the server
will render a new page - Support legacy browser
- Could potentially work
without javascript
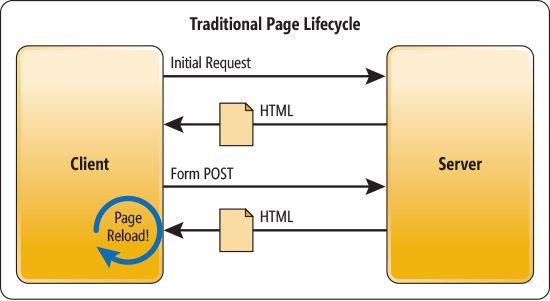
Pros
- Plenty of resources, best practices, solutions and frameworks available
- SEO
- Easy development: Smaller technology stack
- Faster initial page load: Page is rendered on the server side -> sent to browser
Cons
- Slower to load pages.
- Mobile Development
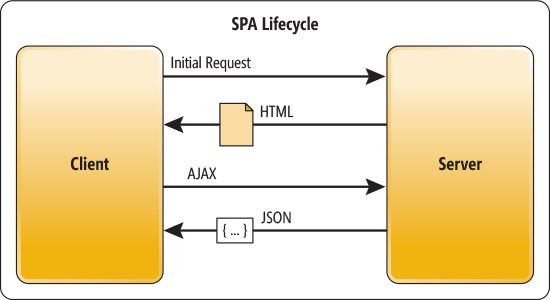
Single Page Application
(Modern Web Apps)
- Perform most of UI logic in web browser
- Load a single web page
- Dynamically update the page
as the user interacts with the app - Provide native app like experience
- No page reloads
- No Extra wait time
- Asynchronous Javascript / XML (AJAX)
Pros
- Very reactive app
(Close to desktop application) - Reduce bandwidth usage
- Decoupled frontend and backend
- Mobile development is easier
- Fast: most resources (HTML + CSS + Scripts) are only loaded once
Cons
- First page load is slower than MPA
- SEO is challenging (Content loaded by AJAX)
- Javascript is strictly required
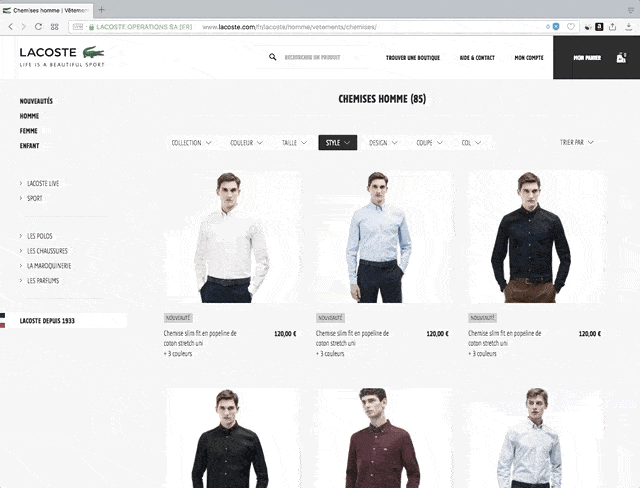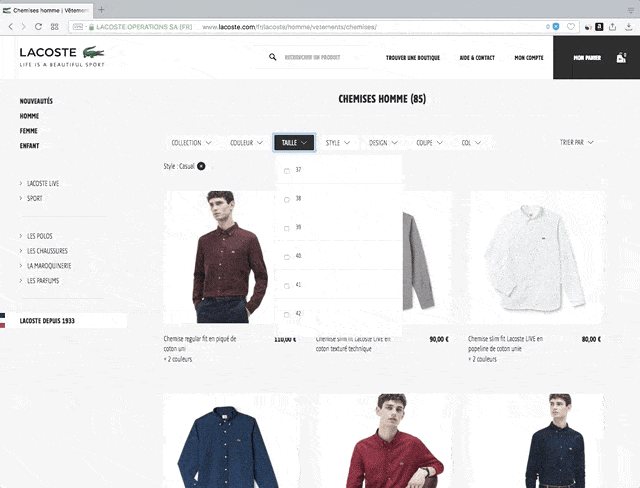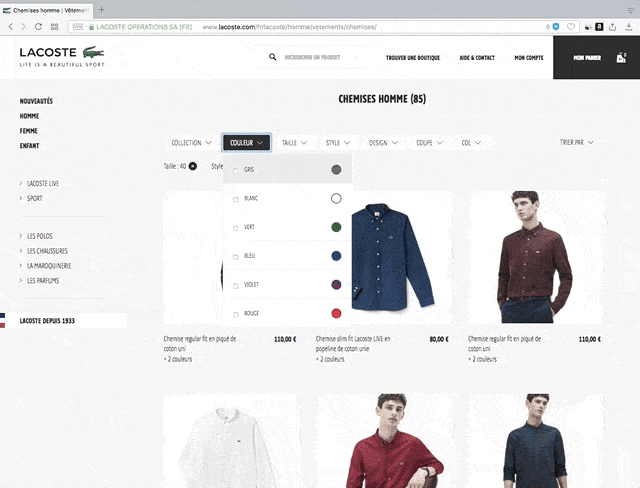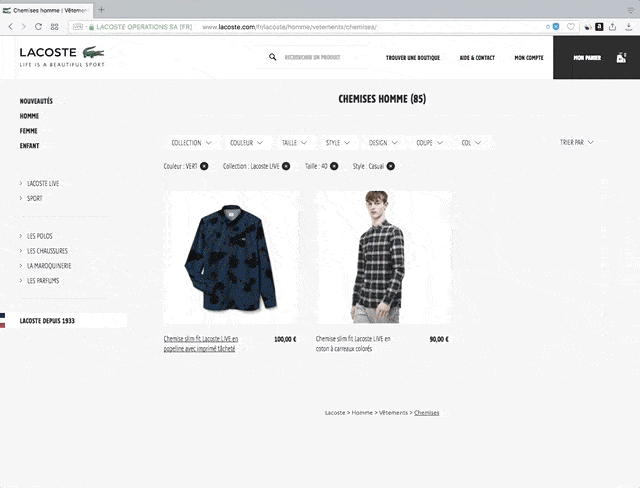
What is framework
- Anything that let us build a web application
- Arrangement in which software provides greater functionality that can be extended by additional user written codes. (Basic structure)
Why use framework?
- Allow standard way of creating the web app
- Developer doesn't have to reinvent the wheel
- Simplify the process of creating web app
- Don't have to start from scratch
- Save Time
- Have reusable functions
- Just focus on business logic
- Designed to be able to deal with third party packages
CSS/UI Framework
- Help create stylized and professional looking web apps
- Grid System
- Color scheme
- Stylize HTML component using CSS
- Look clean and professional
- Usually there are within frontend framewok
Pros
- Faster development
- Responsive by default
- Browser compatibility
- Javascript widgets/plugin
- Documentation & Support
Cons
- Stop developer from learning CSS
- Less customization
- Many sites look the same
- Lots of overriding styles
- Many depend on Jquery for certain things
Bootstrap
- Very well known
- Built by Twitter
- Easy to learn
- Looks professional
- Can be difficult to
customize components

Materialize
- Clean looking
- Lots of styling and color options
- Follow Google's Material
style guide

Foundation
- Lots of example
- Professional looking
Semantic UI
- Lots built-in
- Built-in themes so its' customizable

Grommet
- Has a huge focus on accessibility
- Looks really clean
- Not as used as some of the others
- Made for ReactJS
Front-End Framework
- The part of end-user see and interact with
- Consist of web design and the interation of the site
- CSS
- HTML
- JS
- In most cases, written in Javascript
- Organizing functionality and interactivity
Pros
- Less work for large
frontend applications - Organized, component based design
- Fast performance
(virtual DOM) - Reliable & Tested
- Community & Support
- Great for teams
Cons
- Add complexity for simple projects
- Can be too opinionated/less freedom
- Stop beginners from learning actual JS coding
- Updates can introduce issues
Vue.js
- Easy to learn
- Very fast
- All tools associated with
it are packaged well - Takes parts from Angular and React
and optimizes them - Less widely adopted than some others
- Flexible - Can use it in multiple ways

Angular 2+
- Build by Google
- Popular in enterprise
- Well Supported
- Encourages reusability
- Improves application scalability
- Large learning curve

React
- Build by Facebook
- Popular for startups
- Bundles frontend code into components
- Organizes code and data to
make code reusable - Large learning curve

Ember
- Gives a large amount of
functionality out of the box - Opinionated (Have to use its formatting)
- Steep learning curve

Back-End Framework
- Consist of server, db and
code that interacts with them - Consist of code that gives dynamic
data to the frontend of the site - Written in variety of programming
language- Java
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- NodeJS
- Wide variety of features
Pros
- Save a TON of time
and make things much easier - Very flexible and allow you to build almost anything
- Built in security
- MVC
- Built in routing
- Community, Documentation & Support
Cons
- Can stop beginners from learning the fundamentals of coding
- Some frameworks can be too opinionated/less freedom
Spring
- Java
- Very Fast (Lighweight Container)
- Cross Platform
- Less Opinionated/Flexible

Laravel
- PHP
- Easy to learn
- Fast Execution
- Documentation easily available
Django
- Python
- Happy medium between
very opinionated and less structured - Lot of functionality out of the box
- Difficult to integrate a fancy front-end
- Python's data handling is amazing
Ruby on Rails
- Ruby
- Very opinionated
- Has great tools like scaffolding
(build things fast) - Out of the box functionality
- Ruby takes longer to run programs
than some other programming languages

Express
- Javascript
- Very customizable
- Very lightweight
- Less build-in features
- Node is very fast
Basic feature in framework
1) URL Routing
- www.test.com/user
- www.test.com/booking
- Define which code to hits when url get hits
- Define good URL Pattern to use
2) Database Manipulation
- Manipulate and design database
- Structure the tables and models
- Read and write different entries in database
3) Templating
- Organize the data returned from web app
- Format Data: JSON, Raw, HTML, text, etc.
4) Security
- Most software developer is not security expert
- Use as-is or customize existing security
5) MVC
Model - View - Controller
1) Model == HTML
-
Handle Interaction with db
-
Responsible for moving stuff in and out of db
-
Similar to HTML, which handles the knowledge of website as well as the structure

2) View == CSS
-
Seen by user
-
Display data on screen, which represent data that was manipulated in Model
-
Similar to CSS, which add visual styles to structure.
At this point think of the View as the skin to the Model’s skeletal structure.
Just as the the CSS is the skin to HTML’s skeleton

3) Controller == Web Browser
-
Middle man that takes data to and from the model and user and manipulate it, and routes it properly
-
Brain of application
-
Control the logic for how thing should work and where they should go
-
Similar to web browser, accepts user input and translate it to command, so the page can properly function
-
The browser compiles the CSS and HTML into renderable and manipulatable pixels on the screen
Criteria for choosing the correct framework
Popularity
&
Community size
Sustainability
Support
Security
Documentation
Resource Availability


Framework
vs
Library
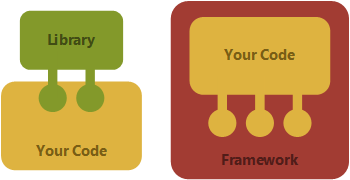
Framework: Reusing behaviors by how abstract classes and component interact with each other
Library: Collection of classes which provide reusable functionalitites
A framework defines a structure that you have to fill, while library has some structure that you have to build around
You call library,
Framework calls you
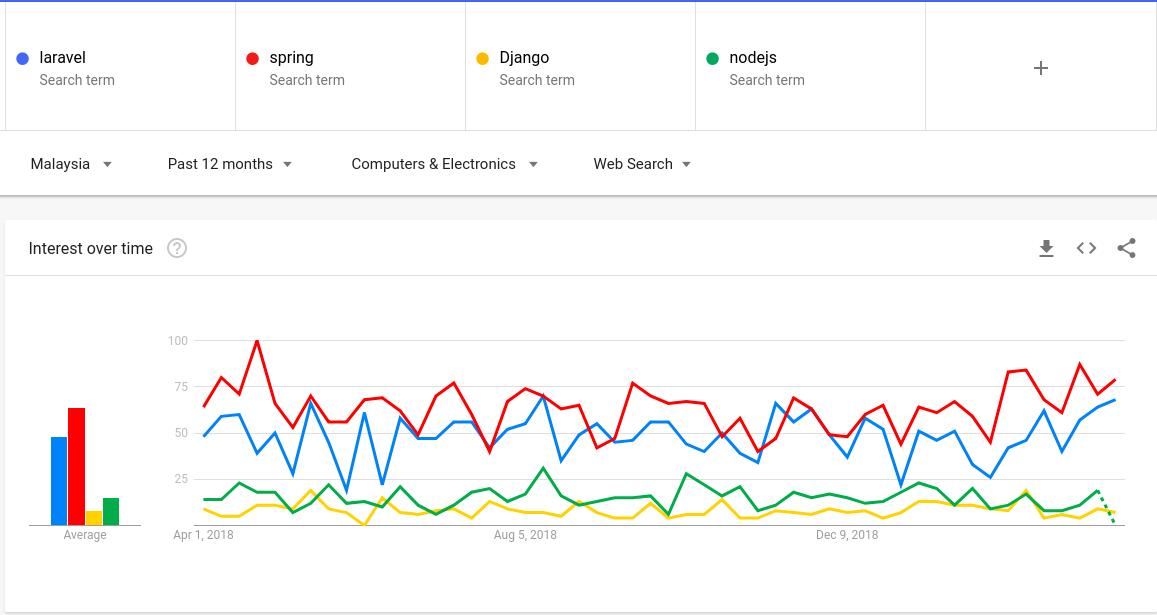
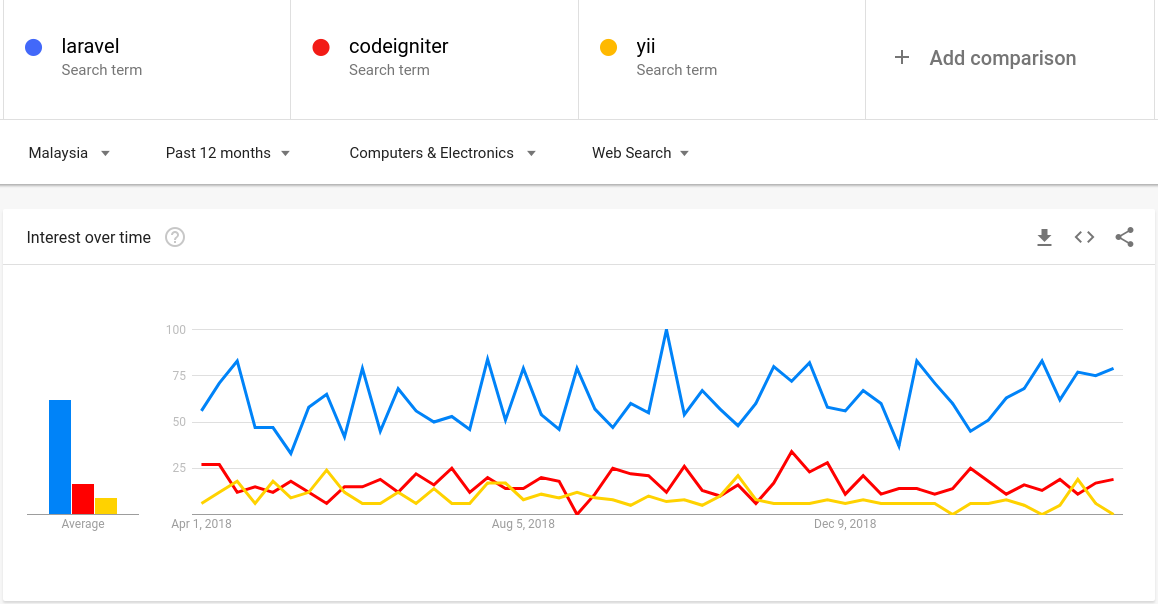
Google Trends
Q & A
There are no secrets to success. It is the result of preparation, hard work, and learning from failure. - Colin Powell
THANK YOU
Web Framework
By Abdullah Fathi
Web Framework
- 388



