TypeScript
A little bit about me

-
I am a developer in the WixOS team.
- Been working with TypeScript from version 0.7 (3 years ago)
- I love games!
- @gilamran
Gil Amran
This lecture:
- What
- Why
- How
How to use TypeScript
How to use TypeScript
What is TypeScript?
JavaScript with Types!

Types?!
Type system:
The main purpose of a type system is to reduce possibilities for bugs in computer programs by defining interfaces between different parts of a computer program, and then checking that the parts have been connected in a consistent way."
Wikipedia
How does it look like?
var name = "John";var name: string = "John";function greet(name) {
console.log(`Hello ${name}`);
}function greet(name: string) {
console.log(`Hello ${name}`);
}function promote(person) {
// code
}function promote(person: {name: string, age: number}) {
// code
}What is it good for?
Developer experience!
- Describes/Documents the code
- Protects from typos
- Code completion
- more...
Developer experience
Some history
1889
Punch cards
1948
Assembly
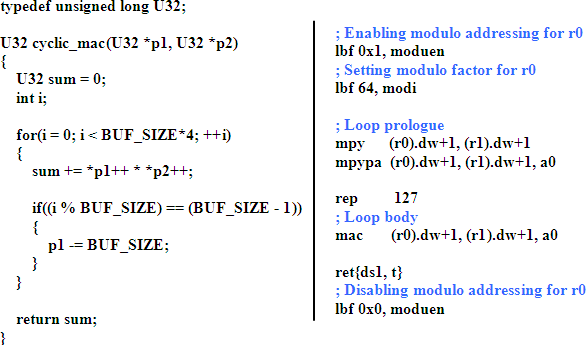
1972
C
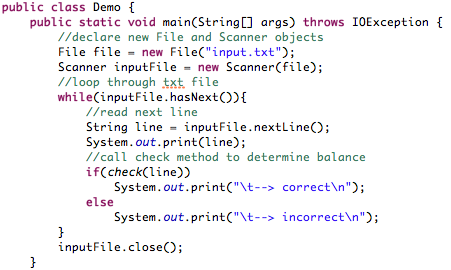
1995
Java
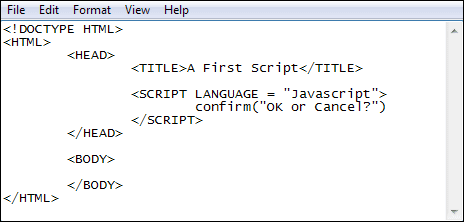
1997
JavaScript
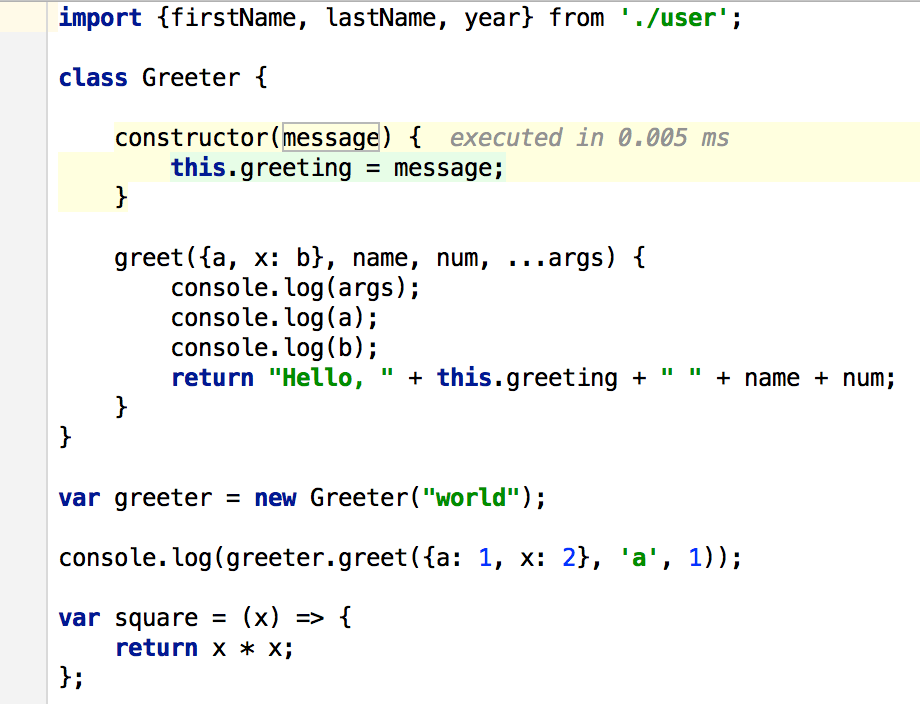
2015
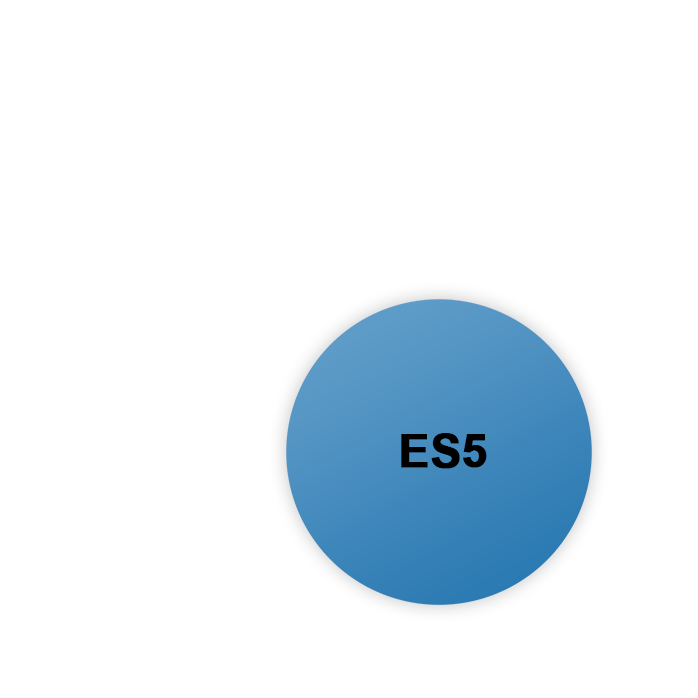
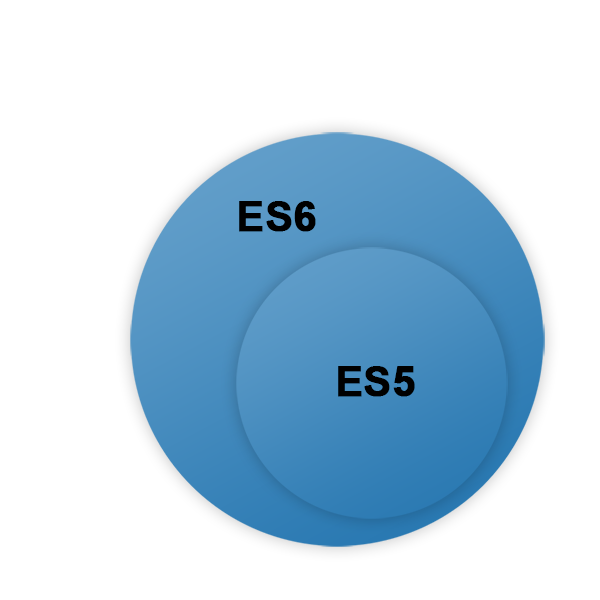
JavaScript - ES6



Basic Types
Basic Types
var x: string;
var y: number;
var z: boolean;
var foo: any;
var bar; // Same as "any"var x;
var y;
var z;
var foo;
var bar;Arrays
var a: any[];
var b: string[];
var p: Product[];
var a;
var b;
var p;funciton parameters
function addTax(tax:number, product: Product) {
.
.
.
}function addTax(tax, product) {
.
.
.
}Functions as types
var func : (name: string) => number;
function process(x: () => string){
x().toLowerCase();
}
var func;
function process(x){
x().toLowerCase();
}return void
function greet(name: string): void {
console.log(`Hello ${name}`);
}function greet(name) {
console.log(`Hello ${name}`);
}Exercise
- Write a function that gets an array of numbers and return an array of strings (toString)
- Write a function that gets an array of numbers and an interval, and return the sum of the numbers spaced by the interval. (sumEvery)
Structures / Interfaces
Structural types
function process(x: {a: string; b: number}) {
return x.a.length;
}interface IThing {
a: number;
b: string;
}
function process(x: IThing){
return x.a.length;
}
Interfaces
function process(x){
return x.a.length;
}
function process(x){
return x.a.length;
}
Structural vs Interface
interface IProduct {
name : string;
price : number;
}
function hasName(product: IProduct){
return product.name.length > 0;
}
var isNamed = hasName({name: 'iPhone', price: 1000});
function hasName(product){
return product.name.length > 0;
}
var isNamed = hasName({name: 'iPhone', price: 1000});Optional fields
interface IPerson {
age : number;
name : string;
address? : string; // <-- optional field
}
function getName(p: IPerson){
return p.name;
}
var name = getName({age:10, name:'Me'});Computed fields
interface IUsersMap {
[userId: string]: IUser;
}
var usersMap: IUsersMap;
var user = usersMap['038373832']; // user is IUserFunction fields
interface IPerson {
age : number;
name : string;
address : string;
walk(distance:number): number; // <-- a Function
}As a Function (Hybrid)
interface IPerson {
age : number;
name : string;
address : string;
walk(distance:number): number;
(): string; // <-- a Function
}Exercise
npm i -g typescript
tsc exercise.ts -w- Develop a small application with the following entities:
- Companies
- Users
- Ads
- A User can have more than one Ads.
- Each Ad hold a view count.
- Write functions to add Company, User, and Ad
- Write a function that assign a User to a Company
- Write a function that returns a list of Ads a Company has.
- Write a function to increase an Ad view count
The future is here
ES2015 / ES6
- Classes with inheritance
- Arrow functions
- Rest & Default parameters
- let and const
- Destructuring
- Spread Operator
- For...of
- Iterators
- Template Strings
- Promise
- Generators
- Exponentiation operator
ES2016 / ES7
- Async Await
ES2017 / ES8
Syntax
let str = `I am ${age} years old`;var str = "I am " + age + " years old";Object.assign(foo, bar);Object.assign(foo, bar);Library (must be polyfilled)
Namespaces
namespace model {
export function init() {
}
export function getState {
}
function thisIsPrivate() {
}
}var model;
(function (model) {
function init() {
}
model.init = init;
function getState() {
}
model.getState = getState;
function thisIsPrivate() {
}
})(model || (model = {}));
You can export
- functions
- interfaces/types
- classes
- enums
Classes
Constructor
class Person {
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
}
}
const person: Person = new Person('John', 'Doe');Functions
class Person {
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
}
walk(distance: number): void {
}
calculateStepSize(): void {
}
}
const person: Person = new Person('John', 'Doe');Class accessors
class Person {
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
}
public walk(distance: number): void {
}
private calculateStepSize(): void {
}
}
const person: Person = new Person('John', 'Doe');
person.walk(5); // ok
person.calculateStepSize(); // ErrorClass fields
class Person {
public age: number;
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
}
public walk(distance: number): void {
}
private calculateStepSize(): void {
}
}
const person: Person = new Person('John', 'Doe');
class Person {
public age: number;
private firstName: string;
private lastName: string;
constructor(firstName: string, lastName: string) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public walk(distance: number): void {
}
private calculateStepSize(): void {
}
}
const person: Person = new Person('John', 'Doe');
class Person {
public age: number;
constructor(private firstName: string, private lastName: string) {
}
public walk(distance: number): void {
}
private calculateStepSize(): void {
}
}
const person: Person = new Person('John', 'Doe');
getters / setters
class Person {
public age: number;
constructor(private firstName: string, private lastName: string) {
}
public walk(distance: number): void {
}
private calculateStepSize(): void {
}
get name():string {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName;
}
set age(value: number): void {
this.age = value;
}
}Exercise
- Convert the Ad object to a class with a "view" function
- Convert the User object to a class with "assignCompany" function
Typescript project
- compiler options
- include/exclude
- files
- outDir
- removeComments
- target
- lib
- sourceMap
tsconfig.json
Exercise
- Convert the the previous exercise to a TypeScript project using tsconfig.json
- Separate it into several files (Use namespaces)
- output to "dist" folder
- Use source maps to be able to debug your original code.
- Target is es5
- Use lib to define es6
Ambient Types
Example for ambient type
declare var _ : any;
_.last([1, 2, 3]); // 3
_.last([1, 2, 3]); // 3declare var _: {
last(arr: any[]): any;
}
_.last([1, 2, 3]); // 3
_.last([1, 2, 3]); // 3
_.last([1, 2, 3]); // ERROR: Cannot find name '_'DefinitelyTyped by the community
-
+4000 contributors
-
+30K commits
-
+11K stars
-
Thousands of definition files
-
node.d.ts
npm install @types/lodash-
node_modules/@types auto included
-
versioning
JavaScript ambient types
declare const Math: {
random(): number;
sqrt(x: number): number;
sin(x: number): number;
.
.
.
};
lib.d.ts by TypeScript
-
21K lines of ambient declarations
-
eval, parseInt, encodeURI
-
Math, Date, RegExp
-
Full DOM declarations
-
And many more...
-
interface Math {
/** The mathematical constant e. This is Euler's number, the base of natural logarithms. */
E: number;
/** The natural logarithm of 10. */
LN10: number;
/** The natural logarithm of 2. */
LN2: number;
/** The base-2 logarithm of e. */
LOG2E: number;
/** The base-10 logarithm of e. */
LOG10E: number;
/** Pi. This is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. */
PI: number;Exercise
- Use ambient types in the previous exercise
npm install @types/node- Use fs to save/load all the entities from the previous exercise
Type inference
Where inference takes over?
var x = 3; // x is a numberclass MyClass {
name = "Foo"; // name is a string
}function foo(value = false) { // value is a boolean
}function calc() {
return 55; // calc returns a number
}
var x = calc(); // x is also a numberbackward inference
interface IHuman {
age: number;
walk(distance:number):void;
}
var man : IHuman = {
age : 120,
walk: function(distance) {
console.log(distance); // distance inferred to be a number
}
}backward inference #2
window.onmousedown = function(mouseEvent) {
// mouseEvent inferred as MouseEvent
console.log(mouseEvent.button);
};Inference can cause errors
var x = 3; // x is a number
x = "45"; // compiler errorvar foo = {};
foo.description = 'I am FOO'; // compiler errorvar x : any = 3; // x can be anything
x = "45";var foo : any = {};
foo.description = 'I am FOO'; // compiler is happyany
var x; // x is any forever
x = '45'; // x is still anyfunction process(x) { // x is any
return x+x*3; // return type is any
}
process(42); // this does not change the type of xType Guards
Type Guards
var x: any;
if (typeof x === 'string') {
console.log(x.subtr(1)); // Error
}
// x is still any here
x.unknown(); // OKinstanceof
class Animal { name:string }
class Cat extends Animal { meow() { } }
var pet: Animal = new Cat();
if (pet instanceof Cat) {
pet.meow(); // OK
} else {
pet.meow(); // Error
}Advanced types
union types
function formatCommandline(command: string[] | string) {
var line = '';
if (typeof command === 'string') {
line = command.trim();
} else {
line = command.join(' ').trim();
}
// Do stuff with line: string
}Intersection types
interface ISerializable {
serialize(): string;
}
interface ILoggable {
log(): void;
}
class Person {
}
const all: ISerializable & ILoggable & Person = someObject;
define a new type
type paddingType = string | number;
function padLeft(value: string, padding: paddingType) {
// ...
}String Literal Type
type CardinalDirection =
"North"
| "East"
| "South"
| "West";
function move(distance: number, direction: CardinalDirection) {
// ...
}
move(1,"North"); // Okay
move(1,"Nurth"); // Error!enums
enum CardSuit {
Clubs,
Diamonds,
Hearts,
Spades
}
// Sample usage
var card = CardSuit.Clubs;
// Safety
card = "not a member of card suit"; // Errorkeyof
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
location: string;
}
type K1 = keyof Person; // "name" | "age" | "location"
type K2 = keyof Person[]; // "length" | "push" | "pop" | "concat" | ...
type K3 = keyof { [x: string]: Person }; // stringreadonly
interface IPerson {
readonly age: number;
readonly height: number;
}ReadonlyArray, Map and Set
interface ReadonlyArray<T> {
...
interface ReadonlyMap<K, V> {
...
interface ReadonlySet<T> {
...Generics
function first<T>(arr: T[]): T {
return arr[0];
}
let foo = first([1, 2, 3]); // foo must be a number
let bar = first(['A', 'B', 'C']); // bar must be a string
function later(): Promise<number> {
// code ...
}
later().then(result => console.log(result)); // result is a numberPartial
// from lib.es6.d.ts
type Partial<T> = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P];
};
type PartialPerson = Partial<Person>;interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
location: string;
}interface PartialPerson {
name?: string;
age?: number;
location?: string;
}Readonly
// from lib.es6.d.ts
type Readonly<T> = {
readonly [P in keyof T]: T[P];
};
/**
* Usage
*/
let foo: Readonly = { 0: 123, 2: 345 };
console.log(foo[0]); // Okay (reading)
foo[0] = 456; // Error (mutating): ReadonlyPick
interface Task {
id: string,
name: string,
assignee: string,
contacts: any[], //for brevity
associatedJob: string,
submissionDate: string,
allocatedTime: number,
expectedCompletion: string,
invoiceNumber: string,
invoiceDueDate: string,
comment: string,
taskAddress: string
...
...
}
type PartialTask = Pick<Task, 'id' | 'name' | 'contacts'>Yoshi and TypeScript
So what?!

Refactor
List parameters
Find occurrences
Go to definition
Code completion
inline errors


TypeScript
By gilamran
TypeScript
- 1,162


