{Git &. GitHub}
Mastering Version Control
# Version control Q&A
Version control Q&A✨

1.What Do You Do When You Make a Mistake?
Have you ever accidentally deleted a file you spent hours working on? What did you do to fix it?
Just like you might try to undo a mistake or go back to a previous version of your work, developers use version control to manage changes in their code - safely and efficiently !
# Version control Q&A
2.How Do You Keep Track of Changes?
When working on a long assignment, how do you track different drafts or changes? do you save different versions like “final,” “final-final,” and “final-v2”?

Developers do something similar but smarter, they use commits to save different versions of their work. No more messy file names!
# Version control Q&A
3.What Happens When You Want to Try Something New?
Ever wanted to try a crazy new idea but worried about ruining your original work?

With version control, you can create a “branch” to experiment with new ideas without affecting the main project. It’s like having a separate area to try out your creative ideas.

# Version control Q&A
# CHAPTER 2
4.How Do You Share Work with Others?
Have you shared a document or presentation with others before?

GitHub is like Google Docs for code, but way more powerful. It lets developers share, review, and improve each other’s code.

# CHAPTER 2
5.How Do You Keep Track of Changes in Group Work?
When working in a group, how do you know who changed what?
GitHub automatically tracks every change and who made it, so you’ll never have to wonder who’s responsible for that line of code.
1.What Do You Do When You Make a Mistake?
Have you ever accidentally deleted a file you spent hours working on? What did you do to fix it?

# Version control Q&A
# CHAPTER 2
1.What Do You Do When You Make a Mistake?
Just like you might try to undo a mistake or go back to a previous version of your work, developers use version control to manage changes in their code - safely and efficiently !
2.How Do You Keep Track of Changes?
When working on a long assignment, how do you track different drafts or changes? do you save different versions like “final,” “final-final,” and “final-v2”?

# Version control Q&A
# CHAPTER 2
2.How Do You Keep Track of Changes?
Developers do something similar but smarter, they use commits to save different versions of their work. No more messy file names!

# CHAPTER 2
3.What Happens When You Want to Try Something New?
Ever wanted to try a crazy new idea but worried about ruining your original work?

# CHAPTER 2
3.What Happens When You Want to Try Something New?
With version control, you can create a “branch” to experiment with new ideas without affecting the main project. It’s like having a separate area to try out your creative ideas.

# CHAPTER 2
4.How Do You Share Work with Others?
GitHub is like Google Docs for code, but way more powerful. It lets developers share, review, and improve each other’s code.

# CHAPTER 2
5.How Do You Keep Track of Changes in Group Work?
When working in a group, how do you know who changed what?
# CHAPTER 2
5.How Do You Keep Track of Changes in Group Work?
GitHub automatically tracks every change and who made it, so you’ll never have to wonder who’s responsible for that line of code.
# CHAPTER 2
What is a Version Control System?
# CHAPTER 2
is a system or a tool that helps you track and manage changes to files over time.
It’s like a personal historian for your project , keeping a full record of every change ever made, in a special database called repository.
Version Control System (VCS)
# CHAPTER 2
Know exactly what changed, when, and who did it.
1.Track changes
Roll back to a previous version if something breaks.
2.Revert mistakes
See differences between updates.
3.Compare versions
Work with others without overwriting each other’s work
4.Collaborate safely
Why do we use it ?
Experiment with new ideas without affecting the main project
5.Create branches
# CHAPTER 2
Think of VCS as a time machine for your work ✨
Did I just break everything? No problem, let me go back to yesterday’s version!
Analogie...
If something goes wrong, you can always travel back to a version that worked perfectly.
# CHAPTER 2
Meet Git: Your Version Control Superhero!

# CHAPTER 2
Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
- Built for developers who needed a fast, reliable, and flexible way to manage code changes
- Works on any operating system: Windows, macOS, Linux
What Is Git ?
Lightning-fast operations
1.Speed
Easy and powerful
2.Branching & Merging
Every user has a full copy of the project history
3.Distributed
Make commits without an internet connection
4.Offline Work
Why Git Stands Out?
Cryptographic hashing ensures data integrity
5.Security
Git isn’t just another VCS, it’s the most popular one in the world
Perfect for solo devs, teams, and huge open-source communities
6.Flexibility
# GitHub
GitHub:
Your Cloud Home for Code


GitHub is a cloud-based platform for hosting and collaborating on Git repositories.
It provides features like code sharing, review and management, making it a popular tool for developers to work together on projects.
What Is Github ?
# GitHub
GitHub is more than just a place to store code !
it’s a collaboration hub for developers around the world...
# GitHub
How do we use Git ?
The question you're probably asking yourself right now
via the command Line
The answer is pretty simple
What is this again !
The command Line ?
# CHAPTER 2
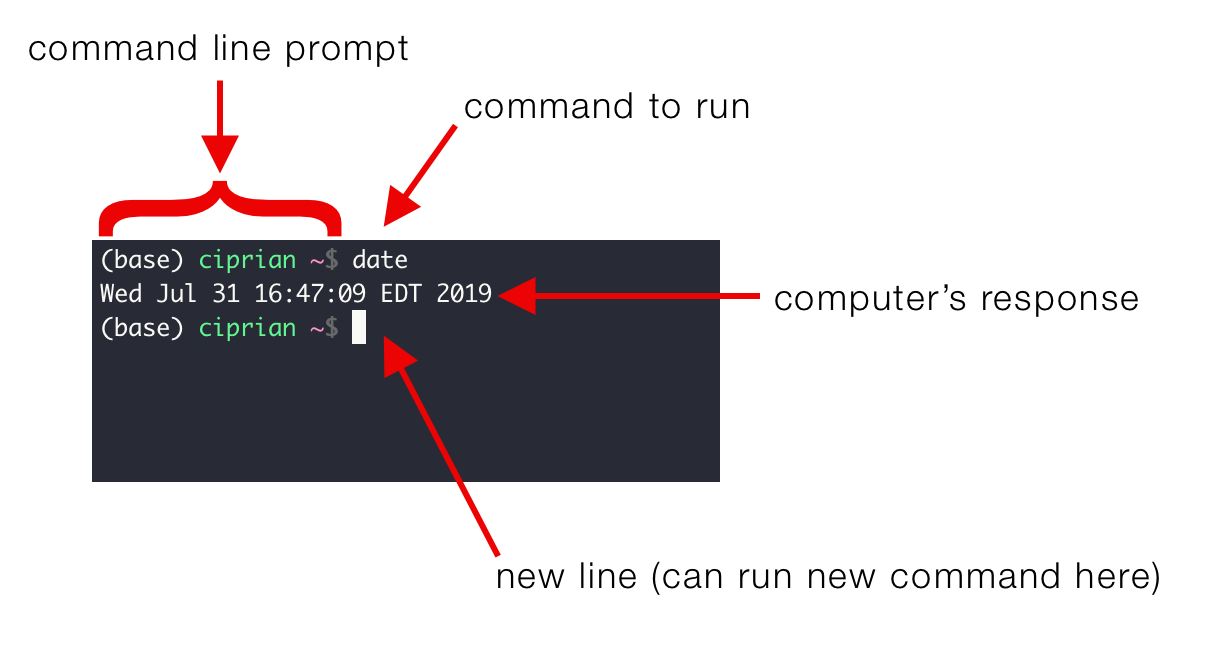
What Is the Command Line?
- The command line interface (CLI) is a text-based way to interact with your computer.
- Instead of clicking buttons, you type commands to perform actions.

# CHAPTER 2
# CHAPTER 2
Installing Git & Git Bash
git —-version# PRESENTING CODE
Checking git’s version
If you see something like git version 2.xx.x, then you're good to go!
# CHAPTER 2
Configuring Git – Setting Up Your Identity
Configure Git settings
git config —global user.name "YOUR NAME"# PRESENTING CODE
git config —global user.email YOUR EMAILgit config —global core.editor "code --wait"
# Note : you must add vsc path to the env variableThese details appear in every commit you make, so make them official!
Git Commands in a Flash! ⚡
# PRESENTING CODE
Basic terms which help to understand git commands
-
Repository => A folder that keeps all your project's files, including commits and branches.
-
Branch => A copy of the repository holding the specific version.
-
Master/Main => The default branch of the repository.
-
Commit => A snapshot of your changes at a point in time, it's a single save of changes to the specific branch.
-
checkout => Switching between the current branch and the one specified in the command.
# PRESENTING CODE
Basic terms which help to understand git commands
-
Merge => Combining changes from one branch into another.
-
Fork => Copying someone else’s repo to work on it independently.
- Head => Most recent commit of the repository you work with.
Your Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git init # Start a new repository# PRESENTING CODE
- Initialize a Repository
git clone [url] # Copy an existing repo- Clone a Repository
Your Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git status
# Note : Shows the current state of the working directory and staged changes,
# letting you see what’s new or what has been modified.# PRESENTING CODE
- View the Status of Your Repository
git log
# Note : Shows a log of all previous commits, including commit messages, author names, and commit IDs.- View Your Commit History
Your Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git add <file>
# Note : Stages the specified file(s) for the next commit.# PRESENTING CODE
- Stage and Commit Changes
git add .
# Note : Stages all files for the next commit.git commit -m "message"
# Note : Save the changes and adds a message to describe the commit.Your Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git branch <branch-name>
# Note : Creates a new branch, which is like a copy of your project where you can work on new features without affecting the main project.# PRESENTING CODE
- Branching
git checkout <branch-name>
# Note :Switches to the specified branch.git merge <branch-name>
# Note : Merges the specified branch into the current branch, combining changes.git branch # List branchesYour Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git remote add origin <url>
# Note : Connects your local repository to a remote GitHub repository.# PRESENTING CODE
- Synchronizing with GitHub
git push
# Note : Uploads your changes from your local repository to GitHub.git pull
# Note : Downloads changes from the GitHub repository to your local machine.git remote -v # Show remote reposYour Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git diff
# Note : Shows unstaged changes.# PRESENTING CODE
- Viewing Differences
git diff --staged
# Note: Shows staged changes only.Your Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git rm --cached <file>
//Note : Stops tracking a file without deleting it locally.# PRESENTING CODE
- Removing Files from Tracking
Your Git Command Cheat Sheet!
git stash
# Note : Temporarily stores changes so you can work on something else, Saves changes without committing.# PRESENTING CODE
- Stashing Changes
git stash apply
# Note : Reapplies the stashed changesgit stash pop
# Note : Applies and removes the stash from the list.# PRESENTING CODE
X
VIDEO
GitHub: Collaboration & More!
# PRESENTING CODE
git clone <url>
Copies an entire repository from GitHub to your local machine.- Cloning a Repository

- Forking
Forking a repository on GitHub creates a copy of it in your account. You can then work on it independently, making changes that don’t affect the original project until you submit a pull request.
GitHub: Collaboration & More!
# PRESENTING CODE
- Code Review and Collaboration Tools
GitHub allows team members to comment on code, suggest changes, and perform code reviews to ensure quality and consistency.
- Pull Requests
Pull requests (PRs) are a feature on GitHub that allows developers to propose changes, review code, and discuss updates before merging them into the main branch. A PR is created when you want your code reviewed before it becomes part of the main codebase.

GitHub: Collaboration & More!
# PRESENTING CODE
- Using .gitignore file
Purpose: Specify files or directories that Git should ignore (e.g., sensitive data, build files).

- GitHub Issues and Project Boards
GitHub issues are used for tracking bugs, features, and other tasks related to a project. Project boards allow teams to organize and prioritize work.
# PRESENTING CODE
Let's practice together !
It's your turn now !
Collaborative Exercice Solution
- Git is a local tool for tracking changes in code.
- GitHub is a cloud-based platform for hosting Git repositories, enabling collaboration, and adding social features.
Summary: Git vs. GitHub

Git &
Github
in Action!
Let's Prractice all what we've learned today
Git & GitHub
By Fatima BENAZZOU
Git & GitHub
- 484



