How do I Google?
The Long complex answer of how I get to google.com Part 3
Quick Review
- Key is pressed on Keyboard
- Keyboard Polls through the Key matrix
- Keyboard Notices a Change and waits until the next USB packet can be sent
- Keyboard sends USB packet to Computer
- The OS gets packet and sends it to the correct Program
Part 1: https://slides.com/generalzero/how-do-i-google
Quick Review
- The computer looks through its cache to turn google.com into an IP Address
- If not found then reaches out to DNS
- That goes through your local router, your IPs Routers until it gets to your DNS server
- The DNS info is queried recursively to get the correct IP address. Caching the responses to make it faster next time.
Part 2: https://slides.com/generalzero/how-do-i-google-9cd485
Whats Next?
KeyboardComputer to ProgramURL Bar in BrowserFinding the Web Server- Sending Data to Web Server
- Retrieving Data from Web Server
- Browser getting other files from webpage
- Browser rendering the Data for the viewer
Assumptions
- Transmitting over Ethernet
- No Ethernet Authentication (802.1X)
- Not over Wifi or Cellular Data
- Not on a VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
- Using IPv4
- Not using IPv6 or 6to4
- Has NAT (Network Address Translation)
- Used to separate Local and Wide Networks
- TLS will not use Session Resumption
- Using HTTP 1.1 not HTTP2 or HTTP3
Protocols



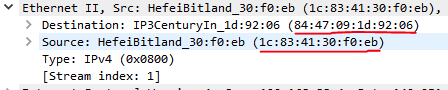
Ethernet II Layer
- Uses Physical Addresses (MAC Address) to route data on the Local Network

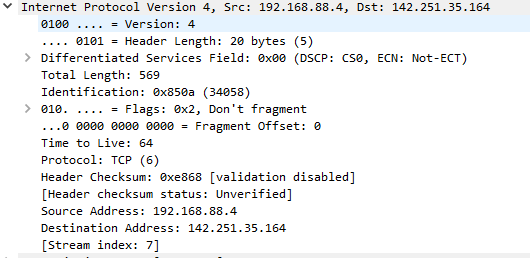
IPv4 Layer
- Used as routing packets across networks

NAT
The reason I you cant access your computer when you aren't home
The reason you cant use 192.168.88.4 to connect to my Computer
NAT Translation
- The source IP (192.168.88.4) is helpful when on the local network but not when google.com is sending its response


NAT Translation
- So the Router will change the Source IP to be your remote IP (100.35.134.67).
- NAT Table
- 100.35.134.67:41186 from 142.251.35.164:443 will be translated to 192.168.88.4:41186 on response


What is TCP
Transmission Control Protocol is a way to deal with a couple of things
- Chunking large data
- Ensuring that the data can be reassembled in the correct order
- Ensuring all data is received
- Re sending data that was lost or corrupted in transfer
- Managing Transfer speeds
Making a Connection


TCP Ports

What is TLS
- Transport Layer Security replaces the older Secure Socket Layer Protocol (SSL)
- Ensure that the server you are talking to matches the domain name.
- Tell each other what options they support
- Encryption, Authentication, Integrity Algorithms
- Support Renegotiation or Data Compression
- Random value used to generate a temporary key for this session.
- The server domain you want to reach

HTTP Request

HTTP Response

Putting It All Together

Todo: Part 4
-
HTML Basics
-
CSS, Images, and media
-
JavaScript
-
Rendering the Google Webpage
How do I Google Part 3
By generalzero
How do I Google Part 3
- 86



