Relay Explained*
George Lee
github.com/keokilee
twitter.com/keokilee
* Relay is Hard
What is Relay?
A Javascript framework for building data-driven React applications
https://facebook.github.io/relay/
https://facebook.github.io/react/blog/2015/03/19/building-the-facebook-news-feed-with-relay.html
http://www.bebetterdeveloper.com/coding/getting-started-react-redux.html
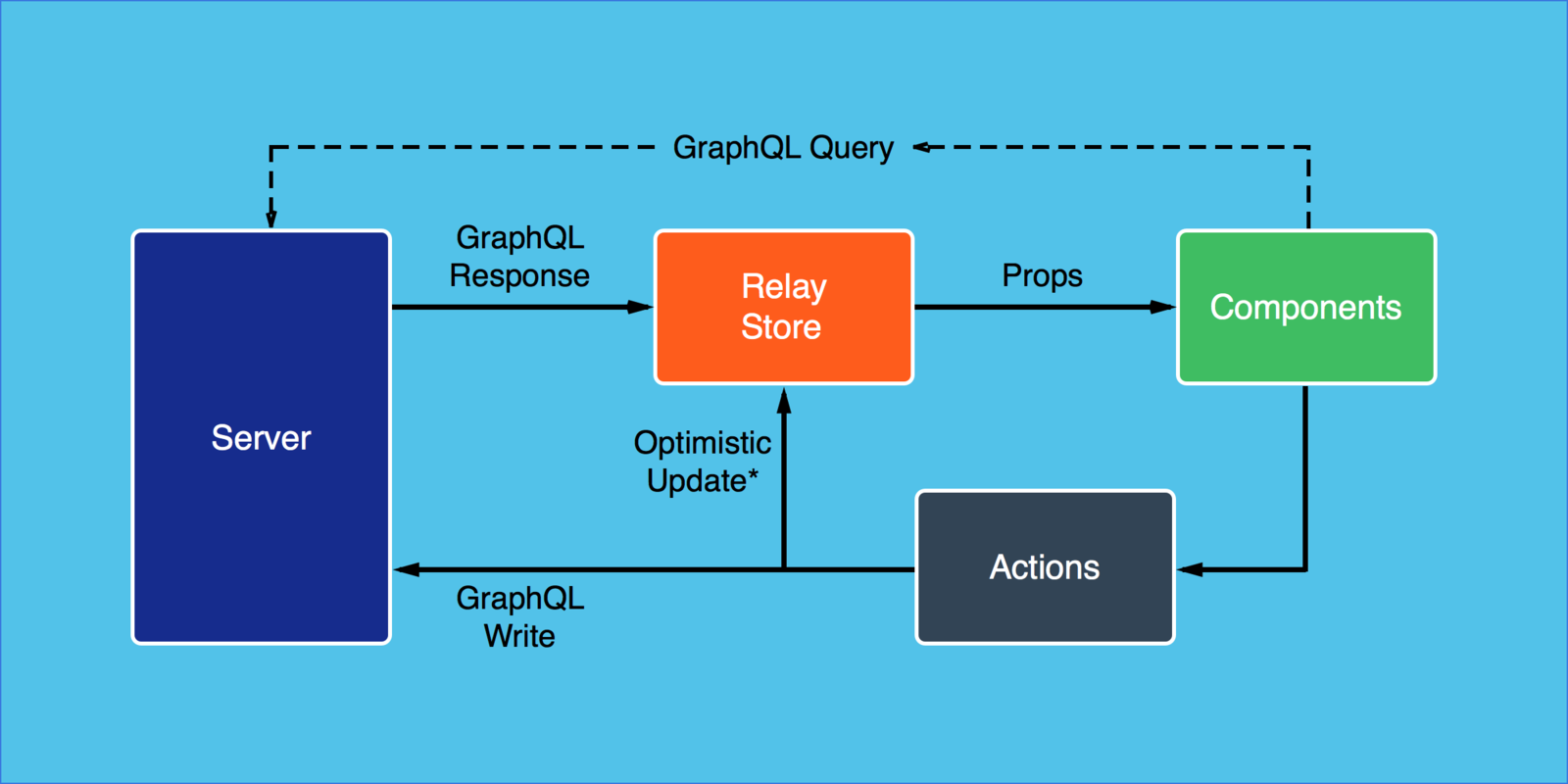
Relay and Flux/Redux can be used together
The Frontend Story
Relay's Expectations
- Your server uses GraphQL
- Component hierarchy matches data hierarchy
Viewer (Logged in user)
News Feed
pagination info
Posts
id
text
avatar
Author
query {
viewer {
name,
news_feed {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage,
hasPreviousPage
},
edges {
cursor,
node {
id,
text,
avatar,
author {
name
}
}
}
}
}
}Relay Gets What's Needed
Posts may have timestamps, but if no components in the tree need it, Relay won't fetch it.
Relay also maintains a cache. If we need the timestamps on another page, Relay will only fetch the new fields.
https://gist.github.com/keokilee/fbf674c3ec6f634b0e5861bc716a7910
Why isn't everyone using Relay?
Relay can work with a basic schema
But if you want to unleash it's full potential ...
Think about your data model differently
| User |
|---|
| name |
| user_posts |
| UserPosts |
|---|
| user |
| posts |
| Post |
|---|
| text |
| avatar |
| author |
Note: Your data may actually be structured like this
User
Post
Post
Post
User
User
Circles are "nodes"
Arrows are "edges"
Relay Jargon
Nodes, connections, and edges
Relay Node
A node is a top level entity in your application. GraphQL types that are nodes implement an interface
- The id field is a global id that encodes the type of object and the database id of the object (Relay uses this to cache on the frontend)
- Given the global id, the node interface can get the type and object id and query the database.
- Given the object, the node interface knows what the type of the object is
var {nodeInterface, nodeField} = nodeDefinitions(
(globalId) => {
var {type, id} = fromGlobalId(globalId);
switch (type) {
case 'User':
return User.get(id)
case 'Post':
return Post.get(id)
}
},
(obj) => {
return obj.name ? UserType : PostType
}
)
const UserType = new GraphQLObjectType({
// ...
// Instead of second arg above, each type can implement isTypeOf
isTypeOf: (obj) => !!obj.name
interfaces: [nodeInterface]
})
const PostType = new GraphQLObjectType({
// ...
interfaces: [nodeInterface]
})Brief Detour: Pagination
Standard Pagination
- Page numbers and page sizes
- Used in many bulletin boards and forums
- What about real time updates?
Cursor Based Pagination
- A page size and a cursor id
- Forward Pagination: "First <page size> after <cursor id>"
- Backward Pagination: "Last <page size> before <cursor id>"
Relay Connection
The connection type represents a one-to-many relationship in Relay. Connections implement the following:
- It supports pagination arguments (first, after, last, before)
- The resolver fetches the data and returns a list of edges along with pagination info
Relay Edge
Edges are the relation between two objects. An edge implements the following interface:
- Edge has a field called "cursor" that the Connection can use in the "after" or "before" arguments
- Edge has a Node

It's Just Pagination
The graphql-relay-js library has helpers for generating a Connection between one entity and another. Other GraphQL implementations have similar helpers.
https://github.com/graphql/graphql-relay-js#connections
Relay-Compliant Schema
The "Viewer"
"Viewer" is the entry point for the components in your app. The name is not special (it could be anything) and there can be more than one.
One restriction: "Viewer" may only take 0 or 1 argument. You'll get an error if you try to access it from Relay otherwise.
Node
"Node" takes one argument, an id (which is a global Relay id). The server takes that id and returns the matching object that implements the node interface.
This is the "nodeField" that was mentioned in the previous section.
Nodes (optional)
Behaves like node, but takes an array of ids and returns the matching objects.
Relay
By George Lee
Relay
- 1,507



