Are You React-ing?

About
@ferrwan


React???
- A tiny JS library
- Thank you Facebook
- Adaptable with another JS
- Component Based
- State & Props things.
- React does need State and Props
- It's MIT Licensed :D
Another Ref
- Virtual DOM
- React Fiber
Installation
-
<script>
-
NPM
-
Magic CRA tool
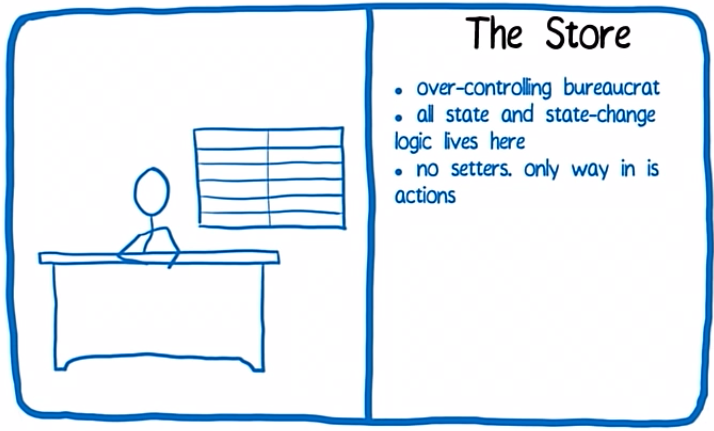
CORE
- Element
- Functional Component
- Class Component
- State
- Props
import React from 'react'
/*{------ FUNCTIONAL COMPONENT -------}*/
/* { ---- ELEMENT ---- } */
const funComponent = () => <h1>Hello KITM fellas!</h1>
/*{------ CLASS COMPONENT -------}*/
class classComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
valueA: '',
}
}
render() {
/* { ---- ELEMENT ---- } */
return <h1>Hello KITM fellas!</h1>
}
}/*{------ FUNCTIONAL COMPONENT -------}*/
class classComponent extends React.Component {
constructor() {}
componentDidMount() {}
componentDidUpdate() {}
componentWillUnmount() {}
// React ^16 Unsafe
componentWillReceiveProps() {}
componentWillUpdate() {}
componentWillMount() {}
// New
componentDidCatch() {}
static getDerivedStateFromProps() {}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {}
}State & Props Work
Local State Change
Nothing Change
Local State Change
Nothing Change
Component Update
Local State Change
Nothing Change
Component Update
So... A component update, all the child re-render ?

Performance ???
Little Theory
Diffing Algorithm
React implements a heuristic O(n) algorithm based on two assumptions:
- Two elements of different types will produce different trees.
- The developer can hint at which child elements may be stable across different renders with a key prop.
https://reactjs.org/docs/reconciliation.html
So is it Fast?
-
shouldComponentUpdate
-
react-virtualize
Sharing props problem
<A>
<B aProps={ ...this.state } />
</A>
<B>
<C bProps={ ...props.aProps } />
</B>
<C>
<D cProps={ ...props.bProps } />
</C>
<D>
<E dProps={ ...props.cProps } />
</D>
<E>
{ this.props.dProps.user }
</E>

Redux
- Just an object
- Single Store
- State is immutable
- Influence from Flux
- Time Travel Debugging
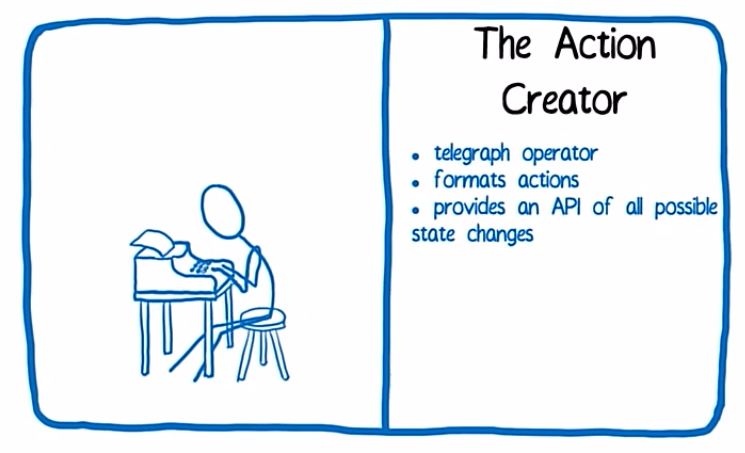
Roles in Redux
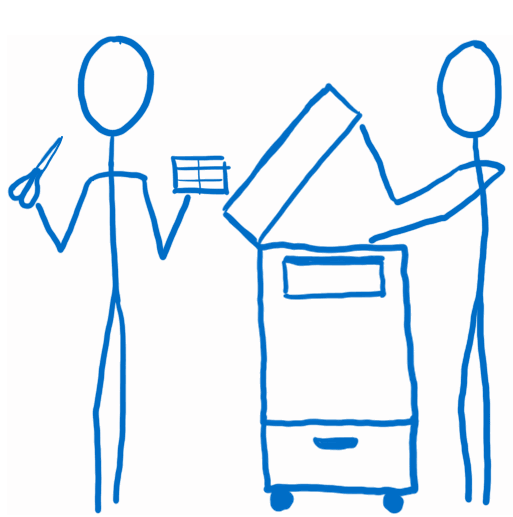
The Reducers
- White-collar workers who are a little overzealous about photocopying
- This is one of the key ideas of Redux. The state object isn’t manipulated directly. Instead, each slice is copied and then all of the slices are combined into a new state object.
Smart and Dumb Component
- Smart components are in charge of the actions.
- Smart components do not have their own CSS styles.
- Smart components rarely emit DOM of their own. Instead, they arrange dumb components, which handle laying out DOM elements.
Layer Binding
- The Provider component: This is wrapped around the component tree. It makes it easy for the root component’s children to hook up to the store using connect().
- connect(): This is a function provided by react-redux. If a component wants to get state updates, it wraps itself using connect(). Then the connect function will set up all the wiring for it, using the selector.
- selector: This is a function that you write. It specifies what parts of the state a component needs as properties.
The Flow
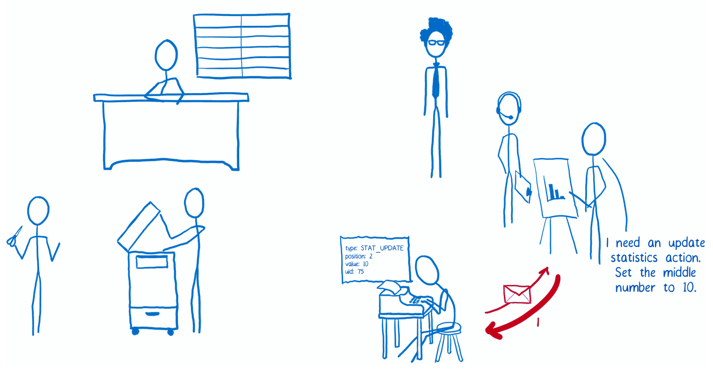
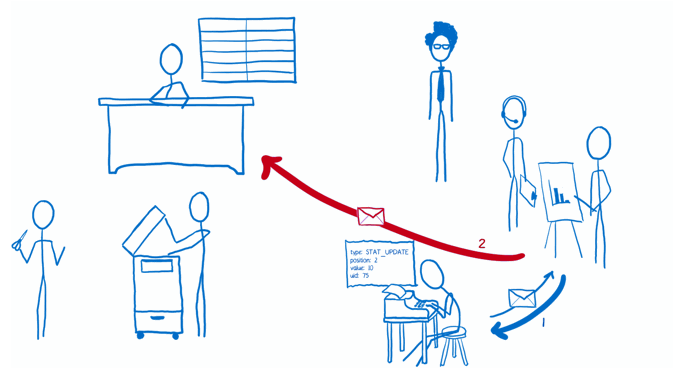
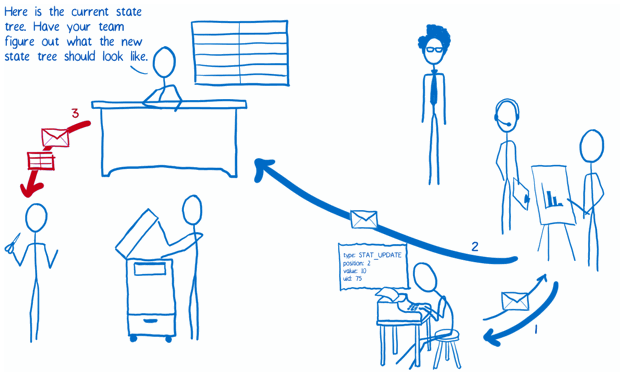
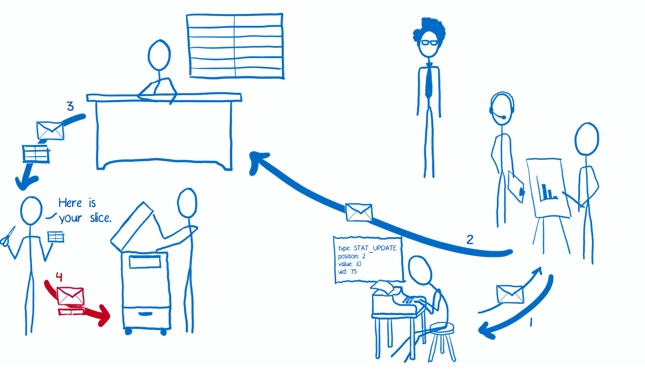
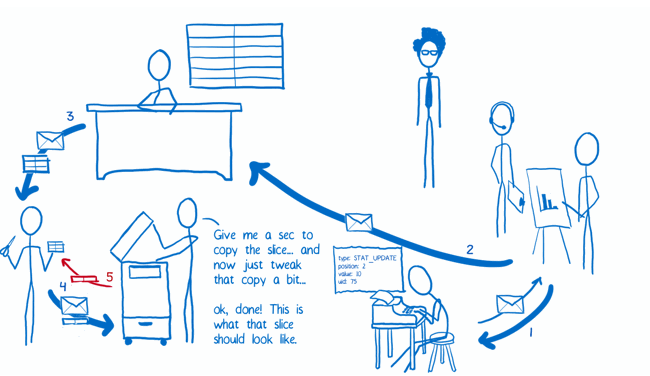
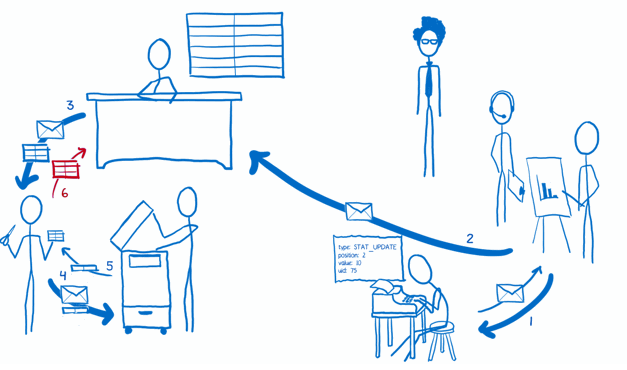
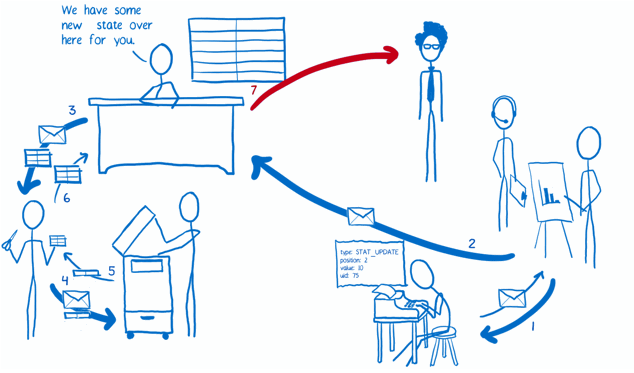
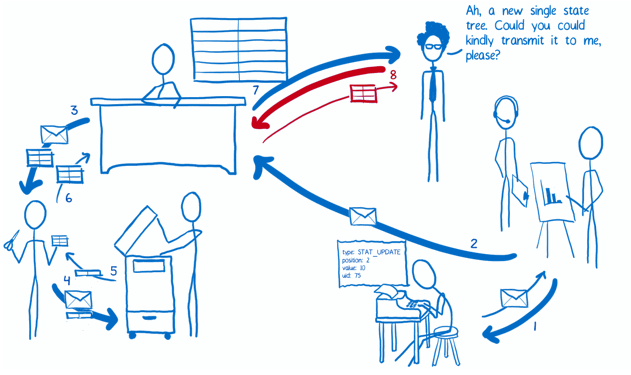
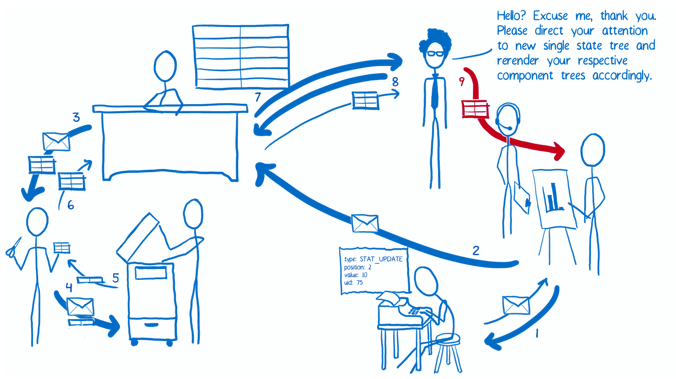
Implementation
Advices
- PascalCase for naming components
- Make a reusable components. DRY
-
Avoid using index for key attribute
-
Use state management if and only if
your app is too big to handle by React - Use Linter. (Programmers are blind)
THANK YOU


React
By Ferry Irawan
React
A brief description about ReactJS and Redux
- 661

