Modular Application
Architecture
Building Plugin-based Architectures
Asmir Mustafic
PHP Yorkshire 2019 - York - UK
Me
Asmir Mustafic
@goetas
Open source
- jms/serializer (contributor/maintainer)
- masterminds/html5 (contributor/maintainer)
- hautelook/templated-uri-bundle (contributor/maintainer)
- goetas-webservices/xsd2php (author)
- goetas-webservices/xsd-reader (author)
- goetas-webservices/soap-client (author)
- goetas/twital (author)
- many others...
Application
Component 1
Component 3
Component 2
Application
Problems
- Too many features, even more than what a whole company can handle
- Even more feature requests! all perfectly legit
Development does not scale
Application
Component 1
Component 3
Component 2
Application
Component 1
Component 3
Component 2
Application
Component 2
Component 3
Component 1
Application core
Component 2
Component 1
Component 3
Multiple applications
Plugins
Plugins ≈ Components
built to run into different copies of the original application
- Independent release cycles
- Developed externally
- Clear dependencies
- Tend to be small and focused
- Potentially different technologies
- Core application is more maintainable
-
Adding features is scalable
-
No coordination needed
-
No coordination needed
- Can create community/partnerships
Why plugins?
Use cases
Symfony
Laravel
Wordpress
Magento
Drupal
more and more...
Extensibility
is a key factor
in software development
My use case
immobinet.it
property management system
- PHP
- ~500 K lines of code
- ~600 sql tables
- countless features
- few hundreds of different instances/installations
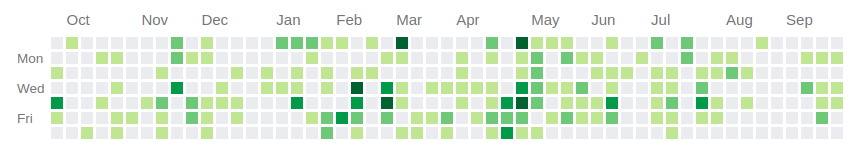
immobinet.it
176 plugins
immobinet.it
- ~30 K lines of code in core
(~7 % of the total)
- 39 sql tables
(~6 % of the total)
Core
How to build a plugin-based software?
-
Traditional Extensible Software
-
Plugin-Based Software
Traditional Extensible Software
Application
Plugin 2
Plugin 3
Plugin 1
Plugin 4
Application
Plugin 2
Plugin 3
Plugin 1
New features require new entry-points
Complexity grows
-
Intentionally limit extensibility
-
Acceptable solution when refactoring legacy software
When to use?
Plugin-Based Software
Application
application core
Plugin
Plugin
Plugin
Plugin
Plugin
-
The way to go when extensibility is the main goal
When to use?
Challenges
-
Plugin registration
- Configuration
- Configuration
-
Exposing features
- Communication
with application and between plugins
- Communication
-
Exposing resources
- Static and dynamic assets
Plugin Registration
Challenges
// code
// code
// code
$plugins; // <-- arrayplugin registration
foreach ($plugins as $plugin) {
// $plugin do something
}-
Which code to load?
-
Where/How to find the code?
Plugin Registration
Convention-based
aka Discovery by the application
Focus on:
Where/How to find that code?
Plugin Registration
Wordpress
Look into file location convention
wp-content/plugins/myplugin/myplugin.php
wp-content/themes/mytheme/style.css wp-content/themes/mytheme/functions.php
wp-content/themes/mytheme/header.php wp-content/themes/mytheme/footer.php
.....
Laravel
"extra": {
"laravel": {
"providers": [
"Goetas\\Debugbar\\ServiceProvider"
],
"aliases": {
"Debugbar": "Goetas\\Debugbar\\Facade"
}
}
},Look into composer.json
Pros
- Simple
- Easy for beginners
- Most used
Cons
- Needs good documentation
- Tends to grow in complexity
- Difficult to handle new cases
- Not easy to exclude some plugins
- Imposes limitations on directory structure
- Less secure
Convention-based
Configuration-based
Focus on:
Which code to load?
Plugin Registration
Symfony
<?php
return [
// ...
Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\FrameworkBundle::class => ['all' => true],
Symfony\Bundle\SecurityBundle\SecurityBundle::class => ['all' => true],
// ...
Goetas\DebugBundle\DebugGoetasBundle::class => ['all' => true],
// ...
];EDIT bundles.php
CakePHP
<?php
class Application extends BaseApplication
{
public function bootstrap()
{
// more plugins here
$this->addPlugin(\Cake\ElasticSearch\Plugin::class);
}
}EDIT Application.php
Pros
- Focus on the plugins to load, not on technology details
- Easy to document
- Generally only one way to load plugins
Cons
- Needs more human intervention
- Difficult to automate
- Difficult for not experienced devs
Configuration-based
Plugin manager
Registration
Drupal
Wordpress
Magento
...
installation is done by
End User
Plugin manager
Plugin manager
Convenient GUI
Application core
Application
Plugin
loader
Plugin
Plugin
Plugin
Plugin
Plugin
Configuration
Registration
Application core
Component 2
Component 1
Application
Other Application
Component 3
Additional information provided
to plugins to make them fit into the application where they are running
Component 4
Component 5
Configuration storage
- files
- database
- environment variables
- plugin-manager
- ...
depends on your
End User
Expose plugin functionalities
Challenges
Entry-points
How many?
Which?
How?
Dependency Injection
and
Dependency Injection Container
Dependency Injection
class Computer
{
protected $hardDrive;
public function __construct()
{
$this->hardDrive = new HardDrive();
}
}
$computer = new Computer();
Without Dependency Injection
class ComputerWithSSD extends Computer
{
public function __construct()
{
patent::__construct();
$this->hardDrive = new SSDDrive();
}
}
$computer = new ComputerWithSSD();
Without Dependency Injection
class Computer
{
private $hardDrive;
public function __construct($hardDrive)
{
$this->hardDrive = $hardDrive;
}
}
$hardDrive = new HardDrive();
$computer = new Computer($hardDrive);
class Computer
{
private $hardDrive;
public function __construct($hardDrive)
{
$this->hardDrive = $hardDrive;
}
}
$hardDrive = new SSDDrive();
$computer = new Computer($hardDrive);
Dependency Injection Container
class Computer
{
private $hardDrive;
private $videoCard;
private $usb = [];
private $cdRom;
// more
public function __construct(
$hardDrive,
$videoCard,
array $usb
// more
) {
}
public function setCDROM($cdRom)
{
$this->cdRom = $cdRom;
}
// more
}
$hardDrive = new HardDrive($size);
if (have_money) {
$videoCard = new NvidiaGPU();
} else {
$videoCard = new IntegratedVideo();
}
$usb[] = new USB2();
$usb[] = new USB2();
$usb[] = new USB3();
$computer = new Computer(
$hardDrive,
$videoCard
$usb
);
if (!laptop) {
$computer->setCDROM(new CDBurner());
}
Without Dependency Injection Container
$container = new Container();// configure with some magic the $container Dependency Injection Container
$computer = $container->getComputer();Dependency Injection Container
- Symfony
- Laravel
- PHP-DI
- Zend
- Pimple
- League
- ...
Combine PHP, XML, YAML, Annotations and many other techniques to achieve magic!
Dependency Injection Container
$container = new Container();
// configure with some magic the $container
$computer = $container->getComputer();Perfect entrypoint for a plugin system
Almost unlimited entry points
Only limitation is the Computer class itself
Dependency Injection Container
$container = new Container();
$plugins; // registered somehow
foreach ($plugins as $plugin) {
$plugin($container);
}
$computer = $container->get('computer');Dependency Injection Container
// load from somewhere a configuration array
$configurations;
foreach ($plugins as $name => $plugin) {
$plugin($container, $configurations[$name]);
}
$computer = $container->get('computer');Expose features
By allowing plugins to configure
the
Dependency Injection Container
Good software design
in the application and plugins
(don't hard-code anything!)
Good software design?
Abstract Factory Builder Factory Method Object Pool Prototype Singleton Adapter Bridge Composite Decorator Facade Flyweight Private Class Data Proxy Chain of responsibility Command Interpreter Iterator Mediator Memento Null Object Observer State Strategy Template method Visitor
Abstract Factory Builder Factory Method Object Pool Prototype Singleton Adapter Bridge Composite Decorator Facade Flyweight Private Class Data Proxy Chain of responsibility Command Interpreter Iterator Mediator Memento Null Object Observer State Strategy Template method Visitor
Mediator Pattern
class Mediator
{
private $events = [];
public function addListener($eventName, $callback)
{
if (!isset($this->events[$eventName])) {
$this->events[$eventName] = [];
}
$this->events[$eventName][] = $callback;
}
public function trigger($eventName, $data = null)
{
foreach ($this->events[$eventName] as $callback) {
$callback($data, $eventName);
}
}
}$mediator = new Mediator();
// plugin 1
$mediator->addListener('menu', function(User $user) {
echo "- Users\n";
});
// plugin 2
$mediator->addListener('menu', function(User $user) {
echo "- Settings\n";
});
// plugin n ...
$mediator->trigger('menu', $user);
- Users
- Settings Implementations
- symfony/event-dispatcher
- doctrine/event-manager
- illuminate/events
- league/event
- PSR-14 event manager
- ...
Symfony event dispatcher
$dispatcher = new EventDispatcher();
// plugin 1
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function() {
echo "- Users\n";
});
// plugin 2
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function() {
echo "- Users\n";
});
$dispatcher->dispatch('menu');
Event data
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function(Event $event) {
$user = $event->getSubject();
if (has_credentials($user)) {
echo " - Settings\n";
}
});
$event = new GenericEvent($user);
$dispatcher->dispatch('menu', $event);
Custom event types
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function(MenuEvent $event) {
$user = $event->getSubject();
$event->addItem("Settings");
});
$event = new MenuEvent($user);
$dispatcher->dispatch('menu', $event);
echo $event->getItems();Priorities
// plugin 1
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function(Event $event) {
// code
});
// plugin 2
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function(Event $event) {
// code
}, 100);Stoping events
$dispatcher->addListener('menu', function(Event $event) {
$user = $event->getSubject();
if ($user) {
$event->addItem("Dashboard");
} else {
$event->addItem("Log in");
$event->stopPropagation();
}
}, 100);
Use cases
- Symfony Events
- Drupal Hooks
- Wordpress Hooks
- Magento Events
- Doctrine Events
- ...
The most common pattern in plugin architectures
Application core
Plugin
Plugin
e
e
e
e
e
e
e
Application
Exposing Resources
(used via code)
translations, templates, configuration files
Challenges
Use the
dependency injection container
and
override object configurations
Exposing Resources
Exposing Resources
class PdfFinder
{
private $locations = [
'/dev/system/drive'
];
public function find(string $name): string
{
foreach ($this->locations as $path) {
if (is_file("$path/$name")) {
return "$path/$name";
}
}
throw new Exception("PDF not found");
}
}Add extra locations for the PDF files?
Exposing Resources
class PdfFinder
{
private $locations = [
'/dev/system/drive'
];
public function find(string $name): string
{
foreach ($this->locations as $path) {
if (is_file("$path/$name")) {
return "$path/$name";
}
}
throw new Exception("PDF not found");
}
public function addLocation(string $path): void
{
$this->locations[] = $path;
}
}Exposing Resources
$container
->getDefinition('pdf.finder')
->addMethodCall('addLocation', ['/home/me/pdf']);A plugin can edit DI service definition
$finder = $container->get('pdf.finder');
// find a PDF
$pdf = $finder->find('test.pdf');
Exposing Resources
(static)
Images, CSS, JS, PDF... files...
Challenges
application/
├── src/
└── public/
├── plugins/
└── index.phpNaive solutions
application/
├── src/
├── plugins/
└── public/
├── plugins-public/
│ ├── plugin-1
│ └── plugin-n*
└── index.phpInstall plugins
in public dir
Copy public assets
in public dir
app/
├── src/
├── plugins/
│ └─── plugin-1/
│ ├── src/
│ └── public
│
└── public/
├── plugins/
│ └── plugin-1*
└── index.phpSymlink files in public folder
-
simple
-
development friendly
-
requires "install" step
-
no permissions control
Pros
Cons
server {
...
location ~ ^/plugins/([a-z]+) {
root /application/plugins/$1/public
}
}Server configuration
nginx.conf
- clean public dir
- highly configurable
- development friendly
- requires server configs
- difficult permissions control
Pros
Cons
if ($hasPermissions) {
header("Content-Type: text/plain");
$fp = fopen("$pluginDir/plugin-1/public/file.txt", "r");
fpassthru($fp);
fclose($fp);
} else {
header('HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized');
}
Serve via application
Pros
- easy to control permissions
- clean public dir
- development friendly
Cons
- bad performance
- PHP has to handle HTTP
improved performance
if ($hasPermissions) {
header("Content-Type: text/plain");
header("X-Sendfile: $pluginDir/plugin-1/public/file.txt");
} else {
header('HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized');
}Serve via application assisted by server
Recap
- Plugin architectures
- Traditional Extensible software
- Plugin-Based software
- Plugin registration
- Exposing features
- DI & DIC
- Software patterns
- Exposing resources
Extra challenges
Performance issues?
Mediator pattern tends to become a bottleneck
Complexity?
Too many events can lead to chaos
Use good naming conventions and have good documentation
Plugin versioning?
Plugin dependencies?
semver
+
existing tools
(as composer)
Thank you!
- Twitter: @goetas_asmir
- Github: @goetas
- LinkedIn: @goetas
- WWW: goetas.com
Modular Application Architecture - PHP Yorkshire 2019
By Asmir Mustafic
Modular Application Architecture - PHP Yorkshire 2019
Long story short: an application is born, an application grows, an application becomes unmaintainable. Often the functionalities added to the application are independent-enough but they end up anyway in the main code base increasing the code size, complexity and coupling. A common strategy to raise application maintainability and extensibility is to have external plugins/bundles/modules keeping the application core as smallest as possible. In this session you will see challenges and solutions when building plugin-based application architectures. By allowing “plugins” you will get third party extensions, independent release cycles, less dependencies and many other advantages.
- 2,529



