Trie & Segment Tree
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
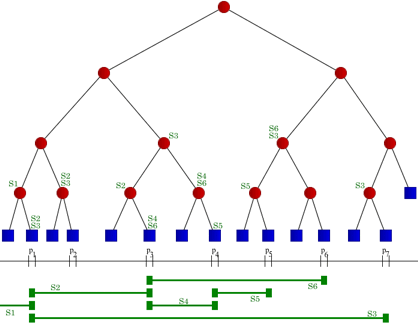
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
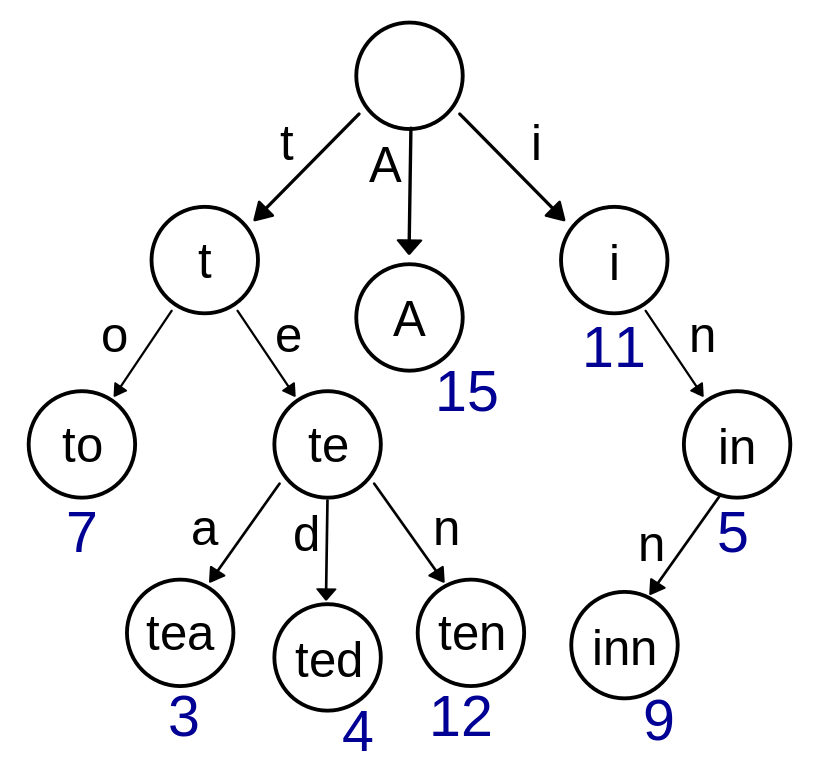
"A","to", "tea", "ted", "ten", "i", "in", "inn"
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Why Trie?
1. Prefix
(autocomplete, dictionary, phone book)
2. Order
3. Hash table?
O(1), but collision O(n)
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Interview
- insert
- search
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
ab
abat
absent
absolute
absolve
absorb
base
basic
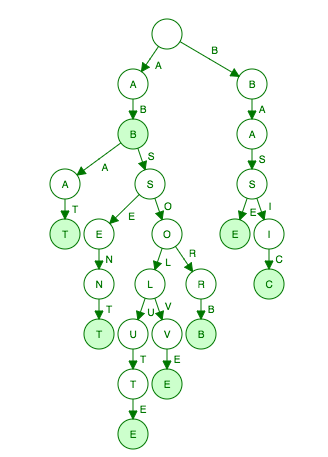
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Trie {
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
}
}
/**
* Assume only lower case a - z.
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
*/Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
class TrieNode {
TrieNode[] children;
boolean isWord;
public TrieNode() {
this.children = new TrieNode[26];
this.isWord = false;
}
}TreeNode
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Trie {
private final char CHAR_A = 'a';
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Inserts a word into the trie.
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (p.children[c - CHAR_A] == null) {
p.children[c - CHAR_A] = new TrieNode();
}
p = p.children[c - CHAR_A];
}
p.isWord = true;
}
}Insert
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Trie {
private final char CHAR_A = 'a';
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Returns if the word is in the trie.
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (p.children[c - CHAR_A] == null) {
return false;
}
p = p.children[c - CHAR_A];
}
return p.isWord;
}
}Search
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Trie {
private final char CHAR_A = 'a';
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Returns if there is any word in the trie
// that starts with the given prefix.
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if (p.children[c - CHAR_A] == null) {
return false;
}
p = p.children[c - CHAR_A];
}
return true;
}
}Startwith
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Trie {
private final char CHAR_A = 'a';
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Inserts a word into the trie.
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (p.children[c - CHAR_A] == null) {
p.children[c - CHAR_A] = new TrieNode();
}
p = p.children[c - CHAR_A];
}
p.isWord = true;
}
// Returns if the word is in the trie.
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode node = helper(word);
return (node != null && node.isWord);
}
// Returns if there is any word in the trie
// that starts with the given prefix.
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return helper(prefix) != null;
}
private TrieNode helper(String s) {
TrieNode p = root;
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (p.children[c - CHAR_A] == null) {
return null;
}
p = p.children[c - CHAR_A];
}
return p;
}
}Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
search with regex
Example
addWord("bad")
addWord("dad")
addWord("mad")
search("pad") -> false
search("bad") -> true
search(".ad") -> true
search("b..") -> true
Trie Tree (Prefix Tree)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Trie {
private final char CHAR_A = 'a';
private final char DOT = '.';
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could
// contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter.
public boolean searchWithRegex(String word) {
return helper(word, 0, root);
}
private boolean helper(String s, int index, TrieNode p) {
if (index == s.length()) {
return p.isWord;
}
char c = s.charAt(index);
if (c == DOT) {
for (int i = 0; i < p.children.length; i++) {
if (p.children[i] != null && helper(s, index + 1, p.children[i])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} else {
return (p.children[c - CHAR_A] != null && helper(s, index + 1, p.children[c - CHAR_A]));
}
}
}search with regex
Word Square
Given a set of words (without duplicates), find all word squares you can build from them.
A sequence of words forms a valid word square if the kth row and column read the exact same string, where 0 ≤ k < max(numRows, numColumns).
For example, the word sequence ["ball","area","lead","lady"] forms a word square because each word reads the same both horizontally and vertically.
b a l l
a r e a
l e a d
l a d y
Note:
There are at least 1 and at most 1000 words.
All words will have the exact same length.
Word length is at least 1 and at most 5.
Each word contains only lowercase English alphabet a-z.
Word Square
Example 1:
Input:
["area","lead","wall","lady","ball"]
Output:
[
[ "wall",
"area",
"lead",
"lady"
],
[ "ball",
"area",
"lead",
"lady"
]
]
Example 2:
Input:
["abat","baba","atan","atal"]
Output:
[
[ "baba",
"abat",
"baba",
"atan"
],
[ "baba",
"abat",
"baba",
"atal"
]
]Explanation:
The output consists of two word squares. The order of output does not matter
(just the order of words in each word square matters).
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Word Square
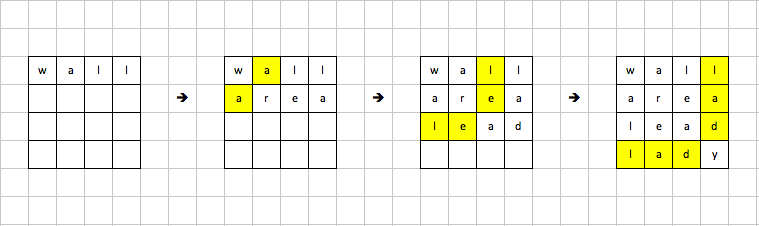
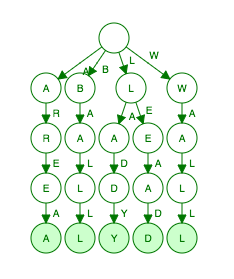
Example: ["wall","area","lead","lady","ball"]
What I care?
All the words with a given prefix
Word Square
Trie Tree
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Solution {
private final char CHAR_A = 'a';
public List<List<String>> wordSquares(String[] words) {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(words == null || words.length == 0) return res;
Node root = buildTree(words);
helper(new ArrayList<String>(), root, res, words[0].length());
return res;
}
private Node buildTree(String[] words) {
Node root = new Node();
for (String word : words) {
Node p = root;
p.list.add(word);
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (p.children[c - CHAR_A] == null) {
p.children[c - CHAR_A] = new Node();
}
p = p.children[c - CHAR_A];
p.list.add(word);
}
}
return root;
}
private void helper(List<String> cur, Node root, List<List<String>> res, int len){
if (cur.size() == len){
res.add(new ArrayList<String>(cur));
} else {
Node p = root;
for (int i = 0; i <= cur.size(); i++) {
if(p == null || p.list.size() == 0) return;
p = (i == cur.size()) ? p : p.children[cur.get(i).charAt(cur.size()) - CHAR_A];
}
for (String word : p.list){
cur.add(word);
helper(cur, root, res, len);
cur.remove(cur.size()-1);
}
}
}
class Node{
Node[] children = new Node[26];
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
}
}Trie Tree Summary
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- Prefix
- Hash Table
- Searching String
Segment Tree
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Sum of Given Range
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
The Problem
We are given an array: arr[0 . . . n-1].
1 Find the sum of elements from index l to r where 0 <= l <= r <= n-1 (Query)
2 Change value of a specified element of the array to a new value x. We need to do arr[i] = x where 0 <= i <= n-1 (Update)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Brute force
Sum: O(n)
Update: O(1)
Sum of Given Range
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
create another array and store sum from start to i at the ith index in this array.
Sum: O(1)
Update: O(n)
Benefits if the number of query operations are large and very few updates.
Sum of Given Range
Is there a way to save the sum more efficiently?
🤔
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Segment Tree
Sum: O(log n)
Update: O(log n)
Optimal solution.
Sum of Given Range
Segment Tree
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
We are given an array: arr[0 . . . n-1].
1 Find the sum of elements from index l to r where 0 <= l <= r <= n-1 (Query)
2 Change value of a specified element of the array to a new value x. We need to do arr[i] = x where 0 <= i <= n-1 (Update)
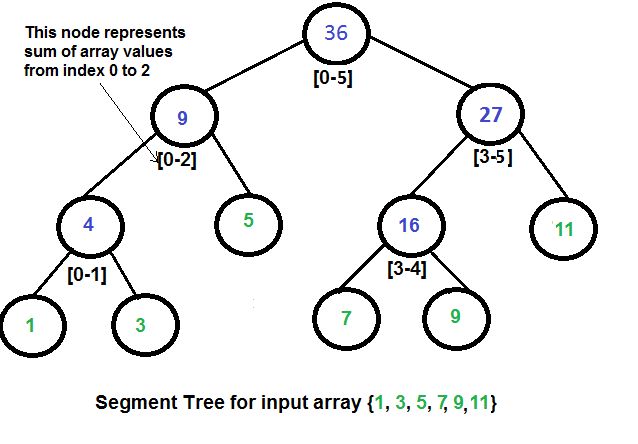
Given nums = [1, 3, 5]
sumRange(0, 2) -> 9
update(1, 2)
sumRange(0, 2) -> 8
What kind of tree this is?
🤔
ex: [1,3,5,7,9,11]
Segment Tree
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Analyze
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class NumArray {
class Node {
int start, end, val;
Node left, right;
public Node(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
Node _root = null;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
_root = new Node(0, 0);
} else {
_root = buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
}
}
First of all
- Class
- Node
- Constructor
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class NumArray {
private Node buildTree(int[] nums, int s, int e) {
Node root = new Node(s, e);
if (s == e) {
root.val = nums[s];
return root;
}
int mid = s + (e - s) / 2;
root.left = buildTree(nums, s, mid);
root.right = buildTree(nums, mid + 1, e);
root.val = root.left.val + root.right.val;
return root;
}
void update(int i, int val) {
update(i, val, _root);
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return query(i, j, _root);
}
}
Then
- Tree construction
- Method interface
(Recursively)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class NumArray {
private void update(int i, int val, Node node) {
if (i < node.start || i > node.end) {
return;
}
if (node.start == node.end && node.start == i) {
node.val = val;
return;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2;
if (i > mid) {
update(i, val, node.right);
} else {
update(i, val, node.left);
}
node.val = node.left.val + node.right.val;
}
private int query(int i, int j, Node node) {
if (i > node.end || j < node.start) {
return 0;
}
if (i <= node.start && j >= node.end) {
return node.val;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2;
int left = query(i, Math.min(mid, j), node.left);
int right = query(Math.max(mid + 1, i), j, node.right);
return left + right;
}
}
- update
- query
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class NumArray {
class Node {
int start, end, val;
Node left, right;
public Node(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
Node _root = null;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
_root = new Node(0, 0);
} else {
_root = buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
}
void update(int i, int val) {
update(i, val, _root);
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return query(i, j, _root);
}
private void update(int i, int val, Node node) {
if (i < node.start || i > node.end) {
return;
}
if (node.start == node.end && node.start == i) {
node.val = val;
return;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2; //make this a method?
if (i > mid) {
update(i, val, node.right);
} else {
update(i, val, node.left);
}
node.val = node.left.val + node.right.val;
}
private int query(int i, int j, Node node) {
if (i > node.end || j < node.start) {
return 0;
}
if (i <= node.start && j >= node.end) {
return node.val;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2; //make this a method?
int left = query(i, Math.min(mid, j), node.left);
int right = query(Math.max(mid + 1, i), j, node.right);
return left + right;
}
private Node buildTree(int[] nums, int s, int e) {
Node root = new Node(s, e);
if (s == e) {
root.val = nums[s];
return root;
}
int mid = s + (e - s) / 2; //make this a method?
root.left = buildTree(nums, s, mid);
root.right = buildTree(nums, mid + 1, e);
root.val = root.left.val + root.right.val;
return root;
}
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
We are given an array: arr[0 . . . n-1].
1 Find the min of elements from index l to r where 0 <= l <= r <= n-1 (Query)
2 Change value of a specified element of the array to a new value x. We need to do arr[i] = x where 0 <= i <= n-1 (Update)
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
You are given an integer array nums and you have to return a new counts array. The counts array has the property where counts[i] is the number of smaller elements to the right of nums[i].
Segment Tree? Really?
🤔
Example:
Given nums = [5, 2, 6, 1]
To the right of 5 there are 2 smaller elements (2 and 1).
To the right of 2 there is only 1 smaller element (1).
To the right of 6 there is 1 smaller element (1).
To the right of 1 there is 0 smaller element.
Return the array [2, 1, 1, 0].Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
What should the node be?
What's the query?
What's the update?
Example:
Given nums = [5, 2, 6, 1]
To the right of 5 there are 2 smaller elements (2 and 1).
To the right of 2 there is only 1 smaller element (1).
To the right of 6 there is 1 smaller element (1).
To the right of 1 there is 0 smaller element.
Return the array [2, 1, 1, 0].Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- Node
- countSmaller
- buildTree
public class Solution {
class Node {
int start, end, count;
Node left, right;
public Node(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) {
int arrMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int arrMax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i : nums) {
arrMin = Math.min(i, arrMin);
arrMax = Math.max(i, arrMax);
}
Node root = buildTree(arrMin, arrMax);
Integer[] res = new Integer[nums.length];
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >=0; i--) {
res[i] = query(root, arrMin, nums[i] - 1);
update(root, nums[i]);
}
return new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(res));
}
private Node buildTree(int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
return new Node(start, end);
}
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
Node root = new Node(start, end);
root.left = buildTree(start, mid);
root.right = buildTree(mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
}
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
- query
- update
public class Solution {
private int query(Node node, int start, int end) {
if (start > node.end || end < node.start) {
return 0;
}
if (start <= node.start && end >= node.end) { // start?
return node.count;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2;
int left = query(node.left, start, Math.min(mid, end));
int right = query(node.right, Math.max(mid, start), end);
return left + right;
}
private int update(Node node, int val) {
if (node.start == node.end && node.start == val) {
node.count += 1;
return node.count;
}
if (val < node.start || val > node.end) {
return node.count;
}
int left = update(node.left, val);
int right = update(node.right, val);
node.count = left + right;
return node.count;
}
}
private int query(Node node, int end) {
if (end < node.start) {
return 0;
}
if (end >= node.end) {
return node.count;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2;
int left = query(node.left, Math.min(mid, end));
int right = query(node.right, end);
return left + right;
}
}Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
public class Solution {
class Node {
int start, end, count;
Node left, right;
public Node(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) {
int arrMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int arrMax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i : nums) {
arrMin = Math.min(i, arrMin);
arrMax = Math.max(i, arrMax);
}
Node root = buildTree(arrMin, arrMax);
Integer[] res = new Integer[nums.length];
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >=0; i--) {
res[i] = query(root, nums[i] - 1);
update(root, nums[i]);
}
return new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(res));
}
private Node buildTree(int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
return new Node(start, end);
}
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
Node root = new Node(start, end);
root.left = buildTree(start, mid);
root.right = buildTree(mid + 1, end);
return root;
}
private int query(Node node, int end) {
if (end < node.start) {
return 0;
}
if (end >= node.end) {
return node.count;
}
int mid = node.start + (node.end - node.start) / 2;
int left = query(node.left, Math.min(mid, end));
int right = query(node.right, end);
return left + right;
}
private int update(Node node, int val) {
if (node.start == node.end && node.start == val) {
node.count += 1;
return node.count;
}
if (val < node.start || val > node.end) {
return node.count;
}
int left = update(node.left, val);
int right = update(node.right, val);
node.count = left + right;
return node.count;
}
}Segment Tree Summary
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
What is segment tree?
- Binary Tree
- Storing intervals (segments)
- Parent cover all children's certain property
- Allows querying which of the stored segments contain a given value.
Homework 22
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Segment Tree
Interval Query
Count of Bigger/Smaller Numbers
Count of Bigger Numbers Before Self [*]
[optional]
Interval Query
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Given an integer array of size n as input.
Implement Query and Update methods.
Each query has two integers as index: [start, end]. Return sum between [start end], inclusive.
Each update has two integers as index and value:
[index, val].
Example
Given array A = [1,2,7,8,5].
- query(0, 2), return 10.
- update(0, 4), change A[0] from 1 to 4.
- query(0, 1), return 6.
- update(2, 1), change A[2] from 7 to 1.
- query(2, 4), return 14.
Count of Smaller/Bigger Numbers
Copyright © 直通硅谷
http://www.zhitongguigu.com/
Give you an integer array (index from 0 to n-1, where n is the size of this array, value from 0 to 10000)
Implement
int[] queryBigger(int[]) and int[] querySmaller(int[])
Example
For array [1,2,7,8,5],
queryBigger([1,8,5]), return [4,0,2]
querySmaller([1,8,5,10]), return [0,4,2,5]
[GoValley-201612] Trie & Segment Tree
By govalley201612
[GoValley-201612] Trie & Segment Tree
Introduction to GoValley
- 1,395



